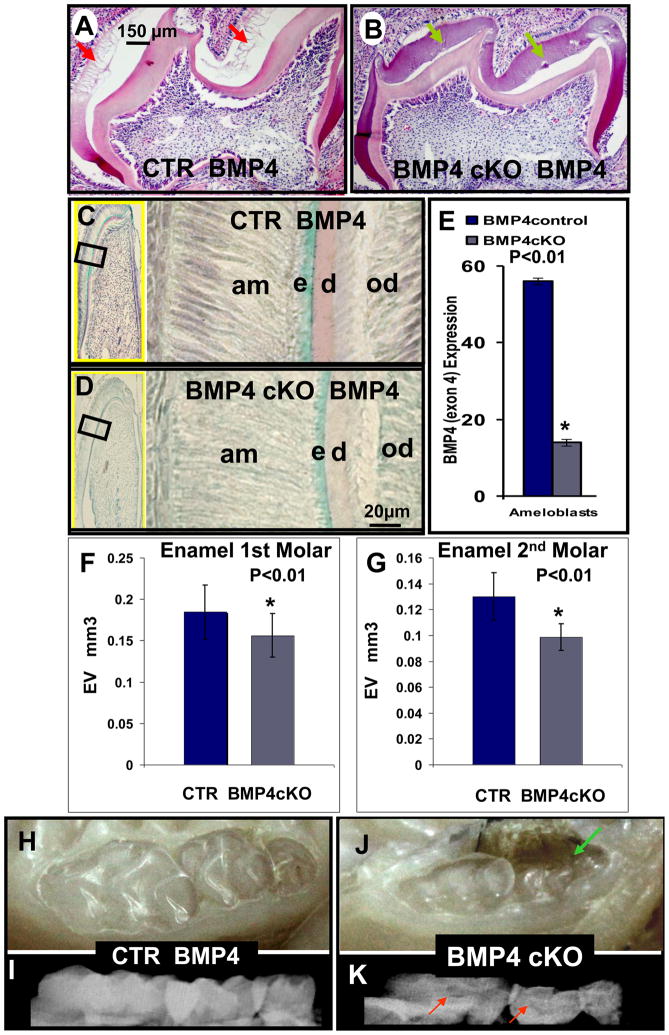
Fig. 6.
Hematoxylin - eosin staining (A, B) and in situ hybridization of BMP4 expression (C, D) in CTR (A, C) and BMP4 cKO (B, D) mice at 8–12 days; Photographs (H and J) and X-rays (I and K) of CTR (H and I) and BMP4 cKO (J and K) mice at 1 year. Hematoxylin – eosin staining, after demineralization of wild type mice, shows that tooth immature enamel matrix was not present as the enamel has matured to >90% mineral phase with little matrix proteins (A - red arrows); however, this immature enamel matrix was still present in BMP4 cKO mice (B - green arrows). These observations were seen in 2 independent sets of animals. BMP4 expression is also reduced in ameloblasts (C and D) of BMP4cKO mice and quantitated in multiple sections and measurements in CTR and BMP4 cKO animals as shown in (E). By quantitative μCT analysis with 4 independent CTR and BMP4 cKO 1 year animals, a 20 to 30% reduction in the enamel volume (EV) as shown in F and G for the 1st and 2nd molars was observed. Also, the BMP4 cKO mice have more transparent teeth (J) with unequal distribution of mineral on the X-ray image, red arrows (K) in comparison to control animals (H and I). We note in some BMP4 cKO animals an apparent periodontal loss that needs further investigation, green arrow (J).