Abstract
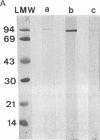
A crude supernatant of hybridoma secreting a monoclonal anti-double-stranded (ds)DNA antibody (PME77 mAb), used to stain fibroblasts (CVI cells) in immunofluorescence, gives a punctuated staining of variable intensity. We had suggested that anti-DNA antibodies bind to cell-surface protein(s) of several cells. When the mAb of this crude supernatant was purified on a dsDNA-cellulose column and a histone-Trisacryl column, the mAb no longer bound to the cell surface. Only when dsDNA plus purified histones was added to the purified antibody did the immune complex strongly and uniformly stain again the cell surface of CVI cells. No significant staining was observed if either DNA or histones were omitted. A signal 94-kDa protein from membrane fractions of CVI, Raji, and RINm cell lines was visualized in immunoblots when mAb-DNA-histone complexes were applied to the nitrocellulose strips. No polypeptide was seen if one component was omitted. This 94-kDa protein behaved like a plasma membrane protein since it required the use of detergent to be solubilized and was quantitatively recovered in the Triton X-114 detergent-rich phase. Moreover, a brief treatment of living cells with trypsin cleared off this protein. Purified nucleosomes could be substituted to DNA-histone complexes, giving rise to identical results. Finally, purified polyclonal anti-DNA antibodies from sera of systemic lupus erythematosus patients labeled a 94-kDa protein provided that DNA-histone complexes were added. Anti-DNA autoantibodies could be pathogenic when they are bound to nucleosomes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arana R., Seligmann M. Antibodies to native and denatured deoxyribonucleic acid in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1867–1882. doi: 10.1172/JCI105677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett R. M., Kotzin B. L., Merritt M. J. DNA receptor dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus and kindred disorders. Induction by anti-DNA antibodies, antihistone antibodies, and antireceptor antibodies. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):850–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faaber P., Rijke T. P., van de Putte L. B., Capel P. J., Berden J. H. Cross-reactivity of human and murine anti-DNA antibodies with heparan sulfate. The major glycosaminoglycan in glomerular basement membranes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1824–1830. doi: 10.1172/JCI112508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gastinel L. N., Pleau J. M., Dardenne M., Sasaki A., Bricas E., Morgat J. L., Bach J. F. High affinity binding sites on plasma membrane obtained from the lymphoblastoid cultured 1301 cell line for highly radioactive serum thymic factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jan 4;684(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar A. F., Chick W. L., Oie H. K., Sims H. L., King D. L., Weir G. C., Lauris V. Continuous, clonal, insulin- and somatostatin-secreting cell lines established from a transplantable rat islet cell tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3519–3523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardin J. A., Thomas J. O. Antibodies to histones in systemic lupus erythematosus: localization of prominent autoantigens on histones H1 and H2B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7410–7414. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holers V. M., Kotzin B. L. Human peripheral blood monocytes display surface antigens recognized by monoclonal antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):991–998. doi: 10.1172/JCI112100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Lety M. A., Bach J. F., Louvard D. Human systemic lupus erythematosus sera contain antibodies against cell-surface protein(s) that share(s) epitope(s) with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Tron F., Bach J. F., Louvard D. A monoclonal anti-DNA antibody also binds to cell-surface protein(s). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3843–3845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob L., Tron F. Monoclonal anti-deoxyribonucleic antibodies. I. Isotype and specificity studies. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):895–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotzin B. L., Lafferty J. A., Portanova J. P., Rubin R. L., Tan E. M. Monoclonal anti-histone autoantibodies derived from murine models of lupus. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2554–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Rauch J., Andrzejewski C., Jr, Mudd D., Furie B., Furie B., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Polyspecific monoclonal lupus autoantibodies reactive with both polynucleotides and phospholipids. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):897–909. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rekvig O. P., Hannestad K. Human autoantibodies that react with both cell nuclei and plasma membranes display specificity for the octamer of histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 in high salt. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1720–1733. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Morimoto C. Isolation of DNA from DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):538–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler D. A., Sipes D. E., Jacob S. T. Anti-RNA polymerase I antibodies in sera of MRL lpr/lpr and MRL +/+ autoimmune mice. Correlation of antibody production with delayed onset of lupus-like disease in MRL +/+ mice. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1760–1770. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki Y., Deng J. S., Tan E. M. A nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation and blast transformation. J Exp Med. 1981 Dec 1;154(6):1899–1909. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.6.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tron F., Charron D., Bach J. F., Talal N. Establishment and characterization of a murine hybridoma secreting monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2805–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tron F., Jacob L., Bach J. F. Binding of a murine monoclonal anti-DNA antibody to Raji cells. Implications for the interpretation of the Raji cell assay for immune complexes. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Mar;14(3):283–286. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]