Abstract
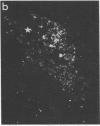
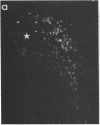
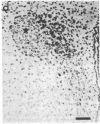
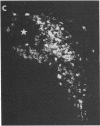
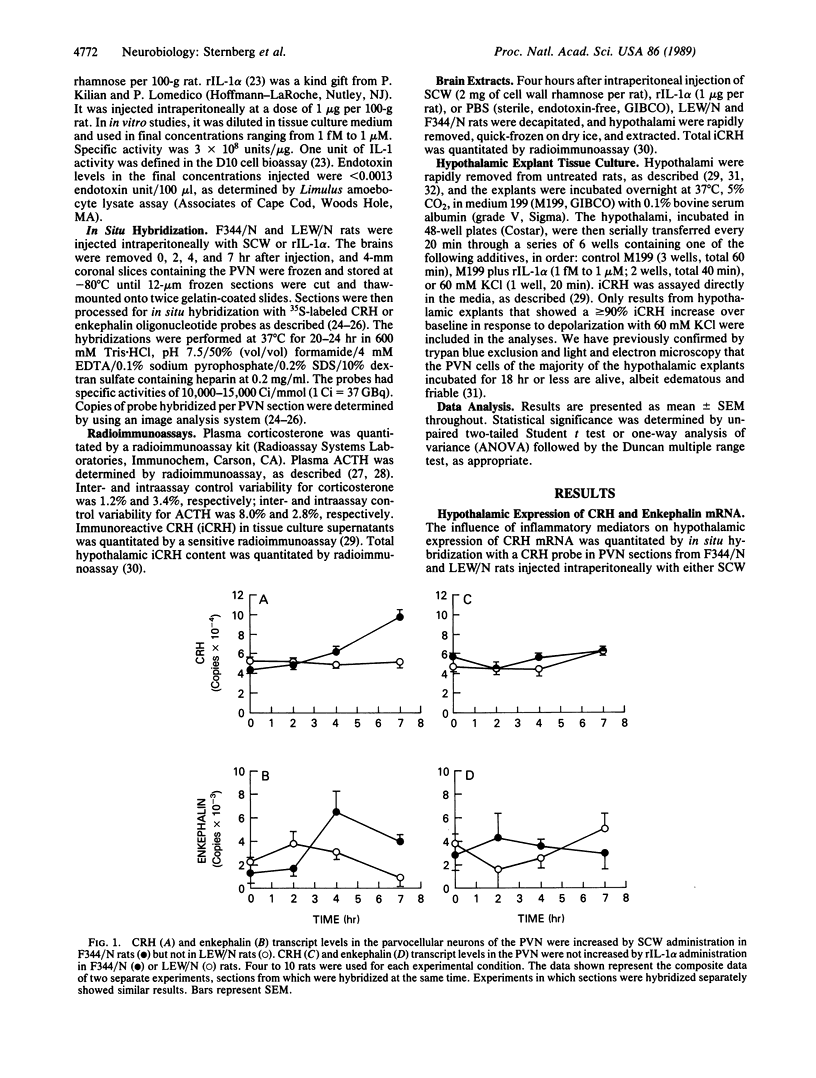
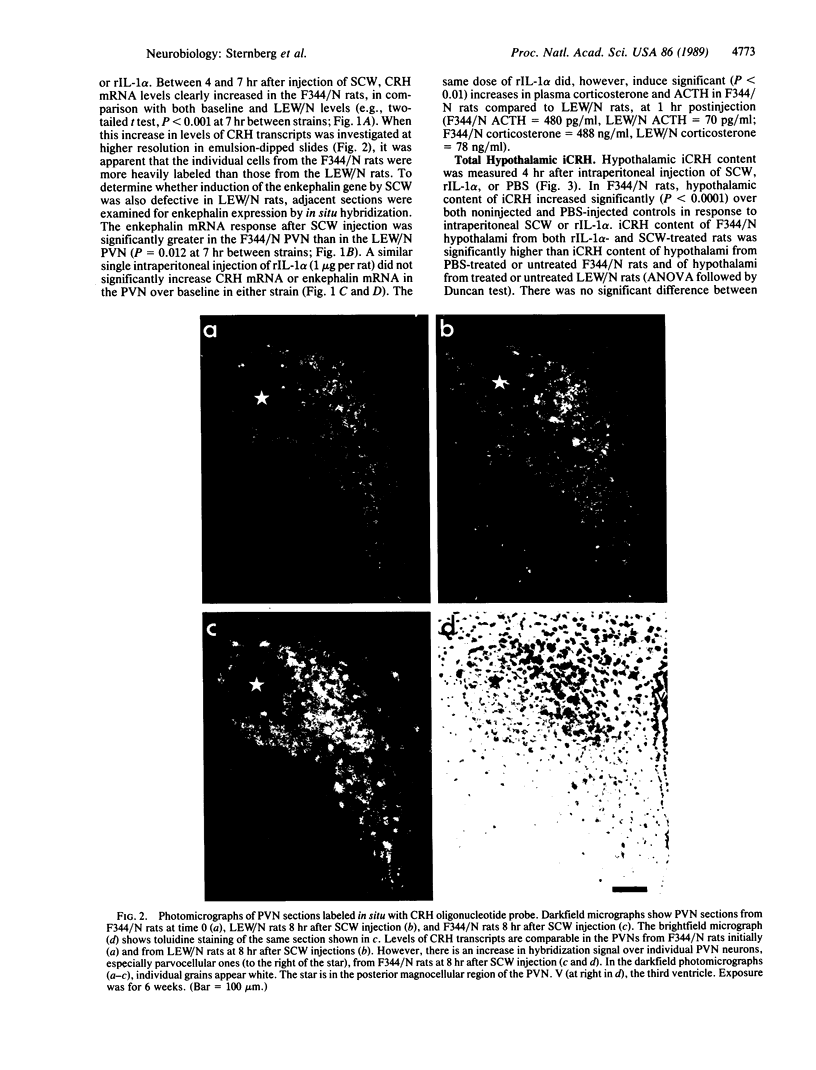
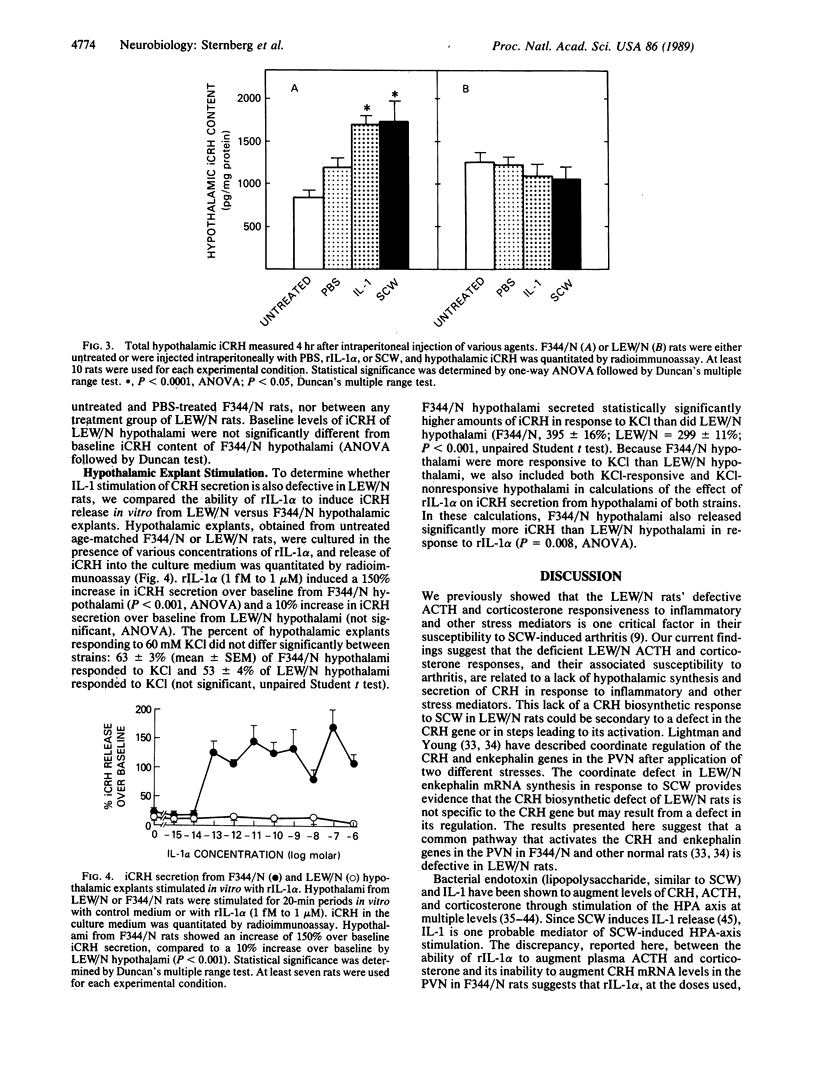
We have recently found that susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall (SCW)-induced arthritis in Lewis (LEW/N) rats is due, in part, to defective inflammatory and stress mediator-induced activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. Conversely, the relative arthritis resistance of histocompatible Fischer (F344/N) rats is related to their intact responses to the same stimuli. Specifically, LEW/N rats, in contrast to F344/N rats, have markedly impaired plasma corticotropin and corticosterone responses to SCW, recombinant human interleukin 1 alpha, the serotonin agonist quipazine, or synthetic rat/human corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). To explore the mechanism of this defect, we examined the functional integrity of the hypothalamic CRH neuron in LEW/N rats compared to F344/N rats. LEW/N rats, in contrast to F344/N rats, showed profoundly deficient paraventricular nucleus CRH mRNA levels and hypothalamic CRH content in response to SCW. Compared to F344/N rats, there was no increase in LEW/N hypothalamic CRH content or CRH release from explanted LEW/N hypothalami in organ culture in response to recombinant interleukin 1 alpha. These data provide strong evidence that the defective LEW/N corticotropin and corticosterone responses to inflammatory and other stress mediators, and the LEW/N susceptibility to experimental arthritis, are due in part to a hypothalamic defect in the synthesis and secretion of CRH. The additional finding of deficient expression in LEW/N rats of the hypothalamic enkephalin gene, which is coordinately regulated with the CRH gene in response to stress, suggests that the primary defect is not in the CRH gene but is instead related to its inappropriate regulation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. B., Calandra G. B., Wilder R. L. Cutaneous inflammatory reactions to group A streptococcal cell wall fragments in Fisher and Lewis inbred rats. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):796–801. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.796-801.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. B., Wilder R. L. Variable severity and Ia antigen expression in streptococcal-cell-wall-induced hepatic granulomas in rats. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):674–679. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.674-679.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderle S. K., Allen J. B., Wilder R. L., Eisenberg R. A., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Measurement of streptococcal cell wall in tissues of rats resistant or susceptible to cell wall-induced chronic erosive arthritis. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):836–837. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.836-837.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beraud E., Reshef T., Vandenbark A. A., Offner H., Friz R., Chou C. H., Bernard D., Cohen I. R. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mediated by T lymphocyte lines: genotype of antigen-presenting cells influences immunodominant epitope of basic protein. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(2):511–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenbosch F., van Oers J., del Rey A., Tilders F., Besedovsky H. Corticotropin-releasing factor-producing neurons in the rat activated by interleukin-1. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):524–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2443979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernton E. W., Beach J. E., Holaday J. W., Smallridge R. C., Fein H. G. Release of multiple hormones by a direct action of interleukin-1 on pituitary cells. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):519–521. doi: 10.1126/science.2821620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besedovsky H., del Rey A., Sorkin E., Dinarello C. A. Immunoregulatory feedback between interleukin-1 and glucocorticoid hormones. Science. 1986 Aug 8;233(4764):652–654. doi: 10.1126/science.3014662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blalock J. E., Smith E. M. A complete regulatory loop between the immune and neuroendocrine systems. Fed Proc. 1985 Jan;44(1 Pt 1):108–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calogero A. E., Gallucci W. T., Chrousos G. P., Gold P. W. Catecholamine effects upon rat hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone secretion in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):839–846. doi: 10.1172/JCI113687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calogero A. E., Gallucci W. T., Gold P. W., Chrousos G. P. Multiple feedback regulatory loops upon rat hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone secretion. Potential clinical implications. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):767–774. doi: 10.1172/JCI113677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspi R. R., Roberge F. G., McAllister C. G., el-Saied M., Kuwabara T., Gery I., Hanna E., Nussenblatt R. B. T cell lines mediating experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) in the rat. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):928–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos G. P., Schulte H. M., Oldfield E. H., Gold P. W., Cutler G. B., Jr, Loriaux D. L. The corticotropin-releasing factor stimulation test. An aid in the evaluation of patients with Cushing's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrousos G. P., Schulte H. M., Oldfield E. H., Gold P. W., Cutler G. B., Jr, Loriaux D. L. The corticotropin-releasing factor stimulation test. An aid in the evaluation of patients with Cushing's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1984 Mar 8;310(10):622–626. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198403083101004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. K., Thorp R. B., Maddox P. A., Brown M. B., Cassell G. H. Murine respiratory mycoplasmosis in F344 and LEW rats: evolution of lesions and lung lymphoid cell populations. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):720–729. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.720-729.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Weber E., Dayer J. M. Synthesis of interleukin 1/endogenous pyrogen in the brain of endotoxin-treated mice: a step in fever induction? J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1696–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths M. M., DeWitt C. W. Genetic control of collagen-induced arthritis in rats: the immune response to type II collagen among susceptible and resistant strains and evidence for multiple gene control. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2830–2836. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross H. A., Ruder H. J., Brown K. S., Lipsett M. B. A radioimmunoassay for plasma corticosterone. Steroids. 1972 Dec;20(6):681–695. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(72)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. L., Yu D. T. Development of an experimental animal model for reactive arthritis induced by Yersinia enterocolitica infection. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):721–726. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.721-726.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian P. L., Kaffka K. L., Stern A. S., Woehle D., Benjamin W. R., Dechiara T. M., Gubler U., Farrar J. J., Mizel S. B., Lomedico P. T. Interleukin 1 alpha and interleukin 1 beta bind to the same receptor on T cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4509–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Kohashi Y., Takahashi T., Ozawa A., Shigematsu N. Suppressive effect of Escherichia coli on adjuvant-induced arthritis in germ-free rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Apr;29(4):547–553. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. J., Allen J. B., Plotz P. H., Wilder R. L. Lactobacillus casei cell wall-induced arthritis in rats: cell wall fragment distribution and persistence in chronic arthritis-susceptible LEW/N and -resistant F344/N rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):939–942. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Changes in hypothalamic preproenkephalin A mRNA following stress and opiate withdrawal. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):643–645. doi: 10.1038/328643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Corticotrophin-releasing factor, vasopressin and pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA responses to stress and opiates in the rat. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:511–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Vasopressin, oxytocin, dynorphin, enkephalin and corticotrophin-releasing factor mRNA stimulation in the rat. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:23–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Guyre P. M., Holbrook N. J. Physiological functions of glucocorticoids in stress and their relation to pharmacological actions. Endocr Rev. 1984 Winter;5(1):25–44. doi: 10.1210/edrv-5-1-25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura H., Motoyoshi S., Kadokawa T. Anti-inflammatory action of interleukin 1 through the pituitary-adrenal axis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun 22;151(1):67–73. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90693-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge S. C., Zabriskie J. B., Osawa H., Diamantstein T., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Administration of group A streptococcal cell walls to rats induces an interleukin 2 deficiency. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):327–332. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapolsky R., Rivier C., Yamamoto G., Plotsky P., Vale W. Interleukin-1 stimulates the secretion of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.2821621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Hill J. M., Chrousos G. P., Kamilaris T., Listwak S. J., Gold P. W., Wilder R. L. Inflammatory mediator-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation is defective in streptococcal cell wall arthritis-susceptible Lewis rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2374–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara A., Gottschall P. E., Dahl R. R., Arimura A. Interleukin-1 stimulates ACTH release by an indirect action which requires endogenous corticotropin releasing factor. Endocrinology. 1987 Oct;121(4):1580–1582. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-4-1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara A., Gottschall P. E., Dahl R. R., Arimura A. Stimulation of ACTH release by human interleukin-1 beta, but not by interleukin-1 alpha, in conscious, freely-moving rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Aug 14;146(3):1286–1290. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)90788-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale W., Vaughan J., Yamamoto G., Bruhn T., Douglas C., Dalton D., Rivier C., Rivier J. Assay of corticotropin releasing factor. Methods Enzymol. 1983;103:565–577. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)03040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Hansen C. Thymus-dependent and -independent regulation of Ia antigen expression in situ by cells in the synovium of rats with streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Differences in site and intensity of expression in euthymic, athymic, and cyclosporin A-treated LEW and F344 rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1160–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI112933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B. Regulation of susceptibility to bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Nov;28(11):1318–1319. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Wahl L. M., Calandra G. B., Wahl S. M. The pathogenesis of group A streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Comparative studies in arthritis resistant and susceptible inbred rat strains. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1442–1451. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L. Proinflammatory microbial products as etiologic agents of inflammatory arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Aug;13(2):293–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloski B. M., Smith E. M., Meyer W. J., 3rd, Fuller G. M., Blalock J. E. Corticotropin-releasing activity of monokines. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1035–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.2997929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9827–9831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Mezey E., Siegel R. E. Quantitative in situ hybridization histochemistry reveals increased levels of corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA after adrenalectomy in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Oct 8;70(2):198–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90463-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]