Abstract
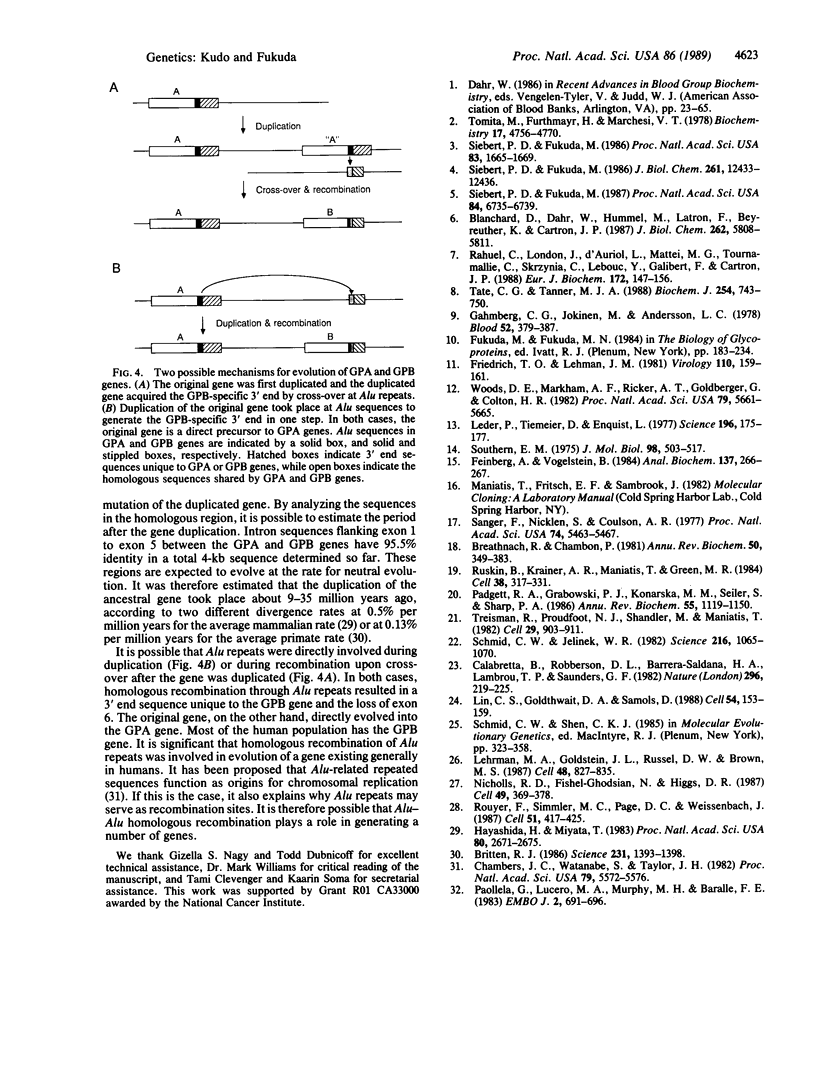
Glycophorins A (GPA) and B (GPB) are two major sialoglycoproteins of the human erythrocyte membrane. Here we present a comparison of the genomic structures of GPA and GPB developed by analyzing DNA clones isolated from a K562 genomic library. Nucleotide sequences of exon-intron junctions and 5' and 3' flanking sequences revealed that the GPA and GPB genes consist of 7 and 5 exons, respectively, and both genes have greater than 95% identical sequence from the 5' flanking region to the region approximately 1 kilobase downstream from the exon encoding the transmembrane regions. In this homologous part of the genes, GPB lacks one exon due to a point mutation at the 5' splicing site of the third intron, which inactivates the 5' cleavage event of splicing and leads to ligation of the second to the fourth exon. Following these very homologous sequences, the genomic sequences for GPA and GPB diverge significantly and no homology can be detected in their 3' end sequences. The transition site from homologous to nonhomologous sequences can be localized within Alu repeat sequences. The analysis of the Alu sequences and their flanking direct repeat sequences suggest that an ancestral genomic structure has been maintained in the GPA gene, whereas the GPB gene has arisen from the acquisition of 3' sequences different from those of the GPA gene by homologous recombination at the Alu repeats during or after gene duplication.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanchard D., Dahr W., Hummel M., Latron F., Beyreuther K., Cartron J. P. Glycophorins B and C from human erythrocyte membranes. Purification and sequence analysis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5808–5811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britten R. J. Rates of DNA sequence evolution differ between taxonomic groups. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1393–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.3082006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta B., Robberson D. L., Barrera-Saldaña H. A., Lambrou T. P., Saunders G. F. Genome instability in a region of human DNA enriched in Alu repeat sequences. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):219–225. doi: 10.1038/296219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers J. C., Watanabe S., Taylor J. H. Dissection of a replication origin of Xenopus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5572–5576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich T. D., Lehman J. M. The state of simian virus 40 DNA in the embryonal carcinoma cells of the murine teratocarcinoma. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Jokinen M., Andersson L. C. Expression of the major sialoglycoprotein (glycophorin) on erythroid cells in human bone marrow. Blood. 1978 Aug;52(2):379–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida H., Miyata T. Unusual evolutionary conservation and frequent DNA segment exchange in class I genes of the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2671–2675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Duplication of seven exons in LDL receptor gene caused by Alu-Alu recombination in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. S., Goldthwait D. A., Samols D. Identification of Alu transposition in human lung carcinoma cells. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90547-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls R. D., Fischel-Ghodsian N., Higgs D. R. Recombination at the human alpha-globin gene cluster: sequence features and topological constraints. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90289-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella G., Lucero M. A., Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. The Alu family repeat promoter has a tRNA-like bipartite structure. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):691–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahuel C., London J., d'Auriol L., Mattei M. G., Tournamille C., Skrzynia C., Lebouc Y., Galibert F., Cartron J. P. Characterization of cDNA clones for human glycophorin A. Use for gene localization and for analysis of normal of glycophorin-A-deficient (Finnish type) genomic DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 15;172(1):147–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Page D. C., Weissenbach J. A sex chromosome rearrangement in a human XX male caused by Alu-Alu recombination. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90637-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruskin B., Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Green M. R. Excision of an intact intron as a novel lariat structure during pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid C. W., Jelinek W. R. The Alu family of dispersed repetitive sequences. Science. 1982 Jun 4;216(4550):1065–1070. doi: 10.1126/science.6281889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Fukuda M. Human glycophorin A and B are encoded by separate, single copy genes coordinately regulated by a tumor-promoting phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12433–12436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Fukuda M. Isolation and characterization of human glycophorin A cDNA clones by a synthetic oligonucleotide approach: nucleotide sequence and mRNA structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1665–1669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert P. D., Fukuda M. Molecular cloning of a human glycophorin B cDNA: nucleotide sequence and genomic relationship to glycophorin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6735–6739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate C. G., Tanner M. J. Isolation of cDNA clones for human erythrocyte membrane sialoglycoproteins alpha and delta. Biochem J. 1988 Sep 15;254(3):743–750. doi: 10.1042/bj2540743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Primary structure of human erythrocyte glycophorin A. Isolation and characterization of peptides and complete amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4756–4770. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Proudfoot N. J., Shander M., Maniatis T. A single-base change at a splice site in a beta 0-thalassemic gene causes abnormal RNA splicing. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Ricker A. T., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for the human complement protein factor B, a class III major histocompatibility complex gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5661–5665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






