Abstract
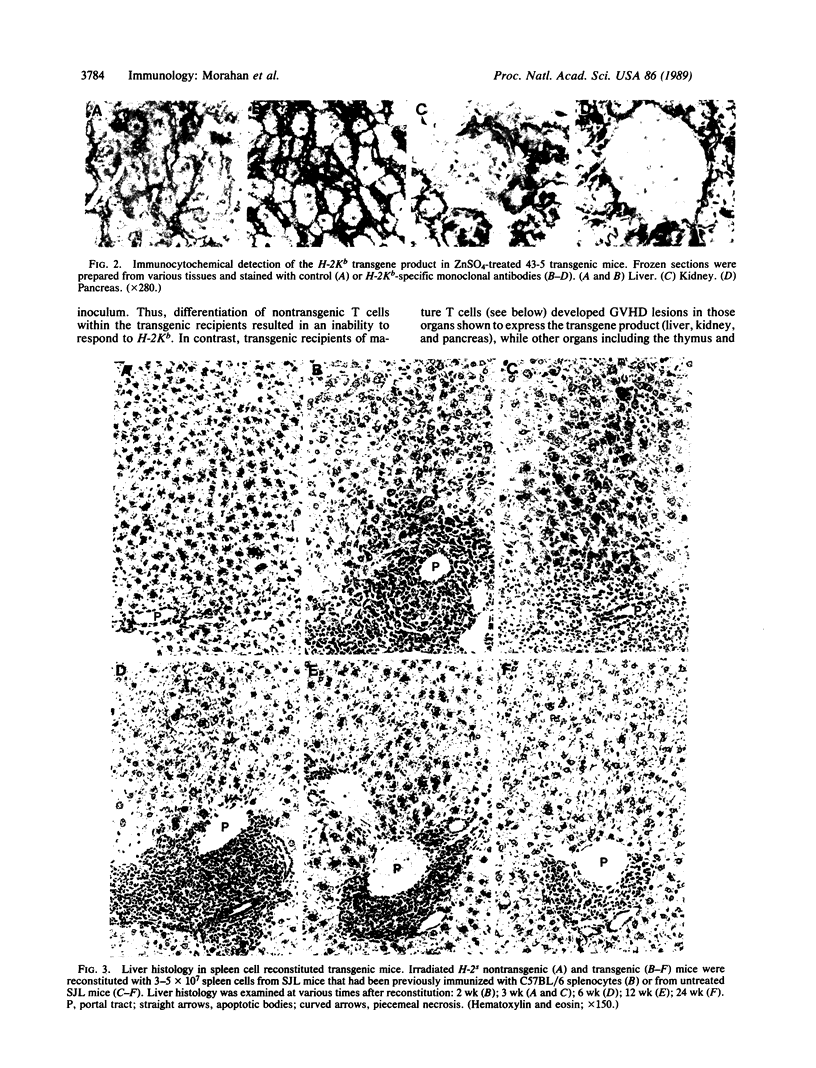
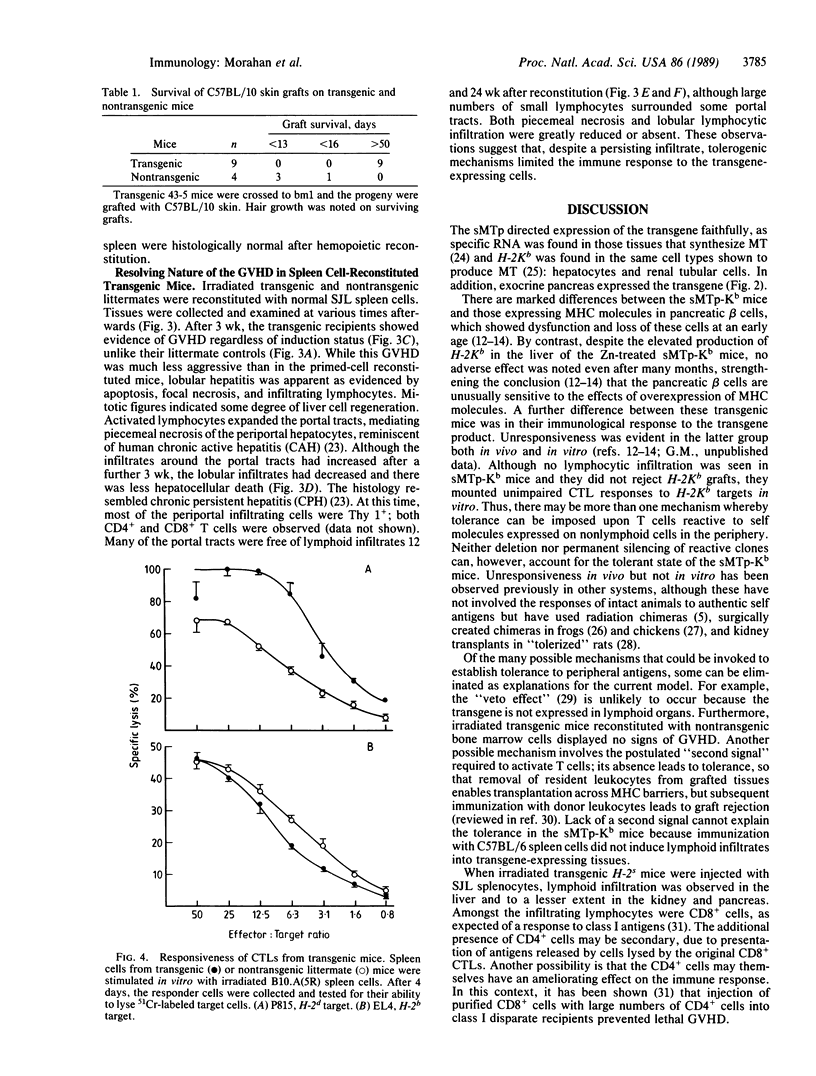
To study the effects of increased expression of major histocompatibility complex class I molecules on the development of self-tolerance, transgenic mice were produced that expressed the H-2Kb gene under the control of the metallothionein promoter. Administration of zinc enhanced transgene expression in liver, kidney and exocrine pancreas. No evidence suggestive of an autoimmune response was found in transgene-expressing tissues in mice otherwise allogeneic to H-2Kb. Despite this lack of responsiveness in vivo, T cells could be stimulated in vitro to lyse H-2Kb-bearing target cells. No infiltration was detected in transgenic mice after irradiation and reconstitution with bone marrow cells. When spleen cells were used for reconstitution, however, dense lymphocytic infiltration was seen, particularly in the portal tracts of the liver, and this was accompanied by piecemeal necrosis and apoptosis of periportal hepatocytes. This aggressive response progressively diminished with time, and by 12 weeks after reconstitution many of the portal tracts were free of infiltration while the others showed no accompanying necrosis. The picture at this stage was similar to that seen in chronic persistent hepatitis. These results suggest that, in addition to negative selection in the thymus, peripheral mechanisms not involving clonal deletion or permanent clonal anergy can prevent immune responses to self molecules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acute and chronic hepatitis revisited. Review by an international group. Lancet. 1977 Oct 29;2(8044):914–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison J., Campbell I. L., Morahan G., Mandel T. E., Harrison L. C., Miller J. F. Diabetes in transgenic mice resulting from over-expression of class I histocompatibility molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):529–533. doi: 10.1038/333529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J., Langman R. E., Cohn M. H-2 antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells induced by concanavalin A: estimation of their relative frequency. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):150–156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Raphael K., McAdam W., Peterson M. G. Expression of active human blood clotting factor IX in transgenic mice: use of a cDNA with complete mRNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):871–884. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallman M. J., Wood K. J., Morris P. J. Specific cytotoxic T cells are found in the nonrejected kidneys of blood-transfused rats. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):566–571. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielson K. G., Ohi S., Huang P. C. Immunochemical detection of metallothionein in specific epithelial cells of rat organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2301–2304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink P. J., Shimonkevitz R. P., Bevan M. J. Veto cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:115–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flajnik M. F., Du Pasquier L., Cohen N. Immune responses of thymus/lymphocyte embryonic chimeras: studies on tolerance and major histocompatibility complex restriction in Xenopus. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jun;15(6):540–547. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer D. H. Metallothionein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:913–951. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssaint E., Torano A., Ivanyi J. Split tolerance induced by chick embryo thymic epithelium allografted to embryonic recipients. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3155–3159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Roehm N., Marrack P. T cell tolerance by clonal elimination in the thymus. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90568-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappler J. W., Staerz U., White J., Marrack P. C. Self-tolerance eliminates T cells specific for Mls-modified products of the major histocompatibility complex. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):35–40. doi: 10.1038/332035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisielow P., Blüthmann H., Staerz U. D., Steinmetz M., von Boehmer H. Tolerance in T-cell-receptor transgenic mice involves deletion of nonmature CD4+8+ thymocytes. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):742–746. doi: 10.1038/333742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Prowse S. J., Simeonovic C. J., Warren H. S. Immunobiology of tissue transplantation: a return to the passenger leukocyte concept. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:143–173. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo D., Burkly L. C., Widera G., Cowing C., Flavell R. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Diabetes and tolerance in transgenic mice expressing class II MHC molecules in pancreatic beta cells. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90497-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Schneider R., Lees R. K., Howe R. C., Acha-Orbea H., Festenstein H., Zinkernagel R. M., Hengartner H. T-cell receptor V beta use predicts reactivity and tolerance to Mlsa-encoded antigens. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):40–45. doi: 10.1038/332040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Morahan G., Allison J. Immunological tolerance: new approaches using transgenic mice. Immunol Today. 1989 Feb;10(2):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90306-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momburg F., Koch N., Möller P., Moldenhauer G., Hämmerling G. J. In vivo induction of H-2K/D antigens by recombinant interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1986 May;16(5):551–557. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Germ-line transformation of mice. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:465–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Mercer J. F. Differential expression of four linked sheep metallothionein genes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jun 1;174(2):425–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Liggitt D., Pitts S. L., Hansen S. E., Stewart T. A. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90414-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snover D. C., Weisdorf S. A., Ramsay N. K., McGlave P., Kersey J. H. Hepatic graft versus host disease: a study of the predictive value of liver biopsy in diagnosis. Hepatology. 1984 Jan-Feb;4(1):123–130. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840040122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Lo D., Gao E. K., Ron Y. T cell selection in the thymus. Immunol Rev. 1988 Jan;101:173–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00737.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Schaefer M., Gao E. K., Korngold R. Role of T cell subsets in lethal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) directed to class I versus class II H-2 differences. I. L3T4+ cells can either augment or retard GVHD elicited by Lyt-2+ cells in class I different hosts. J Exp Med. 1988 Feb 1;167(2):556–569. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.2.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teh H. S., Harley E., Phillips R. A., Miller R. G. Quantitative studies on the precursors of cytotoxic lymphocytes. I. Characterization of a clonal assay and determination of the size of clones derived from single precursors. J Immunol. 1977 Mar;118(3):1049–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Golden L., Zakut R., Mellor A., Fahrner K., Kvist S., Flavell R. A. The DNA sequence of the H-2kb gene: evidence for gene conversion as a mechanism for the generation of polymorphism in histocompatibilty antigens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):453–462. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01444.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]