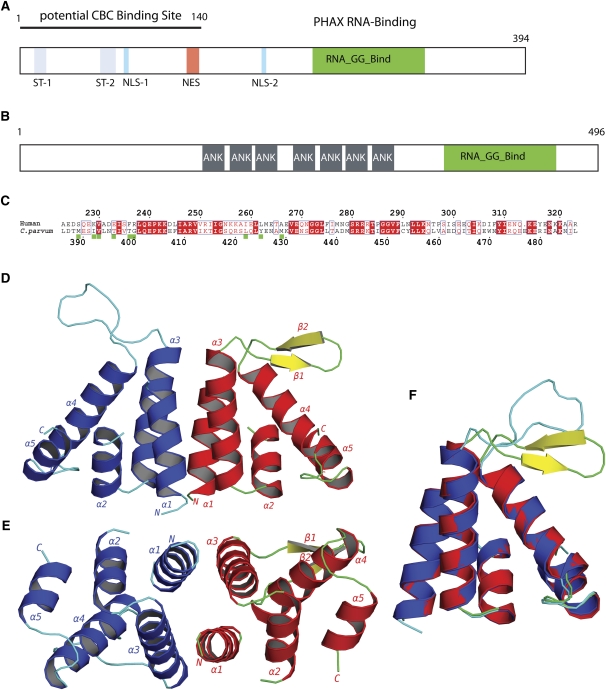
FIGURE 1.
The PHAX RNA-binding domain. (A) Schematic functional organization of human PHAX based on biochemical data showing phosphorylation sites (ST-1, ST-2), bipartite nuclear import sequence (NLS-1, NLS-2), nuclear export sequence (NES), and location of the RNA-binding domain (green) and the CBC binding site. (B) Schematic domain organization of C. parvum protein Q7YZ62, showing the location of ankyrin repeats (gray), and the RNA-GG-bind domain (green). (C) Sequence alignment of human PHAX-RBD and CpGGBD. Green boxes: Residues that are involved in the dimer interface of CpGGBD. (D) Cartoon representation of the AB dimer of the RNA_GG_bind domain from C. parvum. (E) Dimer rotated by 90°. (F) Overlay of monomers A (blue and cyan) and molecule B (red, green, and yellow).