Abstract
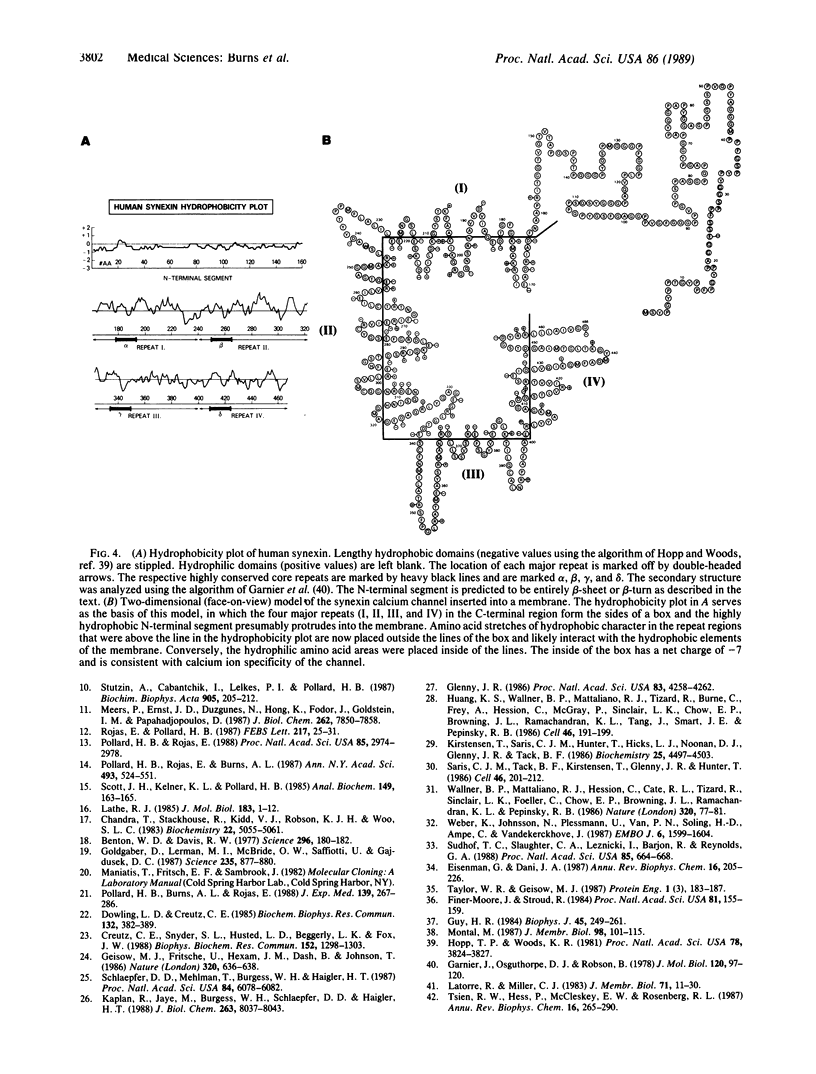
Synexin is a calcium-dependent membrane binding protein that not only fuses membranes but also acts as a voltage-dependent calcium channel. We have isolated and sequenced a set of overlapping cDNA clones for human synexin. The derived amino acid sequence of synexin reveals strong homology in the C-terminal domain with a previously identified class of calcium-dependent membrane binding proteins. These include endonexin II, lipocortin I, calpactin I heavy chain (p36), protein II, and calelectrin 67K. The Mr 51,000 synexin molecule can be divided into a unique, highly hydrophobic N-terminal domain of 167 amino acids and a conserved C-terminal region of 299 amino acids. The latter domain is composed of alternating hydrophobic and hydrophilic segments. Analysis of the entire structure reveals possible insights into such diverse properties as voltage-sensitive calcium channel activity, ion selectivity, affinity for phospholipids, and membrane fusion.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra T., Stackhouse R., Kidd V. J., Robson K. J., Woo S. L. Sequence homology between human alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, and antithrombin III. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5055–5061. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Pazoles C. J., Pollard H. B. Identification and purification of an adrenal medullary protein (synexin) that causes calcium-dependent aggregation of isolated chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2858–2866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Pollard H. B. A Cell-free Model for Protein-Lipid Interactions in Exocytosis: Aggregation and Fusion of Chromaffin Granules in the Presence of Calcium, Synexin, and CIS-Unsaturated Fatty Acids. Biophys J. 1982 Jan;37(1):119–120. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84630-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Snyder S. L., Husted L. D., Beggerly L. K., Fox J. W. Pattern of repeating aromatic residues in synexin. Similarity to the cytoplasmic domain of synaptophysin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 16;152(3):1298–1303. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80426-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E., Sterner D. C. Calcium dependence of the binding of synexin to isolated chromaffin granules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 18;114(1):355–364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91635-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creutz C. E. cis-Unsaturated fatty acids induce the fusion of chromaffin granules aggregated by synexin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):247–256. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling L. G., Creutz C. E. Comparison of synexin isotypes in secretory and non-secretory tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Oct 15;132(1):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman G., Dani J. A. An introduction to molecular architecture and permeability of ion channels. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:205–226. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finer-Moore J., Stroud R. M. Amphipathic analysis and possible formation of the ion channel in an acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):155–159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisow M. J., Fritsche U., Hexham J. M., Dash B., Johnson T. A consensus amino-acid sequence repeat in Torpedo and mammalian Ca2+-dependent membrane-binding proteins. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):636–638. doi: 10.1038/320636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. Two related but distinct forms of the Mr 36,000 tyrosine kinase substrate (calpactin) that interact with phospholipid and actin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4258–4262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R. A structural model of the acetylcholine receptor channel based on partition energy and helix packing calculations. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):249–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84152-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong K., Düzgüneş N., Ekerdt R., Papahadjopoulos D. Synexin facilitates fusion of specific phospholipid membranes at divalent cation concentrations found intracellularly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4642–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R., Jaye M., Burgess W. H., Schlaepfer D. D., Haigler H. T. Cloning and expression of cDNA for human endonexin II, a Ca2+ and phospholipid binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8037–8043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Saris C. J., Hunter T., Hicks L. J., Noonan D. J., Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Primary structure of bovine calpactin I heavy chain (p36), a major cellular substrate for retroviral protein-tyrosine kinases: homology with the human phospholipase A2 inhibitor lipocortin. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 12;25(16):4497–4503. doi: 10.1021/bi00364a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latorre R., Miller C. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J Membr Biol. 1983;71(1-2):11–30. doi: 10.1007/BF01870671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers P., Ernst J. D., Düzgünes N., Hong K. L., Fedor J., Goldstein I. M., Papahadjopoulos D. Synexin-like proteins from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Identification and characterization of granule-aggregating and membrane-fusing activities. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7850–7858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M. Reconstitution of channel proteins from excitable cells in planar lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1987;98(2):101–115. doi: 10.1007/BF01872123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. J., Hughes J. M., Whittaker V. P. Purification and mode of action of synexin: a protein enhancing calcium-induced membrane aggregation. J Neurochem. 1982 Aug;39(2):529–536. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb03977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nir S., Stutzin A., Pollard H. B. Effect of synexin on aggregation and fusion of chromaffin granule ghosts at pH 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Oct 2;903(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Burns A. L., Rojas E. A molecular basis for synexin-driven, calcium-dependent membrane fusion. J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:267–286. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Rojas E., Burns A. L. Synexin and chromaffin granule membrane fusion. A novel "hydrophobic bridge" hypothesis for the driving and directing of the fusion process. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:524–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard H. B., Rojas E. Ca2+-activated synexin forms highly selective, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2974–2978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Pollard H. B. Membrane capacity measurements suggest a calcium-dependent insertion of synexin into phosphatidylserine bilayers. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 8;217(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81235-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlaepfer D. D., Mehlman T., Burgess W. H., Haigler H. T. Structural and functional characterization of endonexin II, a calcium- and phospholipid-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6078–6082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. H., Kelner K. L., Pollard H. B. Purification of synexin by pH step elution from chromatofocusing media in the absence of ampholytes. Anal Biochem. 1985 Aug 15;149(1):163–165. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90489-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutzin A. A fluorescence assay for monitoring and analyzing fusion biological membrane vesicles in vitro. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):274–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80341-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutzin A., Cabantchik Z. I., Lelkes P. I., Pollard H. B. Synexin-mediated fusion of bovine chromaffin granule ghosts. Effect of pH. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 27;905(1):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Südhof T. C., Slaughter C. A., Leznicki I., Barjon P., Reynolds G. A. Human 67-kDa calelectrin contains a duplication of four repeats found in 35-kDa lipocortins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Geisow M. J. Predicted structure for the calcium-dependent membrane-binding proteins p35, p36, and p32. Protein Eng. 1987 Jun;1(3):183–187. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.3.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Hess P., McCleskey E. W., Rosenberg R. L. Calcium channels: mechanisms of selectivity, permeation, and block. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1987;16:265–290. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.16.060187.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Hession C., Cate R. L., Tizard R., Sinclair L. K., Foeller C., Chow E. P., Browing J. L., Ramachandran K. L. Cloning and expression of human lipocortin, a phospholipase A2 inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Nature. 1986 Mar 6;320(6057):77–81. doi: 10.1038/320077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Johnsson N., Plessmann U., Van P. N., Söling H. D., Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J. The amino acid sequence of protein II and its phosphorylation site for protein kinase C; the domain structure Ca2+-modulated lipid binding proteins. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1599–1604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]