Abstract
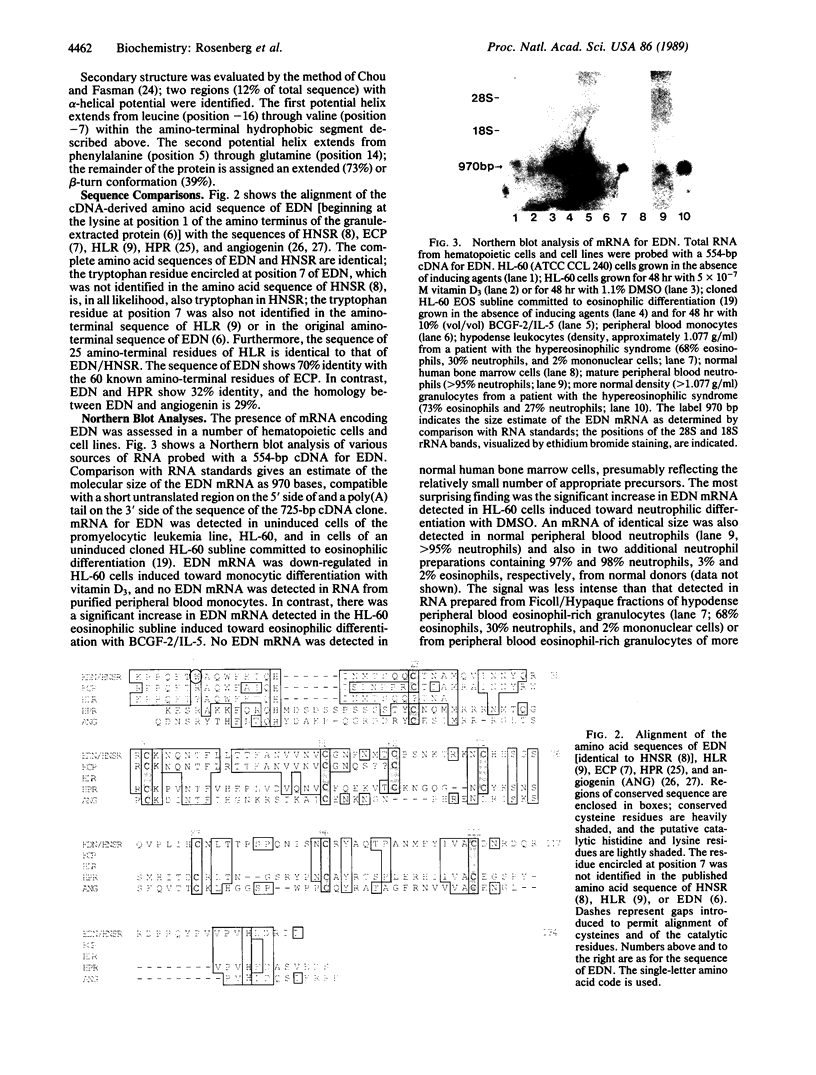
We have isolated a 725-base-pair cDNA clone for human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN). EDN is a distinct cationic protein of the eosinophil's large specific granule known primarily for its ability to induce ataxia, paralysis, and central nervous system cellular degeneration in experimental animals (Gordon phenomenon). The open reading frame encodes a 134-amino acid mature polypeptide with a molecular mass of 15.5 kDa and a 27-residue amino-terminal hydrophobic leader sequence. The sequence of the mature polypeptide is identical to that reported for human urinary ribonuclease [Beintema, J. J., Hofsteenge, J., Iwama, M., Morita, T., Ohgi, K., Irie, M., Sugiyama, R. H., Schieven, G. L., Dekker, C. A. & Glitz, D. G. (1988) Biochemistry 27, 4530-4538] and to the amino-terminal sequence of human liver ribonuclease [Sorrentino, S., Tucker, G. K. & Glitz, D. G. (1988) J. Biol. Chem. 263, 16125-16131]; the cDNA encodes a tryptophan in position 7, which was previously unidentified in the amino acid sequences of EDN or the urinary and liver ribonucleases. Both EDN and the related granule protein, eosinophil cationic protein, have ribonucleolytic activity; sequence similarities among EDN, eosinophil cationic protein, ribonucleases from liver, urine, and pancreas, and angiogenin define a ribonuclease multigene family. mRNA encoding EDN was detected in uninduced HL-60 cells and was up-regulated in cells induced toward eosinophilic differentiation with B-cell growth factor 2/interleukin 5 and toward neutrophilic differentiation with dimethyl sulfoxide. EDN mRNA was detected in mature neutrophils even though EDN-like neurotoxic activity is not found in neutrophil extracts. These results suggest that neutrophils contain a protein that is closely related or identical to EDN.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Venge P., Olsson I., Harley J. B., Fauci A. S., Gleich G. J. Distinctive cationic proteins of the human eosinophil granule: major basic protein, eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2977–2982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi K., Yamanaka M., Murai K., Niho Y., Omae T. Serum acid ribonuclease in myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):2168–2173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akagi K., Yamanaka M., Murai K., Omae T. Purification and properties of acid ribonucleases in human serum and leukocytes. Cancer Res. 1978 Jul;38(7):2163–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker R. L., Gleich G. J., Pease L. R. Acidic precursor revealed in human eosinophil granule major basic protein cDNA. J Exp Med. 1988 Oct 1;168(4):1493–1498. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.4.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beintema J. J., Hofsteenge J., Iwama M., Morita T., Ohgi K., Irie M., Sugiyama R. H., Schieven G. L., Dekker C. A., Glitz D. G. Amino acid sequence of the nonsecretory ribonuclease of human urine. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4530–4538. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beintema J. J., Wietzes P., Weickmann J. L., Glitz D. G. The amino acid sequence of human pancreatic ribonuclease. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):48–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. The HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line: proliferation, differentiation, and cellular oncogene expression. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Graaf F. K., Klaasen-Boor P. Purification and characterization of a complex between cloacin and its immunity protein isolated from Enterobacter cloacae (Clo DF13). Dissociation and reconstitution of the complex. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):107–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Purification of human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Sumi S. M., Klebanoff S. J. Neurotoxicity of human eosinophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischkoff S. A., Pollak A., Gleich G. J., Testa J. R., Misawa S., Reber T. J. Eosinophilic differentiation of the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line, HL-60. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):179–196. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Adolphson C. R. The eosinophilic leukocyte: structure and function. Adv Immunol. 1986;39:177–253. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60351-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Bell M. P., Checkel J. L., Ackerman S. J., McKean D. J. Biochemical and functional similarities between human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil cationic protein: homology with ribonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3146–3150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg U., Widegren B., Arnason U., Egesten A., Olsson I. The cytotoxic eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) has ribonuclease activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1239–1242. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80310-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart G. W., Brew K., Grant G. A., Bradshaw R. A., Lennarz W. J. Primary structural requirements for the enzymatic formation of the N-glycosidic bond in glycoproteins. Studies with natural and synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9747–9753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronquist K. E., Lennarz W. J. Enzymatic conversion of proteins to glycoproteins by lipid-linked saccharides: a study of potential exogenous acceptor proteins. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(1):51–65. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W., Strydom D. J., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Sequence of the cDNA and gene for angiogenin, a human angiogenesis factor. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5494–5499. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara M., Ogawa M., Ohta T., Kurokawa E., Kitahara T., Murata A., Matsuda K., Kosaki G., Watanabe T., Wada H. Radioimmunoassay for human pancreatic ribonuclease and measurement of serum immunoreactive pancreatic ribonuclease in patients with malignant tumors. Cancer Res. 1984 May;44(5):2240–2243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Simonsen C., Scott R., Griffith J., Ellis N., Kennedy J., Campanelli D., Nathan C., Gabay J. Isolation of a complementary DNA clone encoding a precursor to human eosinophil major basic protein. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2295–2308. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina H. A., Kierszenbaum F., Hamann K. J., Gleich G. J. Toxic effects produced or mediated by human eosinophil granule components on Trypanosoma cruzi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Mar;38(2):327–334. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morita T., Niwata Y., Ohgi K., Ogawa M., Irie M. Distribution of two urinary ribonuclease-like enzymes in human organs and body fluids. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):17–25. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwata Y., Ohgi K., Sanda A., Takizawa Y., Irie M. Purification and properties of bovine kidney ribonucleases. J Biochem. 1985 Mar;97(3):923–934. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Ogawa M., Kurihara M., Kitahara T., Kosaki G. Purification, characterization and development of radioimmunoassay of human liver ribonuclease. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Sep 1;124(1):51–62. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90319-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Persson A. M., Winqvist I. Biochemical properties of the eosinophil cationic protein and demonstration of its biosynthesis in vitro in marrow cells from patients with an eosinophilia. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):498–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., Klaasen-Boor P., De Graaf F. K. Mode of action of the cloacin DF13-immunity protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 5;392(1):184–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., Klaasen-Boor P., Sneeuwloper G., De Graaf F. K. Interaction of the complex between cloacin and its immunity protein and of cloacin with the outer and cytoplasmic membranes of sensitive cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11757.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudega B., van der Molen J., de Graaf F. K. In vitro binding of cloacin DF13 to its purified outer membrane receptor protein and effect of peptidoglycan on bacteriocin-receptor interaction. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):964–970. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.964-970.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters M. S., Rodriguez M., Gleich G. J. Localization of human eosinophil granule major basic protein, eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin by immunoelectron microscopy. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):656–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pless D. D., Lennarz W. J. Enzymatic conversion of proteins to glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):134–138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster S. J., Badiavas E. V., Costa-Giomi P., Weinmann R., Erslev A. J., Caro J. Stimulation of erythropoietin gene transcription during hypoxia and cobalt exposure. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sierakowska H., Shugar D. Mammalian nucleolytic enzymes. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1977;20:59–130. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60470-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slifman N. R., Loegering D. A., McKean D. J., Gleich G. J. Ribonuclease activity associated with human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil cationic protein. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2913–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorrentino S., Tucker G. K., Glitz D. G. Purification and characterization of a ribonuclease from human liver. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16125–16131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair D. K., Rybak S. M., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Angiogenin abolishes cell-free protein synthesis by specific ribonucleolytic inactivation of 40S ribosomes. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7263–7268. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J., Fett J. W., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Amino acid sequence of human tumor derived angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5486–5494. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. C., Spry C. J., Peterson C., Venge P., Olsson I. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish between storage and secreted forms of eosinophil cationic protein. Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):182–184. doi: 10.1038/309182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonaga M., Gasson J. C., Quan S. G., Golde D. W. Establishment of eosinophilic sublines from human promyelocytic leukemia (HL-60) cells: demonstration of multipotentiality and single-lineage commitment of HL-60 stem cells. Blood. 1986 May;67(5):1433–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Miyada C. G. Oligonucleotide probes for the screening of recombinant DNA libraries. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:432–442. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weickmann J. L., Elson M., Glitz D. G. Purification and characterization of human pancreatic ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1272–1278. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weickmann J. L., Glitz D. G. Human ribonucleases. Quantitation of pancreatic-like enzymes in serum, urine, and organ preparations. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8705–8710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Peterson C. G., Venge P., Cohn Z. A. Mechanism of membrane damage mediated by human eosinophil cationic protein. Nature. 1986 Jun 5;321(6070):613–616. doi: 10.1038/321613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Niekus H. G., Klootwijk J. Inactivation of bacterial ribosomes in vivo and in vitro by cloacin DF13. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80601-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Spanjaerdt Speckman E. A., Stouthamer A. H. Mode of action of a bacteriocin produced by Enterobacter cloacae DF13. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(3):287–306. doi: 10.1007/BF02219150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]