Different food types modulate worm lifespan and involve the neuropeptide receptor NMUR-1, which acts with the sensory neurons in a bacterial lipopolysaccaharide structure-dependent manner.
Abstract
The type of food source has previously been shown to be as important as the level of food intake in influencing lifespan. Here we report that different Escherichia coli food sources alter Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan. These effects are modulated by different subsets of sensory neurons, which act with nmur-1, a homolog of mammalian neuromedin U receptors. Wild-type nmur-1, which is expressed in the somatic gonad, sensory neurons, and interneurons, shortens lifespan only on specific E. coli food sources—an effect that is dependent on the type of E. coli lipopolysaccharide structure. Moreover, the food type-dependent effect of nmur-1 on lifespan is different from that of food-level restriction. Together our data suggest that nmur-1 processes information from specific food cues to influence lifespan and other aspects of physiology.
Author Summary
Work on the model organisms C. elegans and D. melanogaster has contributed important and often surprising insights into the factors that determine lifespan. One intriguing finding is that lifespan in both animals can be extended or shortened by interfering with the function of neurons that smell or taste food. Indeed, specific taste neurons in C. elegans are required for the lifespan extension due to the restriction of the animals' level of food intake, while certain olfactory neurons in Drosophila inhibit this effect. Here we provide evidence that the sensory system also alters lifespan in response to specific food types as opposed to different food levels. C. elegans that feed on different E. coli strains can have different lifespans, which is not only dependent on the activities of a subset of sensory neurons but can also occur independently of food level restriction. We also show that the neuropeptide receptor NMUR-1 acts with the sensory system to affect lifespan in a manner dependent on the bacterial lipopolysaccharide structure. Thus, we identify both a food-derived factor and a component of a signaling pathway involved in the food-type effects on worm lifespan.
Introduction
The sensory systems of Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster have been shown to modulate the lifespan of these animals [1]–[4]. This sensory influence involves subsets of gustatory and olfactory neurons [2],[3] that either shorten or lengthen lifespan, which suggests that (i) some of the cues that affect lifespan are food-derived and that (ii) these cues can exert different effects on lifespan. Since a reduction in food levels can increase lifespan [5], it is possible that the sensory system influences lifespan by simply regulating the animal's general food intake, and, indeed, the sensory system has been implicated in the lifespan effects of food-level restriction in Drosophila [3]. On the other hand, the sensory influence on lifespan, at least in C. elegans, can be uncoupled from the sensory effects on feeding rate, development, and reproduction [1],[2]. Since the lifespan effect of food-level restriction has been linked to changes in feeding rates and decreased development and reproduction [5], this suggests that the sensory system also affects lifespan through other mechanism(s).
The C. elegans hermaphrodite has 60 sensory neurons with dendrites that terminate in ciliated endings [6]. These specialized structures contain dedicated sensory receptors [7],[8] and are thus the sites of recognition for different types of environmental cues, including gustatory, olfactory, thermal, and mechanical stimuli [9]. Within its natural environment, C. elegans encounters various types of bacteria that can serve as food sources. Similar to the sensory influence on lifespan, some of these food sources have been shown to alter lifespan independently of development and reproduction [10]. At the same time, not all but only a subset of food-sensing neurons influence the lifespan of C. elegans grown on the standard laboratory food source [2], Escherichia coli OP50 [11]. Together these data raise the possibility that sensory neurons promote the lifespan effects of different food sources through a mechanism distinct from that of food-level restriction.
In this study, we have investigated the role of the sensory system in the food-source influence on C. elegans lifespan and the signaling pathway(s) that might be involved in this process. We show that the C. elegans sensory system recognizes food types to affect longevity. We also identify (i) the neuromedin U receptor nmur-1 as a neuropeptide signaling pathway involved in this process and (ii) a food-derived cue, the E. coli lipopolysaccharide (LPS) structure, which elicits the nmur-1 response.
Results
The Sensory System Alters the Effects of Food Types on Lifespan
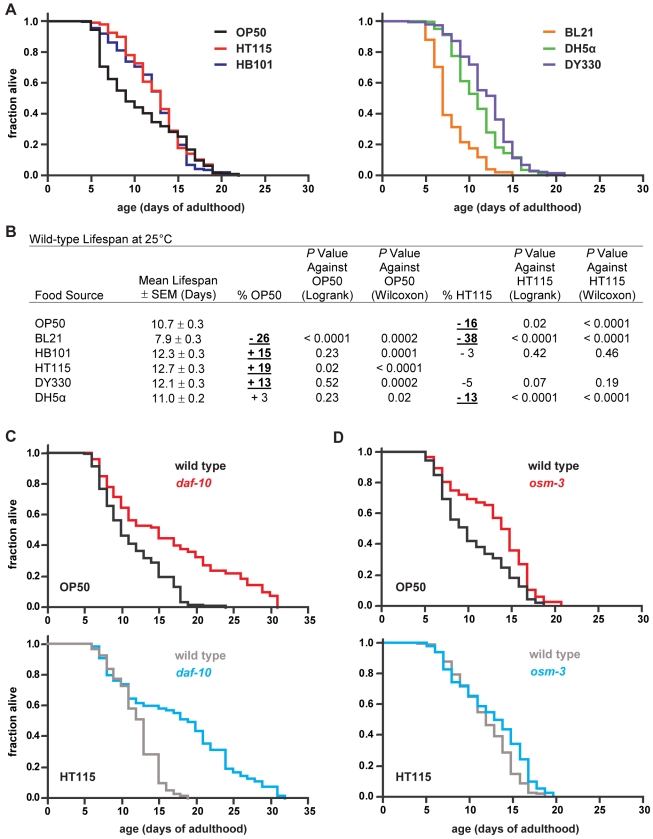
Wild-type C. elegans have altered lifespan on different E. coli strains (Figure 1A and 1B). Indeed, we found that at 25°C the mean lifespan of wild-type worms is shorter on OP50 than on HT115 (Figure 1A and 1B), another food source that is widely used [12],[13]. To test the hypothesis that sensory perception contributes to these food source-dependent effects, we measured the lifespan of sensory mutants on OP50 and HT115 at this temperature.
Figure 1. Sensory neurons modulate the effects of different types of food sources on lifespan.
(A) Wild-type survival plots on different E. coli food sources and (B) statistics for cumulative data from two to three independent trials at 25°C (see Table S3 for statistics on individual trials). The % OP50 and % HT115 in (B) refer to mean lifespan changes relative to the two standard food sources. Bold underlined values indicate a significant difference in survival (Wilcoxon p≤0.01) on a given food source compared to either OP50 or HT115. Logrank test results are given for comparison (see Materials and Methods). (C) The lifespan of daf-10(m79) sensory mutants compared to wild type on two different E. coli food sources. The curves in this and subsequent panels represent cumulative data. Detailed data on these and subsequent survival analyses can be found in Tables 1 and/or S3. (D) The lifespan of wild type and osm-3(n1540) sensory mutants on different E. coli strains.
The gene daf-10 encodes an ortholog of an intraflagellar transport complex protein that is required for cilia formation in a subset of sensory neurons (Table S1) [14],[15]. We observed that the lifespan of daf-10 mutants is extended to the same extent (44% versus 46%; Table 1) compared to that of wild type when grown on either OP50 or HT115 (Figure 1C), which suggests that some sensory neurons shorten lifespan independently of these two food sources.
Table 1. Cumulative adult lifespans at 25°C.
| Strain/Treatment | Mean Lifespan ± SEM (Days) | 75th Percentile (Days) | Number of Animals Observed/Total Initial Animals | % Wild Type | p Value Against Wild Type (Logrank) | p Value Against Wild Type (Wilcoxon) | % of Specified Groups | p Value Against Specified Groups (Logrank) | p Value Against Specified Groups (Wilcoxon) |
| Sensory Mutants | |||||||||
| OP50: Wild type | 11.3±0.4 | 15 | 130/150 (2) | ||||||
| OP50: daf-10(m79) | 16.3±0.9 | 22 | 78/148 (2) | +44 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| HT115: Wild type | 12.1±0.3 | 15 | 124/140 (2) | +7 | 0.94a | 0.02a | |||
| HT115: daf-10(m79) | 17.7±0.8 | 24 | 101/140 (2) | +46 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +9 | 0.29a | 0.13a |
| OP50: Wild type | 10.5±0.3 | 14 | 187/220 (3) | ||||||
| OP50: osm-3(n1540) | 12.9±0.3 | 17 | 192/250 (3) | +23 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| HT115: Wild type | 11.8±0.2 | 15 | 198/220 (3) | +12 | 0.10a | 0.0002a | |||
| HT115: osm-3(n1540) | 12.6±0.3 | 16 | 219/250 (3) | +7 | <0.0001 | 0.02 | −2 | 0.37a | 0.49a |
| nmur-1 Food-Dependence | |||||||||
| OP50: Wild type | 10.7±0.3 | 16 | 240/290 (4) | ||||||
| OP50: nmur-1 | 15.0±0.3 | 18 | 230/292 (4) | +40 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| BL21: Wild type | 7.9±0.3 | 9 | 52/150 (2) | −26 | <0.0001a | 0.0002a | |||
| BL21: nmur-1 | 10.1±0.5 | 14 | 85/150 (2) | +28 | 0.0001 | 0.002 | −33 | <0.0001a | <0.0001a |
| HB101: Wild type | 12.3±0.3 | 15 | 193/220 (3) | +15 | 0.23a | <0.0001a | |||
| HB101: nmur-1 | 15.1±0.2 | 17 | 173/220 (3) | +23 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +1 | 0.25a | 0.38a |
| HT115: Wild type | 12.7±0.3 | 15 | 186/220 (3) | +19 | 0.02a | <0.0001a | |||
| HT115: nmur-1 | 13.3±0.3 | 16 | 166/210 (3) | +5 | 0.06 | 0.08 | −11 | <0.0001a | <0.0001a |
| DY330: Wild type | 12.1±0.3 | 14 | 137/150 (2) | +13 | 0.52a | 0.0002a | |||
| DY330: nmur-1 | 12.8±0.3 | 15 | 126/150 (2) | +6 | 0.05 | 0.11 | −15 | <0.0001a | <0.0001a |
| DH5α: Wild type | 11.0±0.2 | 13 | 196/220 (3) | +3 | 0.23a | 0.02a | |||
| DH5α: nmur-1 | 13.2±0.2 | 16 | 197/220 (3) | +20 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | −12 | <0.0001a | <0.0001a |
| Rescue Experiments | |||||||||
| Line 1 | |||||||||
| OP50: jxEx4 | 10.1±0.4 | 14 | 69/83 (1) | ||||||
| OP50: nmur-1; jxEx12 | 11.9±0.5 | 15 | 54/66 (1) | +18 | 0.01b | 0.009b | |||
| OP50: nmur-1; jxEx4 | 14.4±0.4 | 17 | 73/88 (1) | +42 | <0.0001b | <0.0001b | +21 | 0.0003c | 0.0001c |
| Line 2 | |||||||||
| OP50: jxEx4 | 12.8±0.4 | 17 | 109/127 (2) | ||||||
| OP50: nmur-1; jxEx40 | 14.6±0.5 | 19 | 89/152 (2) | +14 | 0.002b | 0.01b | |||
| OP50: nmur-1; jxEx4 | 17.4±0.4 | 21 | 120/144 (2) | +36 | <0.0001b | <0.0001b | +19 | <0.0001c | <0.0001c |
| HT115: jxEx4 | 11.2±0.3 | 13 | 128/152 (2) | ||||||
| HT115: nmur-1; jxEx40 | 13.3±0.3 | 16 | 146/169 (2) | +19 | <0.0001b | <0.0001b | |||
| HT115: nmur-1; jxEx4 | 12.8±0.2 | 15 | 146/162 (2) | +14 | <0.0001b | <0.0001b | −4 | 0.004c | 0.18c |
| Line 2 and second set of controls | |||||||||
| OP50: jxEx14 | 12.5±0.5 | 15 | 69/80 (1) | ||||||
| OP50: nmur-1; jxEx40 | 12.8±0.5 | 15 | 45/80 (1) | +2 | 0.75b | 0.71b | |||
| OP50: nmur-1; jxEx14 | 15.1±0.5 | 18 | 46/70 (1) | +21 | 0.002b | 0.0003b | +18 | 0.0006c | 0.0008c |
| E. coli LPS-Dependence | |||||||||
| OP50: Wild type | 11.9±0.8 | 17 | 34/40 (1) | ||||||
| OP50: nmur-1 | 17.5±0.5 | 19 | 31/40 (1) | +47 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| CS180: Wild type | 14.3±0.2 | 17 | 205/240 (3) | ||||||
| CS180: nmur-1 | 15.1±0.2 | 17 | 202/240 (3) | +5 | 0.05 | 0.03 | |||
| CS2198: Wild type | 13.2±0.3 | 15 | 141/160 (2) | −8 | 0.006d | 0.001d | |||
| CS2198: nmur-1 | 15.8±0.3 | 19 | 134/161 (2) | +20 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +3 | 0.05d | 0.19d |
| CS2429: Wild type | 13.3±0.2 | 16 | 213/240 (3) | −7 | 0.01d | 0.0003d | |||
| CS2429: nmur-1 | 16.2±0.3 | 19 | 188/240 (3) | +22 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +7 | <0.0001d | 0.002d |
| CS1861: Wild type | 13.4±0.5 | 17 | 72/80 (1) | −3 | 0.99d | 0.61d | |||
| CS1861: nmur-1 | 14.5±0.5 | 17 | 63/80 (1) | +8 | 0.17 | 0.12 | −5 | 0.56d | 0.51d |
| daf-10 Epistasis | |||||||||
| OP50: Wild type | 11.3±0.4 | 15 | 130/150 (2) | ||||||
| OP50: nmur-1 | 15.4±0.4 | 18 | 126/150 (2) | +36 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| OP50: daf-10(m79) | 16.3±0.9 | 22 | 78/148 (2) | +44 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| OP50: daf-10; nmur-1 | 21.1±0.8 | 26 | 75/150 (2) | +87 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +29 | 0.002e | <0.0001e |
| HT115: Wild type | 12.1±0.3 | 15 | 124/140 (2) | ||||||
| HT115: nmur-1 | 12.2±0.4 | 15 | 55/70 (1) | +1 | 0.76 | 0.82 | |||
| HT115: daf-10(m79) | 17.7±0.8 | 24 | 101/140 (2) | +46 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| HT115: daf-10; nmur-1 | 21.8±1.0 | 25 | 32/70 (1) | +80 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +23 | 0.02e | 0.002e |
| osm-3 Epistasis | |||||||||
| OP50: Wild type | 10.5±0.3 | 14 | 187/220 (3) | ||||||
| OP50: nmur-1 | 14.0±0.3 | 17 | 188/220 (3) | +33 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| OP50: osm-3(n1540) | 12.9±0.3 | 17 | 192/250 (3) | +23 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| OP50: osm-3; nmur-1 | 15.2±0.2 | 18 | 220/250 (3) | +45 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +18 | <0.0001f | <0.0001f |
| +9 | 0.005g | 0.009g | |||||||
| HT115: Wild type | 11.8±0.2 | 15 | 198/220 (3) | ||||||
| HT115: nmur-1 | 12.7±0.2 | 15 | 182/220 (3) | +8 | 0.008 | 0.009 | |||
| HT115: osm-3(n1540) | 12.6±0.3 | 16 | 219/250 (3) | +7 | <0.0001 | 0.02 | |||
| HT115: osm-3; nmur-1 | 13.8±0.2 | 17 | 217/250 (3) | +17 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +10 | 0.01f | 0.002f |
| +9 | <0.0001g | 0.001g | |||||||
| CS180: Wild type | 13.8±0.2 | 16 | 143/160 (2) | ||||||
| CS180: nmur-1 | 14.4±0.2 | 17 | 143/160 (2) | +4 | 0.002 | 0.03 | |||
| CS180: osm-3(n1540) | 15.5±0.2 | 17 | 134/160 (2) | +12 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| CS180: osm-3; nmur-1 | 15.7±0.2 | 17 | 136/160 (2) | +14 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +1 | 0.24f | 0.24f |
| +9 | <0.0001g | <0.0001g | |||||||
| CS2429: Wild type | 12.8±0.3 | 16 | 152/160 (2) | ||||||
| CS2429: nmur-1 | 14.2±0.3 | 17 | 147/160 (2) | +11 | <0.0001 | 0.0007 | |||
| CS2429: osm-3(n1540) | 15.3±0.3 | 18 | 140/160 (2) | +20 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| CS2429: osm-3; nmur-1 | 14.8±0.3 | 18 | 148/160 (2) | +16 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | −3 | 0.32f | 0.32f |
| +4 | 0.02g | 0.05g | |||||||
| daf-2 Epistasis on OP50 | |||||||||
| Wild type | 11.6±0.5 | 15 | 62/70 (1) | ||||||
| nmur-1 | 15.3±0.4 | 17 | 61/70 (1) | +32 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| daf-2(e1370) | 33.3±1.2 | 39 | 54/70 (1) | +188 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| daf-2(e1370); nmur-1 | 36.7±1.1 | 43 | 59/71 (1) | +216 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +10 | 0.02h | 0.05h |
| Wild type | 11.8±0.5 | 15 | 76/80 (1) | ||||||
| nmur-1 | 14.8±0.4 | 17 | 72/80 (1) | +25 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| daf-2(e1368) | 21.0±1.1 | 29 | 62/80 (1) | +78 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| daf-2(e1368); nmur-1 | 24.4±0.8 | 29 | 67/80 (1) | +107 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +16 | 0.24i | 0.06i |
| daf-16 Independence on OP50 | |||||||||
| Wild type | 11.7±0.3 | 15 | 128/141 (2) | ||||||
| nmur-1 | 16.6±0.5 | 19 | 57/70 (1) | +42 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| daf-16(mu86) | 9.5±0.3 | 13 | 125/140 (2) | −19 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| daf-16; nmur-1 | 11.8±0.3 | 13 | 127/139 (2) | ±0 | 0.30 | 0.99 | +24 | <0.0001j | <0.0001j |
| aak-2 Independence on OP50 | |||||||||
| Wild type | 11.2±0.5 | 14 | 69/80 (1) | ||||||
| nmur-1 | 14.8±0.3 | 17 | 110/130 (1) | +32 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| aak-2(ok524) | 10.8±0.5 | 13 | 66/80 (1) | −4 | 0.49 | 0.74 | |||
| nmur-1 aak-2 | 13.8±0.4 | 16 | 64/80 (1) | +23 | 0.007 | 0.0001 | +28 | 0.0001k | <0.0001k |
| hsf-1 Independence on OP50 | |||||||||
| Wild type | 11.0±0.3 | 14 | 102/140 (2) | ||||||
| nmur-1 | 14.7±0.4 | 18 | 99/140 (2) | +34 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| hsf-1(sy441) | 7.3±0.1 | 8 | 248/624 (2) | −34 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| hsf-1; nmur-1 | 8.2±0.2 | 10 | 102/744 (2) | −25 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | +12 | <0.0001m | 0.0004m |
| pmk-1 Independence on OP50 | |||||||||
| Wild type | 12.4±0.3 | 16 | 197/240 (3) | ||||||
| nmur-1 | 15.1±0.3 | 18 | 189/240 (3) | +22 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||
| pmk-1(km25) | 12.4±0.3 | 15 | 178/291 (3) | ±0 | 0.62 | 1.0 | |||
| pmk-1; nmur-1 | 14.2±0.3 | 17 | 166/300 (3) | +15 | 0.02 | <0.0001 | +15 | 0.002o | <0.0001o |
We assayed wild-type and mutant worms in parallel in independent trials (details shown in Table S3) and we show statistics from the cumulative experiments on different E. coli strains. The 75th percentile is the age when the fraction of worms alive in each group falls below 0.25. The first number in the fourth column is the number of worms observed as having died, while the second number gives the total number of worms in each experiment, including worms that were censored during the course of the assay. The numbers in parentheses in the fourth column indicate the number of trials performed. Worms that crawled off the plate, exploded, or bagged were censored at the time of the event, allowing these worms to be incorporated into the data set until the censor date and to avoid loss of information. Differences that are significant (p≤0.01) according to the Wilcoxon test, which in most cases are also significant according to the logrank test, are underlined and in boldface type. Differences that are significant only according to the logrank test are italicized. The % difference between wild type and mutants under different conditions is indicated in the fifth column. The % difference between certain groups of worms that are specified by the superscripted symbols is shown in the eighth column. The superscripted symbols indicate the following:
compared to the cumulative data for the same genotype assayed on OP50;
compared to jxEx4[myo-3p::rfp] or jxEx14[myo-3p::rfp] on the same food source;
compared to the rescue line on the same food source;
compared to the cumulative data for the same genotype assayed on CS180;
compared with daf-10(m79) tested on the same food source;
compared with osm-3(n1540) tested in parallel on the same food source;
compared with nmur-1(ok1387) assayed in parallel on the same food source;
compared with daf-2(e1370);
compared with daf-2(e1368);
compared to the cumulative data for daf-16(mu86);
compared with aak-2(ok524);
compared to the cumulative data for hsf-1(sy441); and
compared to the cumulative data for pmk-1(km25);
In contrast, worms that carry mutations in osm-3, which encodes a kinesin motor protein required for cilia formation in a different subset of sensory neurons (Table S1) [16],[17], live long relative to wild type only when grown on OP50, but not when grown on HT115 (Figure 1D; Table 1). This implies that at least some of the osm-3-expressing neurons sense the lifespan-influencing difference(s) between these food sources.
nmur-1 Affects Lifespan in a Food Source-Dependent Manner
Since osm-3 functions in cilia structure formation rather than in directly sensing or translating food-derived cues, we searched for non-structural genes that would act with the sensory system to regulate the food source-dependent effects on lifespan. Candidate genes would include those encoding sensory receptors and downstream signaling molecules, like neuropeptides and their receptors, which help transmit or modulate sensory information. Unlike individual sensory receptors specific for single cues, a single downstream factor may affect the integration of several cues, which would make the effects of this class of genes more readily detectable.
The C. elegans genome has more than 75 neuropeptide-like genes and more than 1,000 G-protein-coupled receptors, some of which function as neuropeptide receptors [9],[18]–[21]. We focused on a subset of these genes based on the availability of mutations and on the evidence that their homologs in other animals regulate feeding and metabolism [19],[21]–[25]. We compared the lifespan of the different mutants on OP50 and HT115.
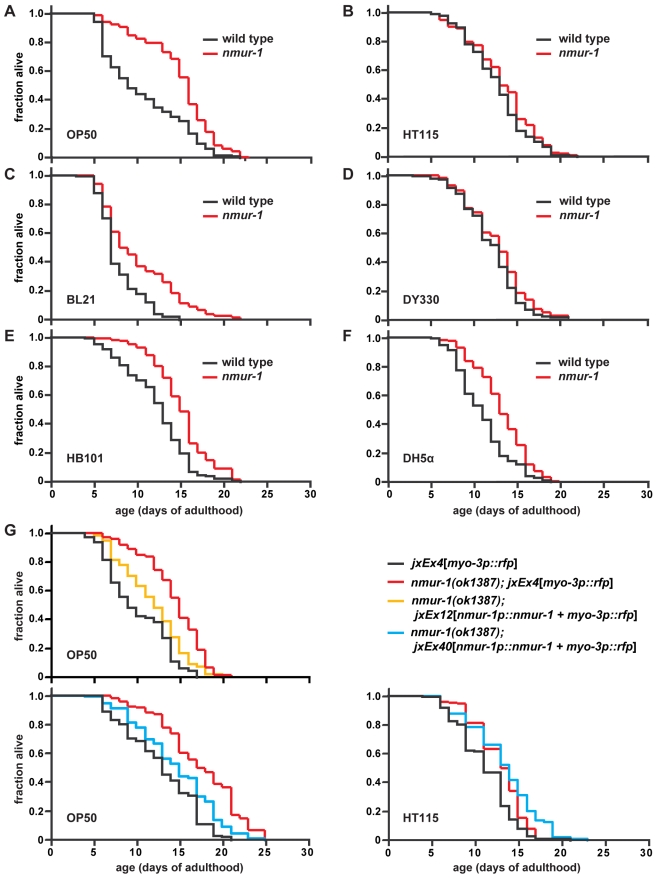
While most neuropeptide signaling pathways had no effect on lifespan on the two food sources tested (Table S2), we found that animals carrying the deletion mutation ok1387 within the gene C48C5.1 live long on OP50 but not on HT115 (Figure 2A and 2B; Tables 1, S2, and S3). C48C5.1 is predicted to encode a seven-transmembrane neuropeptide receptor (Figure S1) with homology to mammalian neuromedin U receptors (NMURs), whose peptide ligand, neuromedin U (NMU), has been shown to regulate food intake [24]. We renamed C48C5.1 as nmur-1, since our study makes it the first phenotypically characterized member of the worm NMUR family, of which there are at least three other members—nmur-2 (K10B4.4), nmur-3 (F02E8.2), and nmur-4 (C30F12.6). As a confirmation that the wild-type function of nmur-1 is to shorten lifespan in a food source-dependent manner, we were able to rescue the long-life phenotype of the nmur-1 mutation on OP50 with the wild-type nmur-1 genomic locus, without shortening lifespan on HT115 (Figure 2G; Tables 1 and S3).
Figure 2. nmur-1 modulates lifespan in a food source-dependent manner.
(A–F) Lifespan of wild-type and nmur-1(ok1387) worms on different E. coli strains, which are indicated in the lower left corner of each panel. (G) The wild-type nmur-1 genomic locus can rescue the food source-dependent long-life phenotype of nmur-1(ok1387) on OP50, without shortening lifespan on HT115. The lifespan of the two rescue lines, nmur-1(ok1387); jxEx12 and nmur-1(ok1387); jxEx40, are compared to wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms that carry the myo-3p::rfp coinjection marker, jxEx4, alone.
nmur-1 Acts with the Sensory System to Modulate the Food-Source Effects on Lifespan
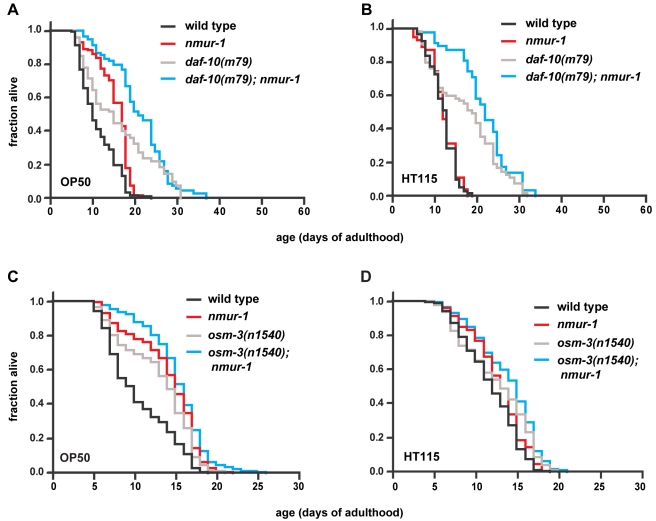
Next, we asked whether sensory neurons regulate the food source-dependent effects on lifespan through nmur-1. We found that loss of nmur-1 still considerably increases the lifespan of daf-10 sensory mutants on OP50 (Figure 3A; Table 1), which indicates that nmur-1 acts in parallel at least to some daf-10-expressing neurons. Surprisingly, loss of nmur-1 extends the lifespan of daf-10 mutants also on HT115 (Figure 3B; Table 1), which may suggest that the lifespan of nmur-1 mutants becomes food source-independent in the absence of daf-10 activity. Thus, nmur-1 appears to be subject not only to activation by certain environmental cues but also to inhibition by others.
Figure 3. nmur-1 acts with the sensory system to regulate lifespan.
(A–B) The effects of nmur-1 on the lifespan of daf-10(m79) mutants as measured on E. coli OP50 and HT115. (C–D) The effects of nmur-1 on the lifespan of osm-3(n1540) mutants as compared on E. coli OP50 and HT115.
In contrast, animals that carry both nmur-1 and osm-3 mutations have a lifespan phenotype similar to that of nmur-1 single mutants on OP50 and HT115 (Figure 3C and 3D; Table 1). This suggests that nmur-1 acts with osm-3 either in a subset of osm-3-expressing sensory neurons or in downstream cells. We observed expression of a gfp reporter for nmur-1 in the spermathecae of the somatic gonad, in several different types of sensory neurons, some of which co-express osm-3 (Table S1) [16], and in interneurons (Table 2), some of which receive inputs from, or modulate the activity of, osm-3-expressing sensory neurons [6]. This expression pattern, together with the genetic interaction between the mutations in nmur-1 and osm-3, suggests that nmur-1 plays a role in the processing of sensory information derived by the worm from various food sources.
Table 2. nmur-1p::gfp expression at 25°C.
| Cell/Tissue | Type | Function |
| ADFL/R | Amphid sensory neurona | Chemosensationb, serotonergic neuronc |
| ADLL/R | Amphid sensory neurona | Chemosensationb, nociceptiond |
| AFDL/R | Amphid sensory neurona | Thermosensatione |
| OLQDL/R, OLQVL/R | Outer labial sensory neurona | Mechanosensationf |
| AIAL/R (?) | Interneurona | Integrates chemosensory informationa , g |
| AIZL/R | Interneurona | Integrates chemo-a , g and thermosensorye information |
| AVKL/R | Interneurona | Unknown |
| DVA | Interneurona | Stretch-receptor-mediated proprioceptionh |
| PVT | Interneurona | Unknown |
| RICL/R | Interneurona | Unknown |
| RIH | Interneurona | Unknown |
| SDQL/R | Interneurona | Unknown |
| PDA | Motor neurona | Innervates posterior body wall muscles |
| ALAa | Neuron | Unknown |
| SIBDL/Ra | Neuron | Unknown |
| SIBVL/Ra | Neuron | Unknown |
| And 2 other head neurons | ||
| Spermatheca | Somatic gonad | Reservoir for maturing spermatids and adult sperm |
The superscripted symbols indicate the references that describe the types and known functions of the corresponding neurons;
[6];
[78];
[83];
[85];
[82];
[86];
[87]; and
[88]. The question mark indicates that the neuron expressing nmur-1p::gfp is likely to be AIA, since its position and morphology are consistent with those known for AIA, but this particular identification remains to be confirmed.
The Effect of nmur-1 on Lifespan Involves the E. coli LPS Structure
We then explored the possible differences between OP50 and HT115, which might be recognized by the worm. OP50 is derived from an E. coli B strain [11], whereas HT115 is from an E. coli K-12 strain [26],[27]. To determine whether nmur-1 affects lifespan only on B strains but not on K-12 strains, we measured the lifespan of nmur-1 mutants on other bacteria derived from these two lineages. Interestingly, we found that nmur-1 mutants live long consistently on the B strain BL21 [28] and on HB101 (Figure 2C and 2E; Tables 1 and S3), a K-12 strain that contains a large stretch of B strain genomic DNA [29]. In contrast, the nmur-1 long-life phenotype is absent on another K-12 strain, DY330 [30], and only occasionally present on the K-12 strain DH5α (Figure 2D and 2F; Tables 1 and S3) [31]. Together these data suggest that nmur-1 affects lifespan in a largely B strain-dependent manner.
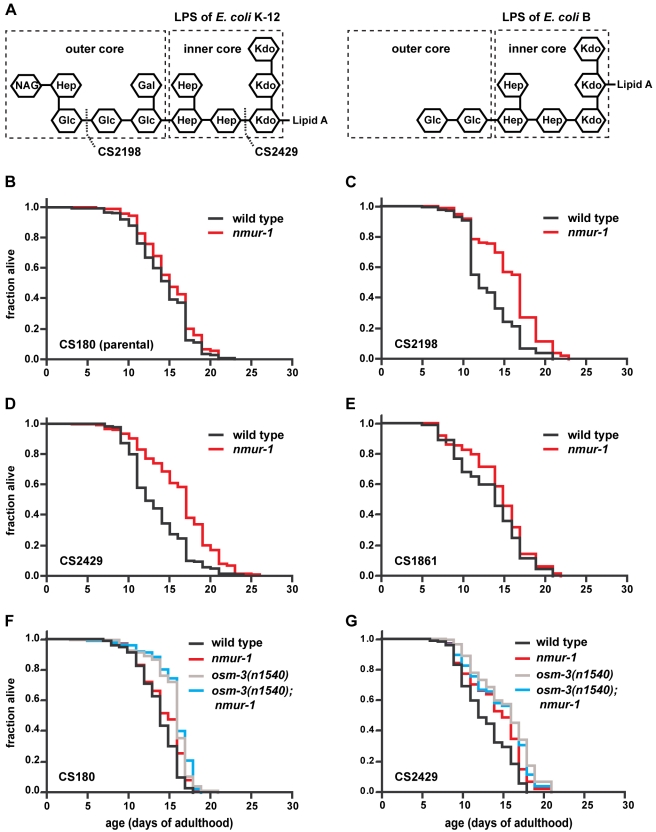
Although the B and K-12 strains clearly would have many differences, one of the few well-characterized molecular differences between these strains lies in the LPS structures (Figure 4A) on their outer membranes [32]–[34]. Since the LPS of the K-12 strain [33],[34] has a longer outer core than the LPS of the B strain [32], we tested whether LPS structure influences lifespan. We compared wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms on E. coli K-12 mutants that have truncated LPS to worms grown on the corresponding K-12 parent strain. We found that wild-type worms live shorter on the LPS truncation mutants CS2198 and CS2429 [35],[36] than on the isogenic parent strain CS180 (Tables 1 and S3), which expresses wild-type K-12 LPS [35]. On the other hand, nmur-1 mutants live long compared to wild type only on the LPS truncation mutants (Figure 4C and 4D; Tables 1 and S3), but not on the K-12 parent strain (Figure 4B; Tables 1 and S3).
Figure 4. The E. coli LPS structure influences C. elegans lifespan in an nmur-1-dependent manner.
(A) The LPS structures of E. coli K-12 and B strains have different sugar compositions [32],[33]. Strain CS180 expresses wild-type K-12 LPS. Strains CS2198 and CS2429 are isogenic derivatives of CS180 and express the indicated truncated forms of K-12 LPS. Strain CS1861 is derived from CS180 and expresses the Shigella dysenteriae 1 O Antigen attached to the tip of the full-length K-12 LPS. (B–E) Survival curves of wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms on CS180, CS2198, CS2429, and CS1861. (F–G) The lifespan of worms carrying mutations in nmur-1 and/or osm-3 as compared on E. coli strains with different LPS structures.
To exclude the possibility that all changes to the LPS will elicit the nmur-1 response, we also measured the lifespan of worms grown on the K-12 strain CS1861 that expresses the Shigella dysenteriae 1 O Antigen fused to the end of the full-length K-12 LPS [36]. We observed no lifespan difference between wild type and nmur-1 mutants on this strain (Figure 4E; Table 1). Together our data suggest that a short E. coli LPS structure can shorten worm lifespan in an nmur-1-dependent manner.
In contrast to nmur-1, we found that osm-3 can affect lifespan independently of the E. coli LPS structure (Figure 4F and 4G; Table 1), which indicates that at least some of the osm-3-expressing neurons detect other food-derived cues. However, even on the CS180 and CS2429 bacterial food sources, nmur-1 and osm-3 appear to act together in influencing lifespan, since osm-3; nmur-1 double mutants have the same lifespan phenotype as osm-3 or nmur-1 single mutants (Figure 4F and 4G; Table 1).
The nmur-1 Food-Source Effect on Lifespan Is Distinct from That of General Food-Level Restriction
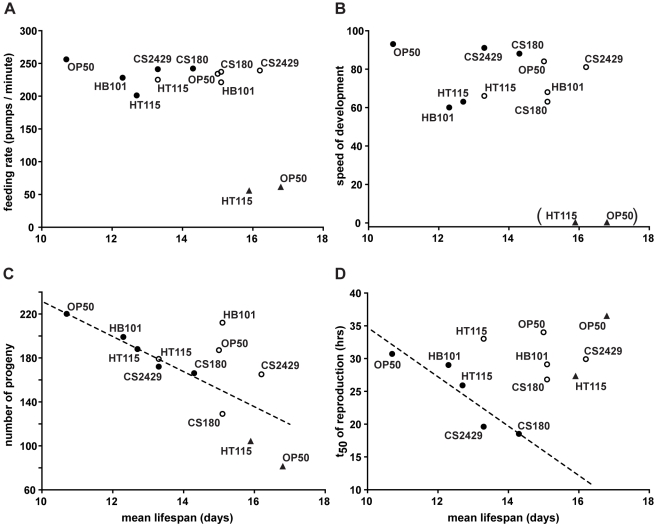
Food type [37] and sensory neurons [3],[38] have been shown to mediate the lifespan extension induced by dietary restriction (DR), which is commonly studied through restriction of food levels. Thus, the food type-dependent effects on lifespan we observe might reflect different levels of DR experienced by wild-type and mutant worms on the various food sources. To address this possibility, we measured the feeding rates, speed of development, total progeny, and the rates of reproduction of wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms on five different E. coli strains (Figures S2 and S3), since restricting food levels is known to change these parameters [5]. For comparison, we used a genetic model for food-level restriction [39], a mutation in eat-2 that impairs pharyngeal function [40], which leads to decreased feeding rates on both OP50 and HT115 (Figure S4A). Unlike the nmur-1 mutation, we found that the eat-2 mutation increases lifespan on both food sources (Figure S4C), which suggests that the food-type effects of nmur-1 are not the same as those of food-level restriction. Moreover, we observed no correlation between lifespan and feeding rates or lifespan and development of wild-type or nmur-1 mutant worms on the different food sources (Figures 5A, 5B, S2A, S2B, S2C, S2D, S3A, and S3B), which is also unlike the reported effects of restricting food levels [5].
Figure 5. nmur-1 exerts its effects on lifespan without inducing signs of food-level restriction.
(A–D) The correlations of lifespan with feeding, development, and reproduction are shown across five different food sources. The figures are compiled from the lifespan data in Tables 1 and S3 and from the data on feeding rates, developmental rates, progeny numbers, and reproduction rates presented in Figures S2, S3, and S4. Pharyngeal pumping rates of young adults (A) and speed of development (B) do not correlate with mean lifespan for wild-type (closed circles) and nmur-1 mutant worms (open circles), nor for the combined data, but are strongly reduced in food level-restricted eat-2(ad1116) mutants (closed triangles). The parentheses around the eat-2 mutant data in (B) mean that the mutant speed of development falls outside the range of our index (see Materials and Methods). Progeny number (C) and t50 of reproduction (D) are inversely correlated with mean lifespan of wild-type worms (closed circles; p = 0.003 for total progeny and p = 0.029 for reproduction time). The dotted lines are the regression lines for total progeny and reproduction time (R2 = 0.960 and 0.837, respectively) calculated from the wild-type data alone. nmur-1 (open circles) exerts an additional, reproduction-independent effect on lifespan, as suggested by the deviation from the regression lines of the corresponding data points for OP50, HB101, and CS2429.
As expected for a genetic model for food-level restriction, we found that the lifespan extension conferred by the eat-2 mutation is accompanied by a decrease in total progeny on OP50 and HT115 (Figures 5C and S4B). Surprisingly, we also found that wild-type worms grown on different food sources do exhibit an inverse correlation between lifespan and number of progeny but that nmur-1 mutants can still live long without a proportionate decrease in total progeny (Figures 5C, S2E, and S3C). This suggests that the food source-dependent effects on lifespan have reproduction-dependent and reproduction-independent components, the latter of which is uncovered by the nmur-1 mutation. Interestingly, we also observed that food sources that increase wild-type lifespan induce the animals to reproduce faster (Figure 5D), which not only differs from eat-2 mutants (Figure 5D) but is also the inverse of the effects shown for food-level restriction on rates of reproduction [5],[41]. At the same time, we again saw no correlation between the nmur-1 mutant lifespan and its rates of reproduction on the different E. coli strains (Figures 5D, S2F, and S3D).
Since our data show that the effects of eat-2 on C. elegans physiology differ from those of nmur-1 or the different food sources, this suggests that the effects of the food sources and nmur-1 on lifespan can be distinct from food-level restriction. Consistent with this idea, we observed that, unlike long-lived, food level-restricted animals that have decreased lipid storage [5], nmur-1 mutants do not exhibit gross changes in fat storage compared to wild type on either OP50 or HT115 (Table S4).
nmur-1 Acts at Least Partly Independently of daf-16 and hsf-1
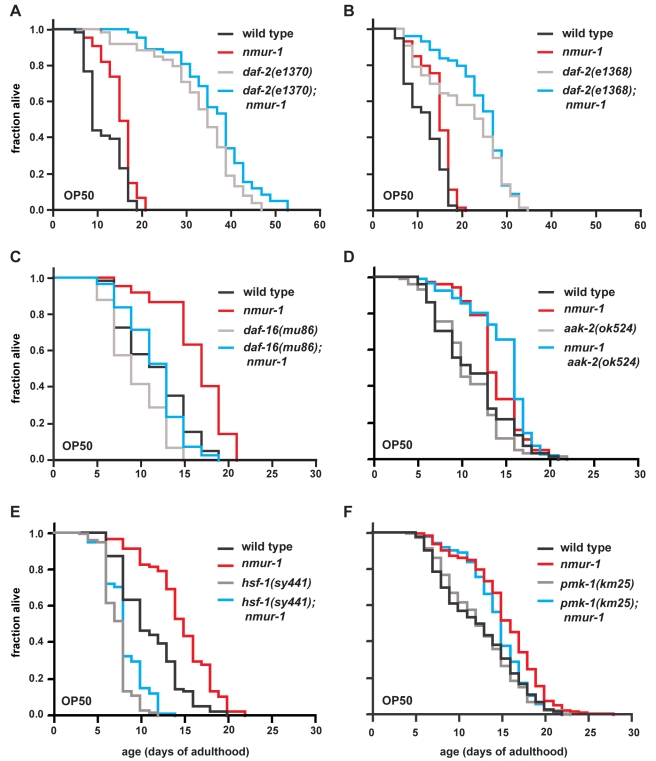
Next, we asked whether nmur-1 acts through the insulin/IGF-1 daf-2 pathway [42], which has been shown to mediate a large part of the sensory influence on lifespan [1]. For example, the increased lifespan of osm-3 sensory mutants on OP50 has been shown to be partly dependent on daf-16 [1], a FOXO transcription factor that acts downstream of and is negatively regulated by daf-2 [43]–[45]. Accordingly, we found that removing nmur-1 does not significantly increase the lifespan of insulin/IGF-1 receptor daf-2 mutant worms (Figure 6A and 6B; Table 1), but loss of nmur-1 can still extend the lifespan of worms carrying a null mutation in daf-16 (Figure 6C; Table 1). Thus, our data suggest that nmur-1, like at least some osm-3-expressing neurons, acts either with daf-2 but at least partly independently of daf-16, or in parallel to the daf-2/daf-16 pathway.
Figure 6. nmur-1 acts at least partly independently of daf-16 and hsf-1.
(A–B) The effect of nmur-1 on daf-2 lifespan is shown for two different daf-2 reduction-of-function mutant backgrounds. Since daf-2 mutants undergo developmental arrest at 25°C, all strains in these experiments were grown at 20°C until the first day of adulthood, when the worms were shifted to 25°C to initiate lifespan measurements. (C) The effect of nmur-1 on lifespan as assayed in a daf-16(mu86) null background. (D–F) The effect of nmur-1 on the respective lifespan of aak-2(ok524), hsf-1(sy441), or pmk-1(km25) mutants.
To identify other factors required for nmur-1 to affect lifespan, we tested how removal of nmur-1 would affect the short lifespan caused by mutations in genes proposed to act independently of daf-16 [46]–[48]. We found that loss of nmur-1 can still extend the lifespan of animals with a mutation in either (i) the AMP-dependent kinase aak-2 (Figure 6D; Table 1), which regulates energy metabolism [46]; (ii) the heat shock transcription factor hsf-1 (Figure 6E; Table 1), which regulates stress response [47],[49],[50]; or (iii) the p38 MAPK pmk-1 (Figure 6F; Table 1), which regulates innate immunity [48],[51]. Although none of these factors appears essential for nmur-1 function, we did observe partial suppression of the nmur-1 phenotype in the hsf-1 mutant background. This could suggest that nmur-1 affects lifespan by acting through several parallel pathways that include hsf-1 and/or daf-16.
Discussion
Food is a complex environmental factor that affects many physiological processes, including lifespan. In the laboratory, C. elegans are grown on agar plates, on which the bacterial lawn that serves as the food source presumably provides a large part of the worm's chemosensory and mechanosensory inputs. Thus, the previous finding that some gustatory and olfactory neurons function either to shorten or lengthen C. elegans lifespan [2] makes it likely that food-derived cues affect longevity through the sensory system.
Some sensory neurons have been shown to be required for the prolonged lifespan conferred by DR [3],[38], i.e., under conditions of limited food availability. However, the fact that the sensory system also modulates lifespan when food is abundant suggests that the sensory influence on lifespan involves more than one mechanism, as illustrated in this and previous studies [1],[2].
Sensory Neurons Recognize Food Types to Affect Lifespan
If food-derived cues alter lifespan through the sensory system, then it is likely that impairment of a specific set of sensory neurons that detect a given set of cues would affect lifespan only on some food sources. In this study, we provide a detailed investigation of the interdependence between food and sensory perception in regulating C. elegans longevity. We show not only that wild-type lifespan is modulated by different E. coli food sources (Figure 1A and 1B) but also that three genes, which have been shown to be expressed and/or act in sensory neurons, have food source-dependent effects on lifespan.
Mutations in two of these genes—osm-3 and nmur-1—increase lifespan on OP50 but not on HT115 (Figures 1D and 2; Tables 1 and S3). Since the effects of these mutations are non-additive (Figure 3C and 3D; Table 1), this suggests that osm-3 and nmur-1 influence lifespan through a common mechanism. On the other hand, a mutation in the third gene, daf-10, not only extends lifespan on both OP50 and HT115 (Figure 1C; Table 1) but also alters the food type-dependence of the nmur-1 effect on lifespan (Figure 3A and 3B; Table 1).
Together with their requirement in the formation of the sensory cilia in subsets of neurons [15],[16], the osm-3 and daf-10 data are consistent with a role for sensory perception in the food source-dependent effects on lifespan. In addition, the identification of a neuropeptide receptor gene, nmur-1, that interacts with osm-3 and daf-10 (Figures 3, 4F and 4G; Table 1) suggests a mechanism through which the sensory system mediates the effects of specific food cues on lifespan. The nmur-1 expression in sensory neurons and interneurons (Table 2) suggests that nmur-1 modulates the transduction of signals downstream of the sensory receptors. Based on the observed interactions among these three genes, we propose the following model: (i) osm-3-expressing sensory neurons detect the presence of certain food-derived cues and transmit this information through an nmur-1-dependent pathway, and (ii) a different set of daf-10-expressing neurons detects other food cues, some of which inhibit nmur-1 activity.
According to this model, the expression patterns (Table S1) of osm-3 [16] and daf-10 [15] should help define the candidate sensory neurons that might recognize the food cues that shorten or extend lifespan through nmur-1. daf-10 is necessary for proper cilia morphology in the mechanosensory CEP neurons and some unidentified neurons in the head and tail sensory organs called the amphids and phasmids, respectively [15]. Several amphid neurons also express osm-3 [16]: these include two pairs of gustatory neurons, ASI and ASG, that have been found to shorten lifespan on OP50 [2], and two other gustatory neuron pairs that co-express nmur-1—ADF, which by itself has no lifespan effect on OP50 [2], and ADL. In addition, osm-3 is expressed outside of the amphid organs in the IL2 inner labial head neurons and in the phasmid tail neurons [16], all of which have been proposed to have chemosensory function [15],[52].
A Neuropeptide Receptor of the NMUR Family Mediates the Sensory Influence on Lifespan
Our discovery of a food source-dependent function for the C. elegans nmur-1 gene is consistent with the known food-associated activities of other members of the NMUR signaling pathway in mammals [24],[53] and insects [54],[55]. In mammals, NMUR2, the receptor isoform expressed in the central nervous system, and its ligand, the octapeptide NMU-8, have been implicated in the regulation of food intake and energy expenditure [24],[53]. In Drosophila, the gene hugin encodes two of the peptide ligands, PK-2 and HUG-γ, recognized by two of four NMUR isoforms [54]–[56]. hugin regulates not only the food-seeking behavior and feeding rate of larvae but also affects the rate of food intake of adult flies in a food type-dependent manner [54]. Like hugin, we find that nmur-1 exerts food-type specific effects on feeding rate (Figure S2A and S2C), although the nmur-1 regulation of this process appears to be parallel to its regulation of lifespan (Figure 5A). Similar to the neuronal expression of nmur-1, Drosophila hugin is expressed in interneurons that appear to relay gustatory information [54]. At present, a potential role for the fly or mammalian NMUR signaling pathways in the regulation of lifespan has not been reported. However, the evolutionary conservation of several aspects of NMUR signaling leads us to speculate that the effects on lifespan by this system might also be conserved across species.
The Drosophila NMU signaling system also includes a second neuropeptide precursor gene, capability, that encodes three other peptide ligands, CAPA-1, CAPA-2, and CAPA-3 (also called PK-1), that can activate three of the fly NMUR isoforms [56]. The C. elegans homolog of capability, nlp-44, has recently been identified [57]. Like capability, it is predicted to give rise to three peptides, one of which activates the receptor encoded by nmur-2 [57]. A mutation of nmur-2 gives no lifespan phenotype on the food sources we have tested (Table S2), but it will be interesting to determine whether peptides derived from nlp-44 can also activate NMUR-1.
A role of nmur-1 in the sensory influence on lifespan is supported by its expression in a number of sensory neurons and interneurons (Table 2). However, it remains possible that sensory cues regulate nmur-1 activity at the level of the somatic gonad, which is the only non-neuronal tissue that expresses the nmur-1 reporter gene (Table 2). At the same time, the expression of nmur-1 in a relatively large number of cells also makes it likely that the parallel effects of nmur-1 on lifespan, feeding rate, development, and reproduction (Figures 5A–5D, S2, and S3) are mediated by its activity in different subsets of cells.
The food source-dependent activities of nmur-1 raise the possibility that other neuropeptide signaling pathways—many of which are associated with the sensory system [18]–[20],[25] —will also affect lifespan or other aspects of physiology only under specific conditions. Although most of the neuropeptide signaling pathways we have screened so far on two food sources show no effect on lifespan (Table S2), it remains possible that they will have effects on other food types. Thus, the large repertoire of neuropeptides and their receptors in C. elegans might serve to translate environmental complexity into appropriate physiological responses.
The Bacterial LPS Represents a Food-Derived Cue that Influences Lifespan
We find that wild-type worms live shorter on the E. coli B strains BL21 and OP50 than on K-12 strains, like HT115 and DY330 (Figure 1A and 1B). Conversely, the nmur-1 mutation causes reproducible lifespan extensions on the B strains but not on the K-12 strains (Figure 2; Tables 1 and S3). Since B and K-12 strains differ in their LPS structure, we have tested the lifespan effects of specific alterations in the K-12 LPS that mimic aspects of the B strain LPS (Figure 4A). Although the effect of LPS on wild-type lifespan is not large, wild-type worms do live longer on full-length than on truncated forms of the K-12 LPS (Tables 1 and S3). We also find that the nmur-1 effect on lifespan is LPS-dependent and suppressed by full-length K-12 LPS but not by its truncated versions (Figure 4; Tables 1 and S3).
Although the LPS experiments were carried out in isogenic bacterial backgrounds, the effects of the LPS alterations might be indirect since they could lead to secondary changes in bacterial metabolism or surface structure. Indeed, LPS truncations have been shown to interfere with the expression of outer membrane proteins, increase capsule polysaccharide levels, and redistribute phospholipids from the inner to the outer leaflet of the outer membrane ([58] and references therein). However, these secondary changes have only been observed with mutations that disrupt the inner core of the LPS, like the mutation present in the CS2429 strain (Figure 4A), and thereby compromise the integrity of the outer membrane [58]. No such effects have been reported for truncations that affect only the LPS outer core, like the mutation in CS2198 (Figure 4A). Thus, the observation that nmur-1 extends lifespan on both CS2429 and CS2198 argues for a direct effect of the bacterial LPS on worm lifespan. Direct recognition of LPS is biologically plausible: LPS is the predominant component of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and is consequently used by multicellular organisms from diverse phyla to recognize bacteria in the context of defense against pathogens [59],[60].
Nevertheless, the LPS structure is clearly only one of potentially many food-derived cues that influence worm lifespan. This is most evident from the LPS-independent lifespan phenotype of osm-3 mutants (Figure 4F and 4G; Table 1), and from the fact that the lifespan extension by the nmur-1 mutation is greater on OP50 than on any other strain with a similar, short LPS (Figure 2; Tables 1 and S3). Thus, changes in lifespan are likely triggered by different sets of sensory neurons in response to a variety of food-derived cues, and loss of nmur-1 interferes with the detection of several of these cues.
The LPS dependence of the nmur-1 phenotype makes it conceivable that nmur-1 may regulate stress-related and innate immune responses elicited by different food sources. We find that nmur-1 can still affect lifespan in the absence of either of three genes, daf-16, hsf-1, and pmk-1, all of which have major roles in stress responses and innate immunity [47]–[51],[61]–[63]. However, the mutations in daf-16 and hsf-1 can partly suppress the nmur-1 lifespan phenotype (Figure 6; Table 1), which makes it possible that the nmur-1 influence on lifespan requires a combination of mechanisms that involve daf-16, hsf-1, and/or other factors.
Food-Type Effects on Lifespan Can Be Distinct from Food-Level Restriction
We find that the food-source influence on wild-type lifespan is strongly correlated with reproductive effects (Figure 5C and 5D), in that increases in lifespan are accompanied not only by a decreased number of total progeny but also a faster rate of reproduction. One possible interpretation of these data is that the different reproductive profiles cause the food source-dependent differences in wild-type lifespan. Indeed, with the exception of BL21, the bacterial diets we have tested seem to affect initial survival more than late-age survival. This is supported by age-specific force of mortality plots (Figure S5A): the different food sources alter wild-type mortality primarily before day 10 of adulthood but have little effect thereafter. It is conceivable that damage inflicted on somatic tissues [64] or neglect of somatic maintenance and repair during reproduction [65] are important determinants of early mortality. In agreement with this idea, we find that long-lived glp-1 mutant worms [66], which are sterile because they generate few or no germ cells [67], have very similar lifespan, at least on OP50, HT115, CS180, and CS2429 (W. M., unpublished data). This suggests that the food type-dependent effects on wild-type lifespan are indeed germline-dependent.
Interestingly, a recent study [68] has shown that different E. coli food sources can differentially affect fat storage in C. elegans. Wild-type worms grown on HB101 or HT115 are found to have lower triacylglyceride (TAG) levels than wild-type worms grown on OP50 [68]. Although that same study and another report [68],[69] question the reliability of fat stains with vital dyes, we also observe a slightly reduced fat storage in wild type on HT115 compared to wild type on OP50, using lipid labeling with a lipophilic fluorophore (Table S4). Thus, a correlation may exist not only between lifespan and reproduction but also between lifespan and TAG levels of wild-type worms. Since germline signals have been proposed to regulate both lifespan and intestinal fat storage [70], the food-type and reproduction-dependent effects on wild-type lifespan may also be mediated by changes in TAG levels.
In contrast, we find that nmur-1 exerts an additional effect on lifespan that is largely independent of reproduction (Figure 5C and 5D) and also appears to be independent of glp-1 on OP50 and CS2429 (B. A. and W. M., unpublished data) and fat storage on OP50 and HT115 (Table S4). Accordingly, the nmur-1 mutation can affect mortality prior to day 10 of adulthood (OP50 and CS180; Figure S5B) on the food sources that significantly reduce the total progeny of nmur-1 mutants (compare OP50 and CS180 in Figures 5C, S2E, and S3C). At the same time, nmur-1 mutants show reduced mortality after day 10, but not past day 16, of adulthood on the short LPS strains OP50 and CS2429 (Figure S5B), the latter of which has no effect on the nmur-1 mutant number of progeny (Figure S3C). Thus, our findings imply that food sources affect lifespan through both reproduction-dependent and reproduction-independent mechanisms, with the second being uncovered by the nmur-1 mutation.
Unlike the longevity-promoting effect of food-level restriction [5],[41], the food type-dependent effects on lifespan that we observe not only have reproduction-independent and fat storage-independent components (Figure 5C and 5D; Table S4) but are also independent of alterations in feeding rate and developmental rate (Figure 5A and 5B). In addition, our data show that different food types and nmur-1 affect initial mortality without decreasing late-age mortality (Figure S5), again unlike food-level restriction, which decreases the slope of the mortality trajectory and thus slows the rate of aging [71]. These data lead us to propose that these two forms of dietary influence on lifespan employ distinct, but possibly overlapping, mechanisms.
Another recent study [72] has shown that different DR regimens for C. elegans require different signaling pathways to affect lifespan. However, some of these regimens altered not only food levels but also the nature of food sources. In fact, at least one of these protocols, which lowered protein levels, does not decrease but increase reproduction ([72] and references therein), which suggests that the lifespan effect of protein restriction, unlike that of other DR protocols, could be partly reproduction-independent. Our data might help explain some of these findings, if one assumes that the net consequence on lifespan of some DR protocols represents a mix of independent effects from food-level restriction and food-type dependence. In the future, it would be of interest to determine whether the food type-dependent effects on lifespan will also require the activities of genes, e.g., the NFE2-related protein skn-1 [38] and the FOXA transcription factor pha-4 [73], that have been implicated in the longevity-promoting effects of DR.
Materials and Methods
Worm Strains and Bacterial Strains
All worm mutant strains used in this study were backcrossed six times to our lab wild-type (N2) strain, with the exception of nmur-1(ok1387), which was backcrossed eight times, and eat-2(ad1116), which was outcrossed once, before generation of different mutant combinations and any phenotypic analysis. The different worm mutant alleles used are indicated within the figures, supplementary tables, and their legends. Worms were grown for at least two generations at 25°C on the same food source used in a given phenotypic analysis, unless otherwise stated.
The E. coli strains used were: OP50 [11], HT115 [rnc14::ΔTn10 λ(DE3) of W3110] [13],[26],[27], BL21(DE3) [28], DY330(DE3) [Δ(argF-lacZ)U169 gal490*(IS2) pglΔ8 rnc<>cat λcI857 Δ(cro-bioA) of W3110] [30], HB101 [29], DH5α [31], CS180 [rfa+] [35], CS2198 [rfaJ19::Tnlac Δlac pyrD+ of CS180] [35], CS2429 [rfaC− of CS180] [36], and CS1861 (CS180 transformed with a plasmid that confers chloramphenicol resistance and encodes the proteins required for the expression of Shigella dysenteriae 1 O Antigen fused to the parent strain K-12 LPS) [36].
Transgenic Worms
We generated two independent rescue lines using standard methods: nmur-1(ok1387); jxEx12[nmur-1p::nmur-1+myo-3p::rfp] and nmur-1(ok1387); jxEx40[nmur-1p::nmur-1+myo-3p::rfp]. The rescue fragment, which is a 7.96 kb-long PCR fragment of the wild-type nmur-1 genomic locus (injected at 100 ng/µl), includes the 2.9 kb sequence upstream of the nmur-1 start codon and the 1 kb sequence downstream of the correct stop codon (see Figure S1). The myo-3p::rfp (gift of Cori Bargmann) was used as a coinjection marker (injected at 100 ng/µl). As controls, we also generated wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms that carry the myo-3p::rfp coinjection marker alone.
We observed that the extrachromosomal array jxEx12 has a large number of arrested embryos and larvae, whereas the extrachromosomal array jxEx40 produces ∼13% arrested larvae (25 arrested worms/196 total worms). These additional phenotypes might be due to a hyperactive NMUR-1 pathway caused by overexpression of the gene from its extrachromosomal copies.
To determine the expression pattern of nmur-1, we generated a transcriptional gfp reporter construct (nmur-1p::gfp; based on the pPD117.01 vector; gift from A. Fire), in which the gfp is flanked by the 2.9 kb sequence upstream of the nmur-1 start codon and by the 1 kb sequence downstream of the correct stop codon, including the newly identified 3′ UTR (see Figure S1). In addition, sequences from the four largest introns, 1, 4, 8, and 10, which may contain regulatory sequences required for expression, were fused downstream of the 1 kb 3′ cis sequences. This construct was injected into wild-type worms at a concentration of 100 ng/µl, and two independent transgenic lines, jxEx36 and jxEx37, were recovered, which show identical patterns of gfp expression.
Bacterial Culture and Assay Plate Preparation
All bacterial strains were grown from single colonies in Luria-Bertani medium overnight at 37°C. However, the medium used to grow the chloramphenicol-resistant strain CS1861 was supplemented with 100 µg/ml chloramphenicol. Nematode-growth agar plates (6 cm in diameter; [11]) were seeded with 100 µl bacterial culture and were allowed to dry at room temperature (23°C). Seeded plates were stored at room temperature and used within 5 d.
Lifespan Assays
The survival analyses of all worm strains on the different bacteria were initiated on the first day of adulthood and carried out at 25°C. Throughout their reproductive period, the worms were transferred daily to new plates to separate them from their progeny. We used the JMP 5.1 (SAS) software to determine Kaplan-Meier estimates of survival probabilities and mean lifespan, and for all statistical comparisons. p values were determined by the logrank and Wilcoxon tests. The logrank test, which places more weight on larger survival times, is appropriate when comparing differences between groups of animals whose ratio of hazard functions (ratio of mortality rates) stays approximately constant over time [74]. However, when the hazard ratios do not stay constant with time, as when one survival curve shows more early deaths than another (e.g., wild type on OP50 versus wild type on HB101 or HT115 in Figure 1A and 1B), the Wilcoxon test is more appropriate for comparing differences between groups [74]. We found that the Wilcoxon test is more sensitive to the lifespan differences we see in most of our experiments, since the nmur-1 mutation and most bacterial food sources clearly affect mean lifespan more than the maximum lifespan, which in fact violates the logrank test assumption of constant hazard ratios. Here we refer to a Wilcoxon p value of ≤0.01 as a significant difference between the various groups of animals. For comparison, we report both the Wilcoxon and logrank test results in all tables.
For mortality plots, the age-specific force of mortality was calculated as Fx = −ln(1−Dx), where Dx is the probability of death between day x−1 and x of adulthood [75]. At least five independent trials of a given lifespan experiment were used to calculate means and standard errors of Fx, which were plotted on a log scale against age.
Measurements of Feeding Rate, Progeny Number, and Rate of Development
Feeding rates were determined on the first and fourth days of adulthood at 25°C by measuring the animals' pharyngeal pumping rates, which reflect the rates at which they eat bacteria [76]. The pumps of the pharyngeal bulbs of individual worms were counted 3 to 5 times over periods of 30 s. Each resulting mean value was then doubled to get “pumps per minute.” A two-way ANOVA test was used to compare the different genotypes on different food sources and p values were calculated with the Tukey post-test.
Developmental rate differences were determined through a population-based assay at 25°C. First-stage (L1) larvae that had hatched within a 2-h time window were collected and allowed to develop for 36.5 h. At this point, the number of second-stage (L2), third-stage (L3), and fourth-stage (L4) larvae, as well as of young adult (YA) or gravid adult (GA) worms were counted. The chi-square test was used to compare the resulting stage distributions across food sources or worm genotypes.
Total progeny and temporal profiles of egg-laying were determined at 25°C by culturing L4 larvae singly on plates of the appropriate food source. The worms were then transferred to new plates regularly until they stopped laying eggs. The eggs were allowed to hatch and the larval progeny were then counted. Two-way ANOVA and the Tukey post-test were used to compare the total number of progeny of genotypes across food sources. To ensure that the data followed a normal distribution, it was necessary to incorporate a statistical censoring procedure to exclude outliers (worms with a very low number of progeny) from the data set before the ANOVA test. Briefly, this involved the tentative identification of outliers and calculation of standard deviation (SD) for the remaining set. Then, from the full data set, we excluded worms that had produced less progeny than the mean minus 2.5 times SD. In general, this procedure led to exclusion of worms with a progeny number smaller than 90, which corresponded to ∼4% of the total data set. The exception is nmur-1 mutant worms feeding on HB101, for which two classes of worms seem to exist: one with a large number of progeny and another with a small number of progeny. In this particular case, censoring caused 25% of worms to be excluded from the analysis and the remaining data set to be biased considerably towards a larger progeny number, as can be seen in Figure S2E.
The temporal profiles of egg-laying were determined from the same statistically censored populations of worms. The Hill function, P(t) = Pmax * tn/(tn+t50 n), was used to fit the cumulative number of progeny over time, where t denotes time, Pmax is the total number of progeny, n the Hill coefficient, and t50 the time until half of the progeny is produced. In Figures S2F and S3D, the data were normalized to Pmax.
For statistical assessments of correlations between mean lifespan and feeding, development, or reproduction on different food sources, we used the Pearson Product Moment test. To determine the correlation between lifespan and development, the stage distributions of the original data were used to calculate “speed of development” values, which are the percentages of worms scored as either young or gravid adults in the corresponding assays. eat-2 mutants have a value of zero on this scale because no mutant worms reached adulthood within 36.5 h after egg-laying. To correlate lifespan and rate of reproduction, the t50 of the fitted temporal reproduction profiles was used.
Supporting Information
Gene architecture and coding sequence of nmur-1 . (A) The gene structure of nmur-1 (C48C5.1) predicted by WormBase (version WS207; www.wormbase.org) consists of only 10 exons (shown in white). However, upon isolation and sequencing of the nmur-1 cDNA, we found that the nmur-1 gene locus includes a terminal 11th exon (shown in black) that encodes an additional 22 amino acids and is followed by a 210 bp 3′ UTR (gray). The extent of the ok1387 deletion is indicated by the hatched bar. (B) The nmur-1 cDNA sequence along with its translated protein sequence. The arrowheads indicate exon-intron boundaries within the DNA sequence, the 3′ UTR is italicized and the poly-A sequence used for priming the reverse transcription of the mRNA is framed. Within the protein sequence, the predicted seven transmembrane domains are underlined. The revised protein sequence shows 45% similarity and 27% identity to human NMUR1 and 47% similarity and 29% identity to human NMUR2 [24].
(0.37 MB TIF)
nmur-1 modulates food source-dependent effects on feeding rate, development, and reproduction. (A–B) Pharyngeal pumping rates of wild-type and mutant worms on different bacteria. Rates are expressed as mean pumps per minute and determined from the indicated number (n) of worms. ** indicates p≤0.001 in this and subsequent panels. Since wild type and nmur-1 mutants pump at a similar rate on HB101, a food source that does increase mutant lifespan compared to wild type (Figure 2E), the nmur-1 regulation of lifespan and feeding rate presumably involve two distinct pathways. (C) The wild-type nmur-1 genomic locus can also rescue the feeding rate phenotypes of nmur-1 mutants on OP50 (p = 0.02) and HT115 (p≤0.001). The rescued worms are compared to wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms that carry the myo-3p::rfp coinjection marker alone. * indicates p≤0.01 in this and later panels. (D) Distribution of developmental stages of wild-type and mutant worms at 36.5 h after hatching on different bacteria. L2, second-stage larvae; L3, third-stage larvae; L4, fourth-stage larvae; YA, young adults. Although both wild type and mutants develop faster on OP50 than on HB101 or HT115 (p<0.001 for either genotype), mutants develop slower than wild type on OP50 (p = 0.01). It should be noted that our observation of a slower wild-type developmental rate on HB101 at 25°C differs from a previous study carried out at 18°C [77], which suggests that temperature can alter the growth-influencing factors of some food sources. (E–F) Total progeny and temporal profiles of reproduction on different bacteria. nmur-1 mutants have less total progeny (E) than wild type on OP50 (p<0.01), and wild type has more progeny on OP50 than on HT115 (p = 0.03). The larger progeny number of nmur-1 mutants on HB101 (p = 0.04) is a consequence of censoring (see Materials and Methods). nmur-1 mutants reproduce more slowly (F) than wild type on HT115 but behave more similarly to wild type on OP50 and HB101.
(0.88 MB TIF)
The influence of the LPS structure on feeding, development, and reproduction of wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms. (A) Wild-type and mutant worms have similar pharyngeal pumping rates on both the CS2429 LPS truncation mutant and the CS180 parent strain. (B) nmur-1 mutant worms develop faster on the E. coli LPS mutant strain than on the E. coli parent strain (p<0.001) but slower than wild-type worms on both E. coli strains (p<0.001 for each case). nmur-1 mutants also (C) produce more offspring on the E. coli truncation mutant than on the E. coli parent strain (** p<0.001) and (D) reproduce at a similar rate, though slower than wild type, on both strains. Together our findings suggest that the nmur-1 regulation of lifespan, feeding rate, development, and reproduction involve more than one pathway and several food-derived factors.
(0.28 MB TIF)
The effect of a genetic model of food-level restriction on feeding, reproduction, and lifespan. Worms carrying the mutation eat-2(ad1116) display a reduced pharyngeal pumping rate (A), a smaller number of progeny (B), and increased lifespan (C) independent of their food source. Mean lifespan of eat-2 mutants: 16.8 d (+47%, p<0.0001) on OP50, 15.9 d (+41%, p<0.0001) on HT115.
(0.39 MB TIF)
Food source-dependent effects on age-specific rates of mortality. (A) Mortality plot of wild type on four different strains of E. coli. (B) Individual comparisons of wild-type and nmur-1 mutants on the four food sources.
(0.68 MB TIF)
Sensory neurons affected by cilium-structure genes. The subsets of sensory neurons affected by two sensory genes, daf-10 [15] and osm-3 [16], partly overlap. The superscripted symbols indicate the references that identify the neurons and their corresponding functions: a, [6]; b, [78],[79],[80]; c, [81]; d, [82]; e, [52]; and f, [83].
(0.03 MB DOC)
Adult lifespans of neuropeptide and neuropeptide receptor mutants tested at 25°C. We measured the lifespan of C. elegans grown on OP50 or HT115 and that carry mutations in genes that encode either neuropeptides or neuropeptide receptors. These neuropeptides or neuropeptide receptors show homologies to members of different neuropeptide signaling pathways in other animals, which are involved in regulating their feeding behavior and metabolism [19],[21]–[25]. The statistical analyses performed on these experiments are as described in the legend of Table 1.
(0.08 MB DOC)
Individual trials of adult lifespans on different food sources at 25°C. The analyses performed here are as described in the legend of Table 1. The superscripted symbols indicate the following: a, compared to the same genotype assayed in parallel on OP50 in independent trials; b, compared to jxEx4[myo-3p::rfp] on the same food source in independent trials; c, compared to the rescue line on the same food source in independent trials; and d, compared to the same genotype assayed in parallel on CS180 in independent trials.
(0.27 MB DOC)
Fat storage of wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms on OP50 and HT115. Fat storage in 1-d-old adults is quantified by labeling the worms with C1-BODIPY-C12 according to Mak et al. [84]. All quantifications are normalized to wild type on OP50 and given as percent ± SEM. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of worms assayed for each condition. The superscript a indicates p = 0.042 compared to wild type on OP50.
(0.03 MB DOC)
Acknowledgments
We thank C. Kenyon, S. Mitani, L. Segalat, the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center, and the C. elegans Gene Knockout Consortium for strains used in this study; C. Bargmann, A. Fire, O. Hobert, G. Jansen, and P. Sternberg for reagents that facilitated the identification of neurons expressing nmur-1p::gfp; T. Chen and J. Klena for providing the E. coli K-12 LPS parent and mutant strains; H. Grosshans and C. Kenyon for other bacterial strains; and M. Pietrzak for DNA sequencing. We also thank J. Apfeld, Q. Ch'ng, J. Hofsteenge, M. Noll, and J. Pielage for critical comments on the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- DR
dietary restriction
- LPS
lipopolysaccharide
- NMU
neuromedin U
- NMUR
neuromedin U receptor
- TAG
triacylglyceride
Footnotes
We would like to disclose that the role of nmur-1 in modulating lifespan is the subject matter of a patent application (PCT/EP2008/061541).
This work was supported by a Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Postdoctoral Fellowship (MA-3995/1) to WM and the Novartis Research Foundation. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Apfeld J, Kenyon C. Regulation of lifespan by sensory perception in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1999;402:804–809. doi: 10.1038/45544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alcedo J, Kenyon C. Regulation of C. elegans longevity by specific gustatory and olfactory neurons. Neuron. 2004;41:45–55. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00816-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Libert S, Zwiener J, Chu X, VanVoorhies W, Roman G, et al. Regulation of Drosophila life span by olfaction and food-derived odors. Science. 2007;315:1133–1137. doi: 10.1126/science.1136610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee S. J, Kenyon C. Regulation of the longevity response to temperature by thermosensory neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Curr Biol. 2009;19:715–722. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.03.041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Klass M. R. Aging in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: major biological and environmental factors influencing life span. Mech Ageing Dev. 1977;6:413–429. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.White J. G, Southgate E, Thomson J. N, Brenner S. The structure of the nervous system of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986;314 doi: 10.1098/rstb.1986.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dwyer N. D, Troemel E. R, Sengupta P, Bargmann C. I. Odorant receptor localization to olfactory cilia is mediated by ODR-4, a novel membrane-associated protein. Cell. 1998;93:455–466. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sengupta P, Chou J. H, Bargmann C. I. odr-10 encodes a seven transmembrane domain olfactory receptor required for responses to the odorant diacetyl. Cell. 1996;84:899–909. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bargmann C. I. Neurobiology of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome. Science. 1998;282:2028–2033. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5396.2028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Garsin D. A, Villanueva J. M, Begun J, Kim D. H, Sifri C. D, et al. Long-lived C. elegans daf-2 mutants are resistant to bacterial pathogens. Science. 2003;300:1921. doi: 10.1126/science.1080147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974;77:71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fraser A. G, Kamath R. S, Zipperlen P, Martinez-Campos M, Sohrmann M, et al. Functional genomic analysis of C. elegans chromosome I by systematic RNA interference. Nature. 2000;408:325–330. doi: 10.1038/35042517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Timmons L, Court D. L, Fire A. Ingestion of bacterially expressed dsRNAs can produce specific and potent genetic interference in Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene. 2001;263:103–112. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bell L. R, Stone S, Yochem J, Shaw J. E, Herman R. K. The molecular identities of the Caenorhabditis elegans intraflagellar transport genes dyf-6, daf-10 and osm-1. Genetics. 2006;173:1275–1286. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.056721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Perkins L. A, Hedgecock E. M, Thomson J. N, Culotti J. G. Mutant sensory cilia in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1986;117:456–487. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90314-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tabish M, Siddiqui Z. K, Nishikawa K, Siddiqui S. S. Exclusive expression of C. elegans osm-3 kinesin gene in chemosensory neurons open to the external environment. J Mol Biol. 1995;247:377–389. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Snow J. J, Ou G, Gunnarson A. L, Walker M. R, Zhou H. M, et al. Two anterograde intraflagellar transport motors cooperate to build sensory cilia on C. elegans neurons. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6:1109–1113. doi: 10.1038/ncb1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li C, Nelson L. S, Kim K, Nathoo A, Hart A. C. Neuropeptide gene families in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;897:239–252. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07895.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nathoo A. N, Moeller R. A, Westlund B. A, Hart A. C. Identification of neuropeptide-like protein gene families in Caenorhabditis elegans and other species. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:14000–14005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.241231298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Husson S. J, Mertens I, Janssen T, Lindemans M, Schoofs L. Neuropeptidergic signaling in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Prog Neurobiol. 2007;82:33–55. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2007.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Keating C. D, Kriek N, Daniels M, Ashcroft N. R, Hopper N. A, et al. Whole-genome analysis of 60 G protein-coupled receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans by gene knockout with RNAi. Curr Biol. 2003;13:1715–1720. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2003.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bendena W. G, Boudreau J. R, Papanicolaou T, Maltby M, Tobe S. S, et al. A Caenorhabditis elegans allatostatin/galanin-like receptor NPR-9 inhibits local search behavior in response to feeding cues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105:1339–1342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0709492105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cho S, Rogers K. W, Fay D. S. The C. elegans glycopeptide hormone receptor ortholog, FSHR-1, regulates germline differentiation and survival. Curr Biol. 2007;17:203–212. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2006.12.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Howard A. D, Wang R, Pong S. S, Mellin T. N, Strack A, et al. Identification of receptors for neuromedin U and its role in feeding. Nature. 2000;406:70–74. doi: 10.1038/35017610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Strand F. L. In: Neuropeptides - Regulators of physiological processes. Stevens C. F, editor. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Takiff H. E, Chen S-M, Court D. L. Genetic analysis of the rnc operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989;171:2581–2590. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.5.2581-2590.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dasgupta S, Fernandez L, Kameyama L, Inada T, Nakamura Y, et al. Genetic uncoupling of the dsRNA-binding and RNA cleavage activities of the Escherichia coli endoribonuclease III - the effect of dsRNA binding on gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1998;28:629–640. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Studier F. W, Rosenberg A. H, Dunn J. J, Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Boyer H. B, Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969;41:459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wilson H. R, Yu D, Peters I. H. K, Zhou J-G, Court D. L. The global regulator RNase III modulates translation repression by the transcription elongation factor N. EMBO J. 2002;21:4154–4161. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdf395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Grant S. G, Jessee J, Bloom F. R, Hanahan D. Differential plasmid rescue from transgenic mouse DNAs into Escherichia coli methylation-restriction mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87:4645–4649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Prehm P, Stirm S, Jann B, Jann K. Cell-wall lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli B. Eur J Biochem. 1975;56:41–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02205.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Prehm P, Schmidt G, Jann B, Jann K. The cell-wall lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli K-12. Structure and acceptor site for O-antigen and other substituents. Eur J Biochem. 1976;70:171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Klena J, Zhang P, Schwartz O, Hull S, Chen T. The core lipopolysaccharide of Escherichia coli is a ligand for the dendritic-cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule nonintegrin CD209 receptor. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:1710–1715. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.5.1710-1715.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pradel E, Parker C. T, Schnaitman C. A. Structures of the rfaB, rfaI, rfaJ, and rfaS genes of Escherichia coli K-12 and their roles in assembly of the lipopolysaccharide core. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:4736–4745. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4736-4745.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang P, Snyder S, Feng P, Azadi P, Zhang S, et al. Role of N-acetylglucosamine within core lipopolysaccharide of several species of gram-negative bacteria in targeting the DC-SIGN (CD209). J Immunol. 2006;177:4002–4011. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.6.4002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mair W, Piper M. D. W, Partridge L. Calories do not explain extension of life span by dietary restriction in Drosophila. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030223. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bishop N. A, Guarente L. Two neurons mediate diet-restriction-induced longevity in C. elegans. Nature. 2007;447:545–549. doi: 10.1038/nature05904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lakowski B, Hekimi S. The genetics of caloric restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:13091–13096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.22.13091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Avery L. The genetics of feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1993;133:897–917. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Weindruch R, Walford R. L. The retardation of aging and disease by dietary restriction. Springfield, IL: C. C. Thomas; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kimura K. D, Tissenbaum H. A, Liu Y, Ruvkun G. daf-2, an insulin receptor-like gene that regulates longevity and diapause in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1997;277:942–946. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5328.942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kenyon C, Chang J, Gensch E, Rudner A, Tabtiang R. A C. elegans mutant that lives twice as long as wild type. Nature. 1993;366:461–464. doi: 10.1038/366461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lin K, Dorman J. B, Rodan A, Kenyon C. daf-16: an HNF-3/forkhead family member that can function to double the life-span of Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1997;278:1319–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5341.1319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ogg S, Paradis S, Gottlieb S, Patterson G. I, Lee L, et al. The Fork head transcription factor DAF-16 transduces insulin-like metabolic and longevity signals in C. elegans. Nature. 1997;389:994–999. doi: 10.1038/40194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Apfeld J, O'Connor G, McDonagh T, DiStefano P. S, Curtis R. The AMP-activated protein kinase AAK-2 links energy levels and insulin-like signals to lifespan in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2004;18:3004–3009. doi: 10.1101/gad.1255404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cohen E, Bieschke J, Perciavalle R. M, Kelly J. W, Dillin A. Opposing activities protect against age-onset proteotoxicity. Science. 2006;313:1604–1610. doi: 10.1126/science.1124646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Troemel E. R, Chu S. W, Reinke V, Lee S. S, Ausubel F. M, et al. p38 MAPK regulates expression of immune response genes and contributes to longevity in C. elegans. PLoS Genet. 2006;2:e183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hsu A. L, Murphy C. T, Kenyon C. Regulation of aging and age-related disease by DAF-16 and heat-shock factor. Science. 2003;300:1142–1145. doi: 10.1126/science.1083701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Morley J. F, Morimoto R. I. Regulation of longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans by heat shock factor and molecular chaperones. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15:657–664. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E03-07-0532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kim D. H, Feinbaum R, Alloing G, Emerson F. E, Garsin D. A, et al. A conserved p38 MAP kinase pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans innate immunity. Science. 2002;297:623–626. doi: 10.1126/science.1073759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hilliard M. A, Bargmann C. I, Bazzicalupo P. C. elegans responds to chemical repellents by integrating sensory inputs from the head and the tail. Curr Biol. 2002;12:730–734. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00813-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hanada R, Teranishi H, Pearson J. T, Kurokawa M, Hosoda H, et al. Neuromedin U has a novel anorexigenic effect independent of the leptin signaling pathway. Nat Med. 2004;10:1067–1073. doi: 10.1038/nm1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Melcher C, Pankratz M. J. Candidate gustatory interneurons modulating feeding behavior in the Drosophila brain. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:e305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Melcher C, Bader R, Walther S, Simakov O, Pankratz M. J. Neuromedin U and its putative Drosophila homolog hugin. PLoS Biol. 2006;4:e68. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040068. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Park Y, Kim Y. J, Adams M. E. Identification of G protein-coupled receptors for Drosophila PRXamide peptides, CCAP, corazonin, and AKH supports a theory of ligand-receptor coevolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:11423–11428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.162276199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lindemans M, Janssen T, Husson S. J, Meelkop E, Temmerman L, et al. A neuromedin-pyrokinin-like neuropeptide signaling system in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;379:760–764. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.12.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Parker C. T, Kloser A. W, Schnaitman C. A, Stein M. A, Gottesman S, et al. Role of the rfaG and rfaP genes in determining the lipopolysaccharide core structure and cell surface properties of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:2525–2538. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2525-2538.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Livaja M, Zeidler D, von Rad U, Durner J. Transcriptional responses of Arabidopsis thaliana to the bacteria-derived PAMPs harpin and lipopolysaccharide. Immunobiology. 2008;213:161–171. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kimbrell D. A, Beutler B. The evolution and genetics of innate immunity. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2:256–267. doi: 10.1038/35066006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lee S. S, Kennedy S, Tolonen A. C, Ruvkun G. DAF-16 target genes that control C. elegans life-span and metabolism. Science. 2003;300:644–647. doi: 10.1126/science.1083614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Murphy C. T, McCarroll S. A, Bargmann C. I, Fraser A, Kamath R. S, et al. Genes that act downstream of DAF-16 to influence the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2003;424:277–283. doi: 10.1038/nature01789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Singh V, Aballay A. Heat-shock transcription factor (HSF)-1 pathway required for Caenorhabditis elegans immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:13092–13097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604050103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Partridge L, Gems D, Withers D. J. Sex and death: what is the connection? Cell. 2005;120:461–472. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kirkwood T. B. Understanding the odd science of aging. Cell. 2005;120:437–447. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Arantes-Oliveira N, Apfeld J, Dillin A, Kenyon C. Regulation of life-span by germ-line stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2002;295:502–505. doi: 10.1126/science.1065768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Austin J, Kimble J. glp-1 is required in the germ line for regulation of the decision between mitosis and meiosis in C. elegans. Cell. 1987;51:589–599. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Brooks K. K, Liang B, Watts J. L. The influence of bacterial diet on fat storage in C. elegans. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e7545. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007545. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Soukas A. A, Kane E. A, Carr C. E, Melo J. A, Ruvkun G. Rictor/TORC2 regulates fat metabolism, feeding, growth, and life span in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genes & Development. 2009;23:496–511. doi: 10.1101/gad.1775409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Wang M. C, O'Rourke E. J, Ruvkun G. Fat metabolism links germline stem cells and longevity in C. elegans. Science. 2008;322:957–960. doi: 10.1126/science.1162011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lenaerts I, van Eygen S, van Fleteren J. Adult-limited dietary restriction slows Gompertzian aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2007;1100:442–448. doi: 10.1196/annals.1395.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Greer E. L, Brunet A. Different dietary restriction regimens extend lifespan by both independent and overlapping genetic pathways in C. elegans. Aging Cell. 2009;8:113–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Panowski S. H, Wolff S, Aguilaniu H, Durieux J, Dillin A. PHA-4/Foxa mediates diet-restriction-induced longevity of C. elegans. Nature. 2007;447:550–555. doi: 10.1038/nature05837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Lee E. T, Go O. T. Survival analysis in public health research. Annu Rev Public Health. 1997;18:105–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.18.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Johnson T. E, Wu D, Tedesco P, Dames S, Vaupel J. W. Age-specific demographic profiles of longevity mutants in Caenorhabditis elegans show segmental effects. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56:B331–B339. doi: 10.1093/gerona/56.8.b331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Avery L, Horvitz H. R. Effects of starvation and neuroactive drugs on feeding in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Exp Zool. 1990;253:263–270. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402530305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Avery L, Shtonda B. B. Food transport in the C. elegans pharynx. J Exp Biol. 2003;206:2441–2457. doi: 10.1242/jeb.00433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Bargmann C. I, Horvitz H. R. Chemosensory neurons with overlapping functions direct chemotaxis to multiple chemicals in C. elegans. Neuron. 1991;7:729–742. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Bargmann C. I, Hartwieg E, Horvitz H. R. Odorant-selective genes and neurons mediate olfaction in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;74:515–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80053-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Bargmann C. I, Horvitz H. R. Control of larval development by chemosensory neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1991;251:1243–1246. doi: 10.1126/science.2006412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Hart A. C, Kass J, Shapiro J. E, Kaplan J. M. Distinct signaling pathways mediate touch and osmosensory responses in a polymodal sensory neuron. J Neurosci. 1999;19:1952–1958. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-06-01952.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Mori I, Ohshima Y. Neural regulation of thermotaxis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1995;376:344–348. doi: 10.1038/376344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Sawin E. R, Ranganathan R, Horvitz H. R. C. elegans locomotory rate is modulated by the environment through a dopaminergic pathway and by experience through a serotonergic pathway. Neuron. 2000;26:619–631. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)81199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Mak H. Y, Nelson L. S, Basson M, Johnson C. D, Ruvkun G. Polygenic control of Caenorhabditis elegans fat storage. Nat Genet. 2006;38:363–368. doi: 10.1038/ng1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Troemel E. R, Chou J. H, Dwyer N. D, Colbert H. A, Bargmann C. I. Divergent seven transmembrane receptors are candidate chemosensory receptors in C. elegans. Cell. 1995;83:207–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90162-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Kaplan J. M, Horvitz H. R. A dual mechanosensory and chemosensory neuron in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90:2227–2231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Chalasani S. H, Chronis N, Tsunozaki M, Gray J. M, Ramot D, et al. Dissecting a circuit for olfactory behaviour in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 2007;450:63–70. doi: 10.1038/nature06292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Li W, Feng Z, Sternberg P. W, Xu X. Z. S. A C. elegans stretch receptor neuron revealed by a mechanosensitive TRP channel homologue. Nature. 2006;440:684–687. doi: 10.1038/nature04538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Gene architecture and coding sequence of nmur-1 . (A) The gene structure of nmur-1 (C48C5.1) predicted by WormBase (version WS207; www.wormbase.org) consists of only 10 exons (shown in white). However, upon isolation and sequencing of the nmur-1 cDNA, we found that the nmur-1 gene locus includes a terminal 11th exon (shown in black) that encodes an additional 22 amino acids and is followed by a 210 bp 3′ UTR (gray). The extent of the ok1387 deletion is indicated by the hatched bar. (B) The nmur-1 cDNA sequence along with its translated protein sequence. The arrowheads indicate exon-intron boundaries within the DNA sequence, the 3′ UTR is italicized and the poly-A sequence used for priming the reverse transcription of the mRNA is framed. Within the protein sequence, the predicted seven transmembrane domains are underlined. The revised protein sequence shows 45% similarity and 27% identity to human NMUR1 and 47% similarity and 29% identity to human NMUR2 [24].
(0.37 MB TIF)
nmur-1 modulates food source-dependent effects on feeding rate, development, and reproduction. (A–B) Pharyngeal pumping rates of wild-type and mutant worms on different bacteria. Rates are expressed as mean pumps per minute and determined from the indicated number (n) of worms. ** indicates p≤0.001 in this and subsequent panels. Since wild type and nmur-1 mutants pump at a similar rate on HB101, a food source that does increase mutant lifespan compared to wild type (Figure 2E), the nmur-1 regulation of lifespan and feeding rate presumably involve two distinct pathways. (C) The wild-type nmur-1 genomic locus can also rescue the feeding rate phenotypes of nmur-1 mutants on OP50 (p = 0.02) and HT115 (p≤0.001). The rescued worms are compared to wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms that carry the myo-3p::rfp coinjection marker alone. * indicates p≤0.01 in this and later panels. (D) Distribution of developmental stages of wild-type and mutant worms at 36.5 h after hatching on different bacteria. L2, second-stage larvae; L3, third-stage larvae; L4, fourth-stage larvae; YA, young adults. Although both wild type and mutants develop faster on OP50 than on HB101 or HT115 (p<0.001 for either genotype), mutants develop slower than wild type on OP50 (p = 0.01). It should be noted that our observation of a slower wild-type developmental rate on HB101 at 25°C differs from a previous study carried out at 18°C [77], which suggests that temperature can alter the growth-influencing factors of some food sources. (E–F) Total progeny and temporal profiles of reproduction on different bacteria. nmur-1 mutants have less total progeny (E) than wild type on OP50 (p<0.01), and wild type has more progeny on OP50 than on HT115 (p = 0.03). The larger progeny number of nmur-1 mutants on HB101 (p = 0.04) is a consequence of censoring (see Materials and Methods). nmur-1 mutants reproduce more slowly (F) than wild type on HT115 but behave more similarly to wild type on OP50 and HB101.
(0.88 MB TIF)
The influence of the LPS structure on feeding, development, and reproduction of wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms. (A) Wild-type and mutant worms have similar pharyngeal pumping rates on both the CS2429 LPS truncation mutant and the CS180 parent strain. (B) nmur-1 mutant worms develop faster on the E. coli LPS mutant strain than on the E. coli parent strain (p<0.001) but slower than wild-type worms on both E. coli strains (p<0.001 for each case). nmur-1 mutants also (C) produce more offspring on the E. coli truncation mutant than on the E. coli parent strain (** p<0.001) and (D) reproduce at a similar rate, though slower than wild type, on both strains. Together our findings suggest that the nmur-1 regulation of lifespan, feeding rate, development, and reproduction involve more than one pathway and several food-derived factors.
(0.28 MB TIF)
The effect of a genetic model of food-level restriction on feeding, reproduction, and lifespan. Worms carrying the mutation eat-2(ad1116) display a reduced pharyngeal pumping rate (A), a smaller number of progeny (B), and increased lifespan (C) independent of their food source. Mean lifespan of eat-2 mutants: 16.8 d (+47%, p<0.0001) on OP50, 15.9 d (+41%, p<0.0001) on HT115.
(0.39 MB TIF)
Food source-dependent effects on age-specific rates of mortality. (A) Mortality plot of wild type on four different strains of E. coli. (B) Individual comparisons of wild-type and nmur-1 mutants on the four food sources.
(0.68 MB TIF)
Sensory neurons affected by cilium-structure genes. The subsets of sensory neurons affected by two sensory genes, daf-10 [15] and osm-3 [16], partly overlap. The superscripted symbols indicate the references that identify the neurons and their corresponding functions: a, [6]; b, [78],[79],[80]; c, [81]; d, [82]; e, [52]; and f, [83].
(0.03 MB DOC)
Adult lifespans of neuropeptide and neuropeptide receptor mutants tested at 25°C. We measured the lifespan of C. elegans grown on OP50 or HT115 and that carry mutations in genes that encode either neuropeptides or neuropeptide receptors. These neuropeptides or neuropeptide receptors show homologies to members of different neuropeptide signaling pathways in other animals, which are involved in regulating their feeding behavior and metabolism [19],[21]–[25]. The statistical analyses performed on these experiments are as described in the legend of Table 1.
(0.08 MB DOC)
Individual trials of adult lifespans on different food sources at 25°C. The analyses performed here are as described in the legend of Table 1. The superscripted symbols indicate the following: a, compared to the same genotype assayed in parallel on OP50 in independent trials; b, compared to jxEx4[myo-3p::rfp] on the same food source in independent trials; c, compared to the rescue line on the same food source in independent trials; and d, compared to the same genotype assayed in parallel on CS180 in independent trials.
(0.27 MB DOC)
Fat storage of wild-type and nmur-1 mutant worms on OP50 and HT115. Fat storage in 1-d-old adults is quantified by labeling the worms with C1-BODIPY-C12 according to Mak et al. [84]. All quantifications are normalized to wild type on OP50 and given as percent ± SEM. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of worms assayed for each condition. The superscript a indicates p = 0.042 compared to wild type on OP50.
(0.03 MB DOC)