Abstract
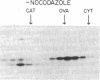
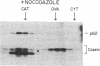
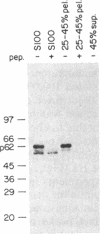
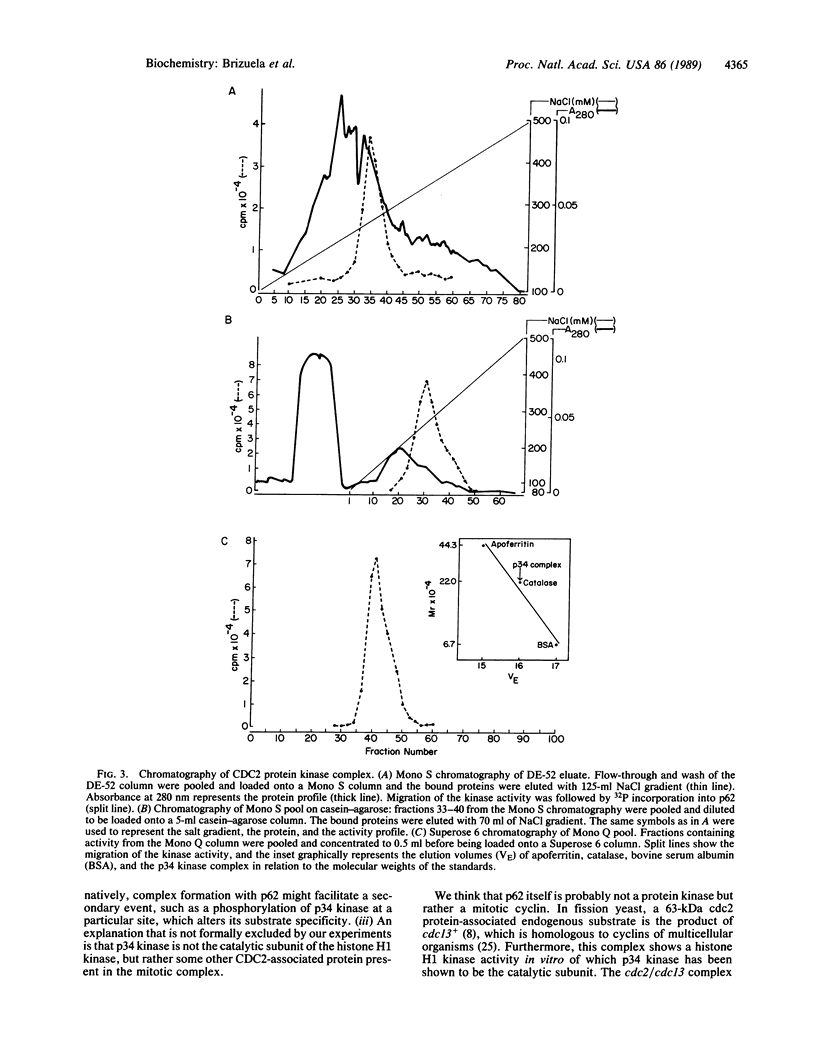
p34 kinase, the product of the CDC2 gene, is a cell-cycle regulated protein kinase that is most active during mitosis. In HeLa cells, p34 kinase has previously been shown to exist in both a low- and a high-molecular-mass form, the latter of which is only found in cells in the G2/M phase of the cell cycle and contains a 62-kDa subunit. Here we show that although each form of the kinase phosphorylates casein in vitro, only the high-molecular-mass form uses histone H1 as substrate. The high-molecular-mass form of p34 kinase from nocodazole-treated HeLa cells was purified 6700-fold. The apparent molecular mass of the mitotic CDC2-encoded protein kinase complex was 220 kDa. The purified enzyme phosphorylated not only its endogenous 62-kDa subunit but also phosphorylated histone H1 with a Km of 3 microM and used ATP 40 times more efficiently than GTP (Km 54 microM and 2 mM, respectively). The enzyme activity was unaffected by cAMP, calcium/calmodulin, or by the heat-stable inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. These characteristics are typical of growth-associated histone H1 kinase from different organisms. These results suggest that CDC2 protein may be activated as an M-phase-specific protein kinase in part by its association with the p62 subunit.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arion D., Meijer L., Brizuela L., Beach D. cdc2 is a component of the M phase-specific histone H1 kinase: evidence for identity with MPF. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R. Control of cell division by very lysine rich histone (F1) phosphorylation. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):257–261. doi: 10.1038/247257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brizuela L., Draetta G., Beach D. p13suc1 acts in the fission yeast cell division cycle as a component of the p34cdc2 protein kinase. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3507–3514. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cyclin in fission yeast. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):738–740. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90933-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Beach D. Activation of cdc2 protein kinase during mitosis in human cells: cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation and subunit rearrangement. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90175-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Brizuela L., Potashkin J., Beach D. Identification of p34 and p13, human homologs of the cell cycle regulators of fission yeast encoded by cdc2+ and suc1+. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90227-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Luca F., Westendorf J., Brizuela L., Ruderman J., Beach D. Cdc2 protein kinase is complexed with both cyclin A and B: evidence for proteolytic inactivation of MPF. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):829–838. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90687-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draetta G., Piwnica-Worms H., Morrison D., Druker B., Roberts T., Beach D. Human cdc2 protein kinase is a major cell-cycle regulated tyrosine kinase substrate. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):738–744. doi: 10.1038/336738a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier J., Norbury C., Lohka M., Nurse P., Maller J. Purified maturation-promoting factor contains the product of a Xenopus homolog of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):433–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindley J., Phear G. A. Sequence of the cell division gene CDC2 from Schizosaccharomyces pombe; patterns of splicing and homology to protein kinases. Gene. 1984 Nov;31(1-3):129–134. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labbe J. C., Lee M. G., Nurse P., Picard A., Doree M. Activation at M-phase of a protein kinase encoded by a starfish homologue of the cell cycle control gene cdc2+. Nature. 1988 Sep 15;335(6187):251–254. doi: 10.1038/335251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake R. S., Salzman N. P. Occurrence and properties of a chromatin-associated F1-histone phosphokinase in mitotic Chinese hamster cells. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 5;11(25):4817–4826. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Hayes M. K., Maller J. L. Purification of maturation-promoting factor, an intracellular regulator of early mitotic events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui Y., Markert C. L. Cytoplasmic control of nuclear behavior during meiotic maturation of frog oocytes. J Exp Zool. 1971 Jun;177(2):129–145. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401770202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Yasuda H., Mita S., Marunouchi T., Yamada M. Evidence for the involvement of H1 histone phosphorylation in chromosome condensation. Nature. 1980 Mar 13;284(5752):181–183. doi: 10.1038/284181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. R., Huebner V. D. Nuclear protein kinases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;59(1-2):81–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00231306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller K., Little M. Chromatin-bound histone 1 kinase activity in synchronized HeLa S3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1989 Jan;180(1):30–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(89)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Thuriaux P., Nasmyth K. Genetic control of the cell division cycle in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jul 23;146(2):167–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00268085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Meijer L., Krebs E. G. Characterization of maturation-activated histone H1 and ribosomal S6 kinases in sea star oocytes. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 1;26(24):7960–7968. doi: 10.1021/bi00398a062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. Negative regulation of mitosis by wee1+, a gene encoding a protein kinase homolog. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Nurse P. The mitotic inducer nim1+ functions in a regulatory network of protein kinase homologs controlling the initiation of mitosis. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90459-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simanis V., Nurse P. The cell cycle control gene cdc2+ of fission yeast encodes a protein kinase potentially regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90390-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunkara P. S., Wright D. A., Rao P. N. Mitotic factors from mammalian cells induce germinal vesicle breakdown and chromosome condensation in amphibian oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2799–2802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodford T. A., Pardee A. B. Histone H1 kinase in exponential and synchronous populations of Chinese hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4669–4676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeilig C. E., Langan T. A. Studies on the mechanism of activation of mitotic histone H1 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):1372–1379. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]