Abstract
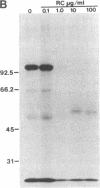
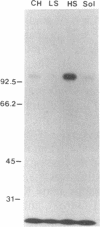
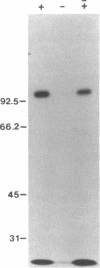
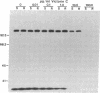
Susceptibility of oats to victoria blight, caused by the fungus Cochliobolus victoriae, and sensitivity to the host-specific toxin victorin, produced by the fungus, are controlled by the dominant allele at the Vb locus. It has been postulated that the Vb locus encodes a toxin receptor, although direct evidence for such a receptor is not available. Our recent studies on structure—activity relationships of the toxin established a methodology for producing 125I-labeled victorin. Electrophoretic analysis of proteins from isogenic susceptible and resistant oat genotypes following treatment of leaves with radiolabeled victorin showed that victorin binds in a covalent and a genotype-specific manner to a 100-kDa protein only in susceptible oat leaf slices. This in vivo binding was competitively displaced by reduced victorin, a nontoxic protective compound, and appeared to be correlated with biological activity. In vitro binding to the 100-kDa protein in leaf extracts showed several differences from in vivo binding. Binding was not genotype specific and required a reducing agent that was not required for in vivo binding. Differential centrifugation showed that the 100-kDa victorin binding protein was not a cytosolic protein but was enriched in a high-speed particulate fraction. The data support the hypothesis that the 100-kDa protein is the victorin receptor.
Keywords: host-selective toxins, Cochliobolus victoriae, Helminthosporium victoriae, victorin receptor
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macko K. A., Hodos W. Near point of accommodation in pigeons. Vision Res. 1985;25(10):1529–1530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(85)90232-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meehan F., Murphy H. C. A New Helminthosporium Blight of Oats. Science. 1946 Nov 1;104(2705):413–414. doi: 10.1126/science.104.2705.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer R. P., Livingston R. S. Host-selective toxins and their role in plant diseases. Science. 1984 Jan 6;223(4631):17–21. doi: 10.1126/science.223.4631.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermans J. F., de Mots A. Spectrophotometric characteristics of chlorophylls a and b and their pheophytins in ethanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 29;109(2):448–453. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolpert T. J., Macko V., Acklin W., Arigoni D. Molecular Features Affecting the Biological Activity of the Host-Selective Toxins from Cochliobolus victoriae. Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):37–41. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]