Abstract
Allergic asthma is a TH2-mediated disease marked by airway inflammation, increased mucus production, and elevated serum IgE in response to allergen provocation. Among its ascribed functions, the neuropeptide Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) is believed to promote a TH2 phenotype when signaling through its VPAC2 receptor. In this study, we assessed the requirement for the VIP/VPAC2 axis in initiating the allergic pulmonary phenotype in a murine model of fungal allergic asthma. C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) and VPAC2 knock-out (KO) mice were sensitized with Aspergillus fumigatus antigen and challenged with an aerosol of live conidia to induce allergic airways disease. WT and KO mice exhibited similar peribronchovascular inflammation, increased number of goblet cells, and elevated serum IgE. However, the absence of VPAC2 receptor resulted in a marked enhancement of MUC5AC mRNA with an associated increase in goblet cells and a reduction in eosinophils in the airway lumen at day 3 when VIP mRNA was undetectable in the KO lung. Sustained elevation of serum IgE was noted in KO mice at day 14, while the level in WT mice declined at this time point. These data suggest that the absence of VPAC2 does not protect mice from developing the signs and symptoms of allergic asthma.
Keywords: Vasoactive intestinal peptide, Matrix metalloproteinase-2, Eosinophil, Vipr2, Allergy, Asthma
1. Introduction
Allergic asthma is a pulmonary syndrome characterized by bronchial inflammation, hyperresponsiveness, excessive mucus production, remodeling, and increased serum IgE in response to allergen provocation. Exposure to the triggering allergen results in the release of chemotactic agents to recruit eosinophils [14] and TH2-type lymphocytes [39], the hallmark leukocytes associated with allergic asthma.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is a ubiquitous, pleiotropic neuropeptide with cytokine properties, produced by cells of the immune system such as macrophages, eosinophils, neutrophils, T and B lymphocytes [32]. Known effects of VIP include, broncho- and vaso-dilation [29], inhibition of smooth muscle cell proliferation [23], and regulation of leukocyte migration [2]. VIP is abundant in the lung, and immune cells contribute to the amounts produced by the non-adrenergic non-cholinergic innervation [22]. The observations that VIP availability is decreased in patients with asthma [4, 25], and that increased airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness occur in the absence of VIP [33], have led to the recognition of VIP as an “anti-asthma” factor.
VIP can function via two G protein-coupled receptors VPAC1 and VPAC2. Most cells of the immune system express both VPAC1 and VPAC2, and macrophages and T cells change their receptor ratio in favor of VPAC2 upon activation [10]. However, the cell type that produces and responds to VIP, as well as the temporal and spatial expression of its receptors, dictate the outcome of the immune response.
Transgenic mice with constitutively upregulated T cell expression of human VPAC2 have been shown to have increased serum IgE and eosinophils [37], supporting the role of the VIP/VPAC2 axis in skewing the immune balance in favor of TH2. In contrast, VPAC2 null mice have increased delayed-type hypersensitivity marked by decreased serum IgE and eosinophilia [15] indicating that VPAC2 may be VIP’s “pro-allergy” receptor.
In the current study, we hypothesized that in the absence of VPAC2, mice would show the amelioration of the hallmark signs and symptoms of allergic asthma in an Aspergillus fumigatus-induced murine model system. Although VPAC2 null mice had a delay and reduction in eosinophils, the absence of VPAC2 did not protect these mice from developing the characteristics of allergic asthma marked by increased serum IgE and goblet cell metaplasia. To our knowledge, this is the first report to determine the outcome of VPAC2 KO animals subjected to a pulmonary allergy model. These findings contribute to our understanding of VIP and its receptors in allergic asthma, emphasizing that the absence of a single VIP receptor, VPAC2, does not result in the amelioration of asthma symptoms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Heterozygous VPAC2 null (KO) mice on C57BL/6 background were a kind gift from Dr. Anthony Harmar, University of Edinburgh, UK. These were crossed to achieve homozygous animals which were used for the study. C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, ME, USA. Animals were housed on Alpha-dri™ paper bedding (Shepherd Specialty Papers, Watertown, TN, USA) in microfilter-topped cages (Ancare, Bellmore, NY, USA) in a specific pathogen-free facility with ad libitum access to food and water. The study described was performed in accordance with IACUC guidelines of North Dakota State University.
2.2. Fungal antigen and Aspergillus fumigatus culture and aerosol inoculation system
Soluble Aspergillus fumigatus antigen was purchased from Greer Laboratories (Lenoir, NC, USA) and fungal culture stock (strain NIH 5233) was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). All experimental procedures utilizing A. fumigatus were conducted with prior approval of the Institutional Biological Safety Office of North Dakota State University. A single lyophilized A. fumigatus culture was reconstituted per ATCC recommendations, and 60-μl aliquots of the suspension were stored at 4°C until use.
An aerosol inoculation chamber with nose ports for three mice was fitted with an inline 25-cm2 culture flask in which a mature (8-day-old), A. fumigatus culture had been grown on Sabouraud Dextrose Agar. Airflow through the culture flask was delivered at 2 psi to liberate the hydrophobic spores and allow their delivery through the chamber, which was housed in a Class II biosafety cabinet for inhalation experiments. The ports were plugged and the chamber was coated with airborne conidia for 10-min prior to animal challenge. The fungal culture was changed with each new set of mice.
2.3. Allergen sensitization and allergen challenge by aerosol delivery
Animals were sensitized with a modification of Hogaboam’s published protocol [18]. Briefly, 10 μg of A. fumigatus antigen (Greer Laboratories) in 0.1 ml normal saline (NS) mixed with 0.1 ml of Imject® Alum (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA) was injected subcutaneously (0.1 ml) and intraperitoneally (0.1 ml). Two weeks later, mice received the first of three weekly intranasal sensitizations with 20 μg of A. fumigatus antigen in 20 μl of NS.
One week after the last sensitization, mice were anesthetized with a cocktail of Ketamine (75 mg/kg) and Xylazine (25 mg/kg) and challenged with a 10-min, nose-only, aerosol exposure to live A. fumigatus spores. Each anesthetized animal was placed supine with its nose in an inoculation port inhaling the fungal spores for 10 min, constituting the allergen challenge. Two weeks following the first allergen challenge, mice were subjected to a second 10-min aerosol fungal challenge. Naïve animals were neither sensitized nor challenged. After the second allergen exposure, sensitized and challenged mice were separated into groups of five for analysis at days 3, 7, and 14.
2.4. Serum sample collection and bronchoalveolar lavage
Approximately 500 μl of blood was removed from each mouse via ocular bleed and centrifuged at 13,000 ×g for 10 min to yield sera which was stored at −20°C until use. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was performed through a tracheostomy tube on each mouse with 1.0 ml of sterile NS. BAL contents were centrifuged at 3000 ×g for 10 min to separate the cells from the fluid. The BAL fluid was stored at −20°C until use, and cells were used for morphometric analysis (see below). Left lungs were harvested and fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for histological analysis. Right lungs were snap frozen in liquid N2 and stored at −20°C for RNA extraction and analysis.
2.5. Morphometric and histological analysis
BAL cells were resuspended in 0.2 – 1.0 ml of NS and cytospun (Shandon Scientific, Runcorn, UK) onto microscope slides and differentially stained (Quick-Dip stain, Mercedes Medical, Sarasota, FL, USA). Cells from five randomly chosen high-powered fields (HPFs) were counted to determine the mean number of each cell type in the airway lumen of each mouse.
Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded lungs were cut longitudinally across the coronal plane in 5-μm sections and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) to assess inflammation or with periodic acid Schiff’s (PAS) stain for goblet cells. Peribronchovascular eosinophils (identified by eosin stained cytoplasm) were counted in 50 randomly selected HPFs by an investigator blind to the treatments and sample groups. Results were reported as the mean per 50 HPFs.
2.6. Quantification of serum IgE and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 in BAL fluid
The amount of total IgE in sera (BD OptEIA, San Diego, CA, USA) and MMP-2 in BAL fluid (Quantikine kit for MMP-2, R&D Systems, MN, USA) were quantified via specific ELISA according to manufacturers’ guidelines. Serum samples were diluted 1/100 and BAL fluid samples were diluted 1/10.
2.7. Real-time qPCR analysis of mean fold change in gene expression
RNA was extracted from lung tissue with Trizol® reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), and 2 μg of DNase treated RNA was used for cDNA synthesis. All necessary reagents for DNase treatment and cDNA synthesis (DNase, random primers, M-MLV reverse transcriptase, dNTPs) were purchased from Promega (Madison, WI, USA). RNA-specific QuantiTect primer assays for MUC5AC, VIP, VPAC1, VPAC2 and for the internal control, HPRT-1, (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA) were used in a Sybr-Green Fast PCR master mix (Qiagen) reaction and run on an ABI-7500 real-time PCR machine (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The 2−ΔΔCT method was used to calculate the relative fold change in gene expression of all samples standardized to naïve controls.
2.8. Statistical analysis
Allergic WT and KO mice were compared against their respective naïve controls and against one another at each time point. An unpaired, Student’s two tailed t-test with Welch’s correction was used to determine statistical significance with Prism GraphPad software (San Diego, CA, USA). All results are expressed as mean ± SEM. p <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
The predominant differences between the WT and VPAC2 KO mice occurred three days after the fungal challenge. At day 3, the WT had a 4.5-fold induction of VIP mRNA in the lung, approximately 400 eosinophils/HPF in the airway lumen, and a 300-fold induction of MUC5AC mRNA. In comparison, the VPAC2 KO mice had no detectable VIP mRNA expression in the lung, about 160 eosinophils/HPF in the airways, and a 750-fold increase in MUC5AC mRNA expression.
3.1. The absence of VPAC2 altered the dynamics of leukocyte recruitment and egression
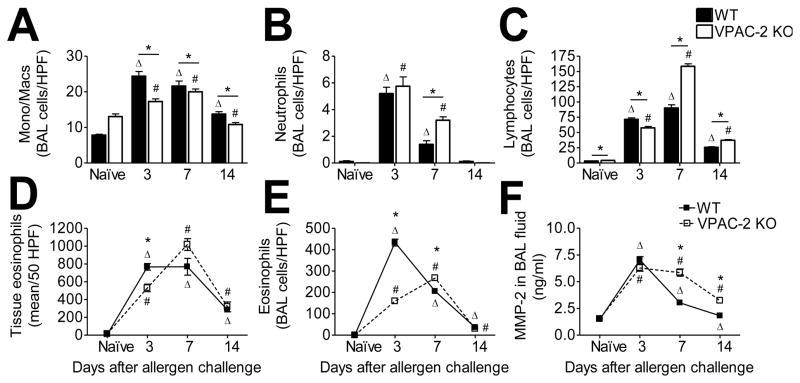
In order to determine whether the absence of VPAC2 played a role in leukocyte recruitment into the sensitized and challenged lungs, we differentially stained and counted the cells extracted via bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) from WT and VPAC2 KO mice at each time point. The naïve VPAC2 KO mice had approximately the same BAL cell profile as the naïve WT mice (Fig 1). All four types of leukocytes analyzed (monocytes/macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes) were significantly increased in the airways as a result of allergen exposure in both WT and KO mice at all time points (Fig 1). Fewer monocytes/macrophages were found in the airways of KO mice at each time point compared to WT (Fig 1A). Neutrophils were the least abundant in allergic airways (~2–5/HPF) in allergen exposed mice of both groups (Fig 1B). The peak in lymphocytes occurred in the both groups at day 7 at which point the number of lymphocytes in the airways of KO was 1.75-fold higher than that of the WT (Fig 1C).
Figure 1.
Leukocyte infiltration was increased as a result of allergen challenge in both WT and KO groups. Monocytes/macrophages (A), neutrophils (B), lymphocytes (C), and eosinophils (E) in cytospun bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) contents were differentially stained and counted. Peribronchovascular eosinophils were counted in 50 random HPFs in H&E stained sections (D). Total MMP-2 in the BAL was quantified via ELISA (F). All data are represented as the mean ± SEM, n=5 mice per group. Δ denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed WT animals compared to their naïve controls, while # denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed KO animals compared to their naïve controls. * indicates p<0.05 between WT and KO.
Eosinophils are the hallmark leukocyte of allergic asthma. We counted the number of eosinophils in the lungs and in the BAL contents based on the eosin staining of the cytoplasmic granules. VPAC2 KO mice appeared to have a delay in eosinophil recruitment into the lung, and a delay and reduction in eosinophil migration into the airway lumen (both peaking at day 7) compared to WT mice which had rapid eosinophil recruitment and egression (Fig 1D and E). MMP-2 advocates leukocyte migration into the airway lumen [5]. Therefore, we measured the amount of MMP-2 available in the BAL fluid in WT and VPAC2 KO mice. The peak in MMP-2 in the WT occurred at day 3 (Fig 1F), corresponding to the leukocyte peaks in the BAL (Fig 1). MMP-2 peaked in the BAL of KO mice at day 7 (Fig 1F) at which time monocytes/macrophages, lymphocytes and eosinophils also peaked in the airway lumen (Fig 1A, C, and E).
3.2. The absence of VPAC2 did not result in a difference in lung inflammation compared to WT mice
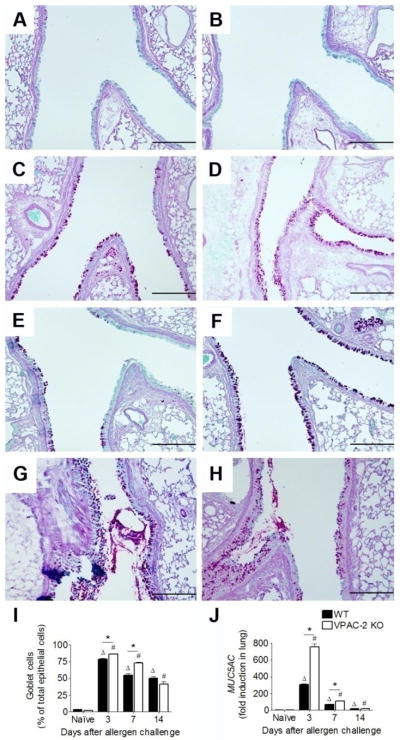
We examined the amount of peribronchovascular inflammation in the lung tissue of allergen exposed animals in comparison to naïve controls with H&E stained tissue sections. Naïve animals of both the WT and VPAC2 KO genotypes had no signs of airway inflammation (Fig 2A and B). Both groups of mice showed massive influx of leukocytes at all time points analyzed (Fig 2C-H). Eosinophils were marginated at the basal ends of the airway epithelia in both groups at all time points although decreasing in number with time (insets, Fig 2C-H). Both WT and KO mice had smooth muscle cell hyperplasia around the blood vessels as a result of allergen sensitization and challenge. However, this characteristic was more evident in the KO mice (Fig 2F). The latest time point (day 14) was still marked by considerable inflammation in both the WT and KO lungs (Fig 2G and H).
Figure 2.
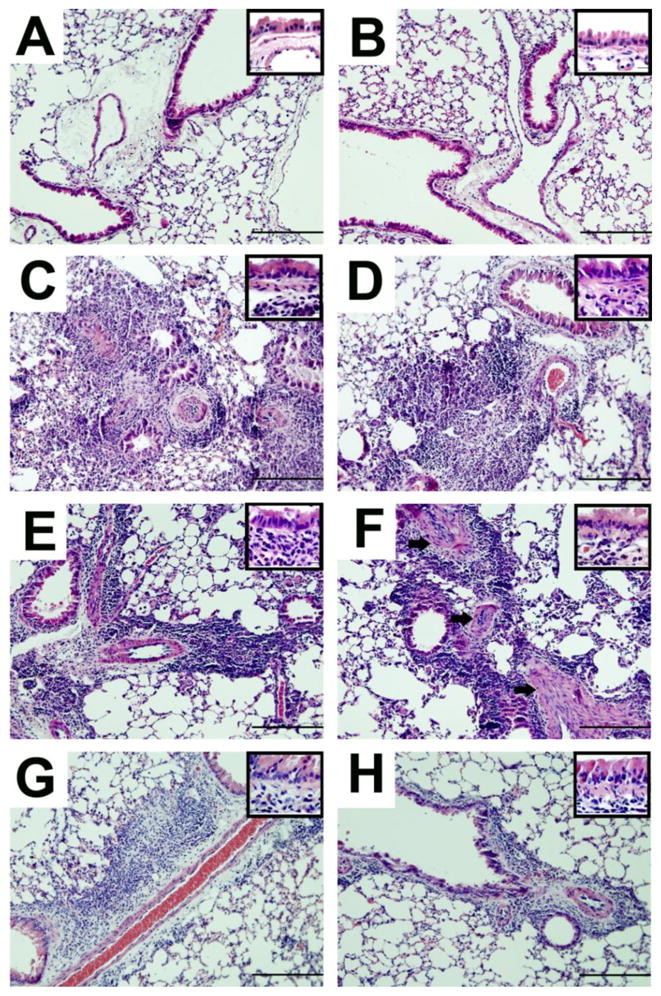
Representative photomicrographs of H&E-stained whole lung sections of naïve and allergen-challenged WT (left column) and VPAC2 KO (right column) mice. Naïve mice in both groups did not show inflammation (WT, A; KO, B). Peribronchovasular accumulation of leukocytes was prominent in both groups at day 3 (WT, C; KO, D). Inflammatory cell recruitment was still substantial at day 7 in both groups (WT, E; KO F), and although slightly subsided continued well into day 14 (WT, G; KO, H). Eosinophils were absent in naïve lungs, but evident in allergic lungs seen marginated at the basolateral ends of the columnar airway epithelia in both groups (insets, C-H). Thickening of the blood vessel walls was observed in both groups, although this was more prominent in the KO (arrows, F). Scale bars = 200 μm, insets = 50 μm
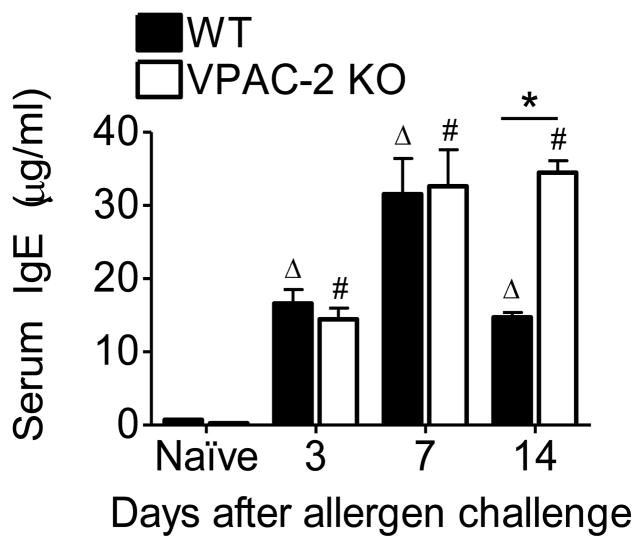
3.3. Serum IgE was increased and sustained in high amounts in the VPAC2 KO
Serum IgE is a hallmark of allergic asthma. We measured the increase in total IgE in response to allergen exposure in the sera of WT and KO mice to determine whether the absence of the VPAC2 receptor would decrease IgE production (Fig 3). All allergen exposed animals at each time point had significantly elevated IgE in the sera compared to naïve controls of both genotypes (Fig 3). Both WT and KO mice at days 3 and 7 produced equivalent amounts of IgE (Fig 3). However, KO mice sustained elevated levels of IgE even at day 14 which was in stark contrast to that of the WT which showed a decreasing trend by this time point (Fig 3).
Figure 3.
Elevated IgE was evident in the sera of WT and VPAC2 KO mice after allergen exposure. All data are represented as the mean ± SEM, n=5 mice per group. Δ denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed WT animals compared to their naïve controls, while # denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed KO animals compared to their naïve controls. * indicates p<0.05 between WT and KO.
3.4. The absence of VPAC2 receptor resulted in enhanced goblet cell metaplasia
Goblet cell (GC) metaplasia and associated increase in mucus production can lead to airway obstruction in allergic asthma. We measured this phenomenon by counting the number of GCs interspersed in the airway columnar epithelium as well as by the induction of MUC5AC in the lung. Naïve animals of both groups did not have PAS stained mucus producing GCs while allergen sensitized and challenged animals had marked GC metaplasia marked by PAS staining of mucus globules (Fig 4). Allergen exposed WT and KO mice had increased number of GCs in the airways at all time points analyzed, although KO mice had significantly more GCs at early time points compared to the WT (Fig 4I). This trend was also observed in the fold induction of MUC5AC (Fig 4J). The mRNA for MUC5AC was approximately 2.5-fold higher in the KO at day 3 compared to their WT counterparts (Fig 4J).
Figure 4.
Representative photomicrographs of PAS-stained whole lung sections of naïve and allergen exposed WT (left panel) and VPAC2 KO (right panel) mice. Goblet cells (GCs) were scarce in naïve animals of WT (A) and KO (B) groups. GCs and mucus were evident in the airways of both groups at days 3 (C & D), 7 (E & F), and 14 (G & H). GCs were counted and reported as the percentage of total epithelial cells that lined the airways (I). The induction of MUC5AC mRNA in lung tissue was measured via real-time qPCR and reported standardized to naïve controls using the 2−ΔΔCt method. While both groups had MUC5AC induction in the allergic state, a marked difference between WT and KO levels occurred at day 3 (J). All data are represented as the mean ± SEM, n=3–5 mice per group. Δ denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed WT animals compared to their naïve controls, while # denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed KO animals compared to their naïve controls. * indicates p<0.05 between WT and KO. Scale bars = 200 μm
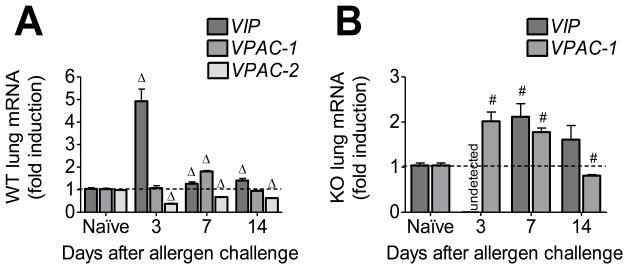
3.5. Allergen sensitization and challenge resulted in altered VIP and VPAC gene expression
We measured the mRNA of VIP and VPAC in allergen sensitized and challenged WT and KO in comparison to their respective naïve controls to determine whether the changes in allergic phenotype could be due to altered expression of VIP and VPAC. While WT animals had a 4.5-fold upregulation of VIP mRNA (Fig 5A), KO mice had undetectable levels of VIP mRNA at day 3 (Fig 5B), which was the only time point at which VIP mRNA expression was significantly different between the WT and KO. The trend in the induction of VPAC1 between the allergen exposed WT and KO mice was similar, marked by an upregulation at day 7 and a downregulation at day 14 (Fig 5A and B). Interestingly, allergen exposed WT mice had significantly downregulated expression of VPAC2 at all time points analyzed (Fig 5A).
Figure 5.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and VPAC receptor mRNA in whole lung of WT (A) and VPAC2 KO (B) standardized to naïve controls using the 2−ΔΔCt method. VIP was markedly upregulated in WT at day 3 (A) while it was undetected in KO (B). Both groups had a similar expression pattern for VPAC1 (A & B), and the WT had a marked downregualtion of VPAC2 at all time points analyzed (A). All data are represented as the mean ± SEM, n=3 mice per group. Δ denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed WT animals compared to their naïve controls, while # denotes p<0.05 of allergen exposed KO animals compared to their naïve controls.
4. Discussion
The hallmark characteristics of allergic asthma such as airway inflammation, hyperresponsiveness, excessive mucus production and increased serum IgE were represented in mice subjected to the A. fumigatus aeroallergen. VIP is a neuropeptide with a broad spectrum of functions which vary based on the immune cell and its expression of receptors. Contrary to previous reports in the literature showing that the VPAC2 knock-out animals have decreased immediate-type hypersensitivity reactions [15], we found that the VPAC2 KO mice were susceptible to the development of allergic asthma exhibiting airway inflammation, goblet cell metaplasia, and elevated serum IgE.
Numerous reports indicate VIP’s ability to impact leukocyte migration [2, 11, 13], inhibit inflammation [33], inhibit airway hyperresponsiveness [33] and smooth muscle cell proliferation [23], and promote a TH2 phenotype [38]. Asthmatics have more eosinophils in the inner airways than the outer airways; however, those in the outer airways are more highly activated [17]. Therefore, the migration of eosinophils into the airway lumen is important in minimizing the damage that can be induced by activated eosinophils in peribronchial areas. Although eosinophils are recognized as producers of VIP [1, 24], VIP’s direct impact on eosinophil migration is limited to one report by Dunzendorfer et al., emphasizing its importance in promoting the migration of eosinophils via VPAC1 [11]. In the absence of VIP (day 3), luminal eosinophils are markedly reduced in the VPAC2 KO mice. The restoration of VIP mRNA to WT-equivalent levels by day 7 in our model also restored eosinophil migration into the airway lumen in the KO, indicating that it is not the absence of the VPAC2 receptor, rather the absence of its ligand (VIP) that causes a delay and reduction in eosinophil migration into the airway lumen. Consequently, the VIP/VPAC1 axis may mediate eosinophil migration to the airway lumen in this model system. Furthermore, VIP has been proposed to be an endogenous modulator of nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) in the lungs [28]. Mice deficient in NFAT produce more IL-4 and IL-5 and have increased eosinophils in the BAL, indicating that the absence of NFAT promotes a TH2 phenotype [36]. In addition, the translocation of NFAT on T cells is inhibited by VIP/VPAC2 signaling [8]. Therefore, the reduction in BAL eosinophils in the KO may result from the absence of the VIP/VPAC2 modulation of NFAT in T cells.
Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) is also an important mediator of leukocyte migration. The retention of leukocytes in the lung tissue can lead to asphyxiation, and has been shown to be a cause of death in patients with asthma [35]. Animals lacking MMP-2 subjected to an asthma model died of asphyxiation resulting from inhibited leukocyte (predominantly eosinophils) egression into the airway lumen [5]. Naïve mice with a targeted deletion in VIP have increased MMP-2 in the BAL [33], and VIP has been shown to downregulate MMP-2 in a model of rheumatoid arthritis [7]. However, in our model, WT and KO mice showed no difference in MMP-2 availability in the BAL fluid or its mRNA expression in the lung (data not shown). Hence, the absence of VPAC2 did not alter MMP-2 expression in the lung in this model of allergic asthma.
Pulmonary inflammation between the WT and VPAC2 KO animals was similar. The accumulation of leukocytes in the lungs of both WT and KO groups in this model implies that, in the absence of VPAC2, VIP may not provide an anti-inflammatory protection mechanism in allergic asthma. While both WT and KO mice exhibited vascular smooth muscle hyperplasia, this feature was more apparent in the VPAC2 KO. VIP-deleted mice have vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation [30]. Together, this indicates that VIP is important in vascular integrity and that this function may be mediated through the VPAC2 receptor.
Constitutive production of mucins by GCs maintains the mucus layer for clearance of inhaled particles through ciliary movement which is promoted by VIP [31]. Goblet cell metaplasia can be induced by TH2 cytokines [27], and the VIP/VPAC2 axis promotes a TH2 response as reported in the VPAC2 transgenics [37]. Of the 20 mucin genes expressed in the lung, MUC5AC predominates in the airway mucus [34] and can be used as a marker of GC metaplasia. VIP is directly linked to the increase in MUC2 expression [19] and increases the expression of mucin genes in cultured colon epithelial cells through VPAC1 [20]. However, to our knowledge, its effect on MUC5AC has not been previously investigated or reported for pulmonary allergy. When VIP mRNA was undetectable in the VPAC2 KO lungs, there were more GCs in the airways, accompanied by a 2.5-fold greater induction of MUC5AC mRNA compared to WT, decreasing the likelihood that the VIP/VPAC1 axis mediates MUC5AC induction in the lung.
Elevated serum IgE is an important hallmark of allergic asthma that is used to diagnose the disease in humans. Contrary to previous reports that indicate the reduction of serum IgE in the VPAC2 KO mouse [15], we have shown that these mice respond to allergen challenge with the same vigor in IgE production as their WT counterparts and elevated levels were sustained longer than in the WT. The differences in our data from that of Goetzl et al. may be due to the disparity in the model systems employed [15]. This indicates that the VIP/VPAC2 axis is not important in mediating IgE production, in fact the absence of VPAC2 may have contributed to the maintenance of serum IgE possibly by initiating the survival of activated TH2 cells [9] to induce B cell activation and class switching. Since VIP has been shown to be important in these mechanisms, perhaps its function is predominantly through VPAC1 rather than VPAC2.
The predominant differences between the WT and VPAC2 KO animals occurred at a time in which VIP mRNA was not detected in the KO. This emphasizes the importance of the ligand (VIP) in altering the immune response in pulmonary allergy. VIP’s anti-inflammatory [6, 12, 22, 26] and anti-asthmatic [16, 21, 23, 29, 33] properties have been clearly demonstrated in the literature. Since multiple receptors (VPAC1, VPAC2, PAC1 [3]) through which VIP can function are available in the lung, one cannot dismiss the possibility that the absence of one receptor may be compensated by the presence of another.
It is apparent that VIP’s role in immunoregulation is complicated and dependent on the disease state, tissue, and environmental factors. In this allergic asthma model system, mice lacking the VPAC2 receptor responded with pathology that is similar to that of WT mice including increased serum IgE, eosinophilic inflammation, and GC metaplasia with associated MUC5AC induction. However, KO mice had a delay and reduction in eosinophil egression into the airway lumen and a dramatic upregulation of MUC5AC when VIP mRNA was undetectable in the lung. This indicates that VPAC2 is necessary for VIP to promote eosinophil migration and downregulate GC metaplasia thereby promoting lung homeostasis by ridding the tissue of a potentially harmful leukocyte and maintaining the integrity of the airway columnar epithelium in this murine model system of allergic asthma. In summary, the absence of the VIP/VPAC2 axis does not protect mice from developing an allergic phenotype.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Anthony Harmar (University of Edinburgh, UK) for providing mice heterozygous for VPAC2 for the generation of VPAC2 knock-out mice. This project was supported by NCRR/NIH 2P20RR015566 (M. Sibi).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Contributor Information
A. E. Samarasinghe, Email: a.samarasinghe@ndsu.edu.
S. A. Hoselton, Email: Scott.Hoselton@ndsu.edu.
J. M. Schuh, Email: Jane.Schuh@ndsu.edu.
References
- 1.Aliakbari J, Sreedharan SP, Turck CW, Goetzl EJ. Selective localization of vasoactive intestinal peptide and substance P in human eosinophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987;148:1440–5. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bondesson L, Norolind K, Liden S, Gafvelin G, Mutt V. Dual effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) on leucocyte migration. Acta Physiol Scand. 1991;141:477–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1991.tb09108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Busto R, Carrero I, Bodega G, Zapatero J, Prieto JC. Immunohistochemical and immunochemical evidence for expression of human lung PACAP/VIP receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2000;921:308–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2000.tb06983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chanez P, Springall D, Vignola AM, Moradoghi-Hattvani A, Polak JM, Godard P, et al. Bronchial mucosal immunoreactivity of sensory neuropeptides in severe airway diseases. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;158:985–90. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.158.3.9608104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Corry DB, Rishi K, Kanellis J, Kiss A, Song Lz LZ, Xu J, et al. Decreased allergic lung inflammatory cell egression and increased susceptibility to asphyxiation in MMP2-deficiency. Nat Immunol. 2002;3:347–53. doi: 10.1038/ni773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Delgado M, Abad C, Martinez C, Juarranz MG, Arranz A, Gomariz RP, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide in the immune system: potential therapeutic role in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. J Mol Med. 2002;80:16–24. doi: 10.1007/s00109-001-0291-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Delgado M, Abad C, Martinez C, Leceta J, Gomariz RP. Vasoactive intestinal peptide prevents experimental arthritis by downregulating both autoimmune and inflammatory components of the disease. Nat Med. 2001;7:563–8. doi: 10.1038/87887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Delgado M, Ganea D. Vasoactive intestinal peptide and pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide inhibit expression of Fas ligand in activated T lymphocytes by regulating c-Myc, NF-kappa B, NF-AT, and early growth factors 2/3. J Immunol. 2001;166:1028–40. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.2.1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Delgado M, Ganea D. VIP and PACAP enhance the in vivo generation of memory TH2 cells by inhibiting peripheral deletion of antigen-specific effectors. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2001;109:372–6. doi: 10.1076/apab.109.4.372.4240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Delgado M, Martinez C, Leceta J, Gomariz RP. Vasoactive intestinal peptide in thymus: synthesis, receptors and biological actions. Neuroimmunomodulation. 1999;6:97–107. doi: 10.1159/000026369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dunzendorfer S, Meierhofer C, Wiedermann CJ. Signaling in neuropeptide-induced migration of human eosinophils. J Leukoc Biol. 1998;64:828–34. doi: 10.1002/jlb.64.6.828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ganea D. Regulatory effects of vasoactive intestinal peptide on cytokine production in central and peripheral lymphoid organs. Advances in Neuroimmunology. 1996;6:61–74. doi: 10.1016/s0960-5428(96)00007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ganea D, Delgado M. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) as modulators of both innate and adaptive immunity. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2002;13:229–37. doi: 10.1177/154411130201300303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Garcia-Zepeda EA, Rothenberg ME, Ownbey RT, Celestin J, Leder P, Luster AD. Human eotaxin is a specific chemoattractant for eosinophil cells and provides a new mechanism to explain tissue eosinophilia. Nat Med. 1996;2:449–56. doi: 10.1038/nm0496-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Goetzl EJ, Voice JK, Shen S, Dorsam G, Kong Y, West KM, et al. Enhanced delayed-type hypersensitivity and diminished immediate-type hypersensitivity in mice lacking the inducible VPAC(2) receptor for vasoactive intestinal peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:13854–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.241503798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Guan CX, Zhang M, Qin XQ, Cui YR, Luo ZQ, Bai HB, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide enhances wound healing and proliferation of human bronchial epithelial cells. Peptides. 2006;27:3107–14. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hamid Q, Song Y, Kotsimbos TC, Minshall E, Bai TR, Hegele RG, et al. Inflammation of small airways in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1997;100:44–51. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6749(97)70193-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hogaboam CM, Blease K, Mehrad B, Steinhauser ML, Standiford TJ, Kunkel SL, et al. Chronic Airway Hyperreactivity, Goblet Cell Hyperplasia, and Peribronchial Fibrosis during Allergic Airway Disease Induced by Aspergillus fumigatus. American Journal of Pathology. 2000;156:723–32. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64775-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hokari R, Lee H, Crawley SC, Yang SC, Gum JR, Jr, Miura S, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide upregulates MUC2 intestinal mucin via CREB/ATF1. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G949–59. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00142.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hollande E, Fanjul M, Claret S, Forgue-Lafitte ME, Bara J. Effects of VIP on the regulation of mucin secretion in cultured human pancreatic cancer cells (Capan-1) In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1995;31:227–33. doi: 10.1007/BF02639438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lilly CM, Stamler JS, Gaston B, Meckel C, Loscalzo J, Drazen JM. Modulation of vasoactive intestinal peptide pulmonary relaxation by NO in tracheally superfused guinea pig lungs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 1993;265:L410–L5. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1993.265.4.L410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maggi CA, Giachetti A, Dey RD, Said SI. Neuropeptides as regulators of airway function: vasoactive intestinal peptide and the tachykinins. Physiol Rev. 1995;75:277–322. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1995.75.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Maruno K, Absood A, Said SI. VIP inhibits basal and histamine-stimulated proliferation of human airway smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 1995;268:L1047–L51. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1995.268.6.L1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mathew RC, Cook GA, Blum AM, Metwali A, Felman R, Weinstock JV. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates T lymphocytes to release IL-5 in murine Schistosomiasis mansoni infection. The Journal of Immunology. 1992;148:3572–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ollerenshaw S, Jarvis D, Woolcock A, Sullivan C, Scheibner T. Absence of immunoreactive vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in tissue from the lungs of patients with asthma. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1989;320:1244–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905113201904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pozo D, Delgado M, Martinez M, Guerrero JM, Leceta J, Gomariz RP, et al. Immunobiology of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) Immunol Today. 2000;21:7–11. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(99)01525-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rogers DF. The airway goblet cell. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35:1–6. doi: 10.1016/s1357-2725(02)00083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Said SI. The vasoactive intestinal peptide gene is a key modulator of pulmonary vascular remodeling and inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1144:148–53. doi: 10.1196/annals.1418.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Said SI. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in asthma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;629:305–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb37985.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Said SI, Hamidi SA, Dickman KG, Szema AM, Lyubsky S, Lin RZ, et al. Moderate pulmonary arterial hypertension in male mice lacking the vasoactive intestinal peptide gene. Circulation. 2007;115:1260–8. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.681718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sakai N, Tamaoki J, Kobayashi K, Isono KKT, Takeuchi S, et al. Vasoactive intestinal peptide stimulates ciliary motility in rabbit tracheal epithelium: modulation by neutral endopeptidase. Regul-Pept. 1991;34:33–41. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(91)90222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Smalley SG, Barrow PA, Foster N. Immunomodulation of innate immune responses by vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP): its therapeutic potential in inflammatory disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009;157:225–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Szema AM, Hamidi SA, Lyubsky S, Dickman KG, Mathew S, Abdel-Razek T, et al. Mice lacking the VIP gene show airway hyperresponsiveness and airway inflammation, partially reversible by VIP. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;291:L880–6. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00499.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Thai P, Loukoianov A, Wachi S, Wu R. Regulation of airway mucin gene expression. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:405–29. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.113006.100441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Tsokos M. Asthma Deaths: Phenomenology, Pathology, and Medicolegal Aspects. Humana Press; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Viola JP, Kiani A, Bozza PT, Rao A. Regulation of allergic inflammation and eosinophil recruitment in mice lacking the transcription factor NFAT1: role of interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-5. Blood. 1998;91:2223–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Voice JK, Dorsam G, Lee H, Kong Y, Goetzl EJ. Allergic diathesis in transgenic mice with constitutive T cell expression of inducible vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor. FASEB J. 2001;15:2489–96. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0671com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Voice JK, Grinninger C, Kong Y, Bangale Y, Paul S, Goetzl EJ. Roles of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in the expression of different immune phenotypes by wild-type mice and T cell-targeted type II VIP receptor transgenic mice. J Immunol. 2003;170:308–14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wardlaw AJ, Guillen C, Morgan A. Mechanisms of T cell migration to the lung. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005;35:4–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2005.02139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]