Abstract
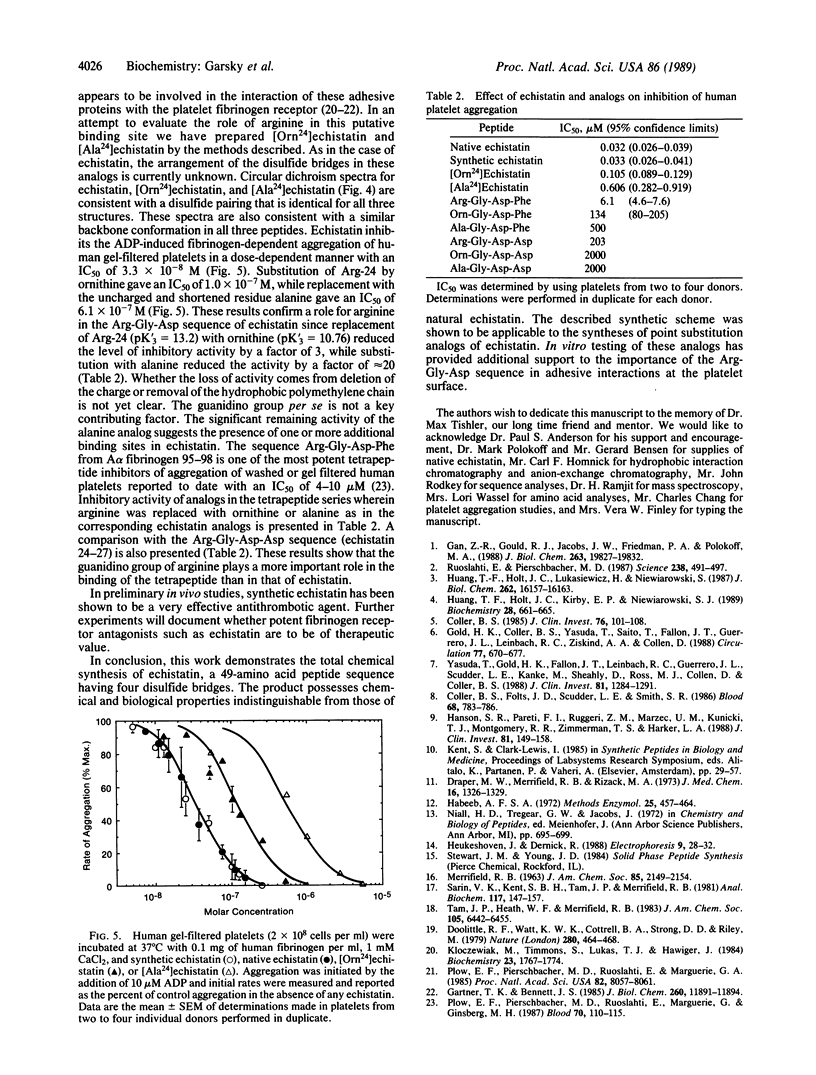
Echistatin, a polypeptide from the venom of the saw-scaled viper, Echis carinatus, containing 49 amino acids and 4 cystine bridges was synthesized by solid-phase methodology in 4% yield. In the final step, air oxidation of the octahydroderivative was found to be optimal at pH 8. The synthetic product was shown to be physically and biologically indistinguishable from native material. It inhibits fibrinogen-dependent platelet aggregation stimulated by ADP with IC50 = 3.3 x 10(-8) M and also prevents aggregation initiated by thrombin, epinephrine, collagen, or platelet-activating factor. Reduction of purified synthetic echistatin to octahydroechistatin with dithiothreitol followed by air oxidation regenerated homogeneous echistatin in quantitative yield. This highly specific refolding strongly suggests that the linear sequence of octahydroechistatin contains all of the information that is required for the proper folding of the peptide. The sequence Arg24-Gly-Asp of echistatin occurs also in adhesive glycoproteins that bind to the platelet fibrinogen receptor--a heterodimeric complex composed of glycoproteins IIb and IIIa. In an effort to evaluate the role of this putative binding site we have synthesized analogs of echistatin with substitution of Arg-24. Replacement with ornithine-24 (Orn-24) resulted in an analog having a platelet aggregation inhibitory activity with IC50 = 1.05 x 10(-7) M. Substitution with Ala-24 gave IC50 = 6.1 x 10(-7) M. The inhibitory activity of the corresponding short sequence analogs Arg-Gly-Asp-Phe (IC50 = 6 x 10(-6) M), Orn-Gly-Asp-Phe (IC50 = 1.3 x 10(-4) M), and Ala-Gly-Asp-Phe (IC50 = 5.0 x 10(-4) M) was also determined. These results suggest that arginine plays a more important role in the binding of the tetrapeptide than in that of echistatin.
Full text
PDF

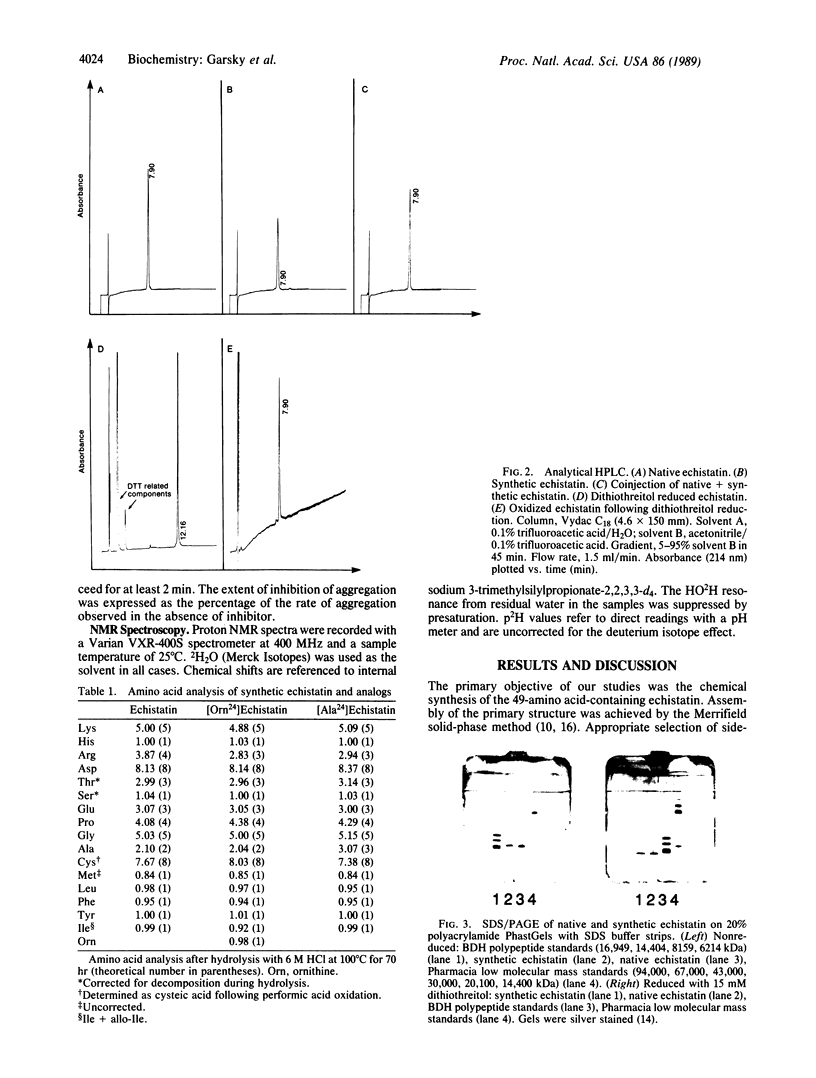
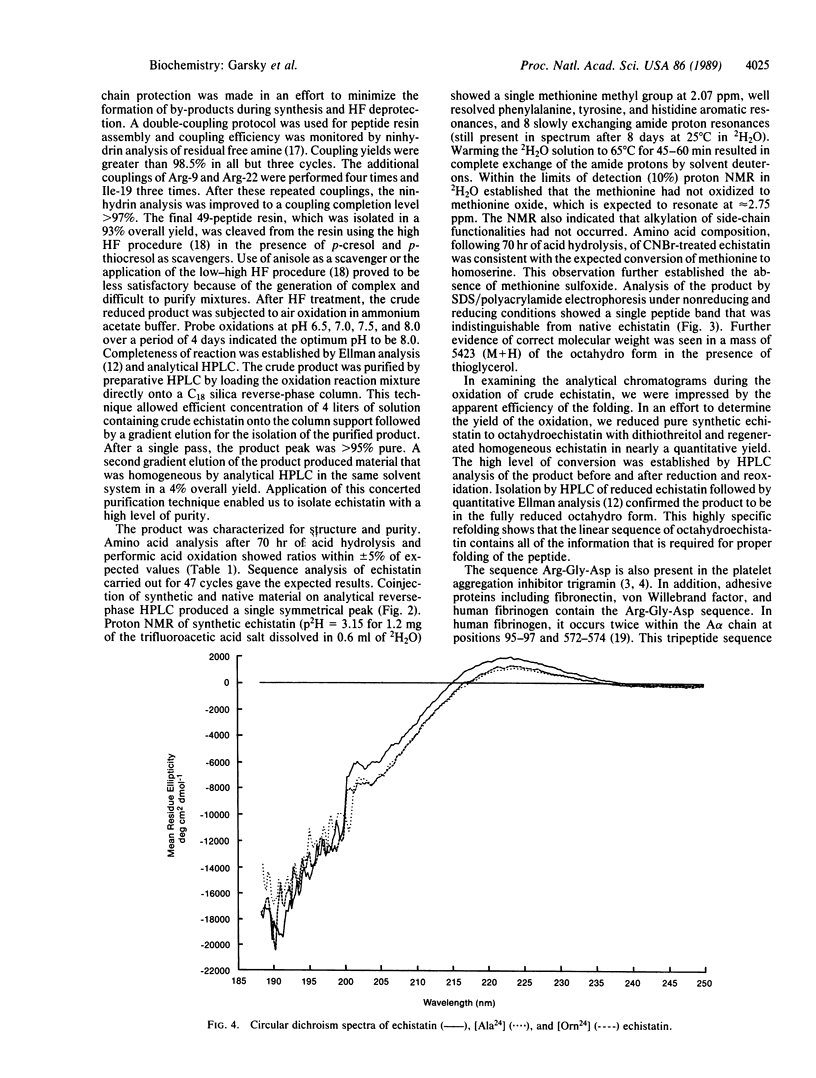
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coller B. S. A new murine monoclonal antibody reports an activation-dependent change in the conformation and/or microenvironment of the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):101–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI111931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Folts J. D., Scudder L. E., Smith S. R. Antithrombotic effect of a monoclonal antibody to the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptor in an experimental animal model. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):783–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Watt K. W., Cottrell B. A., Strong D. D., Riley M. The amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of human fibrinogen. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):464–468. doi: 10.1038/280464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper M. W., Merrifield R. B., Rizack M. A. Lipolytic activity of Met-Arg-His-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly, a synthetic analog of the ACTH (4-10) core sequence. J Med Chem. 1973 Dec;16(12):1326–1330. doi: 10.1021/jm00270a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan Z. R., Gould R. J., Jacobs J. W., Friedman P. A., Polokoff M. A. Echistatin. A potent platelet aggregation inhibitor from the venom of the viper, Echis carinatus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19827–19832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. K., Coller B. S., Yasuda T., Saito T., Fallon J. T., Guerrero J. L., Leinbach R. C., Ziskind A. A., Collen D. Rapid and sustained coronary artery recanalization with combined bolus injection of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator and monoclonal antiplatelet GPIIb/IIIa antibody in a canine preparation. Circulation. 1988 Mar;77(3):670–677. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.77.3.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson S. R., Pareti F. I., Ruggeri Z. M., Marzec U. M., Kunicki T. J., Montgomery R. R., Zimmerman T. S., Harker L. A. Effects of monoclonal antibodies against the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex on thrombosis and hemostasis in the baboon. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jan;81(1):149–158. doi: 10.1172/JCI113286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heukeshoven J., Dernick R. Improved silver staining procedure for fast staining in PhastSystem Development Unit. I. Staining of sodium dodecyl sulfate gels. Electrophoresis. 1988 Jan;9(1):28–32. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150090106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Kirby E. P., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin: primary structure and its inhibition of von Willebrand factor binding to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex on human platelets. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):661–666. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. F., Holt J. C., Lukasiewicz H., Niewiarowski S. Trigramin. A low molecular weight peptide inhibiting fibrinogen interaction with platelet receptors expressed on glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16157–16163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloczewiak M., Timmons S., Lukas T. J., Hawiger J. Platelet receptor recognition site on human fibrinogen. Synthesis and structure-function relationship of peptides corresponding to the carboxy-terminal segment of the gamma chain. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid sequences and fibrinogen binding to platelets. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Pierschbacher M. D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science. 1987 Oct 23;238(4826):491–497. doi: 10.1126/science.2821619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Kent S. B., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda T., Gold H. K., Fallon J. T., Leinbach R. C., Guerrero J. L., Scudder L. E., Kanke M., Shealy D., Ross M. J., Collen D. Monoclonal antibody against the platelet glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa receptor prevents coronary artery reocclusion after reperfusion with recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1284–1291. doi: 10.1172/JCI113446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]