Abstract
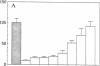
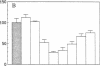
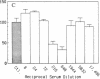
Based on recent reports of antibody-dependent enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in vitro by serum from HIV-1-infected humans, sera from HIV-1 antibody-positive chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) was evaluated for enhancing activity in an in vitro infection assay that uses MT-2 cells (a human lymphoblastoid cell line). Although fresh chimpanzee serum was found to have pronounced infection-enhancing properties in the absence of antibody to HIV-1, this effect was abolished by heat inactivation (57 degrees C, 1 hr) or treatment with cobra venom anticomplementary protein. Heat-inactivated, HIV-1 antibody-positive chimpanzee serum could enhance HIV-1 infection of MT-2 cells in vitro when combined with fresh, normal human serum. By serial serum samples from three HIV-1-infected chimpanzees, HIV-1 antibody-positive chimpanzees are shown to develop enhancing antibodies early in infection (2 mo postchallenge), whereas neutralizing antibodies develop later. Over the course of HIV-1 infection, this enhancing activity decreases while neutralizing activity increases, suggesting a possible role for enhancing and neutralizing activities in HIV-1 pathogenesis. The enhancing activity of an IgG fraction used to passively immunize chimpanzees against HIV-1 infection is shown to be present at dilutions as high as 1:65,000, offering an interesting possible reason for the failure of passive immunization to protect chimpanzees from HIV infection. These results suggest that serum from HIV-1-immunized chimpanzees might be tested to determine whether current HIV-1 candidate vaccines induce production of antibodies that mediate antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV-1 infection in this in vitro assay.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alter H. J., Eichberg J. W., Masur H., Saxinger W. C., Gallo R., Macher A. M., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Transmission of HTLV-III infection from human plasma to chimpanzees: an animal model for AIDS. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):549–552. doi: 10.1126/science.6093251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV infection. Lancet. 1988 Jun 4;1(8597):1285–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV infection. Lancet. 1988 Jun 4;1(8597):1285–1286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew R. M., Esser A. F., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Lysis of oncornaviruses by human serum. Isolation of the viral complement (C1) receptor and identification as p15E. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):844–853. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman P. W., Groopman J. E., Gregory T., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Ferriani R., Riddle L., Shimasaki C., Lucas C., Lasky L. A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 challenge of chimpanzees immunized with recombinant envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5200–5204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardosa M. J., Porterfield J. S., Gordon S. Complement receptor mediates enhanced flavivirus replication in macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):258–263. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecilia D., Gadkari D. A., Kedarnath N., Ghosh S. N. Epitope mapping of Japanese encephalitis virus envelope protein using monoclonal antibodies against an Indian strain. J Gen Virol. 1988 Nov;69(Pt 11):2741–2747. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-11-2741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstead S. B. Pathogenesis of dengue: challenges to molecular biology. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):476–481. doi: 10.1126/science.3277268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Eichberg J. W., Thomas E. K., Zarling J., Singhal M. C., Kosowski S. G., Swenson R. B., Anderson D. C. Effect of immunization with a vaccinia-HIV env recombinant on HIV infection of chimpanzees. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):721–723. doi: 10.1038/328721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Infection of the HTLV-II-bearing T-cell line C3 with HTLV-III/LAV is highly permissive and lytic. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):726–731. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montefiori D. C., Robinson W. E., Jr, Schuffman S. S., Mitchell W. M. Evaluation of antiviral drugs and neutralizing antibodies to human immunodeficiency virus by a rapid and sensitive microtiter infection assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):231–235. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.231-235.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Robey W. G., Gonda M. A., Carter S. G., Fischinger P. J. Absence of cytotoxic antibody to human immunodeficiency virus-infected cells in humans and its induction in animals after infection or immunization with purified envelope glycoprotein gp120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3797–3801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peiris J. S., Porterfield J. S. Antibody-dependent plaque enhancement: its antigenic specificity in relation to Togaviridae. J Gen Virol. 1982 Feb;58(Pt 2):291–296. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-2-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porterfield J. S. Antibody-dependent enhancement of viral infectivity. Adv Virus Res. 1986;31:335–355. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60268-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince A. M., Horowitz B., Baker L., Shulman R. W., Ralph H., Valinsky J., Cundell A., Brotman B., Boehle W., Rey F. Failure of a human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) immune globulin to protect chimpanzees against experimental challenge with HIV. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6944–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Gillespie D. H., Mitchell W. M. Complement-mediated, antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV-1 infection in vitro is characterized by increased protein and RNA syntheses and infectious virus release. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(1):33–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. A human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection-enhancing factor in seropositive sera. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Dec 16;149(2):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90423-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Antibody-dependent enhancement of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. Lancet. 1988 Apr 9;1(8589):790–794. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91657-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. E., Jr, Montefiori D. C., Mitchell W. M. Will antibody-dependent enhancement of HIV-1 infection be a problem with AIDS vaccines? Lancet. 1988 Apr 9;1(8589):830–831. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91695-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda A., Tuazon C. U., Ennis F. A. Antibody-enhanced infection by HIV-1 via Fc receptor-mediated entry. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):580–583. doi: 10.1126/science.2972065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Jr, Cooper N. R., Jensen F. C., Oldstone M. B. Human serum lyses RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1975 Oct 16;257(5527):612–614. doi: 10.1038/257612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]