Abstract
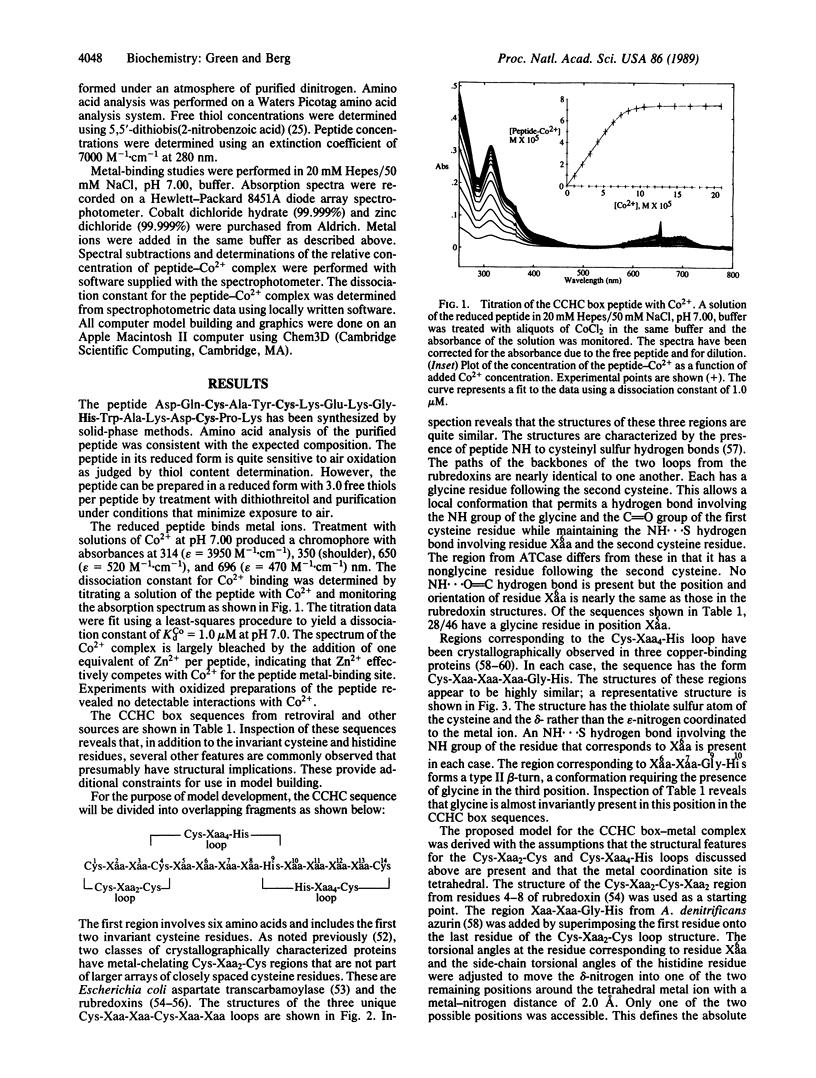
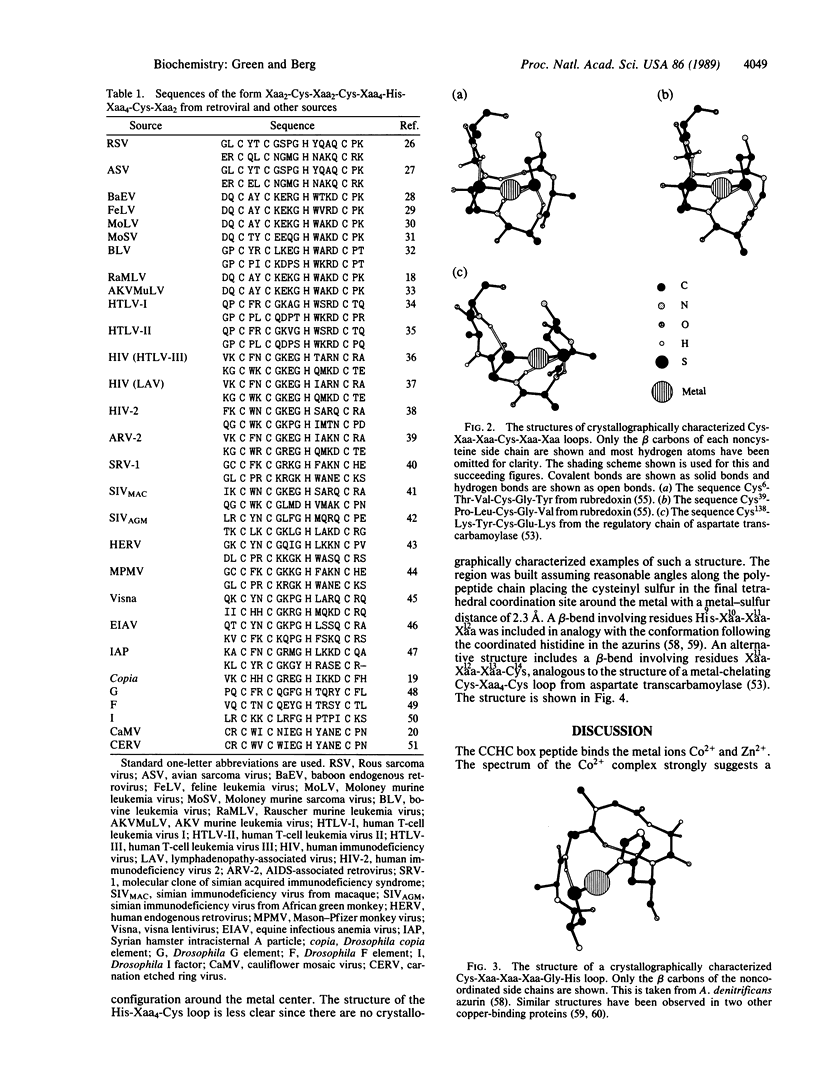
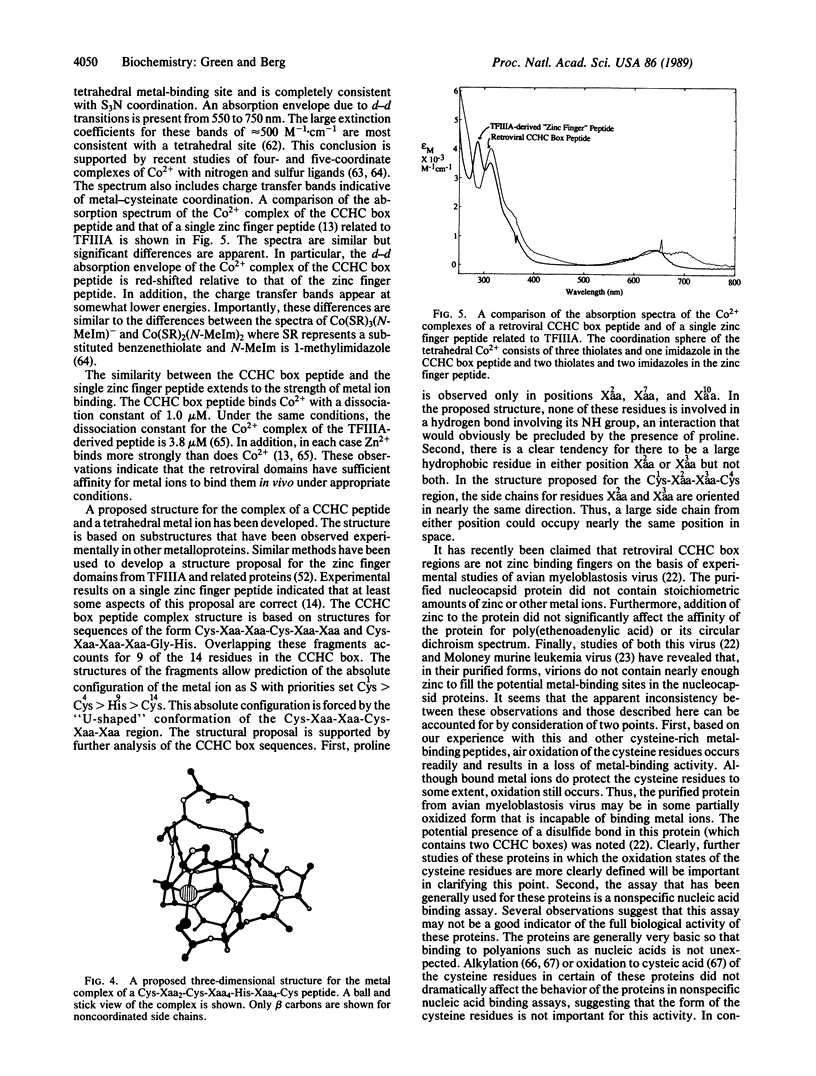
Retroviral gag gene-encoded core nucleic acid binding proteins contain either one or two sequences of the form Cys-Xaa2-Cys-Xaa4-His-Xaa4-Cys. Previously, one of us has proposed that these sequences form metal-binding domains in analogy with the "zinc finger" domains first observed in transcription factor IIIA. We report that an 18-amino acid peptide derived from the core nucleic acid binding protein from Rauscher murine leukemia virus binds metal ions such as Co2+ and Zn2+. The absorption spectrum of the peptide-Co2+ complex is highly suggestive of tetrahedral coordination involving three cysteinates and one histidine. Titration experiments indicate that the dissociation constant for the peptide-Co2+ complex is 1.0 microM and that Zn2+ binds more tightly than Co2+. A detailed three-dimensional structure for this domain based on conserved substructures in other crystallographically characterized metalloproteins and on a detailed analysis of the Cys-Xaa2-Cys-Xaa4-His-Xaa4-Cys sequences from retroviruses and other related sources is proposed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman E. T., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H., Bruschi M., Le Gall J. A structural model of rubredoxin from Desulfovibrio vulgaris at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 5;112(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80159-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adman E., Watenpaugh K. D., Jensen L. H. NH---S hydrogen bonds in Peptococcus aerogenes ferredoxin, Clostridium pasteurianum rubredoxin, and Chromatium high potential iron protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4854–4858. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. N. Structure of azurin from Alcaligenes denitrificans refinement at 1.8 A resolution and comparison of the two crystallographically independent molecules. J Mol Biol. 1988 Oct 20;203(4):1071–1095. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertini I., Luchinat C. High spin cobalt(II) as a probe for the investigation of metalloproteins. Adv Inorg Biochem. 1984;6:71–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. S., Sander C., Argos P. The primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive repeats. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jul 8;186(2):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80723-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti L., Guyader M., Alizon M., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C., Tiollais P., Sonigo P. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from macaque and its relationship to other human and simian retroviruses. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):543–547. doi: 10.1038/328543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland T. D., Morgan M. A., Oroszlan S. Complete amino acid sequence of the basic nucleic acid binding protein of feline leukemia virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90432-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland T. D., Morgan M. A., Oroszlan S. Complete amino acid sequence of the nucleic acid-binding protein of bovine leukemia virus. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 30;156(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Kalyanaraman V. S., Sarngadharan M. G., Gallo R. C. Complete amino acid sequence of human T-cell leukemia virus structural protein p15. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 17;162(2):390–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80793-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey S. N. Amino acid sequence homology in gag region of reverse transcribing elements and the coat protein gene of cauliflower mosaic virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):623–633. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culp J. S., Webster L. C., Friedman D. J., Smith C. L., Huang W. J., Wu F. Y., Rosenberg M., Ricciardi R. P. The 289-amino acid E1A protein of adenovirus binds zinc in a region that is important for trans-activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Casari G. Related polypeptides are encoded by Drosophila F elements, I factors, and mammalian L1 sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5843–5847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P. Close relationship between non-viral retroposons in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 11;16(9):4041–4052. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.9.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diakun G. P., Fairall L., Klug A. EXAFS study of the zinc-binding sites in the protein transcription factor IIIA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):698–699. doi: 10.1038/324698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A., Taylor W. E., Blumberg H., Young E. T. The yeast regulatory protein ADR1 binds in a zinc-dependent manner to the upstream activating sequence of ADH2. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4552–4556. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. H., Lister C. K., Kellett E., Finnegan D. J. Transposable elements controlling I-R hybrid dysgenesis in D. melanogaster are similar to mammalian LINEs. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90815-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franck A., Guilley H., Jonard G., Richards K., Hirth L. Nucleotide sequence of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Berg J. M., Pabo C. O. Metal-dependent folding of a single zinc finger from transcription factor IIIA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4841–4845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukasawa M., Miura T., Hasegawa A., Morikawa S., Tsujimoto H., Miki K., Kitamura T., Hayami M. Sequence of simian immunodeficiency virus from African green monkey, a new member of the HIV/SIV group. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):457–461. doi: 10.1038/333457a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giedroc D. P., Keating K. M., Williams K. R., Konigsberg W. H., Coleman J. E. Gene 32 protein, the single-stranded DNA binding protein from bacteriophage T4, is a zinc metalloprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8452–8456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorelick R. J., Henderson L. E., Hanser J. P., Rein A. Point mutants of Moloney murine leukemia virus that fail to package viral RNA: evidence for specific RNA recognition by a "zinc finger-like" protein sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8420–8424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss J. M., Merritt E. A., Phizackerley R. P., Hedman B., Murata M., Hodgson K. O., Freeman H. C. Phase determination by multiple-wavelength x-ray diffraction: crystal structure of a basic "blue" copper protein from cucumbers. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):806–811. doi: 10.1126/science.3406739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyader M., Emerman M., Sonigo P., Clavel F., Montagnier L., Alizon M. Genome organization and transactivation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):662–669. doi: 10.1038/326662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanas J. S., Hazuda D. J., Bogenhagen D. F., Wu F. Y., Wu C. W. Xenopus transcription factor A requires zinc for binding to the 5 S RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14120–14125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Armour R., Baldwin J. H., Maldonado F., Spiess J., Holley R. W. Amino acid sequence of the BSC-1 cell growth inhibitor (polyergin) deduced from the nucleotide sequence of the cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):79–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Sowder R. C., Smythers G. W., Oroszlan S. Primary structure of the low molecular weight nucleic acid-binding proteins of murine leukemia viruses. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8400–8406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honzatko R. B., Crawford J. L., Monaco H. L., Ladner J. E., Ewards B. F., Evans D. R., Warren S. G., Wiley D. C., Ladner R. C., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal and molecular structures of native and CTP-liganded aspartate carbamoyltransferase from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):219–263. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull R., Sadler J., Longstaff M. The sequence of carnation etched ring virus DNA: comparison with cauliflower mosaic virus and retroviruses. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3083–3090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentoft J. E., Smith L. M., Fu X. D., Johnson M., Leis J. Conserved cysteine and histidine residues of the avian myeloblastosis virus nucleocapsid protein are essential for viral replication but are not "zinc-binding fingers". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7094–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Carner K. R., Masiarz F. R., Tjian R. Isolation of cDNA encoding transcription factor Sp1 and functional analysis of the DNA binding domain. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1079–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90594-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Jentoft J. Characteristics and regulation of interaction of avian retrovirus pp12 protein with viral RNA. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.361-369.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Rubin G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Drosophila transposable element copia: homology between copia and retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai K., Nakaseko Y., Nasmyth K., Rhodes D. Zinc-finger motifs expressed in E. coli and folded in vitro direct specific binding to DNA. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):284–286. doi: 10.1038/332284a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Toh H., Miyata T., Awaya T. Nucleotide sequence of the Syrian hamster intracisternal A-particle gene: close evolutionary relationship of type A particle gene to types B and D oncovirus genes. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):387–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.387-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Yasunaga T., Miyata T., Ushikubo H. Nucleotide sequence of human endogenous retrovirus genome related to the mouse mammary tumor virus genome. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):589–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.589-598.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power M. D., Marx P. A., Bryant M. L., Gardner M. B., Barr P. J., Luciw P. A. Nucleotide sequence of SRV-1, a type D simian acquired immune deficiency syndrome retrovirus. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1567–1572. doi: 10.1126/science.3006247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Sarih L., Gabus C., Litvak S., Keith G., Darlix J. L. Small finger protein of avian and murine retroviruses has nucleic acid annealing activity and positions the replication primer tRNA onto genomic RNA. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1777–1783. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Párraga G., Horvath S. J., Eisen A., Taylor W. E., Hood L., Young E. T., Klevit R. E. Zinc-dependent structure of a single-finger domain of yeast ADR1. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1489–1492. doi: 10.1126/science.3047872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddles P. W., Blakeley R. L., Zerner B. Reassessment of Ellman's reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:49–60. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91010-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Power M. D., Barr P. J., Steimer K. S., Stempien M. M., Brown-Shimer S. L., Gee W. W., Renard A., Randolph A., Levy J. A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of an AIDS-associated retrovirus (ARV-2). Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):484–492. doi: 10.1126/science.2578227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Characterization of a zinc blotting technique: evidence that a retroviral gag protein binds zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Takahashi Y., Shimizu N., Gojobori T., Golde D. W., Chen I. S., Miwa M., Sugimura T. Complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of human T-cell leukemia virus type II: an open reading frame for the protease gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3101–3105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieker L. C., Stenkamp R. E., Jensen L. H., Prickril B., LeGall J. Structure of rubredoxin from the bacterium Desulfovibrio desulfuricans. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81535-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Alizon M., Staskus K., Klatzmann D., Cole S., Danos O., Retzel E., Tiollais P., Haase A., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of the visna lentivirus: relationship to the AIDS virus. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):369–382. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonigo P., Barker C., Hunter E., Wain-Hobson S. Nucleotide sequence of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus: an immunosuppressive D-type retrovirus. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):375–385. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90323-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Casey J. W., Rice N. R. Equine infectious anemia virus gag and pol genes: relatedness to visna and AIDS virus. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):589–594. doi: 10.1126/science.3003905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T. A. Provirus of M7 baboon endogenous virus: nucleotide sequence of the gag-pol region. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):137–145. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.137-145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Van Den Berg D. J., Korn L. J. Structure of the gene for Xenopus transcription factor TFIIIA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2187–2200. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Brown D. D. Mapping functional regions of transcription factor TFIIIA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1684–1696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wain-Hobson S., Sonigo P., Danos O., Cole S., Alizon M. Nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, LAV. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watenpaugh K. D., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Crystallographic refinement of rubredoxin at 1 x 2 A degrees resolution. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):615–633. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



