Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting the elderly population. Mechanistically, the major cause of the disease bases on the altered processing of the amyloid-β (Aβ) precursor protein (APP), resulting in the accumulation and aggregation of neurotoxic forms of Aβ. Aβ derives from the sequential proteolytic cleavage of the β- and γ-secretases on APP. The causes of Aβ accumulation in the common sporadic form of AD are not completely known, but they are likely to include oxidative stress (OS). OS and Aβ are linked to each other since Aβ aggregation induces OS in vivo and in vitro, and oxidant agents increase the production of Aβ. Moreover, OS produces several effects that may contribute to synaptic function and cell death in AD. We and others have shown that the expression and activity of β-secretase (named BACE1; β-site APP cleaving enzyme) is increased by oxidant agents and by lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal and that there is a significant correlation between BACE1 activity and oxidative markers in sporadic AD. OS results from several cellular insults such as aging, hyperglycemia, hypoxic insults that are all well known risk factors for AD development. Thus, our data strengthen the hypothesis that OS is a basic common pathway of Aβ accumulation, common to different AD risk factors.
Keywords: oxidative stress, Alzheimer's disease, BACE1, Alzheimer's risk factors, aging, hypoxia, hyperglycemia
Introduction
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is one of the most common age-related disorders (Bachman et al., 1993). AD is classified into two forms: sporadic AD, which is correlated to aging, and a rare familial early-onset AD (FAD), caused by gene mutations.
The pathological hallmarks of the disease are intraneuronal neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein and deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) fibrils in the extracellular space. Central to the disease is the altered proteolytic processing of the Aβ precursor protein (APP), resulting in overproduction and aggregation of neurotoxic forms of Aβ. APP is an integral membrane protein with a single, membrane spanning domain, a large, extracellular, N-terminus, and a shorter, cytoplasmic C-terminus. The amyloidogenic processing of APP involves two sequential cleavages operated by the β- and γ-secretases at the N- and C-termini of Aβ respectively. The β-secretase (BACE1) cleaves APP at the beginning of the sequence of Aβ, generating an extracellular soluble fragment, called sβAPP, and an intracellular C-terminal end, termed C99. C99 is further cleaved, within the membrane, by the γ-secretase. The γ-cleavage produces Aβ fragments of different length, these being predominantly Aβ 40 and Aβ 42.
The central role of Aβ in the pathogenesis of AD is supported by two major clues. Aggregates of Aβ are neurotoxic and initiate a series of events, including the hyperphosphorylation of tau, which results in neuronal dysfunction and cell death (Yankner, 1996). All genes bearing mutations that cause FAD, APP and presenilins (PS) 1 and 2, facilitate the accumulation of Aβ 42, increasing its production and aggregation (Citron et al., 1992, 1997; Lemere et al., 1996). The cause of modified APP processing and Aβ 42 accumulation in sporadic cases of AD is unclear, but is likely to include oxidative stress (OS).
OS and Aβ are linked each other because Aβ induces OS in vivo and in vitro (Hensley et al., 1994; Mark et al., 1997; Murakami et al., 2005; Tabner et al., 2005), and OS increases the production of Aβ (Paola et al., 2000; Tamagno et al., 2002; Tong et al., 2005).
OS increases is believed to be an early event in AD pathology (Nunomura et al., 2001; Cutler et al., 2004) as it contributes to membrane damage, cytoskeleton alterations and cell death (Perry et al., 2000).
Thus, the identification of a large number of oxidatively modified proteins in common AD and AD animal models (Sultana et al., 2009) suggests that OS plays an important role in AD pathogenesis.
Moreover, extensive oxidative damage observed in “mild cognitive impairment” (MCI) brain regions (Lovell and Markesbery, 2001) suggest that OS may be an early event in progression from normal aging to AD pathology. Based on these notions, it seems likely that increased production of oxygen free radicals (reactive oxygen species, ROS) may act as important mediators of synaptic loss and eventually promote neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques formation (Kern and Behl, 2009).
Our studies, as described below, strengthen the hypothesis that OS may be a basic common pathway of Aβ accumulation and toxicity, which is in turn common to most AD risk factors (Zhu et al., 2004).
Aβ and Oxidative Stress
Growing attention has been focused on oxidative mechanisms of Aβ toxicity as well as the search for novel neuroprotective agents. The ability of toxic Aβ peptides to induce protein oxidation and to inhibit the activity of oxidation-sensitive enzymes is consistent with the hypothesis that Aβ can induce severe oxidative damage.
Transition metals, Cu(II), Zn(II) and Fe(III) favor the neurotoxicity of Aβ, through their reduction, that yields hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (Huang et al., 1999). Using density functional theory calculations, it has been shown that Aβ residue Tyr-10 is a pivotal residue in driving the catalytic production of H2O2 in the presence of Cu(II). It has been found that the phenoxy radical of Aβ Tyr-10 produced by the reaction with ROS causes neurotoxicity and results in the formation of dityrosines which, in turn, accelerate the aggregation of Aβ peptides (Barnham et al., 2004). Another crucial Aβ residue is Met-35; the substitution of Met-35 with cysteine resulted in no protein oxidation in C. elegans model (Yatin et al., 1999). Moreover, it has been suggested that inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase by Aβ 42 could involve the formation of a redox active methionine radical (Crouch et al., 2006). Lipid peroxidation induced by Aβ peptides impairs the function of ion-motive ATPases, glucose and glutamate transporters and of GTP-binding proteins, as the result of their covalent modification by aldehydic end products such as 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) (Mattson, 1997). Moreover, toxic forms of aggregated Aβ peptides favor Ca2+ influx into neurons by inducing membrane-associated OS, rendering neurons vulnerable to excitotoxicity and apoptosis (Bezprozvanny and Mattson, 2008). Aβ is able to create oxidative modifications of proteins involved in cellular defense mechanisms against noxious stimuli and in proteins involved in energy pathways. In a murine knock-in model of AD, entailing APP and PS1 mutations, a direct correlation was demonstrated between the excessive production of Aβ species and the impairment of antioxidant enzymes, with consequent mitochondrial dysfunction (Anantharaman et al., 2006). These are further demonstrations of how increased OS caused by Aβ can lead to increased oxidative modification of proteins and lipids, leading to impaired cellular function and cell death, and consequently to cognitive impairment and AD-like pathology (Sultana et al., 2009).
It is still controversial whether the most deleterious form of Aβ peptide in the early stage of AD is represented by the fibrillar or the soluble oligomeric peptide form (Drouet et al., 2000). Recent literature data suggest that small soluble aggregates of Aβ, including protofibrils and oligomers, may be more toxic than Aβ fibrils (Gong et al., 2003; Kayed et al., 2003; Resende et al., 2008; Picone et al., 2009). These data may help explain, for example, why neurodegeneration and specific spatial learning deficits may occur in AD animal models before the appearance of amyloid plaques (Chui et al., 1999; Koistinaho et al., 2001).
On the other hand OS may be also the cause of Aβ accumulation. Oxidant agents and oxidative products increase APP expression (Cheng and Trombetta, 2004; Patil et al., 2006) and intracellular and secreted Aβ levels in neuronal and non neuronal cells like astrocytes (Frederikse et al., 1996; Misonou et al., 2000; Atwood et al., 2003; Murray et al., 2007). We and others have shown that the expression and activity of BACE1 is increased by oxidants (Tamagno et al., 2002, 2003, 2005; Kao et al., 2004; Tong et al., 2005). Moreover, there is a significant correlation of BACE1 activity with oxidative markers in sporadic AD brain tissue (Borghi et al., 2007), in which a significant increase of BACE1 expression has been shown (Fukumoto et al., 2002; Holsinger et al., 2002; Yang et al., 2003).
We have proposed that a sequence of events link OS, BACE1 induction and apoptotic cell death through an overproduction of Aβ. Initially we have shown that oxidant agents and HNE significantly increase the expression, protein levels and activity of BACE1 in NT2 neurons, without affecting the levels of APP (Tamagno et al., 2002, 2003). These events are followed by an overproduction of Aβ peptides as well as by morphological signs of apoptotic cell death (Tamagno et al., 2005).
Then, we have found that OS increases the γ-secretase activity in cultured cells and in vivo, and that the increased expression of BACE1 induced by OS is regulated by the γ-secretase (Tamagno et al., 2008). These results have major implications for the pathogenesis of sporadic AD. First, they suggest that OS, as effect of aging, can increase the expression of both presenilin 1 (PS1) and BACE1, thereby enhancing Aβ production. OS is the only known factor able to augment the γ-secretase cleavage by increasing the expression of PS1, the catalytic subunit of the endoprotease.
Secondly, our data reveal the existence of a positive feedback loop in which increased γ-secretase activity results in up-regulation of BACE1 expression.
Recently, Minopoli et al. (2007) demonstrated a correlation between the induction of OS and the increase of γ-secretase cleavage on APP. Given that OS can mediate both γ-secretase and BACE1 activities, we suggest that OS is the molecular link between β- and γ-secretase and that, as a consequence, the activities of the two endoproteases are also linked.
Our findings suggested a sequence of pathological events that could contribute to the pathogenesis of the common, sporadic, late onset form of AD. In this review we will examine the role of OS in three of major risk factors for AD, such as aging, hypoxic insults (stroke) and hyperglycemia (diabetes mellitus). Our hypothesis is that OS could be considered a basic common pathway for Aβ accumulation induced by different AD risk factor.
Oxidative Stress in AD and Aging
The major non-genetic risk factor for development of late-onset sporadic AD is aging but the pathological circumstances causing it are still under debate.
OS increases with age through variations in ROS generation, ROS elimination or both (Barja, 2004). The free radical hypothesis of aging implies that accumulation of ROS results in damage of the major cell components: nucleus, mitochondrial DNA, membranes and cytoplasmic proteins (Harman, 1992). It has been proposed that mitochondria play a central role in this process because they are the primary site of ROS formation.
Oxidative damage impairs the cellular antioxidant defense causing a vicious cycle. Recently, the central role of OS in aging was further confirmed by showing that the depletion of mitochondrial cysteine is directly correlated with life span in aerobic organisms (Moosmann and Behl, 2008).
The brain is particularly vulnerable to OS because of its high consumption of oxygen, high levels of polyunsaturated fatty acids, and relatively low levels of antioxidants (Floyd and Hensley, 2002; Mattson et al., 2002). Accumulation of oxidative damage in the brain is particularly deleterious since it is a post-mitotic tissue with neurons exhibiting only a weak self-renewal potential due to their low proliferative capacity. An increased oxidative burden has been observed in the brain of non-demented elderly and of sporadic AD patients (Behl and Moosmann, 2002; Moosmann and Behl, 2002). Membrane lipids are commonly attacked by ROS and peroxidation of lipids is the most frequently analyzed oxidative marker that is increased during aging (Zhu et al., 2006).
The oxidative modification of fatty acids leads to a structural damage membranes and to the generation of several aldehydic end products, such as HNE, which have a high oxidative potential themselves and can severely impair cellular function (Keller and Mattson, 1998). Post mortem analysis of the brains of AD patients found increased levels of lipid peroxidation in brain regions that are affected by an early neurodegeneration (Mielke and Lyketsos, 2006).
Several studies have shown that protein oxidation also increases exponentially with brain aging (Abd El Mohsen et al., 2005) and is associated with a decreased capacity of the antioxidative defense machinery (Rodrigues Siqueira et al., 2005). Importantly, also levels of oxidized proteins correlate with cognitive performance and AD patients exhibit increased levels of protein carbonylation, a key marker for protein oxidation (Keller et al., 2005).
Another well known age-dependent modification is the oxidative damage of DNA. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA cause a respiratory chain dysfunction, which can increase cellular OS. It is well established that mitochondrial mutations accumulate during brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases (Corral-Debrinski et al., 1992; Wang et al., 2005).
Moreover, the extensive oxidative damage observed in “MCI” brain regions, considered a transition stage between normal aging and dementia, suggests that OS may be an early event in progression from normal aging to AD pathology (Sultana et al., 2009; Padurariu et al., 2010).
It has been shown that in MCI patients, plasma levels of non-enzymatic antioxidants and activity of antioxidant enzymes appeared to be decreased when compared to those of controls (Guidi et al., 2006; Sultana et al., 2008), moreover, levels of oxidative markers were showed increased (Lovell and Markesbery, 2001; Williams et al., 2006; Cenini et al., 2008). Based on OS and histopathological similarities, studies of MCI may provide clues about AD pathogenesis and progression, as well as about the development of therapeutics to treat or delay this disorder.
In summary, the oxidative burden observed in healthy brain aging and in early stages of Dementia, confirms that the accumulation of oxidatively modified biomolecules is a general hallmark of brain aging and could be an early event in the progression of MCI to AD.
Oxidative Stress in AD and Hypoxia
It is known that patients with stroke and cerebral infarction are at risk of AD (Rocchi et al., 2009). Hypoxia is a direct consequence of hypoperfusion, which plays a role in the Aβ accumulation.
Oxygen homeostasis is essential for the development and functioning of an organism. Prolonged and severe hypoxia can cause neuronal loss and memory impairment (Koistinaho and Koistinaho, 2005). Recent studies have shown that a history of stroke can increase AD prevalence by approximately twofold in elderly patients (Schneider et al., 2003; Vermeer et al., 2003). The risk is higher when stroke is concomitant with atherosclerotic vascular risk factor (Jellinger, 2002). Recently, it has been proposed that hypoxia can alter APP processing, increasing the activity of the β- and the γ-secretases. Sun et al., (2006) showed that hypoxia significantly up-regulates BACE1 gene expression, resulting in increased β-secretase activity. Moreover, the same Authors found that hypoxia increases Aβ deposition and neuritic plaque formation, as well as memory deficits, providing a molecular mechanistic link of vascular factors with AD. More recently, sequence analysis and gel shift assays revealed binding of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF)-1α, a molecule that regulates oxygen homeostasis (Sharp and Bernaudin, 2004), to the BACE1 promoter. It has been demonstrated that overexpression of HIF-1α in neuronal cells increases BACE1 mRNA and protein levels (Zhang et al., 2007). Hypoxia was also found to increase γ-secretase activity: HIF-1α binds to the promoter of anterior pharynx-defective phenotype (APH-1), a key component of the γ-secretase complex, to up-regulate its expression (Wang et al., 2006; Li et al., 2009).
Collectively these data show that hypoxia increases the β- and the γ-secretase activities, which facilitate the abnormal cleavage of APP, resulting in the acceleration of Aβ production and plaque formation both in vivo and in vitro.
Although it is generally accepted that intracellular ROS levels change during hypoxia, the direction in which this change occurs is still debated. Levels of intracellular ROS increase under hypoxia (Chandel et al., 1998; Dirmeier et al., 2002; Guzy et al., 2005). Chandel et al. (1998) suggested that mitochondria are the source of ROS involved in the hypoxic response. The electron transport chain, which is embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondria, consists of five multiprotein complexes. Complexes I and II oxidize the energy-rich molecules NADH and FADH2, respectively, and transfer the resulting electrons across the inner mitochondrial membrane to cytochrome c, which carries them to complex IV. Complex IV uses the electrons to reduce oxygen to water. Along with carrying electrons, complexes I, II and III generate ROS (Turrens, 2003; Klimova and Chandel, 2008). It is now accepted that hypoxia increases ROS via the mitochondrial transport chain and specifically by the function of complex III (Bell et al., 2007).
The mitochondria-derived ROS are both necessary and sufficient to stabilize and activate HIF-1α. It has been demonstrated that antioxidants reverse hypoxia-induced HIF-1α activation (Hwang et al., 2008). Recent anti-tumorigenic effects of antioxidants have been attributed to the inhibition of HIF-1α-dependent events (Gao et al., 2007). Moreover, the addition of oxidants, such as hydrogen peroxide, induces HIF-1α activity up-regulation in normoxia (Pagé et al., 2008).
We recently showed, both in vivo and in vitro, that hypoxia up-regulates BACE1 expression in a biphasic manner, through two distinct mechanisms: (1) an early release of ROS from mitochondria and (2) a late activation of HIF-1α (Guglielmotto et al., 2009). The data suggests that the early post-hypoxic up-regulation of BACE1 depends on the generation of ROS mediated by sudden interruption of the mitochondrial electron transport chain. The involvement of ROS released by mitochondria was confirmed by complete protection exerted by compounds, such as rotenone and diphenyl-phenylen iodonium, that affect complex I of the mitochondrial electron transport chain (Li and Trush, 1998; Höglinger et al., 2005). This early post-hypoxic up-regulation of BACE1 recapitulates the cascade of events induced by oxidant agents and HNE both in vivo and in vitro (Tamagno et al., 2002, 2005, 2008).
Oxidative Stress in AD and Hyperglycemia
Diabetes mellitus, a complex metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia, is a risk factor for AD, and multiple mechanisms connecting the two diseases have been proposed (Granic et al., 2009; Jones et al., 2009; Kojro and Postina, 2009).
Hyperglycemia enhances the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), senescent protein derivatives that result from the auto-oxidation of glucose and fructose (Bucala and Cerami, 1992). Thus, reducing sugars, such as fructose, glucose and glyceraldehyde are known to react non-enzymatically with the amino groups of proteins to form irreversible Schiff bases and then Amadori products (Takeuchi and Makita, 2001). The early glycation products undergo further complex reactions such as rearrangement, dehydration, and condensation to become irreversibly cross-linked, heterogeneous fluorescent derivatives termed AGEs (Brownlee et al., 1988).
Accumulation of AGEs in various tissues is known to occur in normal aging, and, at an extremely accelerated rate, in diabetes mellitus and renal failure (Jerums et al., 2003; Ahmed and Thornalley, 2007; Goh and Cooper, 2008). AGEs have been detected in vascular walls, lipoproteins and lipid constituents where they lead to macro and microangiopathy and amyloidosis (Schmidt et al., 1999; Gasser and Forbes, 2008).
The involvement of AGEs in brain aging and in AD was reported more than 10 years ago, in studies showing that the microtubule associated protein tau and Aβ, were substrates for glycation (Ledesma et al., 1994; Smith et al., 1994; Vitek et al., 1994; Yan et al., 1994, 1995). Tau is preferentially glycated at its tubulin-binding site, suggesting that glycation may be one of the modifications able to hamper this interaction (Ledesma et al., 1994). Increased extracellular AGEs formation was demonstrated in amyloid plaques in different cortical areas (Kimura et al., 1995), were they may have a role in accelerating the conversion of Aβ from monomers to oligomers or higher molecular weight forms (Loske et al., 2000).
Besides post-translational protein modifications, AGEs have other pathologic effects, at the cellular and molecular levels. Among these are the production of ROS, particularly superoxide and hydrogen peroxide (Carubelli et al., 1995; Ortwerth et al., 1998; Muscat et al., 2007). Indeed, glycated proteins increase the rate of free radical production compared to the native proteins (Neeper et al., 1992).
Another mechanism through which AGEs mediate the production of OS is the interaction with RAGE, which is a multiligand receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily of cell surface molecules (Neeper et al., 1992; Schmidt et al., 1992; Qin et al., 2008).
RAGE is up-regulated in an age-dependent fashion in human tissue (Simm et al., 2004), and increased AGE-RAGE interaction causes OS which it believed to be relevant in the pathogenesis of many age-related diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and AD (Heine and Dekker, 2002; Zlokovic, 2008).
The role of RAGE in the pathogenesis of AD has been extensively studied, since it also binds Aβ (Yan et al., 1996), increasing its influx into the brain through the blood-brain barrier (Arancio et al., 2004; Takuma et al., 2009).
The role of RAGE in Aβ-mediated toxicity was assessed by in recent study performed using a murine transgenic model, with targeted neuronal overexpression of RAGE and mutant APP (Arancio et al., 2004). These mice displayed early abnormalities in spatial learning/memory, accompanied by altered activation of markers of synaptic plasticity, and exacerbated neuropathological findings, indicating that RAGE is an important co-factor for Aβ-induced neuronal perturbation.
Moreover, pre-treatment of cultured neurons from wild type mice with neutralizing antibody to RAGE determined decreased up-take of Aβ and protection from Aβ-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction (Takuma et al., 2009). Similar results are seen in RAGE knock-out neurons.
Very recently, a role of RAGE in the up-regulation of BACE1, the rate limiting enzyme of Aβ production, was reported in an AD animal model (Cho et al., 2009). BACE1 up-regulation was reported in cells over-expressing RAGE and in RAGE-injected brains of Tg2576 mice, harboring a human APP transgene with the Swedish mutation (Cho et al., 2009).
Conclusions
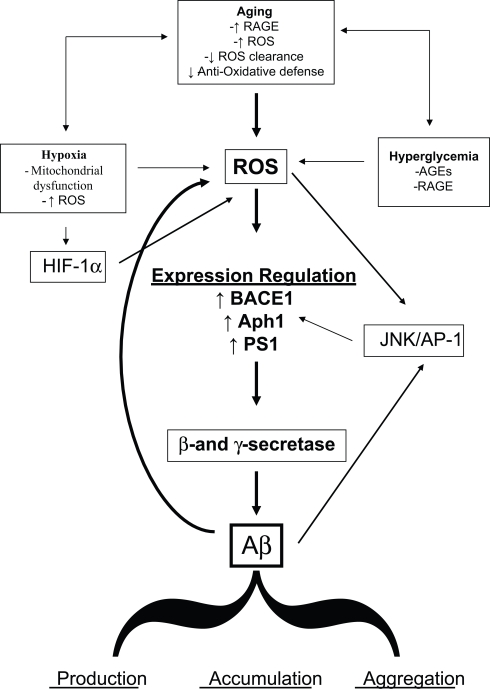
It is expected that, taken into account the increase in life expectancy, the population will continuously age in the next years and virtually everybody has a high probability to become demented. Although this correlation is obvious, the molecular details of the link between aging and cognitive decline are not fully understood. The data here reviewed strongly supported the hypothesis that OS could be a basic common pathway of Aβ accumulation, as determined by different age-related risk factors (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Diagram sketching upstream mediators and downstream consequences of oxidative stress in sporadic AD.
The links between aging and the development of subtle but continuous cellular changes, such as protein, nucleic acids and lipid oxidation have been known for years, and are ever so clear today. It is also evident how such changes have the potential to further undermine the cellular self defense strategies. In the case of AD, these events translate into different mechanisms that lead to impaired clearance, increased accumulation and aggregation of Aβ, and a series of molecular signals that lead to the up-regulation of the enzymes that process APP to generate Aβ itself. In this view, if enough time is allowed for such events to take place, AD pathology and dementia will eventually develop in every brain. The need to understand and control amyloid production and accumulation is ever so necessary now, as the world population is aging at a fast pace.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by Italian Ministry of Health and Regione Piemonte (Elena Tamagno), CARIGE and Telethon Foundation (Massimo Tabaton).
References
- Abd El Mohsen M. M., Iravani M. M., Spencer J. P., Rose S., Fahim A. T., Motawi T. M., Ismail N. A., Jenner P. (2005). Age-associated changes in protein oxidation and proteasome activities in rat brain: modulation by antioxidants. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 336, 386–391 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.201 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed N., Thornalley P. J. (2007). Advanced glycation endproducts: what is their relevance to diabetic complications? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 9, 233–245 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2006.00595.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anantharaman M., Tangpong J., Keller J. N., Murphy M. P., Markesbery W. R., Kiningham K. K., St Clair D. K. (2006). Beta-amyloid mediated nitration of manganese superoxide dismutase: implication for oxidative stress in a APPNLH/NLH X PS-1P264L/P264L double knock-in mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 168, 1608–1618 10.2353/ajpath.2006.051223 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arancio O., Zhang H. P., Chen X., Lin C., Trinchese F., Puzzo D., Liu S., Hegde A., Yan S. F., Stern A., Luddy J. S., Lue L. F., Walker D. G., Roher A., Buttini M., Mucke L., Li W., Schmidt A. M., Kindy M., Hyslop P. A., Stern D. M., Du Yan S. S. (2004). RAGE potentiates Abeta-induced perturbation of neuronal function in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 23, 4096–4105 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600415 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atwood C. S., Obrenovich M. E., Liu T., Chan H., Perry G., Smith M. A., Martins R. N. (2003). Amyloid-beta: a chameleon walking in two worlds: a review of the trophic and toxic properties of amyloid-beta. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 43, 1–16 10.1016/S0165-0173(03)00174-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachman D. L., Wolf P. A., Linn R. T., Knoefel J. E., Cobb J. L., Belanger A. J., White L. R., D'Agostino R. B. (1993). Incidence of dementia and probable Alzheimer's disease in a general population: the Framingham Study. Neurology 43, 515–519 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barja G. (2004). Free radicals and aging. Trends Neurosci. 27, 595–600 10.1016/j.tins.2004.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnham K. J., Haeffner F., Ciccotosto G. D., Curtain C. C., Tew D., Mavros C., Beyreuther K., Carrington D., Masters C. L., Cherny R. A., Cappai R., Bush A. I. (2004). Tyrosine gated electron transfer is key to the toxic mechanism of Alzheimer's disease beta-amyloid. FASEB J. 18, 1427–1429 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behl C., Moosmann B. (2002). Antioxidant neuroprotection in Alzheimer's disease as preventive and therapeutic approach. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33, 182–191 10.1016/S0891-5849(02)00883-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. L., Klimova T. A., Eisenbart J., Moraes C. T., Murphy M. P., Budinger G. R., Chandel N. S. (2007). The Qo site of the mitochondrial complex III is required for the transduction of hypoxic signaling via reactive oxygen species production. J. Cell Biol. 177, 1029–1036 10.1083/jcb.200609074 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Mattson M. P. (2008). Neuronal calcium mishandling and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Trends Neurosci. 31, 454–463 10.1016/j.tins.2008.06.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borghi R., Patriarca S., Traverso N., Piccini A., Storace D., Garuti A., Cirmena G, Odetti P., Tabaton M. (2007). The increased activity of BACE1 correlates with oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 28, 1009–1014 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. (1988). Advanced products of nonenzymatic glycosylation and the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular disease. Diabetes Metab. Rev. 4, 437–451 10.1002/dmr.5610040503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Cerami A. (1992). Advanced glycosylation: chemistry, biology, and implications for diabetes and aging. Adv. Pharmacol. 23, 1–34 10.1016/S1054-3589(08)60961-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carubelli R., Schneider J. E., Jr., Pye Q. N., Floyd R. A. (1995). Cytotoxic effects of autoxidative glycation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 18, 265–269 10.1016/0891-5849(94)E0134-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cenini G., Sultana R., Memo M., Butterfield D. A. (2008). Elevated levels of pro-apoptotic p53 and its oxidative modification by the lipid peroxidation product, HNE, in brain from subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 12, 987–994 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00163.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandel N. S., Maltepe E., Goldwasser E., Mathieu C. E., Simon M. C., Schumacker P. T. (1998). Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 11715–11720 10.1073/pnas.95.20.11715 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. Y., Trombetta L. D. (2004). The induction of amyloid precursor protein and alpha-synuclein in rat hippocampal astrocytes by diethyldithiocarbamate and copper with or without glutathione. Toxicol. Lett. 146, 139–149 10.1016/j.toxlet.2003.09.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J., Son S. M., Jin S. M., Hong H. S., Shin D. H, Kim S. J, Huh K., Mook-Jung I. (2009). RAGE regulates BACE1 and Abeta generation via NFAT1 activation in Alzheimer's disease animal model. FASEB J. 23, 2639–2649 10.1096/fj.08-126383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chui D. H., Tanahashi H., Ozawa K., Ikeda S., Checler F., Ueda O., Suzuki H., Araki W., Inoue H., Shirotani K., Takahashi K., Gallyas F., Tabira T. (1999). Transgenic mice with Alzheimer presenilin 1 mutations show accelerated neurodegeneration without amyloid plaque formation. Nat. Med. 5, 560–564 10.1038/8438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Oltersdorf T., Haass C., McConlogue L., Hung A. Y., Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Lieberburg I., Selkoe D. J. (1992). Mutation of the beta-amyloid precursor protein in familial Alzheimer's disease increases beta-protein production. Nature 360, 672–674 10.1038/360672a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citron M., Westaway D., Xia W., Carlson G., Diehl T., Levesque G., Johnson-Wood K., Lee M., Seubert P., Davis A., Kholodenko D., Motter R., Sherrington R., Perry B., Yao H., Strome R., Lieberburg I., Rommens J., Kim S., Schenk D., Fraser P., St George Hyslop P., Selkoe D. J. (1997). Mutant presenilins of Alzheimer's disease increase production of 42-residue amyloid beta-protein in both transfected cells and transgenic mice. Nat. Med. 3, 67–72 10.1038/nm0197-67 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corral-Debrinski M., Horton T., Lott M. T., Shoffner J. M., Beal M. F., Wallace D. C. (1992). Mitochondrial DNA deletions in human brain: regional variability and increase with advanced age. Nat. Genet. 2, 324–329 10.1038/ng1292-324 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch P. J., Barnham K. J., Duce J. A., Blake R. E., Masters C. L., Trounce I. A. (2006). Copper-dependent inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase by Abeta(1-42) requires reduced methionine at residue 35 of the Abeta peptide. J. Neurochem. 99, 226–236 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04050.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler R. G., Kelly J., Storie K., Pedersen W. A., Tammara A., Hatanpaa K., Troncoso J. C., Mattson M. P. (2004). Involvement of oxidative stress-induced abnormalities in ceramide and cholesterol metabolism in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 101, 2070–2075 10.1073/pnas.0305799101 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirmeier R., O'Brien K. M., Engle M., Dodd A., Spears E., Poyton R. O. (2002). Exposure of yeast cells to anoxia induces transient oxidative stress. Implications for the induction of hypoxic genes. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 34773–34784 10.1074/jbc.M203902200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouet B., Pinçon-Raymond M., Chambaz J., Pillot T. (2000). Molecular basis of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 57, 705–715 10.1007/s000180050035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R. A., Hensley K. (2002). Oxidative stress in brain aging. Implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Aging 23, 795–807 10.1016/S0197-4580(02)00019-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frederikse P. H., Garland D., Zigler J. S., Jr., Piatigorsky J. (1996). Oxidative stress increases production of beta-amyloid precursor protein and beta-amyloid (Abeta) in mammalian lenses, and Abeta has toxic effects on lens epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 10169–10174 10.1074/jbc.271.17.10169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Cheung B. S., Hyman B. T., Irizarry M. C. (2002). Beta-secretase protein and activity are increased in the neocortex in Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 59, 1381–1389 10.1001/archneur.59.9.1381 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao P., Zhang H., Dinavahi R., Li F., Xiang Y., Raman V., Bhujwalla Z. M., Felsher D. W., Cheng L., Pevsner J., Lee L. A., Semenza G. L., Dang C. V. (2007). HIF-dependent antitumorigenic effect of antioxidants in vivo. Cancer Cell 12, 230–238 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.08.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser A., Forbes J. M. (2008). Advanced glycation: implications in tissue damage and disease. Protein Pept. Lett. 15, 385–391 10.2174/092986608784246515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh S. Y., Cooper M. E. (2008). Clinical review: the role of advanced glycation end products in progression and complications of diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 1143–1152 10.1210/jc.2007-1817 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong Y., Chang L., Viola K. L., Lacor P. N., Lambert M. P., Finch C. E., Krafft G. A., Klein W. L. (2003). Alzheimer's disease-affected brain: presence of oligomeric A beta ligands (ADDLs) suggests a molecular basis for reversible memory loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 10417–10422 10.1073/pnas.1834302100 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granic I., Dolga A. M., Nijholt I. M., van Dijk G., Eisel U. L. (2009). Inflammation and NF-kappaB in Alzheimer's disease and diabetes. J. Alzheimers Dis. 16, 809–821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmotto M., Aragno M., Autelli R., Giliberto L., Novo E., Colombatto S., Danni O., Parola M., Smith M. A., Perry G., Tamagno E., Tabaton M. (2009). The up-regulation of BACE1 mediated by hypoxia and ischemic injury: role of oxidative stress and HIF1alpha. J. Neurochem. 108, 1045–1056 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05858.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidi I., Galimberti D., Lonati S., Novembrino C., Bamonti F., Tiriticco M., Fenoglio C., Venturelli E., Baron P., Bresolin N., Scarpini E. (2006). Oxidative imbalance in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 27, 262–269 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzy R. D., Hoyos B., Robin E., Chen H., Liu L., Mansfield K. D., Simon M. C., Hammerling U., Schumacker P. T. (2005). Mitochondrial complex III is required for hypoxia-induced ROS production and cellular oxygen sensing. Cell Metab. 1, 401–408 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.05.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harman D. (1992). Free radical theory of aging. Mutat. Res. 275, 257–266 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine R. J., Dekker J. M. (2002). Beyond postprandial hyperglycaemia: metabolic factors associated with cardiovascular disease. Diabetologia 45, 461–475 10.1007/s00125-001-0726-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensley K., Carney J. M., Mattson M. P., Aksenova M., Harris M, Wu J. F, Floyd R. A., Butterfield D. A. (1994). A model for beta-amyloid aggregation and neurotoxicity based on free radical generation by the peptide: relevance to Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 3270–3274 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3270 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglinger G. U., Lannuzel A., Khondiker M. E., Michel P. P., Duyckaerts C., Féger J., Champy P., Prigent A., Medja F., Lombes A., Oertel W. H., Ruberg M., Hirsch E. C. (2005). The mitochondrial complex I inhibitor rotenone triggers a cerebral tauopathy. J. Neurochem. 95, 930–939 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03493.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holsinger R. M., McLean C. A., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L., Evin G. (2002). Increased expression of the amyloid precursor beta-secretase in Alzheimer's disease. Ann. Neurol. 51, 783–786 10.1002/ana.10208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X., Cuajungco M. P., Atwood C. S., Hartshorn M. A., Tyndall J. D., Hanson G. R., Stokes K. C., Leopold M., Multhaup G., Goldstein L. E., Scarpa R. C., Saunders A. J., Lim J., Moir R. D., Glabe C., Bowden E. F., Masters C. L., Fairlie D. P., Tanzi R. E., Bush A. I. (1999). Cu(II) potentiation of Alzheimer abeta neurotoxicity. Correlation with cell-free hydrogen peroxide production and metal reduction. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 37111–37116 10.1074/jbc.274.52.37111 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang K. Y., Oh Y. T., Yoon H., Lee J., Kim H., Choe W., Kang I. (2008). Baicalein suppresses hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha protein accumulation and activation through inhibition of reactive oxygen species and PI 3-kinase/Akt pathway in BV2 murine microglial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 444, 264–269 10.1016/j.neulet.2008.08.057 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger K. A. (2002). The pathology of ischemic-vascular dementia: an update. J. Neurol. Sci. 203–204, 153–157 10.1016/S0022-510X(02)00282-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerums G., Panagiotopoulos S., Forbes J., Osicka T., Cooper M. (2003). Evolving concepts in advanced glycation, diabetic nephropathy, and diabetic vascular disease. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 419, 55–62 10.1016/j.abb.2003.08.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A., Kulozik P., Ostertag A., Herzig S. (2009). Common pathological processes and transcriptional pathways in Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes. J. Alzheimers Dis. 16, 787–808 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. C., Krichevsky A. M., Kosik K. S., Tsai L. H. (2004). BACE1 suppression by RNA interference in primary cortical neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 1942–1949 10.1074/jbc.M309219200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayed R., Head E., Thompson J. L., McIntire T. M., Milton S. C., Cotman C. W., Glabe C. G. (2003). Common structure of soluble amyloid oligomers implies common mechanism of pathogenesis. Science 300, 486–489 10.1126/science.1079469 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. N., Mattson M. P. (1998). Roles of lipid peroxidation in modulation of cellular signaling pathways, cell dysfunction, and death in the nervous system. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 105–116 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. N., Schmitt F. A., Scheff S. W., Ding Q., Chen Q., Butterfield D. A., Markesbery W. R. (2005). Evidence of increased oxidative damage in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 64, 1152–1156 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern A., Behl C. (2009). The unsolved relationship of brain aging and late-onset alzheimer disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1790, 1124–1132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Takamatsu J., Araki N., Goto M., Kondo A., Miyakawa T., Horiuchi S. (1995). Are advanced glycation end-products associated with amyloidosis in Alzheimer's disease? Neuroreport 6, 866–868 10.1097/00001756-199504190-00010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimova T., Chandel N. S. (2008). Mitochondrial complex III regulates hypoxic activation of HIF. Cell Death Differ. 15, 660–666 10.1038/sj.cdd.4402307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinaho M., Koistinaho J. (2005). Interactions between Alzheimer's disease and cerebral ischemia – focus on inflammation. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 48, 240–250 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.12.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koistinaho M., Ort M., Cimadevilla J. M., Vondrous R., Cordell B., Koistinaho J., Bures J., Higgins L. S. (2001). Specific spatial learning deficits become severe with age in beta-amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice that harbor diffuse beta-amyloid deposits but do not form plaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 98, 14675–14680 10.1073/pnas.261562998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojro E., Postina R. (2009). Regulated proteolysis of RAGE and AbetaPP as possible link between type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 16, 865–878 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledesma M. D., Bonay P., Colaço C., Avila J. (1994). Analysis of microtubule-associated protein tau glycation in paired helical filaments. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 21614–21619 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemere C. A., Lopera F., Kosik K. S., Lendon C. L., Ossa J., Saido T. C., Yamaguchi H., Ruiz A., Martinez A., Madrigal L., Hincapie L., Arango J. C., Anthony D. C., Koo E. H., Goate A. M., Selkoe D. J., Arango J. C. (1996). The E280A presenilin 1 Alzheimer mutation produces increased A beta 42 deposition and severe cerebellar pathology. Nat. Med. 2, 1146–1150 10.1038/nm1096-1146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Zhang X., Yang D., Luo G., Chen S., Le W. (2009). Hypoxia increases Abeta generation by altering beta- and gamma-cleavage of APP. Neurobiol. Aging 30, 1091–1098 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.10.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Trush M. A. (1998). Diphenyleneiodonium, an NAD(P)H oxidase inhibitor, also potently inhibits mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253, 295–299 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9729 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loske C., Gerdemann A., Schepl W., Wycislo M., Schinzel R., Palm D., Riederer P., Münch G. (2000). Transition metal-mediated glycoxidation accelerates cross-linking of beta-amyloid peptide. Eur. J. Biochem. 267, 4171–4178 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01452.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovell M. A., Markesbery W. R. (2001). Ratio of 8-hydroxyguanine in intact DNA to free 8-hydroxyguanine is increased in Alzheimer disease ventricular cerebrospinal fluid. Arch. Neurol. 58, 392–396 10.1001/archneur.58.3.392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark R. J., Lovell M. A., Markesbery W. R., Uchida K., Mattson M. P. (1997). A role for 4 hydroxynonenal, an aldehydic product of lipid peroxidation, in disruption of ion homeostasis and neuronal death induced by amyloid beta-peptide. J. Neurochem. 68, 255–264 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P. (1997). Cellular actions of beta-amyloid precursor protein, and its soluble, and fibrillogenic derivatives. Physiol. Rev. 77, 1081–1132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P., Chan S. L., Duan W. (2002). Modification of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders by genes, diet, and behavior. Physiol. Rev. 82, 637–672 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mielke M. M., Lyketsos C. G. (2006). Lipids and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: is there a link? Int. Rev. Psychiatry 18, 173–186 10.1080/09540260600583007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minopoli G., Stante M., Napolitano F., Telese F., Aloia L., De Felice M., Di Lauro R., Pacelli R., Brunetti A., Zambrano N., Russo T. (2007). Essential roles for Fe65, Alzheimer amyloid precursor-binding protein, in the cellular response to DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 831–835 10.1074/jbc.C600276200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misonou H., Morishima-Kawashima M., Ihara Y. (2000). Oxidative stress induces intracellular accumulation of amyloid beta-protein(Abeta) in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochemistry 39, 6951–6959 10.1021/bi000169p [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moosmann B., Behl C. (2002). Antioxidants as treatment for neurodegenerative disorders. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 11, 1407–1435 10.1517/13543784.11.10.1407 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moosmann B., Behl C. (2008). Mitochondrially encoded cysteine predicts animal lifespan. Aging Cell 7, 32–46 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2007.00349.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Irie K., Ohigashi H., Hara H., Nagao M., Shimizu T., Shirasawa T. (2005). Formation and stabilization model of the 42-mer Abeta radical: implications for the long-lasting oxidative stress in Alzheimer's disease. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 15168–15174 10.1021/ja054041c [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray I. V., Liu L., Komatsu H., Uryu K., Xiao G., Lawson J. A., Axelsen P. H. (2007). Membrane-mediated amyloidogenesis and the promotion of oxidative lipid damage by amyloid beta proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 9335–9345 10.1074/jbc.M608589200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muscat S., Pelka J., Hegele J., Weigle B., Münch G., Pischetsrieder M. (2007). Coffee and Maillard products activate NF-kappaB in macrophages via H2O2 production. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 51, 525–535 10.1002/mnfr.200600254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neeper M., Schmidt A. M., Brett J., Yan S. D., Wang F., Pan Y. C., Elliston K., Stern D., Shaw A. (1992). Cloning and expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced glycosylation end products of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14998–15004 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunomura A., Perry G., Aliev G., Hirai K., Takeda A., Balraj E. K., Jones P. K., Ghanbari H., Wataya T., Shimohama S., Chiba S., Atwood C. S., Petersen R. B., Smith M. A. (2001). Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 60, 759–767 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortwerth B. J., James H., Simpson G., Linetsky M. (1998). The generation of superoxide anions in glycation reactions with sugars, osones, and 3-deoxyosones. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 245, 161–165 10.1006/bbrc.1998.8401 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padurariu M., Ciobica A., Hritcu L., Stoica B., Bild W., Stefanescu C. (2010). Changes of some oxidative stress markers in the serum of patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 469, 6–10 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.11.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagé E. L., Chan D. A., Giaccia A. J., Levine M., Richard D. E. (2008). Hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha stabilization in nonhypoxic conditions: role of oxidation and intracellular ascorbate depletion. Mol. Biol. Cell 19, 86–94 10.1091/mbc.E07-06-0612 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paola D., Domenicotti C., Nitti M., Vitali A., Borghi R., Cottalasso D., Zaccheo D., Odetti P., Strocchi P., Marinari U. M., Tabaton M., Pronzato M. A. (2000). Oxidative stress induces increase in intracellular amyloid beta-protein production and selective activation of betaI and betaII PKCs in NT2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 268, 642–646 10.1006/bbrc.2000.2164 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil S., Sheng L., Masserang A., Chan C. (2006). Palmitic acid-treated astrocytes induce BACE1 upregulation and accumulation of C-terminal fragment of APP in primary cortical neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 406, 55–59 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.07.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Nunomura A., Hirai K., Takeda A., Aliev G., Smith M. A. (2000). Oxidative damage in Alzheimer's disease: the metabolic dimension. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 18, 417–421 10.1016/S0736-5748(00)00006-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picone P., Bondi M. L., Picone P., Bondi M. L., Montana G., Bruno A., Pitarresi G., Giammona G., Di Carlo M. (2009). Ferulic acid inhibits oxidative stress and cell death induced by Ab oligomers: improved delivery by solid lipid nanoparticles. Free Radic. Res. 43, 1133–1145 10.1080/10715760903214454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin J., Goswami R., Dawson S., Dawson G. (2008). Expression of the receptor for advanced glycation end products in oligodendrocytes in response to oxidative stress. J. Neurosci. Res. 86, 2414–2422 10.1002/jnr.21692 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resende R., Ferreiro E., Pereira C., Resende de Oliveira C. (2008). Neurotoxic effect of oligomeric and fibrillar species of amyloid-beta peptide 1-42: involvement of endoplasmic reticulum calcium release in oligomer-induced cell death. Neuroscience 155, 725–737 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocchi A., Orsucci D., Tognoni G., Ceravolo R., Siciliano G. (2009). The role of vascular factors in late-onset sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Genetic and molecular aspects. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 6, 224–237 10.2174/156720509788486644 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues Siqueira I., Fochesatto C., da Silva Torres I. L., Dalmaz C., Alexandre Netto C. (2005). Aging affects oxidative state in hippocampus, hypothalamus and adrenal glands of Wistar rats. Life Sci. 78, 271–278 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.04.044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. M., Vianna M., Gerlach M., Brett J., Ryan J., Kao J., Esposito C., Hegarty H., Hurley W., Clauss M. (1992). Isolation and characterization of two binding proteins for advanced glycosylation end products from bovine lung which are present on the endothelial cell surface. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14987–14997 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt A. M., Yan S. D., Wautier J. L., Stern D. (1999). Activation of receptor for advanced glycation end products: a mechanism for chronic vascular dysfunction in diabetic vasculopathy and atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 84, 489–497 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Wilson R. S., Cochran E. J., Bienias J. L., Arnold S. E., Evans D. A., Bennett D. A. (2003). Relation of cerebral infarctions to dementia and cognitive function in older persons. Neurology 60, 1082–1088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp F. R., Bernaudin M. (2004). HIF1 and oxygen sensing in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 437–448 10.1038/nrn1408 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simm A., Casselmann C., Schubert A., Hofmann S., Reimann A., Silber R. E. (2004). Age associated changes of AGE-receptor expression: RAGE upregulation is associated with human heart dysfunction. Exp. Gerontol. 39, 407–413 10.1016/j.exger.2003.12.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Taneda S., Richey P. L., Miyata S., Yan S. D., Stern D., Sayre L. M., Monnier V. M., Perry G. (1994). Advanced Maillard reaction end products are associated with Alzheimer disease pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 5710–5714 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5710 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultana R., Perluigi M., Butterfield D. A. (2009). Oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer's disease (AD), mild cognitive impairment and animal models of AD: role of Abeta in pathogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 118, 131–150 10.1007/s00401-009-0517-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sultana R., Piroddi M., Galli F., Butterfield D. A. (2008). Protein levels and activity of some antioxidant enzymes in hippocampus of subjects with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Neurochem. Res. 33, 2540–2546 10.1007/s11064-008-9593-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X., He G., Qing H., Zhou W., Dobie F., Cai F., Staufenbiel M., Huang L. E., Song W. (2006). Hypoxia facilitates Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis by up-regulating BACE1 gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 18727–18732 10.1073/pnas.0606298103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabner B. J., El-Agnaf O. M., Turnbull S., German M. J., Paleologou K. E., Hayashi Y., Cooper L. J., Fullwood N. J., Allsop D. (2005). Hydrogen peroxide is generated during the very early stages of aggregation of the amyloid peptides implicated in Alzheimer disease and familial British dementia. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 35789–35792 10.1074/jbc.C500238200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi M., Makita Z. (2001). Alternative routes for the formation of immunochemically distinct advanced glycation end-products in vivo. Curr. Mol. Med. 1, 305–315 10.2174/1566524013363735 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuma K., Fang F., Zhang W., Yan S., Fukuzaki E., Du H., Sosunov A., McKhann G., Funatsu Y., Nakamichi N., Nagai T., Mizoguchi H., Ibi D., Hori O., Ogawa S., Stern D. M., Yamada K., Yan S. S. (2009). RAGE-mediated signaling contributes to intraneuronal transport of amyloid-beta and neuronal dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. US.A. 106, 20021–20026 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagno E., Bardini P., Obbili A., Vitali A., Borghi R., Zaccheo D., Pronzato M. A., Danni O., Smith M. A., Perry G., Tabaton M. (2002). Oxidative stress increases expression and activity of BACE in NT2 neurons. Neurobiol. Dis. 10, 279–288 10.1006/nbdi.2002.0515 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagno E., Guglielmotto M., Aragno M., Borghi R., Autelli R., Giliberto L., Muraca G., Danni O., Zhu X., Smith M. A., Perry G., Jo D. G., Mattson M. P., Tabaton M. (2008). Oxidative stress activates a positive feedback between the gamma- and beta-secretase cleavages of the beta-amyloid precursor protein. J. Neurochem. 104, 683–695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagno E., Guglielmotto M., Bardini P., Santoro G., Davit A., Di Simone D., Danni O., Tabaton M. (2003). Dehydroepiandrosterone reduces expression and activity of BACE in NT2 neurons exposed to oxidative stress. Neurobiol. Dis. 14, 291–301 10.1016/S0969-9961(03)00131-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamagno E., Parola M., Bardini P., Piccini A., Borghi R., Guglielmotto M., Santoro G., Davit A., Danni O., Smith M. A., Perry G., Tabaton M. (2005). Beta-site APP cleaving enzyme up-regulation induced by 4-hydroxynonenal is mediated by stress-activated protein kinases pathways. J. Neurochem. 92, 628–636 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02895.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong Y., Zhou W., Fung V., Christensen M. A., Qing H., Sun X., Song W. (2005). Oxidative stress potentiates BACE1 gene expression and Abeta generation. J. Neural Transm. 112, 455–469 10.1007/s00702-004-0255-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turrens J. F. (2003). Mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen species. J. Physiol. 552, 335–344 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.049478 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeer S. E., Prins N. D., den Heijer T., Hofman A., Koudstaal P. J., Breteler M. M. (2003). Silent brain infarcts and the risk of dementia and cognitive decline. N. Engl. J. Med. 348, 1215–1222 10.1056/NEJMoa022066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek M. P., Bhattacharya K., Glendening J. M., Stopa E., Vlassara H., Bucala R., Manogue K., Cerami A. (1994). Advanced glycation end products contribute to amyloidosis in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 4766–4770 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4766 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Xiong S., Xie C., Markesbery W. R., Lovell M. A. (2005). Increased oxidative damage in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 93, 953–962 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03053.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Zhang Y. W., Zhang X., Liu R., Zhang X., Hong S., Xia K., Xia J., Zhang Z., Xu H. (2006). Transcriptional regulation of APH-1A and increased gamma-secretase cleavage of APP and Notch by HIF-1 and hypoxia. FASEB J. 20, 1275–1277 10.1096/fj.06-5839fje [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. I., Lynn B. C., Markesbery W. R., Lovell M. A. (2006). Increased levels of 4 hydroxynonenal and acrolein, neurotoxic markers of lipid peroxidation, in the brain in Mild Cognitive Impairment and early Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Aging 27, 1094–1099 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.06.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S. D., Chen X., Fu J., Chen M., Zhu H., Roher A., Slattery T., Zhao L., Nagashima M., Morser J., Migheli A., Nawroth P., Stern D., Schmidt A. M. (1996). RAGE and amyloid-beta peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 382, 685–691 10.1038/382685a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S. D., Chen X., Schmidt A. M., Brett J., Godman G., Zou Y. S., Scott C. W., Caputo C., Frappier T., Smith M. A. (1994). Glycated tau protein in Alzheimer disease: a mechanism for induction of oxidant stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 7787–7791 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7787 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan S. D., Yan S. F., Chen X., Fu J., Chen M., Kuppusamy P., Smith M. A., Perry G., Godman G. C., Nawroth P. (1995). Non-enzymatically glycated tau in Alzheimer's disease induces neuronal oxidant stress resulting in cytokine gene expression and release of amyloid beta-peptide. Nat. Med. 1, 693–639 10.1038/nm0795-693 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L. B., Lindholm K., Yan R., Citron M., Xia W., Yang X. L., Beach T., Sue L., Wong P., Price D., Li R., Shen Y. (2003). Elevated beta-secretase expression and enzymatic activity detected in sporadic Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 9, 3–4 10.1038/nm0103-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A. (1996). Mechanisms of neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 16, 921–932 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80115-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatin S. M., Varadarajan S., Link C. D., Butterfield D. A. (1999). In vitro and in vivo oxidative stress associated with Alzheimer's amyloid beta-peptide (1-42). Neurobiol. Aging 20, 325–330 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X., Zhou K., Wang R., Cui J., Lipton S. A., Liao F. F., Xu H., Zhang Y. W. (2007). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha)-mediated hypoxia increases BACE1 expression and beta-amyloid generation. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 10873–10880 10.1074/jbc.M608856200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X., Raina A. K., Perry G., Smith M. A. (2004). Alzheimer's disease: the two-hit hypothesis. Lancet Neurol. 3, 219–226 10.1016/S1474-4422(04)00707-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Carvey P. M., Ling Z. (2006). Age-related changes in glutathione and glutathione-related enzymes in rat brain. Brain Res. 1090, 35–44 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.03.063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zlokovic B. V. (2008). New therapeutic targets in the neurovascular pathway in Alzheimer's disease. Neurotherapeutics 5, 409–414 10.1016/j.nurt.2008.05.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]