Abstract
The Philadelphia chromosome associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) has been linked to a hybrid BCR/ABL protein product that differs from that found in chronic myelogenous leukemia. This implies that the molecular structures of the two chromosomal translocations also differ. Localization of translocation breakpoints in Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL has been impeded due to the only partial characterization of the BCR locus. We have isolated the entire 130-kilobase BCR genomic locus from a human cosmid library. A series of five single-copy genomic probes from the 70-kilobase first intron of BCR were used to localize rearrangements in 8 of 10 Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALLs. We have demonstrated that these breakpoints are all located at the 3' end of the intron around an unusual restriction fragment length polymorphism caused by deletion of a 1-kilobase fragment containing Alu family reiterated sequences. This clustering is unexpected in light of previous theories of rearrangement in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia that would have predicted a random dispersion of breakpoints in the first intron in Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. The proximity of the translocation breakpoints to this constitutive deletion may indicate shared mechanisms of rearrangement or that such polymorphisms mark areas of the genome prone to recombination.
Full text
PDF

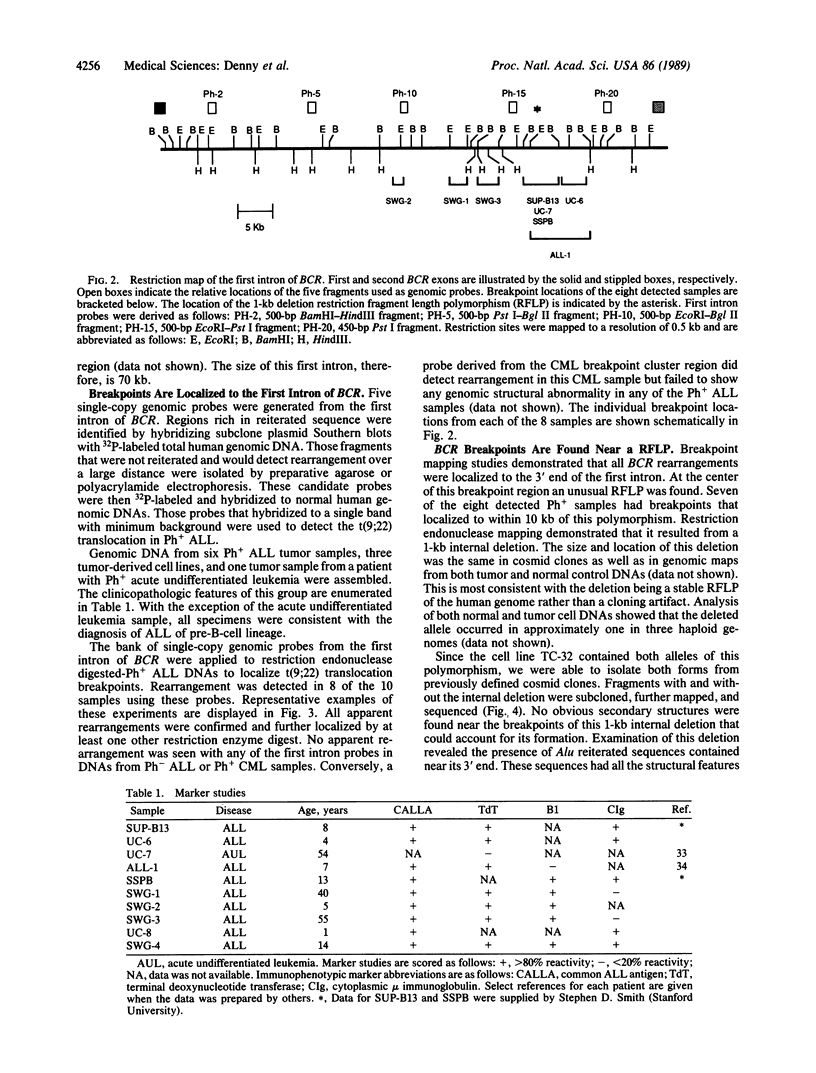


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Neriah Y., Daley G. Q., Mes-Masson A. M., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. The chronic myelogenous leukemia-specific P210 protein is the product of the bcr/abl hybrid gene. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):212–214. doi: 10.1126/science.3460176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. C., Karhi K. K., Rayter S. I., Heisterkamp N., Eridani S., Powles R., Lawler S. D., Groffen J., Foulkes J. G., Greaves M. F. A novel abl protein expressed in Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):635–637. doi: 10.1038/325635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. J., Chen Z., Grausz J. D., Hillion J., d'Auriol L., Flandrin G., Larsen C. J., Berger R. Molecular cloning of a 5' segment of the genomic phl gene defines a new breakpoint cluster region (bcr2) in Philadelphia-positive acute leukemias. Leukemia. 1988 Oct;2(10):634–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. J., Flandrin G., Daniel M. T., Valensi F., Baranger L., Grausz D., Bernheim A., Chen Z., Sigaux F., Berger R. Philadelphia-positive acute leukemia: lineage promiscuity and inconsistently rearranged breakpoint cluster region. Leukemia. 1988 May;2(5):261–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. S., McLaughlin J., Crist W. M., Champlin R., Witte O. N. Unique forms of the abl tyrosine kinase distinguish Ph1-positive CML from Ph1-positive ALL. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.3541203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. S., McLaughlin J., Timmons M., Pendergast A. M., Ben-Neriah Y., Dow L. W., Crist W., Rovera G., Smith S. D., Witte O. N. Expression of a distinctive BCR-ABL oncogene in Ph1-positive acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL). Science. 1988 Feb 12;239(4841 Pt 1):775–777. doi: 10.1126/science.3422516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Huebner K., Isobe M., Fainstain E., Lifshitz B., Shtivelman E., Canaani E. Mapping of four distinct BCR-related loci to chromosome region 22q11: order of BCR loci relative to chronic myelogenous leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia breakpoints. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7174–7178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean M., Park M., Vande Woude G. F. Characterization of the rearranged tpr-met oncogene breakpoint. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):921–924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donis-Keller H., Green P., Helms C., Cartinhour S., Weiffenbach B., Stephens K., Keith T. P., Bowden D. W., Smith D. R., Lander E. S. A genetic linkage map of the human genome. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Griffin C. A., ar-Rushdi A., Valtieri M., Hoxie J., Finan J., Emanuel B. S., Rovera G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Heterogeneity of chromosome 22 breakpoint in Philadelphia-positive (Ph+) acute lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1807–1811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Stephenson J. R., Heisterkamp N., de Klein A., Bartram C. R., Grosveld G. Philadelphia chromosomal breakpoints are clustered within a limited region, bcr, on chromosome 22. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld G., Verwoerd T., van Agthoven T., de Klein A., Ramachandran K. L., Heisterkamp N., Stam K., Groffen J. The chronic myelocytic cell line K562 contains a breakpoint in bcr and produces a chimeric bcr/c-abl transcript. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):607–616. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:333–342. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stam K., Groffen J., de Klein A., Grosveld G. Structural organization of the bcr gene and its role in the Ph' translocation. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):758–761. doi: 10.1038/315758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stephenson J. R., Groffen J., Hansen P. F., de Klein A., Bartram C. R., Grosveld G. Localization of the c-ab1 oncogene adjacent to a translocation break point in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):239–242. doi: 10.1038/306239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans A., Heisterkamp N., von Linden M., van Baal S., Meijer D., van der Plas D., Wiedemann L. M., Groffen J., Bootsma D., Grosveld G. Unique fusion of bcr and c-abl genes in Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):33–40. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Schmid C. W. Repetitive sequences in eukaryotic DNA and their expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:813–844. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Singer J. W., Collins S. J., Witte O. N. Cell lines and clinical isolates derived from Ph1-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia patients express c-abl proteins with a common structural alteration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1810–1814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Witte O. N. An alteration of the human c-abl protein in K562 leukemia cells unmasks associated tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Witte O. N. Detection of c-abl tyrosine kinase activity in vitro permits direct comparison of normal and altered abl gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3116–3123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzrock R., Shtalrid M., Romero P., Kloetzer W. S., Talpas M., Trujillo J. M., Blick M., Beran M., Gutterman J. U. A novel c-abl protein product in Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):631–635. doi: 10.1038/325631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Duplication of seven exons in LDL receptor gene caused by Alu-Alu recombination in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Exon-Alu recombination deletes 5 kilobases from the low density lipoprotein receptor gene, producing a null phenotype in familial hypercholesterolemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3679–3683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert M. L., Hutton J. J., Wiginton D. A., States J. C., Kaufman R. E. Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency due to deletion of the ADA gene promoter and first exon by homologous recombination between two Alu elements. J Clin Invest. 1988 May;81(5):1323–1327. doi: 10.1172/JCI113458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. A deletion involving Alu sequences in the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain gene of French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15396–15399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Leppert M., O'Connell P., Wolff R., Holm T., Culver M., Martin C., Fujimoto E., Hoff M., Kumlin E. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) markers for human gene mapping. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1616–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.3029872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro R. C., Abromowitch M., Raimondi S. C., Murphy S. B., Behm F., Williams D. L. Clinical and biologic hallmarks of the Philadelphia chromosome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):948–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. Oncogene chromosome breakpoints and alu sequences. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):559–559. doi: 10.1038/317559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer F., Simmler M. C., Page D. C., Weissenbach J. A sex chromosome rearrangement in a human XX male caused by Alu-Alu recombination. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90637-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973 Jun 1;243(5405):290–293. doi: 10.1038/243290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. M., Carrino J. J., Dickler M. N., Leibowitz D., Smith S. D., Westbrook C. A. Heterogeneity of genomic fusion of BCR and ABL in Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2795–2799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saglio G., Guerrasio A., Tassinari A., Ponzetto C., Zaccaria A., Testoni P., Celso B., Rege Cambrin G., Serra A., Pegoraro L. Variability of the molecular defects corresponding to the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in human hematologic malignancies. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1203–1208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumm J. W., Knowlton R. G., Braman J. C., Barker D. F., Botstein D., Akots G., Brown V. A., Gravius T. C., Helms C., Hsiao K. Identification of more than 500 RFLPs by screening random genomic clones. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 Jan;42(1):143–159. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Secker-Walker L. M., Cooke H. M., Browett P. J., Shippey C. A., Norton J. D., Coustan-Smith E., Hoffbrand A. V. Variable Philadelphia breakpoints and potential lineage restriction of bcr rearrangement in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):784–791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtalrid M., Talpaz M., Kurzrock R., Kantarjian H., Trujillo J., Gutterman J., Yoffe G., Blick M. Analysis of breakpoints within the bcr gene and their correlation with the clinical course of Philadelphia-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):485–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Canaani E. Fused transcript of abl and bcr genes in chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Nature. 1985 Jun 13;315(6020):550–554. doi: 10.1038/315550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Roe B. A., Canaani E. Alternative splicing of RNAs transcribed from the human abl gene and from the bcr-abl fused gene. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam K., Heisterkamp N., Grosveld G., de Klein A., Verma R. S., Coleman M., Dosik H., Groffen J. Evidence of a new chimeric bcr/c-abl mRNA in patients with chronic myelocytic leukemia and the Philadelphia chromosome. N Engl J Med. 1985 Dec 5;313(23):1429–1433. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198512053132301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Lewis K. A., Ruiz J. C., Rothenberg B., Zhao J., Evans G. A. Cosmid vectors for rapid genomic walking, restriction mapping, and gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang-Peng J., Triche T. J., Knutsen T., Miser J., Kao-Shan S., Tsai S., Israel M. A. Cytogenetic characterization of selected small round cell tumors of childhood. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1986 Apr 1;21(3):185–208. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(86)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Klein A., van Agthoven T., Groffen C., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Grosveld G. Molecular analysis of both translocation products of a Philadelphia-positive CML patient. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7071–7082. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Kessel A. G., Turc-Carel C., de Klein A., Grosveld G., Lenoir G., Bootsma D. Translocation of oncogene c-sis from chromosome 22 to chromosome 11 in a Ewing sarcoma-derived cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):427–429. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]