Abstract
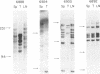
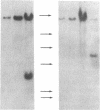
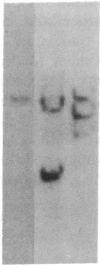
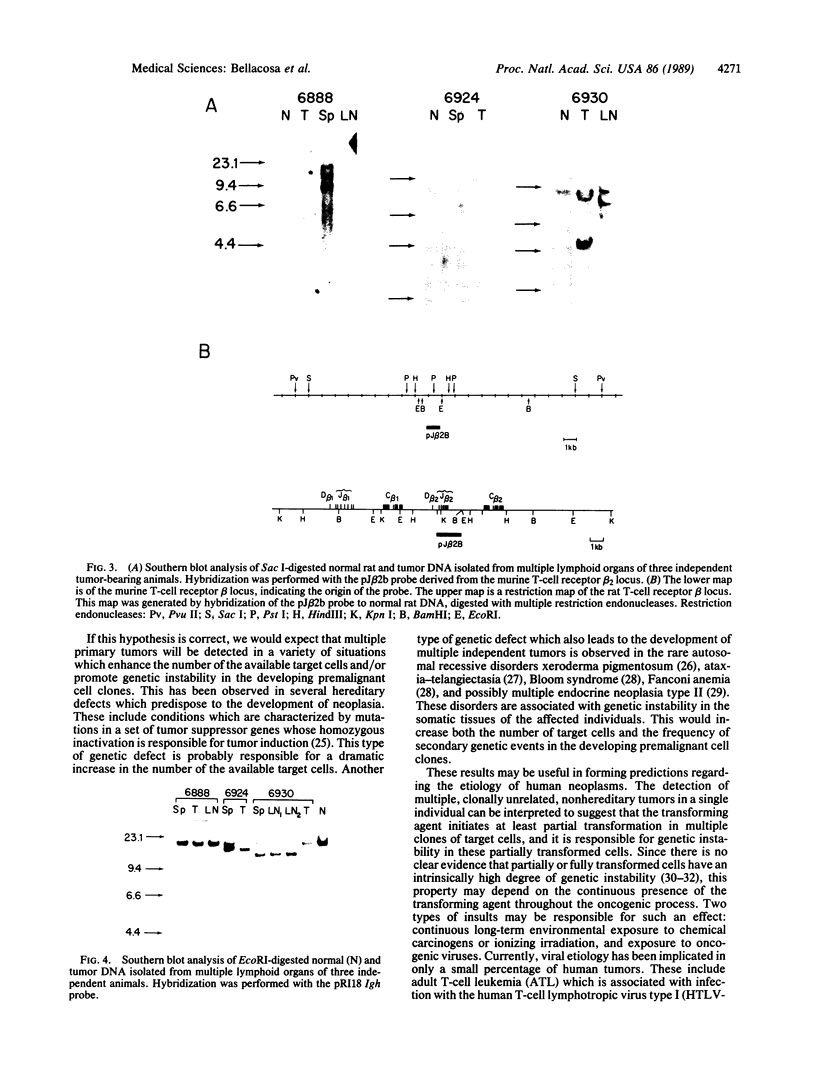
Tumor cell DNA derived from different lymphoid organs of 30 rats serially inoculated at birth with Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMuLV) was examined by Southern blot analysis and hybridization to the following DNA probes: MoMuLV long terminal repeat (LTR), Moloney leukemia virus integration regions 1, 2, 3, and 4 (Mlvi-1, Mlvi-2, Mlvi-3, and Mlvi-4), T-cell receptor beta locus, and immunoglobulin heavy chain locus. This analysis revealed that the tumors segregating in different lymphoid organs in 10% of the animals were clonally unrelated. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that the MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas are polyclonal in origin. At least two factors may be responsible for this phenomenon: (i) increase in the number of the available target cells in virus-infected animals, and (ii) genetic instability associated with provirus integration in the developing premalignant clones.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asjö B., Skoog L., Palminger I., Wiener F., Isaak D., Cerny J., Fenyö E. M. Influence of genotype and the organ of origin on the subtype of T-cell in Moloney lymphomas induced by transfer of preleukemic cells from athymic and thymus-bearing mice. Cancer Res. 1985 Mar;45(3):1040–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Defective repair replication of DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):652–656. doi: 10.1038/218652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Adams J. M., Kemp D. J. Somatic rearrangements forming active immunoglobulin mu genes in B and T lymphoid cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4943–4947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis B. R., Chandy K. G., Brightman B. K., Gupta S., Fan H. Effects of nonleukemogenic and wild-type Moloney murine leukemia virus on lymphoid cells in vivo: identification of a preleukemic shift in thymocyte subpopulations. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):423–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.423-430.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou-Pachnis A., Lohse M. A., Furano A. V., Tsichlis P. N. Insertion of long interspersed repeated elements at the Igh (immunoglobulin heavy chain) and Mlvi-2 (Moloney leukemia virus integration 2) loci of rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2857–2861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmore E., Kakunaga T., Barrett J. C. Comparison of spontaneous mutation rates of normal and chemically transformed human skin fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1983 Apr;43(4):1650–1655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. Primordial cell pool size and lineage relationships of five human cell types. Ann Hum Genet. 1973 Jul;37(1):39–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1973.tb01813.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J. Use of genetic markers to study cellular origin and development of tumors in human females. Adv Cancer Res. 1972;15:191–226. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60375-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A., Hobart M., Hengartner H., Rabbitts T. H. An immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene is altered in two T-cell clones. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):897–899. doi: 10.1038/286897a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y. I., Sugamura K., Hinuma Y. Healthy carriers of a human retrovirus, adult T-cell leukemia virus (ATLV): demonstration by clonal culture of ATLV-carrying T cells from peripheral blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4780–4782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Perlmutter A. P., Gilbert W. Monoclonal AKR/J thymic leukemias contain multiple JH immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7433–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T. C., Pathak S., Samaan N., Hickey R. C. Chromosome instability in patients with medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. JAMA. 1981 Nov 6;246(18):2046–2048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Enjuanes L., Lee J. C., Keller J. The immune response to C-type viruses and its potential role in leukemogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;101:31–49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68654-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato A., Hays E. F. Development of virus-accelerated thymic lymphoma in AKR mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Sep;75(3):491–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendal W. S., Frost P. Metastatic potential and spontaneous mutation rates: studies with two murine cell lines and their recently induced metastatic variants. Cancer Res. 1986 Dec;46(12 Pt 1):6131–6135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson A. G., Jr Genetics of human cancer. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:231–251. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Ihle J. N. Chronic immune stimulation is required for Moloney leukaemia virus-induced lymphomas. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):407–409. doi: 10.1038/289407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Ihle J. N. Increased responses to lymphokines are correlated with preleukemia in mice inoculated with Moloney leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7712–7716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLONEY J. B. Biological studies on a lymphoid-leukemia virus extracted from sarcoma 37. I. Origin and introductory investigations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Apr;24:933–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Minard K., Mjolsness S., Kronenberg M., Goverman J., Hunkapiller T., Prystowsky M. B., Yoshikai Y., Fitch F., Mak T. W. Mouse T cell antigen receptor: structure and organization of constant and joining gene segments encoding the beta polypeptide. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakada K., Yamaguchi K., Furugen S., Nakasone T., Nakasone K., Oshiro Y., Kohakura M., Hinuma Y., Seiki M., Yoshida M. Monoclonal integration of HTLV-I proviral DNA in patients with strongyloidiasis. Int J Cancer. 1987 Aug 15;40(2):145–148. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. Mechanisms of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2203–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Smith P. J. Ataxia telangiectasia: an inherited human disorder involving hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation and related DNA-damaging chemicals. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:291–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Lee A. E., Dickson C. Concerted activation of two potential proto-oncogenes in carcinomas induced by mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):628–631. doi: 10.1038/320628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. M., German J. Bloom's syndrome and Fanconi's anemia: demonstration of two distinctive patterns of chromosome disruption and rearrangement. Humangenetik. 1974;25(4):299–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00336905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch T. G., Arnstein P., Manohar V., Leiserson W. M., Chused T. M. Proliferation of infected lymphoid precursors before Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Jan;74(1):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Lohse M. A., Szpirer C., Szpirer J., Levan G. Cellular DNA regions involved in the induction of rat thymic lymphomas (Mlvi-1, Mlvi-2, Mlvi-3, and c-myc) represent independent loci as determined by their chromosomal map location in the rat. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):938–942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.938-942.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Hu L. F. A common region for proviral DNA integration in MoMuLV-induced rat thymic lymphomas. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):445–449. doi: 10.1038/302445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsichlis P. N., Strauss P. G., Lohse M. A. Concerted DNA rearrangements in Moloney murine leukemia virus-induced thymomas: a potential synergistic relationship in oncogenesis. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.258-267.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Human T-lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):395–403. doi: 10.1038/317395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashina K., Heppner G. H. Correlation of frequency of induced mutation and metastatic potential in tumor cell lines from a single mouse mammary tumor. Cancer Res. 1985 Sep;45(9):4015–4019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Intracellular surveillance of persisting viral infections. Human genital cancer results from deficient cellular control of papillomavirus gene expression. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):489–491. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]