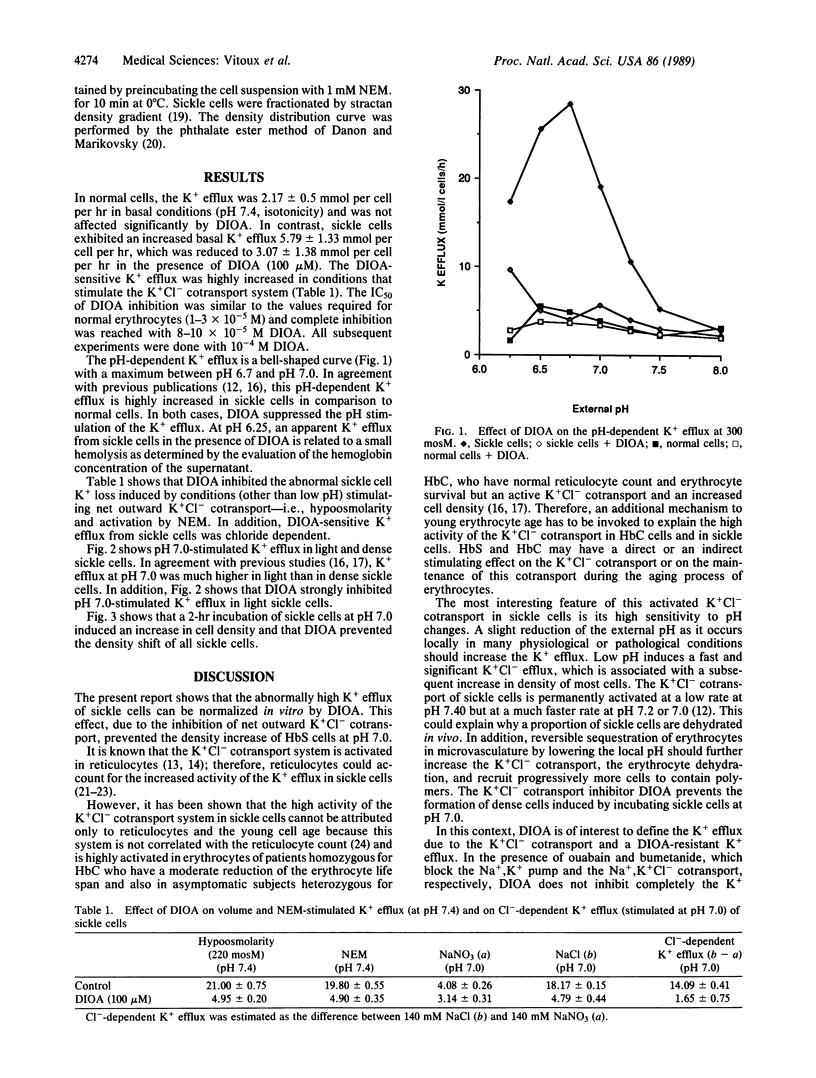
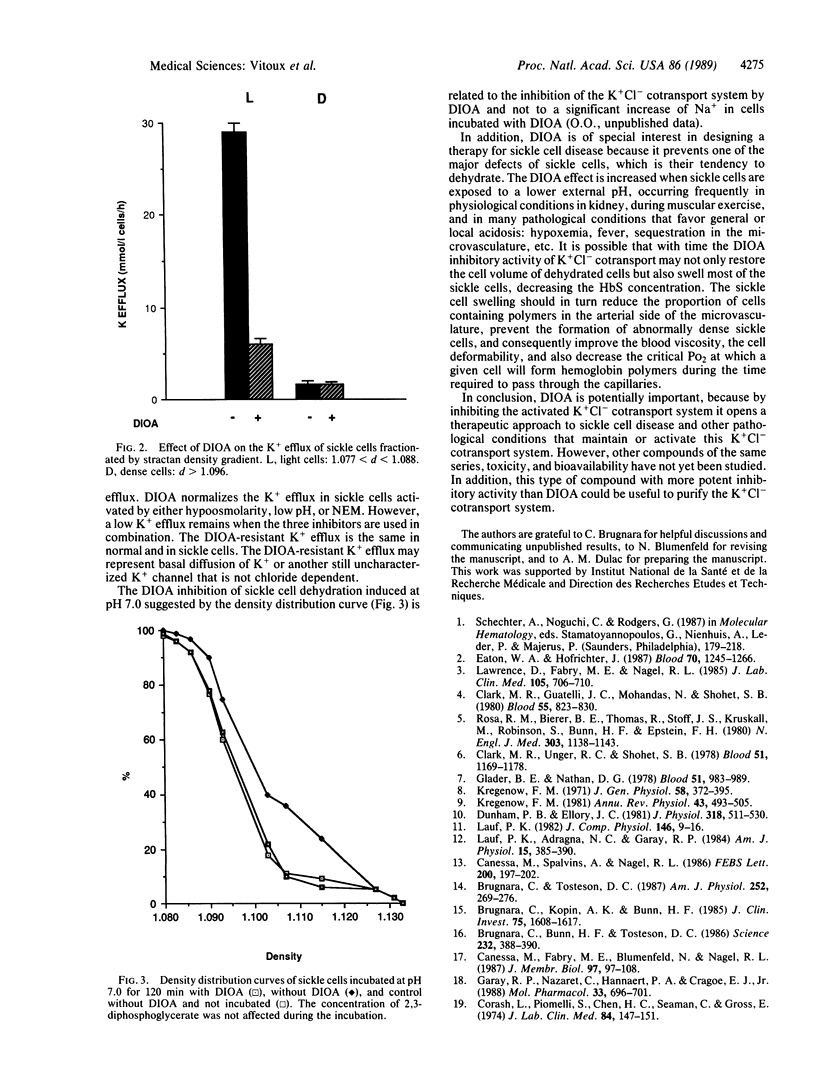
Abstract
[(Dihydroindenyl)oxy]alkanoic acid (DIOA) was recently introduced as a potent inhibitor of the K+Cl- cotransport system without side effects on other cation transport systems [Garay, R. P., Nazaret, C., Hannaert, P.A. & Cragoe, E. J., Jr. (1988) Mol. Pharmacol. 33, 696-701]. In sickle cells, an abnormal activation of this K+Cl- cotransport system was proposed to be involved in cell K+ loss and dehydration. We found that DIOA inhibited the abnormal sickle cell K+ loss and specifically reduced sickle cell density upon stimulation of the net outward K+Cl- cotransport--i.e., low pH, hypoosmolarity, and activation by N-ethylmaleimide. DIOA opens another therapeutic approach to sickle cell disease by inhibiting cell dehydration, which favors HbS polymerization and reduces erythrocyte deformability.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brugnara C., Bunn H. F., Tosteson D. C. Regulation of erythrocyte cation and water content in sickle cell anemia. Science. 1986 Apr 18;232(4748):388–390. doi: 10.1126/science.3961486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugnara C., Kopin A. S., Bunn H. F., Tosteson D. C. Regulation of cation content and cell volume in hemoglobin erythrocytes from patients with homozygous hemoglobin C disease. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1608–1617. doi: 10.1172/JCI111867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa M., Fabry M. E., Blumenfeld N., Nagel R. L. Volume-stimulated, Cl(-)-dependent K+ efflux is highly expressed in young human red cells containing normal hemoglobin or HbS. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(2):97–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01869416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa M., Spalvins A., Nagel R. L. Volume-dependent and NEM-stimulated K+,Cl- transport is elevated in oxygenated SS, SC and CC human red cells. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 5;200(1):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80538-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Guatelli J. C., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Influence of red cell water content on the morphology of sickling. Blood. 1980 May;55(5):823–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Unger R. C., Shohet S. B. Monovalent cation composition and ATP and lipid content of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 Jun;51(6):1169–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corash L. M., Piomelli S., Chen H. C., Seaman C., Gross E. Separation of erythrocytes according to age on a simplified density gradient. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Jul;84(1):147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANON D., MARIKOVSKY V. DETERMINATION OF DENSITY DISTRIBUTION OF RED CELL POPULATION. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Oct;64:668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Ellory J. C. Passive potassium transport in low potassium sheep red cells: dependence upon cell volume and chloride. J Physiol. 1981 Sep;318:511–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton W. A., Hofrichter J. Hemoglobin S gelation and sickle cell disease. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1245–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garay R. P., Nazaret C., Hannaert P. A., Cragoe E. J., Jr Demonstration of a [K+,Cl-]-cotransport system in human red cells by its sensitivity to [(dihydroindenyl)oxy]alkanoic acids: regulation of cell swelling and distinction from the bumetanide-sensitive [Na+,K+,Cl-]-cotransport system. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):696–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glader B. E., Nathan D. G. Cation permeability alterations during sickling: relationship to cation composition and cellular hydration of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. C., Ellory J. C. Evidence for the presence of volume-sensitive KCl transport in 'young' human red cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 26;858(2):317–320. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kregenow F. M. Osmoregulatory salt transporting mechanisms: control of cell volume in anisotonic media. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:493–505. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kregenow F. M. The response of duck erythrocytes to nonhemolytic hypotonic media. Evidence for a volume-controlling mechanism. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Oct;58(4):372–395. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.4.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence C., Fabry M. E., Nagel R. L. Red cell distribution width parallels dense red cell disappearance during painful crises in sickle cell anemia. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Jun;105(6):706–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa R. M., Bierer B. E., Thomas R., Stoff J. S., Kruskall M., Robinson S., Bunn H. F., Epstein F. H. A study of induced hyponatremia in the prevention and treatment of sickle-cell crisis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Nov 13;303(20):1138–1143. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198011133032002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



