Abstract
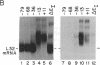
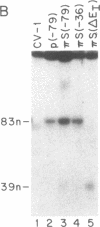
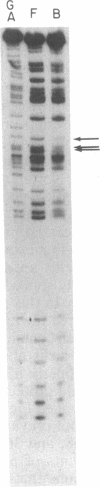
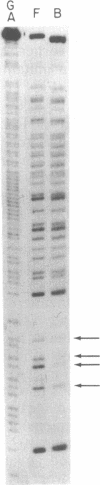
To identify the elements that regulate transcription of the mouse gene encoding ribosomal protein L32 (rpL32), we transfected monkey kidney (COS or CV-1) cells with mutants bearing progressive 5' deletions or an internal deletion in exon I and measured their transient expression by S1 nuclease protection analysis. When the mutant genes were tested in the vector pi SVHSplac, which contains a short segment of the oriregion of simian virus 40, maximum expression was observed with as little as 36 base pairs of 5' flanking sequence, and the mutant bearing the exon I deletion was expressed very efficiently. However, when the genes were tested in a simple prokaryotic (pUC) vector, the expression was increased 3- to 4-fold by sequences between -36 and -159, and the exon I segment was absolutely required for expression. Gel mobility-shift and methylation interference analyses revealed that a nuclear factor specifically binds to a GGCTGCCATC sequence within this exon I segment. These results, taken together with other recent findings, indicate that the elements involved in transcriptional regulation of the rpL32 gene are distributed over a 200-base-pair region that spans the cap site. The contributions of some of these elements are apparently masked in the presence of simian virus 40 ori-region elements.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Heat shock regulatory elements function as an inducible enhancer in the Xenopus hsp70 gene and when linked to a heterologous promoter. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):753–760. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90789-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. Properties of a mouse ribosomal protein promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8545–8549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Marcu K. B., Perry R. P. The synthesis and processing of the messenger RNAs specifying heavy and light chain immunoglobulins in MPC-11 cells. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1495–1509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner M., Perry R. P. Characterization of the multigene family encoding the mouse S16 ribosomal protein: strategy for distinguishing an expressed gene from its processed pseudogene counterparts by an analysis of total genomic DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3560–3576. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]