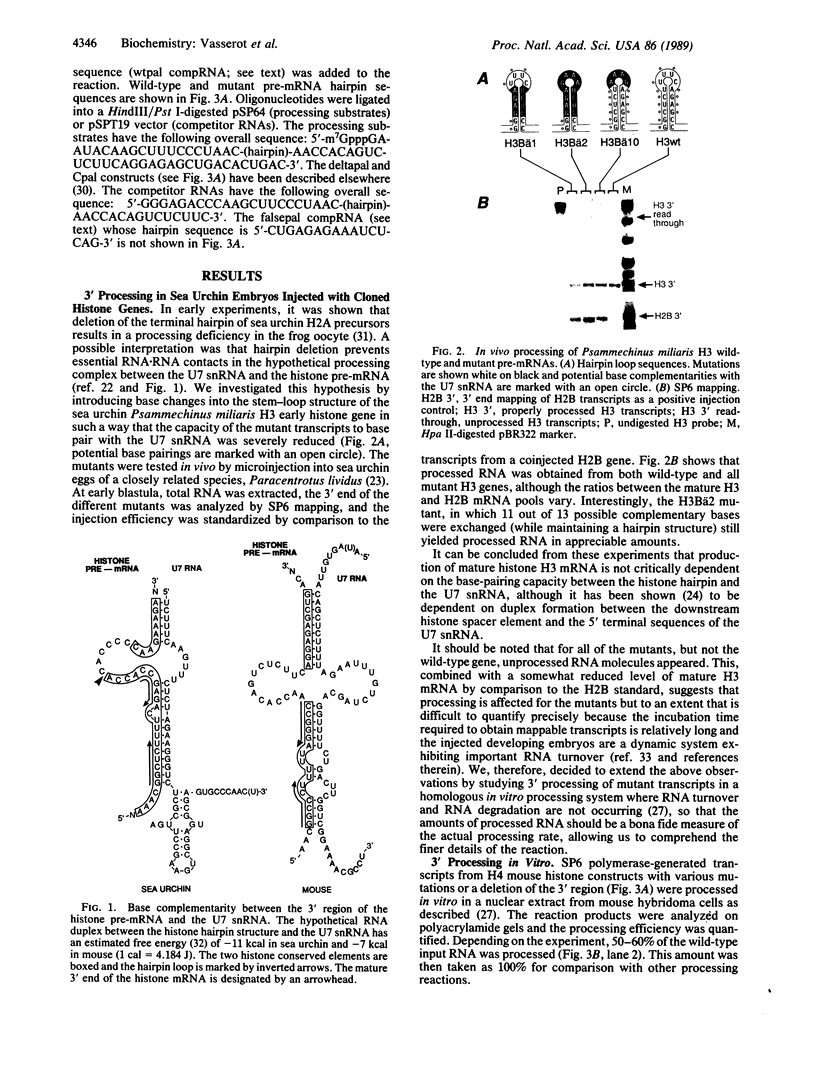
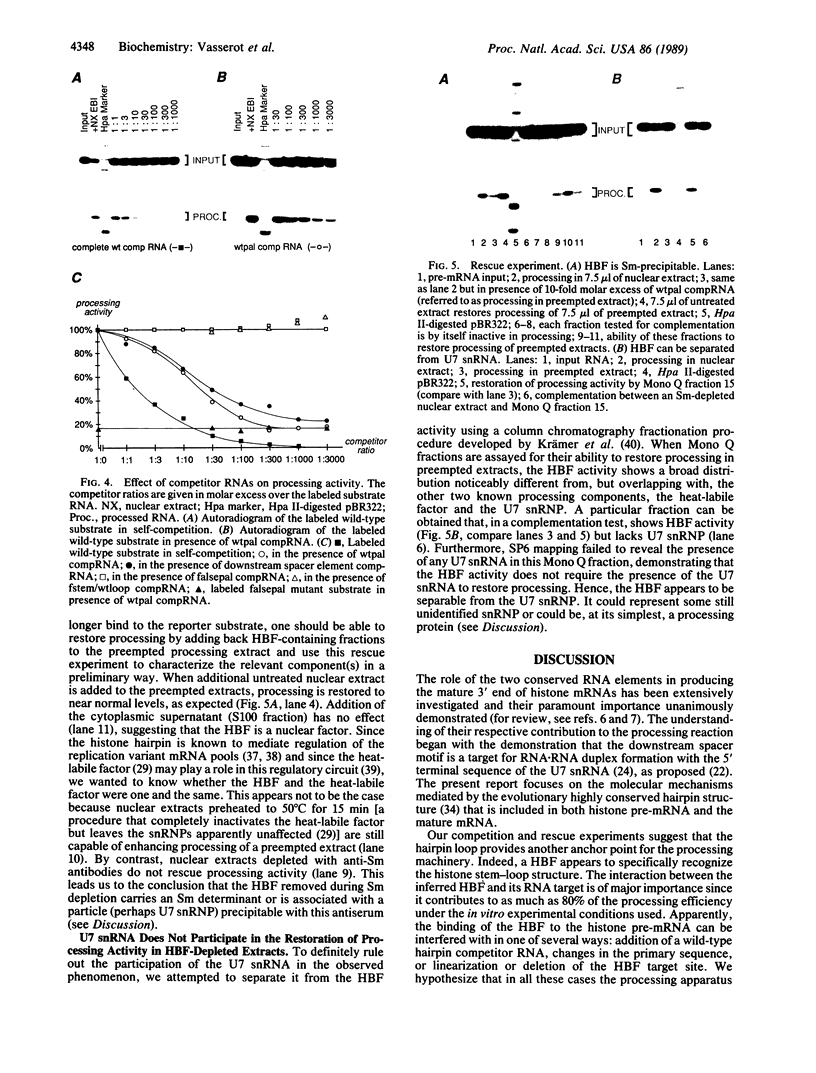
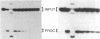Abstract
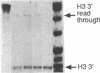
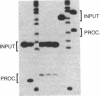
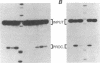
The hairpin loop structure and the downstream spacer element of histone mRNA precursors are both needed for efficient 3' end formation in vivo and in vitro. Though generally considered as a single processing signal, these two motifs are involved in different types of interaction with the processing machinery. Whereas RNA duplex formation between the downstream spacer element and the U7 small nuclear RNA is essential for processing, we show here that base pairing between the histone stem-loop structure and the U7 RNA is not relevant. Our experiments demonstrate that a processing factor other than the U7 RNA makes contact with the highly conserved hairpin structure of the histone precursor. The recognition of the target site by the processing factor is structure and sequence specific. Prevention of this interaction results in an 80% decrease of 3' cleavage efficiency in vitro. The hairpin binding factor is Sm-precipitable and can be partially separated from the U7 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle on a Mono Q column.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aziz N., Munro H. N. Iron regulates ferritin mRNA translation through a segment of its 5' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8478–8482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Folk W., Birnstiel M. L. The terminal RNA stem-loop structure and 80 bp of spacer DNA are required for the formation of 3' termini of sea urchin H2A mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90176-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of authentic 3' termini of an H2A mRNA in vivo is dependent on a short inverted DNA repeat and on spacer sequences. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bram R. J., Young R. A., Steitz J. A. The ribonuclease III site flanking 23S sequences in the 30S ribosomal precursor RNA of E. coli. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90513-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Birnsteil M. L. A regulatory sequence near the 3' end of sea urchin histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):2997–3008. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. E., Farnham P. J., Platt T. Synthetic sites for transcription termination and a functional comparison with tryptophan operon termination sites in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4180–4184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotten M., Gick O., Vasserot A., Schaffner G., Birnstiel M. L. Specific contacts between mammalian U7 snRNA and histone precursor RNA are indispensable for the in vitro 3' RNA processing reaction. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):801–808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M., Lienhard S., Parisot R. F. Intracellular transport of microinjected 5S and small nuclear RNAs. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):572–577. doi: 10.1038/295572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick O., Krämer A., Keller W., Birnstiel M. L. Generation of histone mRNA 3' ends by endonucleolytic cleavage of the pre-mRNA in a snRNP-dependent in vitro reaction. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1319–1326. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gick O., Krämer A., Vasserot A., Birnstiel M. L. Heat-labile regulatory factor is required for 3' processing of histone precursor mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8937–8940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin G. M., Schaufele F., Schaffner G., Birnstiel M. L. Functional analysis of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1076–1084. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall K. B., Green M. R., Redfield A. G. Structure of a pre-mRNA branch point/3' splice site region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):704–708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Frick M., Keller W. Separation of multiple components of HeLa cell nuclear extracts required for pre-messenger RNA splicing. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17630–17640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn S. P., Kasper L. M., Gardner J. F. Contributions of RNA secondary structure and length of the thymidine tract to transcription termination at the thr operon attenuator. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):472–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Schümperli D. RNA 3' processing regulates histone mRNA levels in a mammalian cell cycle mutant. A processing factor becomes limiting in G1-arrested cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1721–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Stauber C., Schindler R., Schümperli D. Faithful cell-cycle regulation of a recombinant mouse histone H4 gene is controlled by sequences in the 3'-terminal part of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Pandey N. B. Multiple regulatory steps control histone mRNA concentrations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowry K. L., Steitz J. A. Identification of the human U7 snRNP as one of several factors involved in the 3' end maturation of histone premessenger RNA's. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1682–1687. doi: 10.1126/science.2825355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols M., Söll D., Willis I. Yeast RNase P: catalytic activity and substrate binding are separate functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1379–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romaniuk P. J., Lowary P., Wu H. N., Stormo G., Uhlenbeck O. C. RNA binding site of R17 coat protein. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 24;26(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1021/bi00380a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufele F., Gilmartin G. M., Bannwarth W., Birnstiel M. L. Compensatory mutations suggest that base-pairing with a small nuclear RNA is required to form the 3' end of H3 messenger RNA. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):777–781. doi: 10.1038/323777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümperli D. Cell-cycle regulation of histone gene expression. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):471–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soldati D., Schümperli D. Structural and functional characterization of mouse U7 small nuclear RNA active in 3' processing of histone pre-mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1518–1524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Lee S. I. Amount of RNA secondary structure required to induce an alternative splice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3194–3198. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber C., Lüscher B., Eckner R., Lötscher E., Schümperli D. A signal regulating mouse histone H4 mRNA levels in a mammalian cell cycle mutant and sequences controlling RNA 3' processing are both contained within the same 80-bp fragment. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3297–3303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04643.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Galli G., Busslinger M., Birnstiel M. L. The cDNA sequences of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA suggest specific contacts between histone mRNA precursor and U7 RNA during RNA processing. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2801–2807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Separation and characterization of a poly(A) polymerase and a cleavage/specificity factor required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. S., Nomura M. Translational regulation of the L11 ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli: mutations that define the target site for repression by L1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 10;15(7):3085–3096. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.7.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitelli L., Kemler I., Lauber B., Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M. Developmental regulation of micro-injected histone genes in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1988 May;127(1):54–63. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90188-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]