Abstract
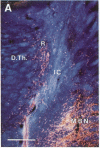
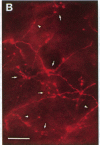
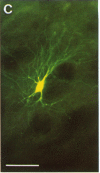
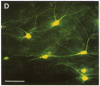
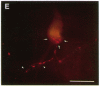
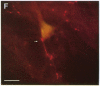
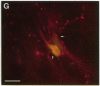
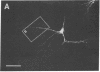
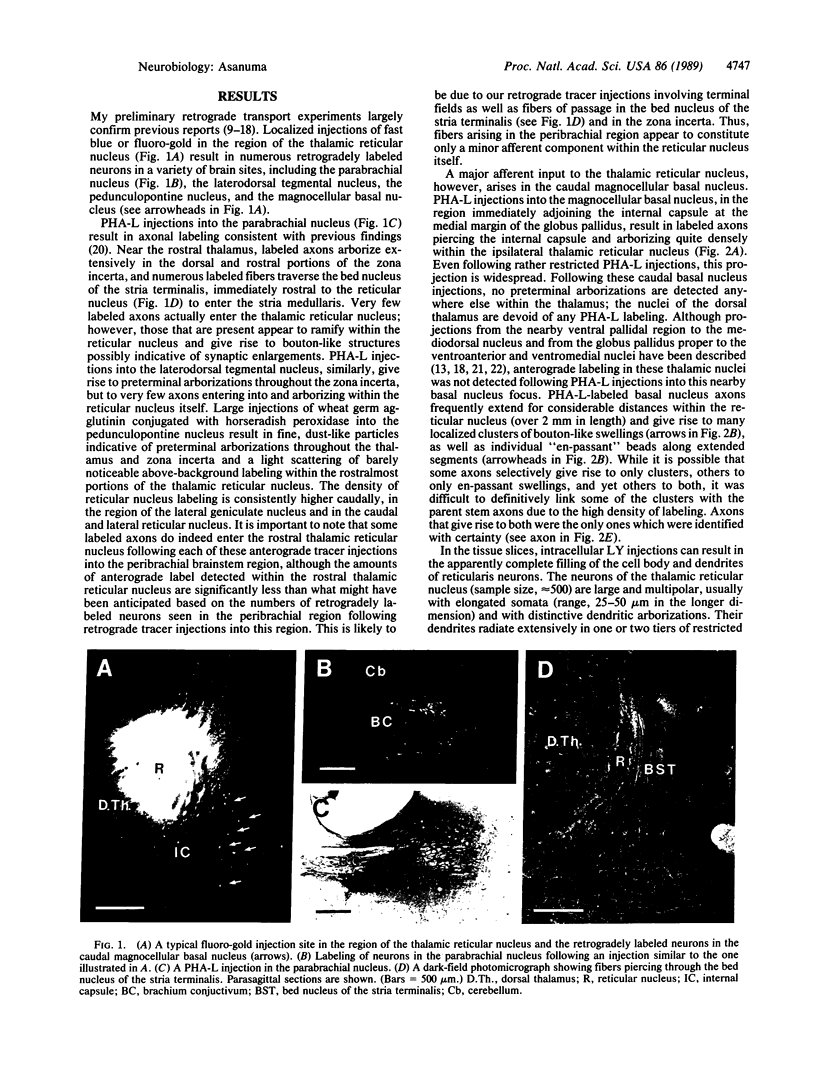
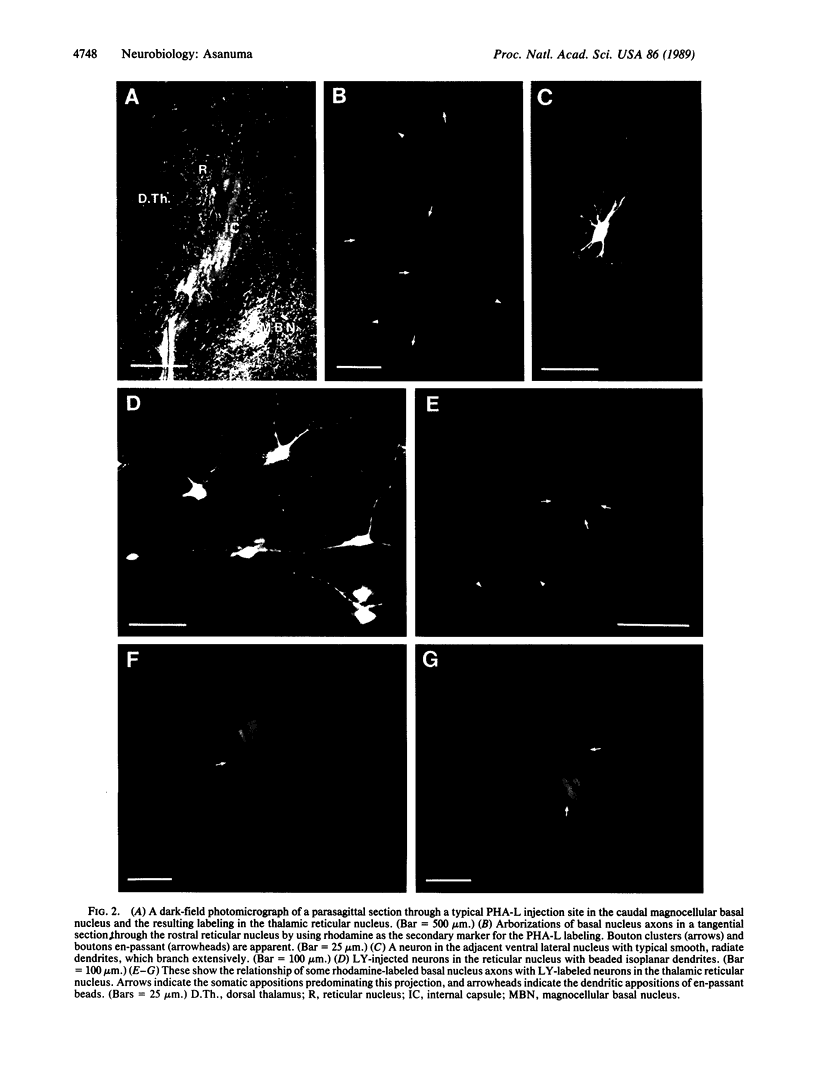
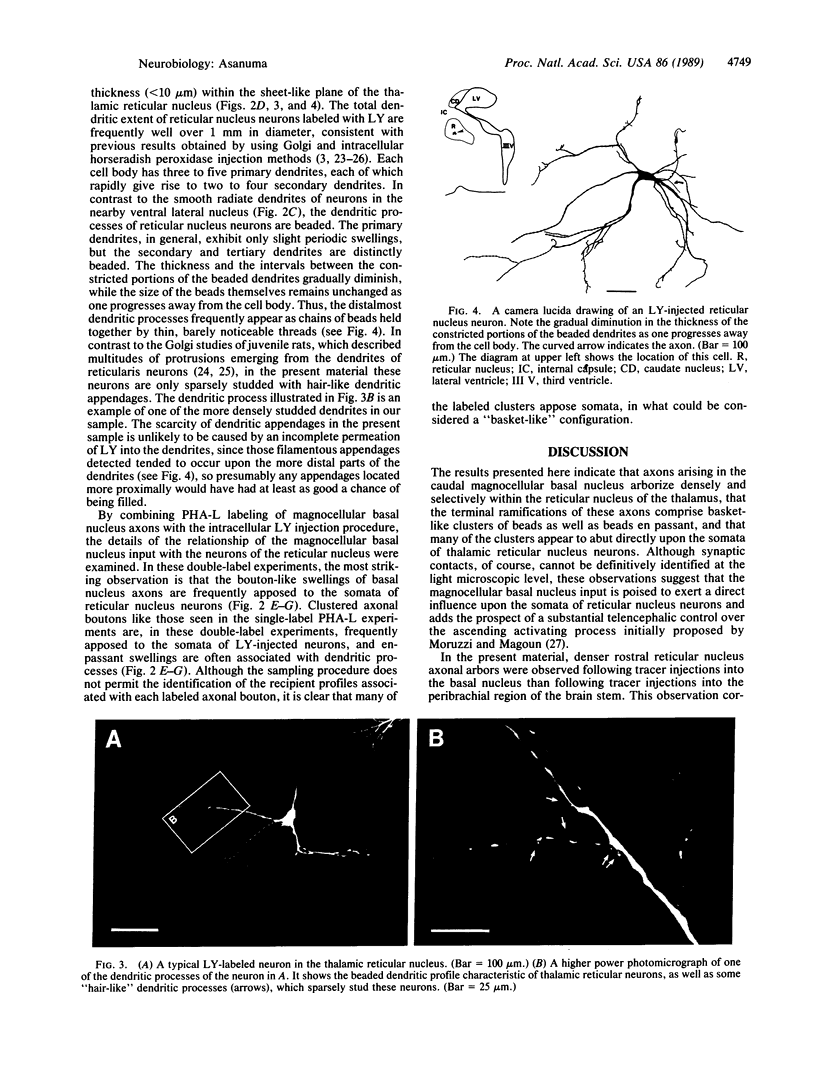
A dense axonal plexus, arising in a portion of the magnocellular basal nucleus, was identified in the thalamic reticular nucleus in adult rats. The details of these axonal arbors as well as their relation to the neurons of the reticular nucleus were investigated by using Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin injections into the basal nucleus and intracellular injections of Lucifer yellow into reticular nucleus neurons. Axons arising in the caudal basal nucleus at the medial margin of the globus pallidus do not enter the dorsal thalamus but are confined to the reticular nucleus, where they arborize widely and densely. Neurons in the reticular nucleus are large, with sparsely spined and beaded dendrites, which radiate within the plane of the nucleus. Bouton-like swellings along basal nucleus axons are often found apposed to the somata of reticular nucleus neurons, although many are also apposed to dendrites. These morphological observations suggest a second potentially significant route, in addition to its well-known direct cortical projection, through which the magnocellular basal nucleus could influence cortical function: it may, by strategically modulating the excitability of reticular nucleus neurons, alter the general state of the thalamus and hence affect the initial transmission of information to the cortex.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buzsaki G., Bickford R. G., Ponomareff G., Thal L. J., Mandel R., Gage F. H. Nucleus basalis and thalamic control of neocortical activity in the freely moving rat. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4007–4026. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04007.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARMAN J. B., COWAN W. M., POWELL T. P. CORTICAL CONNEXIONS OF THE THALAMIC RETICULAR NUCLEUS. J Anat. 1964 Oct;98:587–598. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lima A. D., Singer W. The brainstem projection to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the cat: identification of cholinergic and monoaminergic elements. J Comp Neurol. 1987 May 1;259(1):92–121. doi: 10.1002/cne.902590107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. S., Buchwald N. A., Hull C. D., Levine M. S. GABAergic basal forebrain neurons project to the neocortex: the localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase and choline acetyltransferase in feline corticopetal neurons. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jun 22;272(4):489–502. doi: 10.1002/cne.902720404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freund T. F., Antal M. GABA-containing neurons in the septum control inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):170–173. doi: 10.1038/336170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Sawchenko P. E. An anterograde neuroanatomical tracing method that shows the detailed morphology of neurons, their axons and terminals: immunohistochemical localization of an axonally transported plant lectin, Phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L). Brain Res. 1984 Jan 9;290(2):219–238. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90940-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallanger A. E., Levey A. I., Lee H. J., Rye D. B., Wainer B. H. The origins of cholinergic and other subcortical afferents to the thalamus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Aug 1;262(1):105–124. doi: 10.1002/cne.902620109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallanger A. E., Wainer B. H. Ultrastructure of ChAT-immunoreactive synaptic terminals in the thalamic reticular nucleus of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Dec 22;278(4):486–497. doi: 10.1002/cne.902780403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M. The afferent and efferent connections of the ventromedial thalamic nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1979 Feb 1;183(3):487–517. doi: 10.1002/cne.901830304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Vaughn J. E., Barber R. P., Roberts E. GABA neurons are the major cell type of the nucleus reticularis thalami. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 3;200(2):341–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90925-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahnsen H., Llinás R. Electrophysiological properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurones: an in vitro study. J Physiol. 1984 Apr;349:205–226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. G. Some aspects of the organization of the thalamic reticular complex. J Comp Neurol. 1975 Aug 1;162(3):285–308. doi: 10.1002/cne.901620302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey A. I., Hallanger A. E., Wainer B. H. Choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity in the rat thalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Mar 15;257(3):317–332. doi: 10.1002/cne.902570302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey A. I., Hallanger A. E., Wainer B. H. Cholinergic nucleus basalis neurons may influence the cortex via the thalamus. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Feb 10;74(1):7–13. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Llinás R., Jahnsen H. Electrophysiology of mammalian thalamic neurones in vitro. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):406–408. doi: 10.1038/297406a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay-Sim A., Sefton A. J., Martin P. R. Subcortical projections to lateral geniculate and thalamic reticular nuclei in the hooded rat. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Jan 1;213(1):24–35. doi: 10.1002/cne.902130103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minderhoud J. M. An anatomical study of the efferent connections of the thalamic reticular nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1971 May 26;112(4):435–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00234497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montero V. M., Singer W. Ultrastructure and synaptic relations of neural elements containing glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in the perigeniculate nucleus of the cat. A light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. Exp Brain Res. 1984;56(1):115–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00237447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montero V. M. Ultrastructural identification of synaptic terminals from the axon of type 3 interneurons in the cat lateral geniculate nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Oct 8;264(2):268–283. doi: 10.1002/cne.902640210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Madariaga A., Deschênes M. Morphology and electrophysiological properties of reticularis thalami neurons in cat: in vivo study of a thalamic pacemaker. J Neurosci. 1986 Aug;6(8):2134–2145. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-08-02134.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertel W. H., Graybiel A. M., Mugnaini E., Elde R. P., Schmechel D. E., Kopin I. J. Coexistence of glutamic acid decarboxylase- and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in neurons of the feline nucleus reticularis thalami. J Neurosci. 1983 Jun;3(6):1322–1332. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-06-01322.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara P. T., Lieberman A. R., Hunt S. P., Wu J. Y. Neural elements containing glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the rat; immunohistochemical studies by light and electron microscopy. Neuroscience. 1983;8(2):189–211. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara P. T., Lieberman A. R. The thalamic reticular nucleus of the adult rat: experimental anatomical studies. J Neurocytol. 1985 Jun;14(3):365–411. doi: 10.1007/BF01217752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent A., Paré D., Smith Y., Steriade M. Basal forebrain cholinergic and noncholinergic projections to the thalamus and brainstem in cats and monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Nov 8;277(2):281–301. doi: 10.1002/cne.902770209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paré D., Smith Y., Parent A., Steriade M. Projections of brainstem core cholinergic and non-cholinergic neurons of cat to intralaminar and reticular thalamic nuclei. Neuroscience. 1988 Apr;25(1):69–86. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saper C. B., Loewy A. D. Efferent connections of the parabrachial nucleus in the rat. Brain Res. 1980 Sep 22;197(2):291–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91117-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel M. E., Scheibel A. B. The organization of the nucleus reticularis thalami: a Golgi study. Brain Res. 1966 Jan;1(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(66)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer W. Control of thalamic transmission by corticofugal and ascending reticular pathways in the visual system. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):386–420. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sofroniew M. V., Priestley J. V., Consolazione A., Eckenstein F., Cuello A. C. Cholinergic projections from the midbrain and pons to the thalamus in the rat, identified by combined retrograde tracing and choline acetyltransferase immunohistochemistry. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 11;329(1-2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90527-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Deschênes M., Domich L., Mulle C. Abolition of spindle oscillations in thalamic neurons disconnected from nucleus reticularis thalami. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Dec;54(6):1473–1497. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.54.6.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Domich L., Oakson G., Deschênes M. The deafferented reticular thalamic nucleus generates spindle rhythmicity. J Neurophysiol. 1987 Jan;57(1):260–273. doi: 10.1152/jn.1987.57.1.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Llinás R. R. The functional states of the thalamus and the associated neuronal interplay. Physiol Rev. 1988 Jul;68(3):649–742. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1988.68.3.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Parent A., Hada J. Thalamic projections of nucleus reticularis thalami of cat: a study using retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase and fluorescent tracers. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Nov 10;229(4):531–547. doi: 10.1002/cne.902290407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steriade M., Parent A., Paré D., Smith Y. Cholinergic and non-cholinergic neurons of cat basal forebrain project to reticular and mediodorsal thalamic nuclei. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 7;408(1-2):372–376. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolf N. J., Butcher L. L. Cholinergic systems in the rat brain: III. Projections from the pontomesencephalic tegmentum to the thalamus, tectum, basal ganglia, and basal forebrain. Brain Res Bull. 1986 May;16(5):603–637. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(86)90134-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen C. T., Conley M., Hendry S. H., Jones E. G. The morphology of physiologically identified GABAergic neurons in the somatic sensory part of the thalamic reticular nucleus in the cat. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2254–2268. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02254.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm D. S., Zaborszky L., Alheid G. F., Heimer L. The ventral striatopallidothalamic projection: II. The ventral pallidothalamic link. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Jan 22;255(4):592–605. doi: 10.1002/cne.902550410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Biasi S., Frassoni C., Spreafico R. GABA immunoreactivity in the thalamic reticular nucleus of the rat. A light and electron microscopical study. Brain Res. 1986 Dec 3;399(1):143–147. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90608-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]