Abstract
Genome sequencing of Streptomyces species has highlighted numerous potential genes of secondary metabolite biosynthesis. The mining of cryptic genes is important for exploring chemical diversity. Here we report the metabolite-guided genome mining and functional characterization of a cryptic gene by biochemical studies. Based on systematic purification of metabolites from Streptomyces sp. SN-593, we isolated a novel compound, 6-dimethylallylindole (DMAI)-3-carbaldehyde. Although many 6-DMAI compounds have been isolated from a variety of organisms, an enzyme catalyzing the transfer of a dimethylallyl group to the C-6 indole ring has not been reported so far. A homology search using known prenyltransferase sequences against the draft sequence of the Streptomyces sp. SN-593 genome revealed the iptA gene. The IptA protein showed 27% amino acid identity to cyanobacterial LtxC, which catalyzes the transfer of a geranyl group to (−)-indolactam V. A BLAST search against IptA revealed much-more-similar homologs at the amino acid level than LtxC, namely, SAML0654 (60%) from Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877 and SCO7467 (58%) from S. coelicolor A3(2). Phylogenetic analysis showed that IptA was distinct from bacterial aromatic prenyltransferases and fungal indole prenyltransferases. Detailed kinetic analyses of IptA showed the highest catalytic efficiency (6.13 min−1 μM−1) for l-Trp in the presence of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), suggesting that the enzyme is a 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp synthase (6-DMATS). Substrate specificity analyses of IptA revealed promiscuity for indole derivatives, and its reaction products were identified as novel 6-DMAI compounds. Moreover, ΔiptA mutants abolished the production of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde as well as 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp, suggesting that the iptA gene is involved in the production of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde.
Natural products have been an important resource for drug discovery and development. Actinomycetes have been a rich source of natural products, and a wide variety of these chemicals have been used as medicinal drugs (7, 40) and as bioprobes (56) for the elucidation of biological functions. Recently, the screening of bioactive compounds from microorganisms has often resulted in the identification of previously isolated compounds. The decreasing hit rate for new chemicals has reduced the advantage of natural product screening. However, genome sequencing of Streptomyces species highlighted numerous potential areas with metabolic diversity (4, 25, 42). The number of cryptic gene clusters was much larger than that of secondary metabolites identified from each strain. In addition, the cryptic gene clusters contained genes encoding plenty of unique modification enzymes that had the potential to expand the chemical diversity in drug seeds.
To uncover cryptic gene clusters that might code for biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, genome sequence-guided metabolite identification has been performed in combination with heterologous expression, gene knockout, and complementation analyses and silent gene activation studies. Many microbial metabolites have been discovered through genome mining approaches (5, 8, 26, 29, 34, 41, 50). On the other hand, predictions of protein function are not always successful from BLAST searches, because the substrates or products of unknown enzyme reactions cannot be predicted correctly. Only the type of protein function can be annotated by a homology search. The major difficulty for the identification of cryptic gene clusters is a lack of chemical information. Most gene clusters remain dormant or less active if there are no specific chemicals or physiological signals. Therefore, the discovery of secondary metabolites that are normally expressed at very low levels opens up a strategy for addressing the functions of cryptic gene clusters or unique genes. We performed a metabolite profiling and genome draft sequence analysis of a reveromycin A-producing strain, Streptomyces sp. SN-593 (43). Based on systematic isolation of secondary metabolites, we isolated a novel compound, 6-dimethylallylindole (DMAI)-3-carbaldehyde. There are many isolation reports on 6-DMAI derivatives from Streptomyces sp. (39, 46, 48), fungi (17, 24, 49), and plants (2, 3). However, the gene responsible for dimethylallyl transfer to the C-6 indole ring has not been identified for all living organisms. Because the unique modification enzyme retains a high potential to expand the diversity of natural products, we started a homology search and cloning of the target gene. Here we report the heterologous expression and biochemical characterization of a novel indole prenyltransferase (IptA) catalyzing the transfer of a dimethylallyl group to the C-6 indole ring.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals.
Ammonium salts of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP), farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), and geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) were purchased from Sigma. Ampicillin, kanamycin, and chloramphenicol were purchased from Nacalai (Kyoto, Japan). The indole derivatives with the highest purity were purchased from Wako, Sigma, Aldrich, Fluka, Alfa Aesar, and MP Biochemicals. Brevianamide F and tryprostatin B were isolated from Aspergillus fumigatus (27).
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and culture conditions.
The bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. Streptomyces sp. SN-593 cultures (43) were routinely grown at 28°C in an SY (0.1% yeast extract, 0.1% NZ-amine, 2% starch, and 1.5% agar) slant. For analysis of metabolites, one slant culture was inoculated into a 500-ml cylindrical flask containing 70 ml of YMG medium (0.5% malt extract [Difco], 0.5% yeast extract [Difco], 1.0% glucose, pH 6, before sterilization) for 3 days at 28°C on a rotary shaker at 150 rpm. One milliliter of preculture was inoculated into 500-ml cylindrical flasks containing 70 ml of the producing medium (2% potato dextrose [Difco], 1% malt extract [Difco], 1% dried yeast [Asahi beer], 5% tomato juice [Table Land; Maruzen Foods], 0.1% K2HPO4, 0.1% NaCl, 0.03% MgSO4·7H2O, 0.01% NaNO3, 0.005% ZnSO4·7H2O, and 0.005% CuSO4·5H2O, pH 6.5, before autoclaving) and was cultured for 5 days at 28°C on the same rotary shaker. Escherichia coli strains were grown at 37°C in LB broth (1% tryptone, 0.5% yeast extract, and 1% NaCl), LB Miller agar (Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Japan), or Terrific broth (1.2% Bacto tryptone, 2.4% yeast extract, 0.4% glycerol, 0.231% KH2PO4, and 1.254% K2HPO4). Ampicillin (100 μg ml−1), kanamycin (50 μg ml−1), and chloramphenicol (15 μg ml−1) were added for selection of plasmid-containing E. coli cells.
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains, plasmids, and primers
| Strain, plasmid, or primer | Relevant characteristic(s) or primer sequence (5′-3′) | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| Streptomyces sp. SN-593 | Wild-type reveromycin A-producing strain | 43 |
| E. coli DH5α | Cloning host | Takara |
| E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) | Host strain for recombinant protein expression | Invitrogen |
| E. coli EPI300-T1 | Host strain for fosmid library construction | Epicentre Biotechnology |
| E. coli BW 25113 | lacIqrrnBT14 ΔlacZWJ16hsdR514 ΔaraBADAH33 ΔrhaBADLD78 (derivative of the F− λ−E. coli K-12 strain BD792 [CGSC6159]) | 12 |
| E.coli conjugation strain | E. coli GM2929 hsdS::Tn10 carrying pUB307-aph::Tn7 | 26 |
| Plasmids | ||
| pUC118 | General cloning vector with multiple cloning sites; 2- to 5-kb DNA fragments from Streptomyces sp. SN-593 were inserted into HincII site | Takara |
| pET28b | T7 RNA polymerase-dependent recombinant protein expression vector; an N-terminal His6 tag allows protein purification by Ni-affinity column chromatography | Takara |
| pET28b(+)-iptA | The iptA fragment (1,158 bp) was inserted into NdeI and XhoI sites of pET28b(+) | This study |
| pCC1FOS | Optimum vector for constructing a fosmid library harboring about 40 kb of DNA fragments | Epicentre Biotechnology |
| pKU250 | E. coli-Streptomyces conjugation vector | 29 |
| pIM | DNA region between BamHI and KpnI sites was removed from pKU250 | This study |
| pIM-ΔiptA | iptA gene disruption plasmid | This study |
| pKD46 | Red recombinase expression plasmid | 12 |
| pKD13 | Template plasmid for FRT-flanked kanamycin resistance gene | 12 |
| Primers | ||
| NdeI-F | GGAATTCCATATGGTGACCGGCGGCCGCTCCCCGAa | This study |
| XhoI-R | CCGCTCGAGTCAGCGTCCGATCCCGGGCCCGGTa | This study |
| iptA-For-P4 | GAGCCGACGCAGCTCGGTGGTCTCGTCACCGACCAGCTCATTCCGGGGATCCGTCGACCb | This study |
| iptA-Rev-P1 | CTGCACCGCGTACGCCTCGGAGGAGACGTAGACGGTGACTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTCb | This study |
| iptA-SalI-F | GTCGACCTGCTCAACGACTACGCC | This study |
| iptA-SalI-R | GTCGACCATCAGCAGGGCCGTACC | This study |
Underlining indicates the corresponding restriction enzyme sites.
Underlining shows the 39-bp sequence homologous to the target DNA region.
Isolation and structural determination of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde.
Ten liters of culture broth from producing medium was extracted with an equal volume of acetone and concentrated to remove acetone. The pH of the aqueous extract was adjusted to 4 by adding acetic acid, and the extract was extracted twice with an equal volume of ethyl acetate. The organic layer was concentrated in vacuo to give 6 g of dark red residue. The concentrated extract was applied to a silica gel column (120-g silica-packed column [ISCO Combi Flash Companion]), equilibrated with chloroform, and eluted with a 97:3 to 95:5 mixture of chloroform-methanol. Subsequently, the fraction was separated by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) on a Senshu Pak Pegasil ODS column with methanol-0.05% formic acid in an H2O gradient system (70 to 100% methanol in 40 min) to obtain 70 subfractions. Subfraction 20 was purified on a reversed-phase HPLC (RP-HPLC) with a Senshu Pak Pegasil ODS column by the elution of acetonitrile-0.05% HCOOH in an H2O gradient system (70 to 90% acetonitrile in 30 min). It gave 1.3 mg of pale yellow powder.
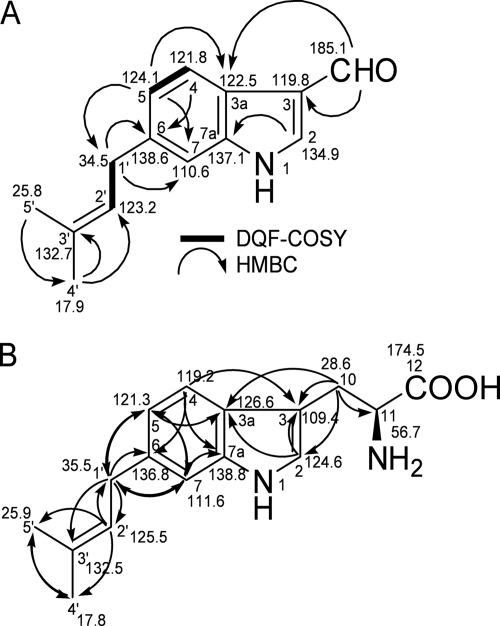
The molecular formula was established by high-resolution past atom bombardment mass spectrometry (HRFAB-MS) on a JEOL JMS-700 instrument as C14H15NO (m/z 214.1245 [M + H]+; calculated value for C14H16NO, 214.1232): the UV (methanol) λmax (log ɛ) values were 215 (3.95), 246 (3.91), 265 (3.93), and 295 (3.82) nm. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra were recorded with CDCl3 at 500 MHz on a JEOL ECP500 spectrometer. The NMR data suggested that the compound had a dimethylallyl group, as follows: δC 17.7 (C-4′, δH 1.73, s, 3H), 25.8 (C-5′, δH 1.75, s, 3H), 132.7 (C-3′), 123.2 (C-2′, δH 5.35, t, 1H, J = 7 Hz), and 34.5 (C-1′, δH 3.45, d, 2H, J = 7 Hz) ppm. The structure was confirmed by analysis of the two-dimensional (2D) NMR spectra. The HSQC spectrum revealed connections between protons and carbons. The DQF-COSY spectra showed the connectivity between H-4 and H-5 and between H-1′ and H-2′, which was supported by the coupling constants in the 1H NMR spectrum. The observed long-range correlations in the HMBC spectrum are shown in Fig. 1. In addition, H-2 and H-7 were observed as singlet protons in the 1H NMR spectrum. These data allowed the identification of the 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde structure. Assuming that the H-7 was attached to C-4, the dimethylallyl group might be located at C-5. In that case, however, the observed long-range correlation from the proton at 7.14 ppm (H-7) to C-3a was unlikely, because it was a four-bond distance. Thus, the dimethylallyl group was located at C-6, and the structure was determined to be 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde.
FIG. 1.
Structures of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde (A) and 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp (B) with key 2D NMR correlations. The bold lines and arrows show DQF-COSY and HMBC correlations, respectively.
Genome sequencing and homology search.
The draft sequence of the Streptomyces sp. SN-593 genome was determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy. Plasmid libraries with an average insert size of 2 to 5 kb were constructed. A fosmid library of Streptomyces sp. SN-593 was created using a copy control fosmid library production kit (Epicentre Biotechnology). The fosmid clones harbored about 40 kb of DNA fragments in the vector. End sequencing was carried out using a BigDye Terminator ver3.1 kit (Applied Biosystems). Sequencing products were run on automated model 3730xl capillary sequencers (Applied Biosystems). The Sanger data were assembled with the KB/Phrap/Consed system (15, 16, 19). A homology search was then carried out against the generated contig data, using BLASTP (1). Low-quality regions in the selected contig sequence were resequenced by PCR, primer walking, and shattered insert libraries (37).
DNA manipulation.
DNA isolation and manipulation were performed as described previously (45). Genomic DNA was isolated from Streptomyces sp. SN-593 as described in Practical Streptomyces Genetics (28). DNA fragments were isolated from agarose by use of a gel extraction kit (Qiagen). Plasmids were purified using Wizard Plus SV miniprep kits (Promega). PCR amplification was carried out using a DNAEngine Peltier thermal cycler (Bio-Rad).
Expression and purification of His-tag-free IptA for biochemical analysis.
A PCR fragment of 1,158 bp containing iptA was amplified from fosmid clone 4C04, using PrimeSTAR DNA polymerase (TaKaRa) and the primers listed in Table 1. After overnight LB-kanamycin (50 μg ml−1) culture of E. coli BL21 Star (DE3) that harbored pET28b(+)-iptA, cells were inoculated into 3 liters of Terrific broth-kanamycin (50 μg ml−1) and cultured at 37°C. Preculture was added to reach an initial optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of 0.1. When the absorbance at 600 nm reached a value of 0.5, IPTG (isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside) was added to a final concentration of 0.5 mM. After growth for 6 h at 28°C, cells were harvested by centrifugation and frozen at −80°C. All subsequent steps were carried out at 4°C. After thawing on ice, cells were suspended in 100 ml buffer A (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 500 mM NaCl, 5 mM imidazole, and 10% glycerol) including 0.5 mg ml−1 lysozyme and 500 U Benzonase (Sigma). The cell suspension was sonicated 10 times on ice for 10 s each, with 1-min intervals between each sonication (Tomy UD-200 sonicator). Cellular debris was removed by centrifugation (10,000 × g for 30 min) (Tomy SRX-201 instrument). The supernatant was applied to a Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) column (2 × 8 cm) (Qiagen) that was equilibrated with buffer A and washed with 100 ml of buffer A containing 0.2% Tween 20. After being washed with 100 ml of buffer A, the column was further washed with 100 ml of buffer A containing 40 mM imidazole. His-tag-binding protein (33 mg) was eluted with 85 ml of buffer A containing 200 mM imidazole. Protein (30 mg) from the Ni-NTA fraction was used for large-scale reactions for product identification. The remaining His-tagged IptA was treated with 100 units of thrombin and dialyzed against 1 liter of buffer B (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 500 mM NaCl, and 10% glycerol) for 3 h and against 2 liters of buffer B for 10 h. The pass-through fraction from the Ni-NTA column (2 × 8 cm) was applied directly to a benzamidine Sepharose column (1.5 × 3 cm) to remove thrombin. The purity of His-tag-free IptA (1.27 mg) was analyzed by SDS-PAGE (33).
To investigate its multimeric status, IptA was dialyzed against buffer C (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 200 mM NaCl, and 10% glycerol) and applied to a Superdex 200 column (GE Healthcare), previously equilibrated with buffer C, at a flow rate of 0.8 ml min−1. The column was calibrated with ferritin (440 kDa), aldolase (158 kDa), conalbumin (75 kDa), ovalbumin (43 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa), RNase A (13.7 kDa), and aprotinin (6.5 kDa). The elution was established over 80 min, and the peak corresponding to a molecular mass of 40 kDa was concentrated to 0.915 mg ml−1 with Amicon Ultracel-30K microconcentrators (Millipore Corporation) and stored at −80°C for enzyme characterization. The highly purified His-tag-free IptA protein was used for biochemical characterization.
Prenyltransferase assay.
Standard assays were performed in 1.5-ml tubes with a final reaction volume of 100 μl containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.2 mM DMAPP, 0.5 mM substrate, and 16 to 60 pmol purified enzyme. For kinetic analyses, the substrate (prenyl acceptor) concentration was varied from 10 to 1,000 μM for l-Trp, 2 to 1,000 μM for l-abrine, 2 to 1,000 μM for α-methyl-dl-Trp, 2 to 500 μM for 5-hydroxy-l-Trp, and 1 to 1,000 μM for indole-3-carbaldehyde. The prenyl donor (DMAPP) concentration was varied from 6 to 240 μM. After preincubation of the reaction mixture at 30°C for 3 min, the reactions were initiated by the addition of enzyme and allowed to proceed for 0.5 min (l-Trp), 1 min (l-abrine), 0.5 min (α-methyl-dl-Trp), 1 min (5-hydroxy-l-Trp), or 90 min (indole-3-carbaldehyde). The reaction was terminated by the rapid addition of 0.5 μl formic acid and mixing by vortexing. After the addition of 10 μl acetonitrile, the mixture was centrifuged at 20,000 × g for 10 min (Kubota 3700 machine) at 4°C to remove protein. The supernatant was subjected to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and the area under the prenylated product peak was measured. The amount of the prenylated product peak was calculated with a standard curve, which was obtained by using the maximum UV wavelength of each substrate. All of the substrates used were subjected to HPLC at a concentration range of 0.01 to 1 nmol for their calibration. The enzyme-specific activity (nmol product formed min−1 nmol enzyme−1) for various indole substrates was calculated by time-dependent product formation. The kinetic constants were calculated by nonlinear regression fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation. Kinetic constants calculated from Lineweaver-Burk, Eadie-Hofstee, and Hanes-Woolf plots were not significantly different from those derived from nonlinear regression.
Analyses of enzyme reaction products.
An electrospray ionization (ESI)-MS analysis was carried out by using a Waters Alliance HPLC system equipped with a mass spectrometer (Q-Trap; Applied Biosystems). The HPLC conditions were as follows: column, XTerraMSC18 5-μm (2.1 × 150 mm) column; flow rate, 0.2 ml min−1; solvent A, H2O containing 0.05% formic acid; and solvent B, acetonitrile. After injection of the sample into a column equilibrated with 10% solvent B, the column was developed with a linear gradient of 10% to 100% solvent B over 30 min. Mass spectra were collected in either ESI-negative or ESI-positive mode.
Structural analyses of enzyme reaction products.
For the identification of enzyme reaction products, 10 ml of reaction mixture containing 0.2 to 1.8 mg purified His-tagged IptA was incubated for 12 h with Trp derivatives, such as l-Trp, 5-hydroxy-l-Trp, 4-methyl-dl-Trp, 5-methoxy-l-Trp, 6-methyl-dl-Trp, and l-abrine. The solutions of reactants were concentrated by an evaporator to a volume of 2 ml, and 400 μl was injected into a Senshu Pak Pegasil ODS column (10 × 250 mm; SSC). The isolation was carried out using a Waters 600 HPLC system with a photodiode array detector (model 2996 PDA detector), and conditions of the preparations were as follows: flow rate, 4.5 ml min−1; solvent A, water containing 0.05% formic acid; and solvent B, acetonitrile. After injection of the sample into a column equilibrated with 35% acetonitrile, the column was developed by same-solvent isocratic elution for 60 min.
(i) 6-Dimethylallyl-l-Trp.
The molecular formula was established as C16H20N2O2 by HRFAB-MS (m/z 273.1637 [M + H]+; calculated value for C16H21N2O2, 273.1603): the UV (methanol) λmax (log ɛ) values were 226 (4.14), 250 (3.75), and 288 (3.55) nm; [α]D24, +19.4 (c 0.07, methanol). The NMR spectra were recorded with CD3OD, and the structural assignments were confirmed by the 1H, 13C, COSY, HSQC, and HMBC NMR spectra. A dimethylallyl group was confirmed by the NMR data as follows: δC 17.8 (C-4′, δH 1.73, s, 3H), 25.9 (C-5′, δH 1.73, s, 3H), 132.5 (C-3′), 125.5 (C-2′, δH 5.34, t, 1H, J = 7.3 Hz), and 35.5 (C-1′, δH 3.40, d, 2H, J = 7.3 Hz). The indole ring system was confirmed by the comparison of 13C NMR chemical shifts with those of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde and long-range correlations in the HMBC spectra (Fig. 1B). The assignments of the indole ring were as follows: δC 124.6 (C-2, δH 7.11, s 1H), 109.4 (C-3), 126.6 (C-3a), 119.2 (C-4, δH 7.58, d, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 121.3 (C-5, δH 6.88, dd, 1H, J = 8.0, 1.2 Hz), 136.8 (C-6), and 111.6 (C-7, δH 7.14, br s, 1H) ppm. In addition, the long-range correlation from H-1′ to C-5, C-6, and C-7 suggested that the dimethylallyl group was attached to the C-6 position of the indole ring. Thus, the structure was determined to be 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp.
(ii) 5-Hydroxy-6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp.
The molecular formula was established as C16H20N2O3 by HRESI-TOF-MS (m/z 287.1421 [M − H]−; calculated value for C16H19N2O3, 287.1395); [α]D26, +90.5° (c 0.081, methanol). UV (methanol) λmax (log ɛ) values were 226 (4.32) and 285 (3.74) nm. The NMR spectra were recorded with CD3OD, and the 1H and 13C chemical shift assignments were confirmed by 1H, 13C, DQF-COSY, HSQC, and HMBC spectra, as follows: δC 174.6 (s, C-12), 150.0 (s, C-5), 133.5 (s, C-7a), 132.6 (s, C-3′), 126.9 (s, C-3a), 126.0 (s, C-6), 124.8* (d, C-2), 124.7* (d, C-2′), 112.5 (d, C-7), 108.6 (s, C-3), 103.3 (d, C-4), 56.5 (d, C-11), 29.9 (t, C-1′), 28.9 (t, C-10), 26.0 (q, C-5′), and 17.8 (q, C-4′). *, 13C chemical shifts were exchangeable at C-2 and C-2′, as follows: δH 7.05 (1H, s, H-2), 7.03 (1H, s, H-7), 6.99 (1H, s, H-4), 5.36 (1H, t, J = 7.3 Hz, H-2′), 3.80 (1H, br dd, J = 9.2, 3.7 Hz, H-11), 3.43 (1H, dd, J = 15.1, 3.7 Hz, H-10a), 3.36 (2H, d, J = 7.3 Hz,H-1′), 3.02 (1H, dd, J = 15.1, 10.1 Hz H-10b), 1.74 (3H, s, Me-5′), and 1.71 (3H, s, Me-4′). The position of the C-6 substituent was confirmed by the long-range correlations from H-1′ to C-5, C-6, and C-7 in the HMBC spectrum.
(iii) 4-Methyl-6-dimethylallyl-Trp.
The molecular formula was established as C17H22N2O2 by HRESI-TOF-MS (m/z 287.1770 [M + H]+; calculated value for C17H23N2O2, 287.1759). The proton chemical shifts in CD3OD were assigned as follows: δH 7.07 (1H, s, H-2), 6.96 (1H, s, H-5), 6.60 (1H, s, H-7), 5.32 (1H, t, J = 7.3 Hz, H-2′), 3.77 (1H, br s, H-11), 3.76 (1H, br s, H-10b), 3.07 (1H, dd, J = 15.1, 10.5 Hz, H-10), 2.68 (3H, s, 4-Me), 1.73 (6H, s, Me-4′, 5′); [α]D26, −40.8° (c 0.047, methanol). The UV (methanol) λmax (log ɛ) values were 226 (3.26) and 272 (2.45) nm. The confirmation of the 6-dimethylallyl substituent was established by the observation of two signals, at δH 6.96 (H-5, s, 1H) and 6.60 (H-7, s, 1H) ppm, as singlets in the 1H NMR spectrum.
(iv) 5-Methoxy-6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp.
The molecular formula was established as C17H22N2O2 by HRFAB-MS (m/z 303.1775 [M + H]+; calculated value for C17H23N2O2, 303.1708); [α]D24, +4.6 (c 0.065, methanol). The UV (methanol) λmax (log ɛ) values were 226 (3.79), 274 (3.33), and 298 (3.39) nm. The 1H and 13C chemical shifts were assigned as follows: δC 174.7 (s, C-12), 153.7 (s, C-5), 133.4 (s, C-7a), 132.5 (s, C-3′), 127.1 (s, C-6), 126.7 (d, C-3a), 124.73 (d, C-2), 124.69 (d, C-2′), 112.7 (d, C-7), 109.3 (s, C-3), 100.0 (d, C-4), 56.6 (d, C-11), 56.4 (q, 5-OMe), 30.1 (t, C-1′), 26.0 (q, C-5′), 28.8 (t, C-10), and 17.8 (q, C-4′); and δH 7.19 (1H, s, H-4), 7.09 (1H, s, H-7), 7.07 (1H, s, H-2), 5.31 (1H, t, J = 7.3 Hz, H-2′), 3.88 (3H, s, 5-OMe), 3.84 (1H, br dd, J = 3.7, 9.2 Hz, H-11), 3.47 (1H, dd, J = 3.7, 15.1 Hz, H-10b), 3.34 (2H, d, J = 6.9 Hz, H-1′), 3.08 (1H, dd, J = 9.2, 15.1 Hz, H-10b), 1.72 (3H, s, Me-5′), and 1.70 (3H, s, Me-4′). The position of the dimethylallyl substituent was assigned at C-6 by the observation of two signals of H-4 and H-7 as a singlet in the 1H NMR spectrum. It was confirmed by the long-range correlations of H-1′ with C-6 and C-7 in the HMBC spectrum.
(v) 6-Methyl-7-dimethylallyl-Trp.
[α]D26, −155.6° (c 0.03, methanol). The UV (methanol) λmax (log ɛ) values were 221 (4.17) and 281 (3.46) nm. HRESI-TOF-MS showed m/z 287.17374 [M + H]+ (calculated value for C17H23N2O2, 287.17595). 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts were as follows: δC 137.9 (s, C-7a), 132.4 (s, C-3′), 129.8 (s, C-6), 127.2 (s, C-3a), 124.5 (d, C-2), 123.8 (d, C-2′), 123.6 (d, C-5), 123.4 (s, C-7), 116.9 (d, C-4), 110.5 (s, C-3), 57.1 (d, C-11), 29.5 (t, C-10), 27.9 (t, C-1′), 25.8 (q, C-5′), 19.2 (q, 6-Me), and 18.1 (q, C-4′); and δH 7.41 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-4), 7.10 (1H, s, H-2), 6.86 (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz, H-5), 5.09 (1H, t, J = 6.4 Hz, H-2′), 3.76 (1H, br dd, J = 7.3, 4.1 Hz, H-11), 3.54 (2H, br d, J = 6.4Hz, H-1′), 3.41 (1H, br s, H-10a), 3.05 (1H, br s, H-10b), 2.33 (3H, s, 6-Me), 1.82 (3H, s, Me-4′), and 1.67 (3H, s, Me-5′). These data were found to be identical to those for 6-methyl-7-dimethylallyl-Trp.
(vi) 6-Dimethylallyl-l-abrine.
The molecular formula was established as C17H22N2O2 by HRESI-TOF-MS as follows: m/z 285.1585 [M − H]−; calculated value for C17H21N2O2, 285.1603; [α]D26, −73.9° (c 0.044, methanol). The UV (methanol) λmax (log ɛ) values were 225 (4.57), 271 (3.87), and 292 (3.80) nm. The NMR spectra were recorded with CD3OD. The structure was supported by comparison of the 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts with those of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde and also confirmed by the analysis of HMBC correlations. The 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts were assigned as follows: δC 173.5 (s, C-12), 138.8 (s, C-7a), 136.8 (s, C-6), 132.5 (s, C-3′), 126.7 (s, C-3a), 125.5 (d, C-2′), 124.7 (d, C-2), 121.3 (d, C-5), 119.2 (d, C-4), 111.6 (d, C-7), 108.7 (s, C-3), 65.3 (d, C-11), 35.5 (t, C-1′), 33.1 (q, 11-NH-Me), 27.7 (t, C-10), 25.9 (q, C-5′), and 17.8 (q, C-4′); and δH 7.57 (1H, d, J = 8.2 Hz, H-4), 7.14 (2H, br s, H-2, 7), 6.88 (1H, dd, J = 8.2, 1.4 Hz, H-5), 5.34 (1H, t, J = 7.3 Hz, H-2′), 3.75 (1H, br dd, J = 7.3, 4.1 Hz, H-11), 3.44 (1H, dd, J = 15.6, 4.1 Hz, H-10a), 3.39 (2H, br d, J = 7.3 Hz, H-1′), 3.24 (1H, dd, J = 15.6, 7.3 Hz, H-10b), 2.55 (3H, s, 11-NH-Me), and 1.73 (6H, s, Me-4′,5′). The dimethylallyl group was attached at the C-6 position by the observation of the H-5 signal as a double doublet, with coupling constants of 8.2 and 1.4 Hz, in the 1H NMR spectrum. It was also supported by the long-range correlations of H-1′ with C-5, C-6, and C-7 in the HMBC spectrum.
Plasmid construction and disruption of iptA gene.
The fosmid clone 4C04 was digested with BamHI and BglII. The 7.89-kb BamHI fragment containing the iptA gene fragment was separated by 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis and ligated into a pIM vector to construct pIM-iptA (Table 1). The iptA gene was inactivated by PCR-targeted gene replacement according to the literature protocol (22). Plasmids (pKD46 and pKD13) and E. coli BW25113 were supplied by Hirotada Mori (Nara Institute of Science and Technology). Chloramphenicol-resistant (Cmr) pKD46, containing λ Red-mediated recombination functions, was used with ampicillin-resistant pIM-iptA. The pIM-iptA plasmid was transformed into E. coli BW25113 harboring pKD46. The iptA gene was then replaced with the aphII gene cassette to construct an iptA gene disruption vector (pIM-ΔiptA). Plasmid pKD13 was used as the template for the aphII gene cassette (12). The primer pairs listed in Table 1 were used to construct pIM-ΔiptA.
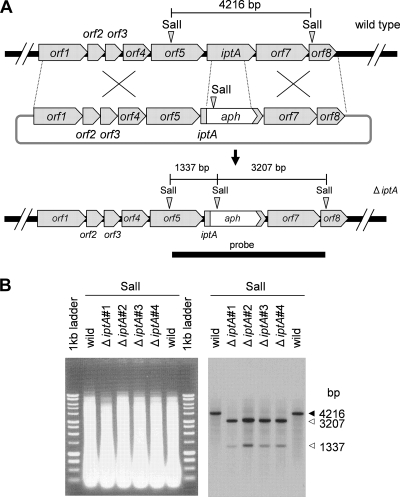
Conjugation was performed according to a standard procedure (28), with the following modifications. Streptomyces sp. SN-593 spores were suspended in SY medium and incubated at 28°C for 4 h. The spores were mixed with E. coli GM2929 hsdS::Tn10 (pUB307::Tn7) (26) harboring pIM-ΔiptA and spread onto a modified MS [3% soy flour, 2% d-(−)-mannitol, 2% agar] plate (20 ml) containing 25 mM MgCl2. After incubation at 28°C for 20 h, each plate was overlaid with 1.5 ml of sterilized water to give a final concentration of 20 μg ml−1 thiostrepton and 5 μg ml−1 carumonum. An SY plate containing 0.5 μg ml−1 ribostamycin (Sigma) was used for second selection. After SY culture (70 ml) and sporulation on the MS plate, four iptA gene disruptants were selected by the ribostamycin-resistant and thiostrepton-sensitive phenotype. Gene replacement was confirmed by Southern blot analysis.
Preparation of probes for Southern hybridization.
DNA probes for Southern analysis were amplified from pIM-ΔiptA by use of PrimeSTAR DNA polymerase under the following conditions: 98°C for 10 s and 25 cycles of 98°C for 10 s, 66°C for 5 s, and 68°C for 3.5 min. The primers used are listed in Table 1. The amplified DNA was purified by gel extraction and labeled with AlkPhos Direct labeling reagents (GE Healthcare).
LC-MS detection of 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp and 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde.
The wild type and the iptA gene disruptant were inoculated into a 500-ml cylindrical flask containing 70 ml of SY medium for 2 days at 28°C. One milliliter of the preculture was inoculated into a 500-ml cylindrical flask containing 70 ml of the producing medium. Five days after inoculation at 28°C, a total of 280 ml of culture broth was extracted with an equal volume of acetone and concentrated to remove acetone. The pH of the aqueous extract was adjusted to 4 by adding acetic acid and then extracted twice with a half-volume of ethyl acetate. After sodium sulfate treatment, the ethyl acetate layer was concentrated in vacuo to give about 170 mg of red residue. The concentrated extract was applied to an MPLC system (ISCO) equipped with a RediSep column (12-g silica gel column; ISCO). To collect 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde reproducibly, stepwise elution (100 ml) was performed at a flow rate of 30 ml min−1, using a chloroform-methanol solvent system (100:0, 100:1, 100:5, 100:10, 100:20, 100:50, 50:50, and 0:100). The chloroform-methanol (100:1) fraction (39 mg) containing 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde was concentrated and dissolved in 20 ml of methanol. The sample (5 μl) was applied to LC-MS analysis. To detect 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp, the water layer after ethyl acetate extraction was extracted twice with a half-volume of n-butanol. The n-butanol layer was concentrated and dissolved in 2 ml of methanol, and the sample (1 μl) was applied to LC-MS analysis. LC/ESI-MS was performed as described in “Analyses of enzyme reaction products.”
Nucleotide sequence accession number.
The GenBank accession number for the analyzed sequence is AB512764.
RESULTS
Identification of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde and discovery of novel prenyltransferase.
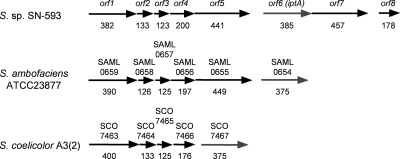
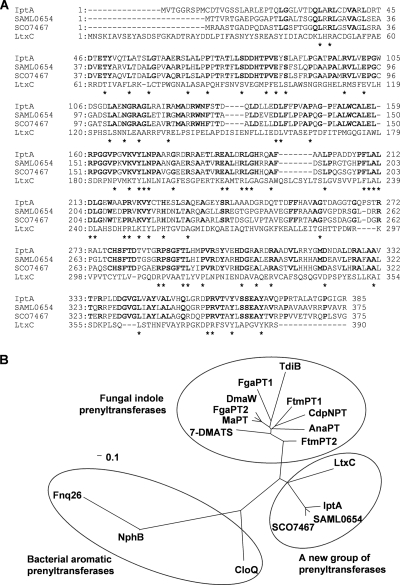
Based on a UV- and LC-MS-guided approach, we isolated a novel natural product, 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde, from Streptomyces sp. SN-593 (Fig. 1A). Although 6-DMAI-related compounds are widely distributed in living organisms (Table 2), the biosynthetic gene has not been reported. Therefore, the finding of a unique 6-DMAI metabolite prompted us to clone the gene responsible for the dimethylallyl transfer to the C-6 indole ring. The contig information obtained from genome draft sequencing of Streptomyces sp. SN-593 was utilized to search for the gene. BLAST searches against all known prenyltransferases revealed one putative prenyltransferase, designated IptA in the genetic organizations shown in Fig. 2 and Table 3. The genomic DNA sequence of iptA consists of 1,158 bp, and the predicted gene product comprises 385 amino acids with a molecular mass of 41.3 kDa. IptA showed weak homology (E value of 9e−16, 27% amino acid identity) to LtxC, which was found in the lyngbyatoxin A biosynthetic gene cluster from the cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscule (14). A BLAST search against IptA revealed much-more-similar homologs than LtxC, i.e., SAML0654 (60%) from Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877 and SCO7467 (58%) from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), at the amino acid level (Fig. 3A). Phylogenetic analysis showed three distinct groups: bacterial aromatic prenyltransferases, fungal indole prenyltransferases, and a new group of prenyltransferases which includes IptA, SAML0654, and SCO7467 (Fig. 3B). These new prenyltransferases from Streptomyces are positioned between bacterial aromatic prenyltransferases and fungal indole prenyltransferases.
TABLE 2.
Summary of 6-dimethylallylindole metabolites
FIG. 2.
Distributions of IptA homologs in Streptomyces spp. The genetic organization harboring orf6 (iptA) from Streptomyces sp. SN-593 is compared with the genetic organizations for S. ambofaciens ATCC 23877 and S. coelocolor A3(2). Numbers of amino acid residues are shown below the arrows.
TABLE 3.
Gene annotation and comparison with homologous proteins in the public databasea
| ORF (gene) no. | Size (aa) | Function (speculated) | Gene product description in NCBI database (species) | % Identity/% similarity (E value) | GenBank accession no. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 382 | Histidine kinase | Putative sensor histidine kinase (Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 53653) | 77/84 (2e−166) | ZP_05517175 |
| 2 | 133 | Unknown | Hypothetical protein (Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 53653) | 88/93 (1e−60) | ZP_05517174 |
| 3 | 123 | Unknown | Hypothetical protein (Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 53653) | 80/87 (6e−42) | ZP_05517173 |
| 4 | 200 | ATP/GTP-binding protein | Putative ATP/GTP-binding protein (Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 53653) | 87/92 (1e−93) | ZP_05517172 |
| 5 | 441 | P450 | Putative cytochrome P450 (Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877) | 66/81 (6e−177) | CAJ89641 |
| 6 (iptA) | 385 | Indole prenyltransferase | Hypothetical protein (Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877) | 60/69 (7e−107) | CAJ89640 |
| 7 | 457 | Tryptophan indole-lyase | Putative tryptophanase (Streptomyces sp. AA4) | 65/76 (1.3e−163) | ZP_05476463 |
| 8 | 178 | Unknown | Hypothetical protein (Streptomyces hygroscopicus ATCC 53653) | 68/82 (1e−68) | ZP_05518023 |
The date of analysis was November 2009.
FIG. 3.
Multiple sequence alignment of IptA homologs and phylogenetic analysis of microbial prenyltransferases. (A) The amino acids conserved in all four proteins are indicated by asterisks. Dashes indicate gaps introduced for optimization of the alignment. IptA is from Streptomyces sp. SN-593 (GenBank accession no. AB512764), SAML0654 is from Streptomyces ambofaciens ATCC 23877 (CAJ89640), SCO7467 is from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) (NP_631515), and LtxC is from a cyanobacterium (AAT12285). Bold letters show the identical amino acids among IptA, SAML0654, and SCO7467. (B) Phylogenetic tree of microbial prenyltransferases. CLUSTALW (http://clustalw.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/top-j.html) was used for alignment. An unrooted phylogenetic tree was produced using the TREE VIEW program (http://taxonomy.zoology.gla.ac.uk/). The scale bar corresponds to a genetic distance of 0.1 substitution per position. The Streptomyces prenyltransferases (GenBank accession no.) used were Fnq26 (CAL34104) from Streptomyces cinnamonensis, NphB (BAE00106) from Streptomyces sp. CL 190, and CloQ (AAN65239) from Streptomyces roseochromogenes. The fungal indole prenyltransferases (GenBank accession no.) used were DmaW (Q6X2E0) from Claviceps purpurea; FtmPT1 (AAX56314), FtmPT2 (EU622826), FgaPT1 (XP_756136), FgaPT2 (AAX08549), CdpNPT (ABR14712), and 7-DMATS (ABS89001) from Aspergillus fumigatus; TdiB (ABU51603) from Aspergillus nidulans; MaPT (ABZ80612) from Malbranchea aurantiaca; and AnaPT (EAW16181) from Neosartorya fischeri.
Heterologous expression and purification of prenyltransferase.
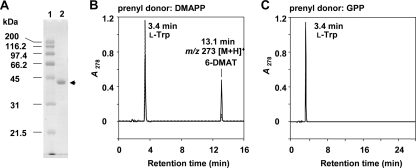
For biochemical characterization, the iptA gene was amplified and cloned into the pET28b(+) expression vector. The construct was introduced into E. coli BL21 Star (DE3). Induction with IPTG, NTA column purification, thrombin digestion, removal of the His tag by a second Ni-NTA column, and benzamidine Sepharose and Superdex 200 column chromatographies resulted in purified His-tag-free IptA, with a molecular mass of 41 kDa (Fig. 4A). By Superdex 200 gel filtration experiments, IptA was eluted in the fraction corresponding to a molecular mass of 40.0 kDa, suggesting a monomeric property.
FIG. 4.
SDS-PAGE and HPLC chromatograms of IptA assays. (A) SDS-12.5% PAGE analysis of purified His-tag-free IptA. Lane 1, molecular mass markers; lane 2, purified enzyme (arrow). The enzyme purification was described in Materials and Methods. Protein was stained with Coomassie brilliant blue R-250. (B) IptA (60 pmol enzyme) was incubated with l-Trp (0.5 mM) and DMAPP (0.2 mM). The enzyme reaction product was analyzed by LC-MS under the conditions described in Materials and Methods. Dotted and solid lines indicate product profiles after 1- and 10-min reactions, respectively. (C) IptA (100 pmol enzyme) was incubated with l-Trp (0.5 mM) and GPP (0.1 mM) for 120 min.
Characterization of enzyme activity.
Because of weak homology to LtxC, which catalyzes the transfer of a geranyl group to (−)-indolactam V, and the isolation of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde, the function of IptA was speculated to be 6-dimethylallyl transfer to l-Trp or directly to indole-3-carbaldehyde. LC-MS analyses of the IptA reaction product with l-Trp and DMAPP clearly showed a prenylated product peak with a retention time of 13.1 min (Fig. 4B). The reaction product was identified as 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp by NMR and MS analyses (Fig. 1B). We also tested the reaction with GPP, because LtxC utilized GPP as a prenyl donor. However, geranylated l-Trp was not detected by LC-MS (Fig. 4C). In addition, when IPP, FPP, or GGPP was mixed with l-Trp instead of DMAPP, no prenylated product was detected, indicating that IptA specifically utilizes DMAPP as a prenyl donor. When IptA was incubated with (−)-indolactam V in the presence of DMAPP or GPP, no prenylated product was detected.
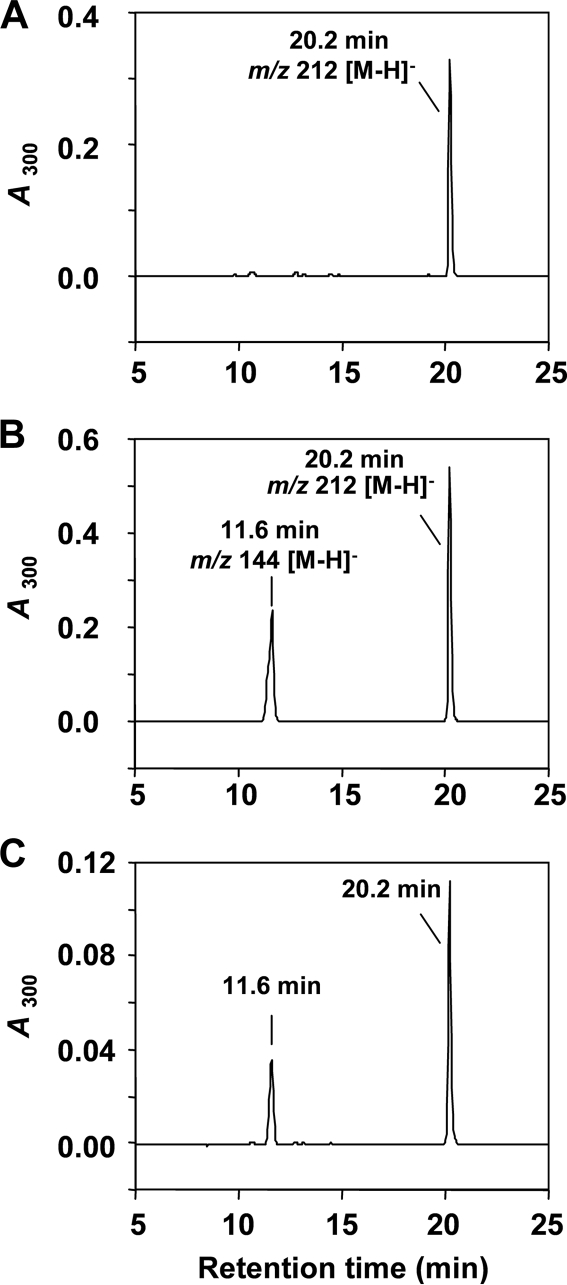
To evaluate the formation of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde, IptA was incubated with indole-3-carbaldehyde in the presence of DMAPP. The reaction product analyses by LC-MS showed the same retention time, UV spectrum, and molecular ion (m/z 212 [M − H]−) as the authentic reference of purified 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde (Fig. 5). Comparison of specific activities between l-Trp and indole-3-carbaldehyde indicated that the reaction of IptA with indole-3-carbaldehyde was much less effective than that with l-Trp (Table 4). Consequently, the detailed enzymatic properties of IptA were characterized mainly for 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp synthase (6-DMATS) activity.
FIG. 5.
HPLC chromatograms of IptA reaction product from indole-3-carbaldehyde. (A) LC-MS analysis of purified authentic 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde was performed as described in Materials and Methods. (B) LC-MS analysis of the enzyme reaction product. IptA (7.4 μmol enzyme) reacted with indole-3-carbaldehyde (0.1 mM) and DMAPP (0.1 mM) under the assay conditions described in Materials and Methods. (C) Authentic 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde and the enzyme reaction product were mixed and analyzed by LC-MS.
TABLE 4.
Substrate specificity for tryptophan derivatives with modified side chains
ND, not detected.
The specific activity for l-Trp of 63.7 nmol product formed min−1 nmol enzyme−1 was set as 100%. The amount of reaction product was calculated by the HPLC peak area. Values are averages ± standard deviations (SD) for three independent experiments.
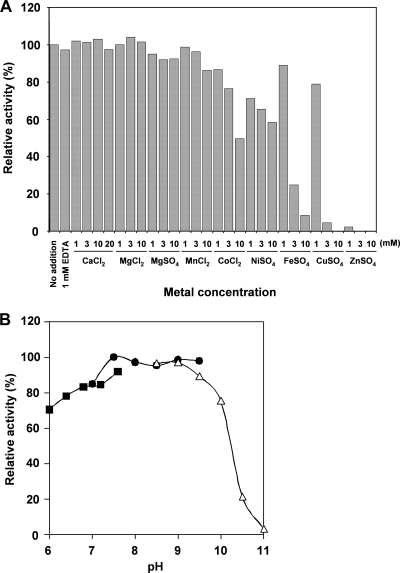
Metal dependency, optimum pH, and heat stability.
Effects of divalent metal ions on 6-DMATS activity were tested at a concentration range of 1 to 20 mM (Fig. 6A). The addition of 1 to 3 mM Ca2+, Mg2+, or Mn2+ did not induce an enhancement of 6-DMATS activity. The addition of 10 mM Co2+ or Ni2+ reduced 40 to 50% of the activity. The addition of 3 to 10 mM Fe2+, Cu2+, or Zn2+ strongly inhibited the enzyme activity. Moreover, the presence of 1 mM EDTA did not inhibit 6-DMATS activity, suggesting that a metal ion is not essential for its activity. When indole-3-carbaldehyde was used as the substrate, no metal dependency was observed.
FIG. 6.
Effects of metal and pH on 6-DMATS activity. (A) The concentration of 8 divalent metal ions was varied from 1 to 10 mM in the standard assay solution. (B) The assay was conducted at a pH range of 6.0 to 11, using 50 mM NaH2PO4 (solid squares), 50 mM Tris-HCl (solid circles), and 50 mM glycine-NaOH buffer (open triangles).
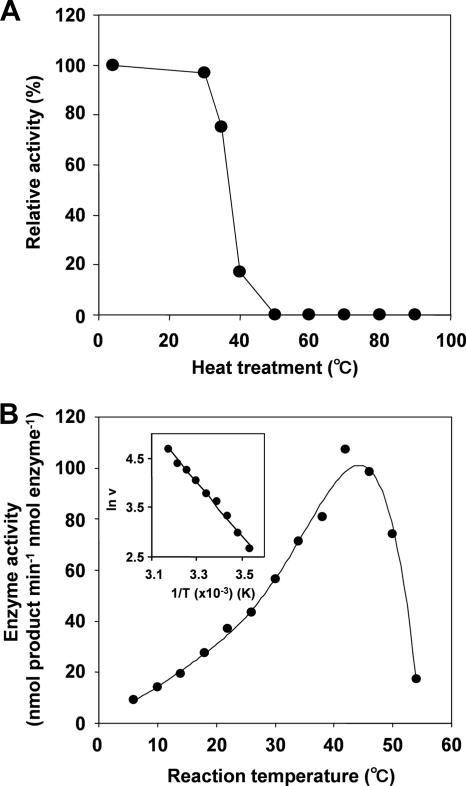
The effect of pH on the 6-DMATS activity was relatively broad, and maximal product formation was observed at pH 7.0 to 9.5 (Fig. 6B). Moreover, heat treatment at 50°C for 5 min abolished the 6-DMATS activity (Fig. 7A). The effect of temperature on the enzyme activity was also tested. The activation energy was estimated to be 46 kJ mol−1 by an Arrhenius plot, whose curve was straight over the range of 10 to 42°C (Fig. 7B).
FIG. 7.
Heat stability (A) and effects of temperature (B) on 6-DMATS activity.
Analyses of substrate specificity for indole compounds.
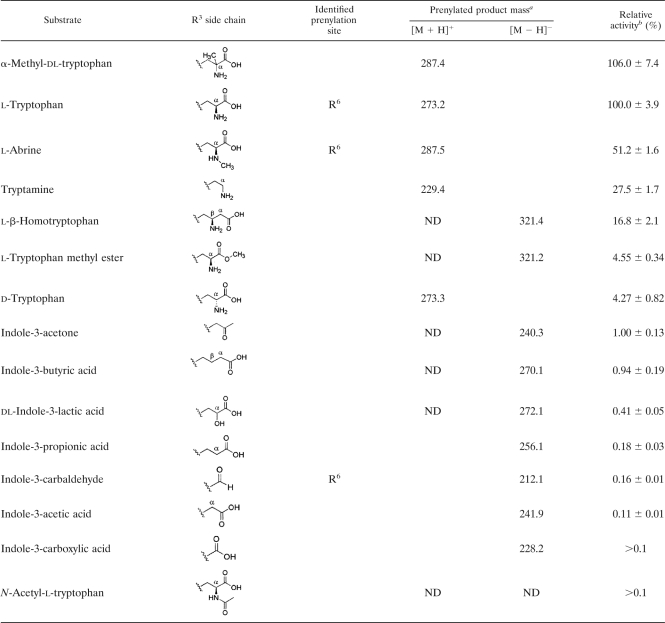
To address substrate specificity, IptA was incubated with 15 Trp derivatives with a modified R3 side chain (Table 4). α-Methylation of dl-Trp retained the relative activity (106%). However, the methylation of the α-amino moiety of l-Trp (l-abrine) reduced the relative activity (51.2%). Changes in the stereochemistry of the amino group (d-Trp) resulted in a reduction in relative activity (4.3%). The exchange of the α-amino group of Trp with a hydroxyl group (dl-indole-3-lactic acid) and the deamination of l-Trp (indole-3-propionic acid) significantly reduced relative activity (0.41 and 0.18%, respectively). Acetylation of the α-amino moiety (N-acetyl-l-Trp) led to a loss of activity, suggesting that the amino group is important for optimum substrate recognition by IptA. Moreover, the decarboxylation of l-Trp (tryptamine) and the insertion of the methylene group in the α-position (l-β-homotryptophan) resulted in a decrease of relative activity (27.5% and 16.8%, respectively). In addition, the methyl ester of the carboxyl group (l-Trp methyl ester) resulted in a reduction of relative activity (4.6%), suggesting that the carboxyl group is also important for optimum substrate recognition by IptA. When l-Trp-containing dipeptides, such as brevianamide F (cyclo-l-Trp-l-Pro) and tryprostatin B, were incubated with IptA, no prenylated product was observed, supporting the role of the carboxyl group and amino group for substrate recognition. Moreover, when l-Phe, l-Tyr, l-Pro, or l-His, instead of l-Trp, was mixed with DMAPP, no prenylated product was detected. These results also suggested the role of the indole ring in the IptA reaction.
To address substrate specificity in detail, IptA was incubated with 11 Trp derivatives with a modified indole ring (Table 5). The substrates, modified at C-1, C-4, and C-5 of the indole ring, did not significantly reduce relative activity. NMR analyses demonstrated that 5-hydroxy-l-Trp, 4-methyl-dl-Trp, and 5-methoxy-l-Trp were converted into 6-dimethylallyl products, all of which turned out to be novel compounds. Consistent with these results, IptA hardly reacted with 6-chloro- and 6-bromo-dl-Trp. However, methyl modification at C-6 of the indole ring (6-methyl-dl-Trp) resulted in a 7-dimethylallyl product with 9.3% relative activity. A cocrystal structure analysis using 6-methyl-dl-Trp would be indispensable to explain the shift of the dimethylallyl transfer site to C-7 of the indole ring.
TABLE 5.
Substrate specificity for tryptophan derivatives with a modified indole ring
The specific activity of 63.7 nmol product formed min−1 nmol enzyme−1 for l-Trp was indicated as 100%. The amount of reaction product was calculated by HPLC peak area. Values are averages ± SD for three independent experiments. ND, not detected.
Kinetic parameters for Trp derivatives.
Kinetic parameters of IptA were investigated for the prenyl acceptors l-Trp, l-abrine, α-methyl-dl-Trp, 5-hydroxy-l-Trp, and indole-3-carbaldehyde (Table 6). The IptA reaction apparently followed Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The Km and kcat values for l-Trp were 9.4 ± 0.9 μM and 57.6 ± 0.9 min−1, respectively, giving a catalytic efficiency of 6.13 min−1 μM−1. l-Abrine showed a higher Km value (16.9 ± 0.9 μM) and a lower kcat value (38.5 ± 0.5 min−1) than those for l-Trp. Although α-methyl-dl-Trp and 5-hydroxy-l-Trp showed higher kcat values (67.4 ± 1.4 and 75.2 ± 2.8 min−1, respectively) than that for l-Trp, their Km values (32.0 ± 2.8 and 41.0 ± 5.3 μM, respectively) were higher than that for l-Trp. Consequently, the catalytic efficiencies of l-abrine (2.28 min−1 μM−1), α-methyl-dl-Trp (2.11 min−1 μM−1), and 5-hydroxy-l-Trp (1.83 min−1 μM−1) were 2.7 to 3.3 times lower than that of l-Trp. In addition, the Km and kcat values for indole-3-carbaldehyde were 19.9 ± 0.8 μM and 0.095 ± 0.001 min−1, respectively. The catalytic efficiency of indole-3-carbaldehyde (0.0048 min−1 μM−1) was about 1,300 times lower than that of l-Trp.
TABLE 6.
Comparison of kinetic constants for indole substratesa
| Substrate | Km (μM) | kcat (min−1) | kcatKm−1 (min−1 μM−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| l-Trp | 9.4 ± 0.9 | 57.6 ± 0.9 | 6.13 |
| l-Abrine | 16.9 ± 0.9 | 38.5 ± 0.5 | 2.28 |
| α-Methyl-dl-Trp | 16.0 ± 1.4 | 67.4 ± 1.4 | 4.21 |
| 5-Hydroxy-l-Trp | 41.0 ± 5.3 | 75.2 ± 2.8 | 1.83 |
| Indole-3-carbaldehyde | 19.9 ± 0.8 | 0.095 ± 0.001 | 0.0048 |
| DMAPPb | 6.2 ± 0.8 | 70.7 ± 1.6 | 11.4 |
| DMAPPc | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 0.108 ± 0.001 | 0.064 |
Constants were calculated by nonlinear regression fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation.
l-Trp was used as the substrate.
Indole-3-carbaldehyde was used as the substrate.
Moreover, the kinetic parameters of IptA were also evaluated for the prenyl donor DMAPP. The 6-DMATS activity of IptA was slightly inhibited with increasing concentrations of DMAPP. The kcat value (70.7 ± 1.6 min−1) obtained from DMAPP kinetics was 1.2 times higher than that of l-Trp (57.9 ± 0.9 min−1), as measured in the presence of 0.2 mM DMAPP. Consistent with the results for l-Trp, the prenyl transfer to indole-3-carbaldehyde was also slightly inhibited with increasing concentrations of DMAPP. The kcat value (0.108 ± 0.001 min−1) obtained from DMAPP kinetics was 1.1 times higher than that for indole-3-carbaldehyde (0.095 ± 0.001 min−1), as measured in the presence of 0.2 mM DMAPP. These results are consistent with the report for MaPT (13).
Disruption of iptA gene and LC-MS analysis.
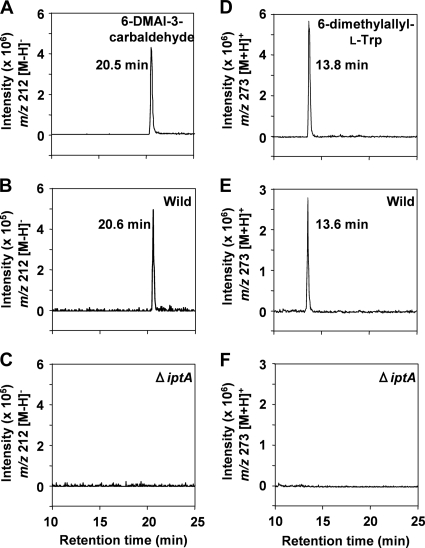
To address the role of the iptA gene in the biosynthesis of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde, we constructed an iptA-inactivated mutant (Fig. 8) and analyzed the metabolites by LC-MS. All of the ΔiptA mutants abolished the production of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde (Fig. 9C), suggesting that the iptA gene is involved in the production of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde. In addition, the ΔiptA mutants also abolished the production of 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp (Fig. 9F).
FIG. 8.
Gene disruption of iptA and Southern blot analysis. (A) Scheme of iptA disruption and restriction map of wild-type and ΔiptA mutant strains. The bar shows the expected fragment size (bp) after SalI digestion. A 4,550-bp probe was amplified by oligonucleotide primers iptA-SalI-F and iptA-SalI-R (Table 1). (B) Southern blot analysis of the wild type (lanes 2 and 7) and of ΔiptA mutants (lanes 3 to 6) in individual isolations. Genomic DNAs digested with SalI were applied to a 0.9% agarose gel and stained by ethidium bromide. Southern blot analysis indicated the expected sizes of the DNA fragments from wild-type and ΔiptA mutant strains. The arrows indicate the expected sizes of the DNA fragments from the wild type (solid) and the ΔiptA mutants (open), respectively.
FIG. 9.
LC-MS analysis of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde and 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp from culture extracts of the wild-type strain and the ΔiptA mutant strain. The culture, extraction, and LC-MS analysis were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Authentic standards of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde (A) and 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp (D) were analyzed. The production of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde from the MPLC fraction of the wild type (B) or the ΔiptA mutant strain (C) was analyzed. The production of 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp from n-butanol extracts of the wild type (E) and the ΔiptA mutant strain (F) was analyzed. The chromatograms shown in panels A, B, and C are the extracted ion chromatograms of m/z 212 [M − H]−. The chromatograms shown in panels D, E, and F are the extracted ion chromatograms of m/z 273 [M + H]+.
DISCUSSION
Indole prenyltransferases have been characterized from fungal strains by S. M. Li (35, 36). The ABBA prenyltransferase family has also been characterized extensively (23, 32, 38, 44, 52). However, there has been no report of the gene responsible for indole 6-prenyltransferase. Metabolite profiling and genome mining using Streptomyces sp. SN-593 successfully shed light on the missing gene iptA (Fig. 2; Table 3), which was phylogenetically distinct from other prenyltransferases (Fig. 3B). Consistent with the isolation reports for prenylindole compounds from Streptomyces, highly homologous genes [SAML0654 from S. ambofaciens ATCC 23877 and SCO7467 from S. coelicolor A3(2)] were also found in the Streptomyces genome database. Interestingly, the gene organization of S. ambofaciens differs from that of Streptomyces sp. SN-593 by lacking a homolog of orf7 and orf8. The gene organization of S. coelicolor A3(2) differs from that of Streptomyces sp. SN-593 by lacking a homolog of orf5, orf7, and orf8. Each Streptomyces strain does not seem to produce a fixed secondary metabolite.
We speculated that the biosynthesis of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde might start from prenylation of l-Trp, because the catalytic efficiency of l-Trp was about 1,300 times higher than that of indole-3-carbaldehyde (Table 6). Based on this speculation, 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp might accumulate to a detectable amount in Streptomyces sp. SN-593 culture broth. If independent pathways exist for the biosynthesis of 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp and 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde, the amounts of the products should be correlated with the catalytic efficiency of IptA. Therefore, we examined the presence of 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp, as well as 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde, by LC-MS analysis (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Surprisingly, we identified that the amount of 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp (1.3 mg from a 10-liter culture) was three times lower than that of 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde (4.2 mg from a 10-liter culture). Because the gene annotation (Table 3) indicated the presence of tryptophanase, the low yield of 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp might be explained by the conversion into 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde. However, we must await a final conclusion until the demonstration of incorporation of labeled 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp into 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde. At present, we cannot rule out the possibility that 6-DMAI-3-carbaldehyde was produced in part from indole-3-carbaldehyde, because it was isolated from Streptomyces sp. SN-593 culture broth. Recently, a genome-minimized Streptomyces avermitilis host for the heterologous expression of various secondary metabolite gene clusters was reported (29). Because the S. avermitilis host lacks an iptA homolog, the heterologous expression of the whole gene organization (Fig. 2) will give us detailed information on the biosynthesis of the secondary metabolite.
In this study, detailed biochemical properties of IptA were compared with those of fungal indole prenyltransferases (see Table S1 in the supplemental material). To characterize the multimeric property of IptA, gel filtration analysis was performed using His-tag-free enzyme. IptA showed a monomeric feature, which is similar to the case for FtmPT1 (21) and 7-DMATS (30) from A. fumigatus. On the other hand, indole prenyltransferases such as FtmPT2 (20), FgaPT1 (54), and FgaPT2 (53) from A. fumigatus and DMATS from Claviceps purpurea (18) have been reported to be dimer proteins, indicating that the multimeric status of indole prenyltransferases has variation.
It was known that the activity of indole prenyltransferase is affected by the presence of metals, especially Mg2+ or Ca2+. Therefore, the 6-DMATS activity of IptA was measured in the presence of different metal ions at concentrations ranging from 1 to 20 mM (Fig. 6A). The results clearly showed that the 6-DMATS activity was independent of the presence of metal ions. The independency of divalent metals was similar to that of FtmPT2 (20) and FgaPT1 (54) from A. fumigatus and MaPT (13) from Malbranchea aurantiaca. In contrast, other indole prenyltransferases, such as CdpNTP (58), FtmPT1 (21), FgaPT2 (53), and 7-DMATS (31) from A. fumigatus and 4-DMATS from C. purpurea (18), had enhanced activity in the presence of Mg2+ or Ca2+. This indicates that enhancement of enzyme activity by divalent cations is not conserved among the indole prenyltransferases (see Table S1 in the supplemental material).
The Km and kcat values for l-Trp and DMAPP (Table 6) are comparable to those for other indole prenyltransferases, such as FgaPT2 (51, 53), MaPT (13), and 4-DMATS (18). Substrate specificity analyses (Tables 4 and 5) and kinetic parameters for indole substrates (Table 6) strongly suggested that the natural function of IptA was as a 6-DMATS. IptA is the first example of an indole prenyltransferase identified from Streptomyces. Moreover, it should be emphasized that IptA revealed substrate promiscuity for indole compounds and produced novel 6-DMAI products, such as 6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp, 5-hydroxy-6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp, 4-methyl-6-dimethylallyl-Trp, 5-methoxy-6-dimethylallyl-l-Trp, and 6-dimethylallyl-l-abrine. For these substrate specificity analyses, we utilized commercially available dl- mixtures of substrate. Although we could not determine an exact conversion ratio of l- to d- reaction products, it can be speculated that l-Trp derivatives react better than the d- forms. The significant preference for l- over d-Trp is shown in Table 4.
Prenylated indole derivatives are widely distributed in nature and show diverse biological and pharmacological activities (57). Prenylation is important for the order of biosynthesis and the formation of bioactive compounds (6, 9-11, 27, 47, 55, 57, 59). Here we demonstrated that IptA widely accepted indole substrates and produced novel 6-DMAI compounds. Therefore, chemoenzymatic synthesis or pathway engineering of secondary metabolites by use of IptA might allow us to derivatize natural products with improved biological activities.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to T. Kuzuyama and N. Kato for their precious advice. We thank J. Ishikawa for gene annotation, E. Oowada for gene annotation and disruption, and K. Aramaki for the isolation of secondary metabolites.
This work was supported in part by a Creative Scientific Research grant and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print on 26 March 2010.
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://jb.asm.org/.
REFERENCES
- 1.Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Archenbach, H., C. Renner, and R. Waibel. 1995. The hexalobines, diprenylated indoles from Hexalobus crispiflorus and Hexalobus monopetalus. Liebigs Ann. 1995:1327-1337. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Archenbach, H., and B. Raffelsberger. 1979. 3,6-Bis(γ,γ-dimethylallyl)-indole from Uvaria elliotiana. Tetrahedron Lett. 28:2571-2574. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bentley, S. D., K. F. Chater, A. M. Cerdeno-Tarraga, G. L. Challis, N. R. Thomson, K. D. James, D. E. Harris, M. A. Quail, H. Kieser, D. Harper, A. Bateman, S. Brown, G. Chandra, C. W. Chen, M. Collins, A. Cronin, A. Fraser, A. Goble, J. Hidalgo, T. Hornsby, S. Howarth, C. H. Huang, T. Kieser, L. Larke, L. Murphy, K. Oliver, S. O'Neil, E. Rabbinowitsch, M. A. Rajandream, K. Rutherford, S. Rutter, K. Seeger, D. Saunders, S. Sharp, R. Squares, S. Squares, K. Taylor, T. Warren, A. Wietzorrek, J. Woodward, B. G. Barrell, J. Parkhill, and D. A. Hopwood. 2002. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bergmann, S., J. Schumann, K. Scherlach, C. Lange, A. A. Brakhage, and C. Hertweck. 2007. Genomics-driven discovery of PKS-NRPS hybrid metabolites from Aspergillus nidulans. Nat. Chem. Biol. 3:213-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Botta, B., G. Delle Monache, P. Menendez, and A. Boffi. 2005. Novel prenyltransferase enzymes as a tool for flavonoid prenylation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 26:606-608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Clardy, J., and C. Walsh. 2004. Lessons from natural molecules. Nature 432:829-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Corre, C., L. Song, S. O'Rourke, K. F. Chater, and G. L. Challis. 2008. 2-Alkyl-4-hydroxymethylfuran-3-carboxylic acids, antibiotic production inducers discovered by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105:17510-17515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cui, C. B., H. Kakeya, G. Okada, R. Onose, and H. Osada. 1996. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, tryprostatins A, B and other diketopiperazines produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological properties. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 49:527-533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cui, C. B., H. Kakeya, and H. Osada. 1996. Novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitors, tryprostatins A, B and other diketopiperazines produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. II. Physico-chemical properties and structures. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 49:534-540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cui, C. B., H. Kakeya, and H. Osada. 1996. Spirotryprostatin B, a novel mammalian cell cycle inhibitor produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 49:832-835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Datsenko, K. A., and B. L. Wanner. 2000. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 97:6640-6645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ding, Y., R. M. Williams, and D. H. Sherman. 2008. Molecular analysis of a 4-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase from Malbranchea aurantiaca. J. Biol. Chem. 283:16068-16076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Edwards, D. J., and W. H. Gerwick. 2004. Lyngbyatoxin biosynthesis: sequence of biosynthetic gene cluster and identification of a novel aromatic prenyltransferase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126:11432-11433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ewing, B., and P. Green. 1998. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res. 8:186-194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ewing, B., L. Hillier, M. C. Wendl, and P. Green. 1998. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. I. Accuracy assessment. Genome Res. 8:175-185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Fredenhagen, A., F. Petersen, M. Tintelnot-Blomley, J. Rosel, H. Mett, and P. Hug. 1997. Semicochliodinol A and B: inhibitors of HIV-1 protease and EGF-R protein tyrosine kinase related to asterriquinones produced by the fungus Chrysosporium merdarium. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 50:395-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gebler, J. C., and C. D. Poulter. 1992. Purification and characterization of dimethylallyl tryptophan synthase from Claviceps purpurea. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 296:308-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gordon, D., C. Abajian, and P. Green. 1998. Consed: a graphical tool for sequence finishing. Genome Res. 8:195-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Grundmann, A., T. Kuznetsova, S. Afiyatullov, and S. M. Li. 2008. FtmPT2, an N-prenyltransferase from Aspergillus fumigatus, catalyses the last step in the biosynthesis of fumitremorgin B. Chembiochem 9:2059-2063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Grundmann, A., and S. M. Li. 2005. Overproduction, purification and characterization of FtmPT1, a brevianamide F prenyltransferase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Microbiology 151:2199-2207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gust, B., G. L. Challis, K. Fowler, T. Kieser, and K. F. Chater. 2003. PCR-targeted Streptomyces gene replacement identifies a protein domain needed for biosynthesis of the sesquiterpene soil odor geosmin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 100:1541-1546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Heide, L. 2009. Prenyl transfer to aromatic substrates: genetics and enzymology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 13:171-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hong Lu, W. X. Z., J. C. Meng, J. Hu, and R. X. Tan. 2000. New bioactive metabolites produced by Colletotrichum sp., an endophytic fungus in Artemisia annua. Plant Sci. 151:67-73. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ikeda, H., J. Ishikawa, A. Hanamoto, M. Shinose, H. Kikuchi, T. Shiba, Y. Sakaki, M. Hattori, and S. Omura. 2003. Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat. Biotechnol. 21:526-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jiang, J., C. N. Tetzlaff, S. Takamatsu, M. Iwatsuki, M. Komatsu, H. Ikeda, and D. E. Cane. 2009. Genome mining in Streptomyces avermitilis: a biochemical Baeyer-Villiger reaction and discovery of a new branch of the pentalenolactone family tree. Biochemistry 48:6431-6440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kato, N., H. Suzuki, H. Takagi, Y. Asami, H. Kakeya, M. Uramoto, T. Usui, S. Takahashi, Y. Sugimoto, and H. Osada. 2009. Identification of cytochrome P450s required for fumitremorgin biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. Chembiochem 10:920-928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kieser, T., M. J. Bibb, M. J. Buttner, K. F. Chater, and D. A. Hopwood (ed.). 2000. Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Foundation, Norwich, United Kingdom.
- 29.Komatsu, M., T. Uchiyama, S. Omura, D. E. Cane, and H. Ikeda. 2010. Genome-minimized Streptomyces host for the heterologous expression of secondary metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107:2646-2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kremer, A., and S. M. Li. 2008. Potential of a 7-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase as a tool for production of prenylated indole derivatives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 79:951-961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kremer, A., L. Westrich, and S. M. Li. 2007. A 7-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase from Aspergillus fumigatus: overproduction, purification and biochemical characterization. Microbiology 153:3409-3416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kuzuyama, T., J. P. Noel, and S. B. Richard. 2005. Structural basis for the promiscuous biosynthetic prenylation of aromatic natural products. Nature 435:983-987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Laemmli, U. K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lautru, S., R. J. Deeth, L. M. Bailey, and G. L. Challis. 2005. Discovery of a new peptide natural product by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1:265-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li, S. M. 2009. Applications of dimethylallyltryptophan synthases and other indole prenyltransferases for structural modification of natural products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 84:631-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li, S. M. 2009. Evolution of aromatic prenyltransferases in the biosynthesis of indole derivatives. Phytochemistry 70:1746-1757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.McMurray, A. A., J. E. Sulston, and M. A. Quail. 1998. Short-insert libraries as a method of problem solving in genome sequencing. Genome Res. 8:562-566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Metzger, U., C. Schall, G. Zocher, I. Unsold, E. Stec, S. M. Li, L. Heide, and T. Stehle. 2009. The structure of dimethylallyl tryptophan synthase reveals a common architecture of aromatic prenyltransferases in fungi and bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106:14309-14314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Motohashi, K., K. Irie, T. Toda, Y. Matsuo, H. Kasai, M. Sue, K. Furihata, and H. Seto. 2008. Studies on terpenoids produced by actinomycetes. 5-Dimethylallylindole-3-carboxylic acid and A80915G-8′-acid produced by marine-derived Streptomyces sp. MS239. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 61:75-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Newman, D. J., and G. M. Cragg. 2007. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 70:461-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Nguyen, T., K. Ishida, H. Jenke-Kodama, E. Dittmann, C. Gurgui, T. Hochmuth, S. Taudien, M. Platzer, C. Hertweck, and J. Piel. 2008. Exploiting the mosaic structure of trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthases for natural product discovery and pathway dissection. Nat. Biotechnol. 26:225-233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ohnishi, Y., J. Ishikawa, H. Hara, H. Suzuki, M. Ikenoya, H. Ikeda, A. Yamashita, M. Hattori, and S. Horinouchi. 2008. Genome sequence of the streptomycin-producing microorganism Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J. Bacteriol. 190:4050-4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Osada, H., H. Koshino, K. Isono, H. Takahashi, and G. Kawanishi. 1991. Reveromycin A, a new antibiotic which inhibits the mitogenic activity of epidermal growth factor. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 44:259-261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Saleh, O., Y. Haagen, K. Seeger, and L. Heide. 2009. Prenyl transfer to aromatic substrates in the biosynthesis of aminocoumarins, meroterpenoids and phenazines: the ABBA prenyltransferase family. Phytochemistry 70:1728-1738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sambrook, J., and D. W. Russell. 2001. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
- 46.Sanchez Lopez, J. M., M. Martinez Insua, J. Perez Baz, J. L. Fernandez Puentes, and L. M. Canedo Hernandez. 2003. New cytotoxic indolic metabolites from a marine Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 66:863-864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sanz-Cervera, J. F., E. M. Stocking, T. Usui, H. Osada, and R. M. Williams. 2000. Synthesis and evaluation of microtubule assembly inhibition and cytotoxicity of prenylated derivatives of cyclo-l-Trp-l-Pro. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8:2407-2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sasaki, T., Y. Igarashi, M. Ogawa, and T. Furumai. 2002. Identification of 6-prenylindole as an antifungal metabolite of Streptomyces sp. TP-A0595 and synthesis and bioactivity of 6-substituted indoles. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 55:1009-1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Sekiya, S. 1983. Isocochliodinol and neocochliodinol, bis(3-indolyl)-benzoquinones from Chaetomium spp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 31:2998-3001. [Google Scholar]
- 50.Song, L., F. Barona-Gomez, C. Corre, L. Xiang, D. W. Udwary, M. B. Austin, J. P. Noel, B. S. Moore, and G. L. Challis. 2006. Type III polyketide synthase beta-ketoacyl-ACP starter unit and ethylmalonyl-CoA extender unit selectivity discovered by Streptomyces coelicolor genome mining. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128:14754-14755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Steffan, N., I. A. Unsold, and S. M. Li. 2007. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of prenylated indole derivatives by using a 4-dimethylallyltryptophan synthase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Chembiochem 8:1298-1307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tello, M., T. Kuzuyama, L. Heide, J. P. Noel, and S. B. Richard. 2008. The ABBA family of aromatic prenyltransferases: broadening natural product diversity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 65:1459-1463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Unsold, I. A., and S. M. Li. 2005. Overproduction, purification and characterization of FgaPT2, a dimethylallyltryptophan synthase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Microbiology 151:1499-1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Unsold, I. A., and S. M. Li. 2006. Reverse prenyltransferase in the biosynthesis of fumigaclavine C in Aspergillus fumigatus: gene expression, purification, and characterization of fumigaclavine C synthase FGAPT1. Chembiochem 7:158-164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Usui, T., M. Kondoh, C. B. Cui, T. Mayumi, and H. Osada. 1998. Tryprostatin A, a specific and novel inhibitor of microtubule assembly. Biochem. J. 333:543-548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Usui, T., and H. Osada. 2000. Biochemical tools for investigating cell function, p. 125-305. In H. Osada (ed.), Bioprobes. Springer, Tokyo, Japan.
- 57.Williams, R. M., E. M. Stocking, and J. F. Sanz-Cervera. 2000. Biosynthesis of prenylated alkaloids derived from tryptophan. Topics Curr. Chem. 209:97-173. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yin, W. B., H. L. Ruan, L. Westrich, A. Grundmann, and S. M. Li. 2007. CdpNPT, an N-prenyltransferase from Aspergillus fumigatus: overproduction, purification and biochemical characterisation. Chembiochem 8:1154-1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhao, S., K. S. Smith, A. M. Deveau, C. M. Dieckhaus, M. A. Johnson, T. L. Macdonald, and J. M. Cook. 2002. Biological activity of the tryprostatins and their diastereomers on human carcinoma cell lines. J. Med. Chem. 45:1559-1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.