Abstract
The metabolic incorporation of stable isotopes such as 13C or 15N into proteins has become a powerful tool for qualitative and quantitative proteome studies. We recently introduced a method that monitors heavy isotope incorporation into proteins and presented data revealing the metabolic activity of various species in a microbial consortium using this technique. To further develop our method using an liquid chromatography (LC)-mass spectrometry (MS)-based approach, we present here a novel approach for calculating the incorporation level of 13C into peptides by using the information given in the decimal places of peptide masses obtained by modern high-resolution MS. In the present study, the applicability of this approach is demonstrated using Pseudomonas putida ML2 proteins uniformly labeled via the consumption of [13C6]benzene present in the medium at concentrations of 0, 10, 25, 50, and 100 atom %. The incorporation of 13C was calculated on the basis of several labeled peptides derived from one band on an SDS-PAGE gel. The accuracy of the calculated incorporation level depended upon the number of peptide masses included in the analysis, and it was observed that at least 100 peptide masses were required to reduce the deviation below 4 atom %. This accuracy was comparable with calculations of incorporation based on the isotope envelope. Furthermore, this method can be extended to the calculation of the labeling efficiency for a wide range of biomolecules, including RNA and DNA. The technique will therefore allow a highly accurate determination of the carbon flux in microbial consortia with a direct approach based solely on LC-MS.
The metabolic incorporation of stable isotopes such as 13C or 15N into proteins has become a powerful component of qualitative and quantitative proteome studies (1). Incorporation of heavy isotopes can be used to analyze microbial processes such as turnover rates and also to help to establish structure-function relationships within microbial communities. Stable isotope probing (SIP1) techniques based on DNA-SIP (2) and RNA-SIP (3) have been used for this purpose previously. With the introduction of protein-SIP (4), the need for an accurate alternative method for calculating label incorporation into biomolecules arose. Protein-SIP has several advantages compared with DNA/RNA-SIP, the most important being its capacity to detect dynamic levels of incorporation, whereas only labeled or unlabeled states can be categorized by means of DNA/RNA-SIP because of the need to separate 13C-DNA/RNA by density gradient centrifugation. Quantitative analysis of 13C incorporation levels is of the utmost importance, especially when unraveling carbon fluxes through either microbial communities or food webs with different trophic levels.
In contrast to the incorporation of isotopically labeled amino acids, which is often used in quantitative proteomics (5), metabolic labeling by growth substrates and nutrients (e.g. salts) is often imperfect and makes the processing of mass spectrometry (MS) data difficult. For example, when the incorporation of 13C exceeds ∼2 atom %, common database search algorithms fail to identify peptides and proteins. The problem can only be managed successfully if a stable, known degree of 13C incorporation can be achieved during the experiment (6). Using a low labeling efficiency of roughly 5 atom %, Huttlin et al. (6) chose the altered envelope chain for calculating the incorporation and simultaneously used the signal intensity for a quantitative comparison with the sample that had a natural abundance of 13C. Database approaches for peptide identification can cope only with the natural abundance of carbon isotopes; they fail if the incorporation of 13C significantly exceeds the natural isotope abundance or if incorporation patterns occur in unpredictable ways (7).
The simplest method for determining the incorporation level is to compare the unlabeled average mass of the monoisotopic peptide with the mass of the labeled protein, as estimated by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization or electrospray ionization MS (8, 9). A more advanced approach for determining the isotopic mass distribution of peptides is based on the isotopic distribution of the peaks of a peptide envelope (10, 11). Here, for a given isotopomer, the incorporation efficiency is defined as the percentage of incorporated 13C atoms with relation to the total number of carbon atoms with the natural isotope abundance (approximately 1.01 atom % 13C). As a reference, the theoretical isotopic distribution of a peptide is calculated based upon an algorithm described elsewhere (12). The isotope distribution of both unlabeled and labeled peptides can subsequently be used to calculate the incorporation level. For this method, an Excel spreadsheet (ProSIPQuant.xls) was developed (4). A similar approach, also based on the calculation of isotopic distributions, has been used in other studies (7). In these studies, however, the identification of the peptides is limited to those that have unlabeled counterparts; in addition, an exact calculation can be hampered by overlapping signals coming from additional peaks with similar masses.
In the present study, we describe a new way of determining the isotope incorporation level. Our method makes use of characteristic patterns in the digits after the decimal point of the peptide masses generated by high-accuracy instruments such as the linear ion trap LTQ-Orbitrap (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). For tryptic peptides, typical regularities in the decimal places of the monoisotopic masses have been observed (13, 14). These observations have been explored in detail for theoretical and experimental data of proteins originating from Helicobacter pylori (15). As a result, a rule called the “half decimal place rule” (HDPR) was defined; it states that the decimal place is nearly half of the first digit for tryptic peptides with masses in the range of 500–1,000 Da. In other words, the exact mass of a peptide is equal to its nominal mass times ∼1.005. Because the difference between 12C and 13C is slightly greater than 1 Da, exactly 1.0033548378, the decimal places of a tryptic peptide's mass are shifted in a regular manner by the incorporation level and lead to a significantly increased slope for the digits in the third and fourth place after the decimal point. This shift can be used to estimate the incorporation level of heavy isotopes into the protein. Detecting such shifts requires the highly accurate measurement possible with modern mass spectrometers such as the LTQ-Orbitrap, the Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance, or the quadrupole time of flight. In this communication, we demonstrate the applicability of this approach using Pseudomonas putida ML2 proteins labeled uniformly via the consumption of [13C6]benzene with five different substrate concentrations (0, 10, 25, 50, and 100 atom % of 13C). The 13C incorporation was calculated based on several labeled peptides derived from different proteins in one SDS-PAGE band. By these means, we have established a method that allows the determination of 13C incorporation into proteins and can be used to assess the metabolic activity of a given species within a mixed community.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Materials
The chemicals used were purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) and Sigma (Munich, Germany). They were all of at least analytical grade quality. Fully labeled [13C6]benzene (≥ 99 atom % 13C) was obtained from Campro-Scientific (Veenendaal, The Netherlands). Benzene has a natural isotope composition of approximately 1.077 to 1.078 atom % 13C. Benzene with natural isotope abundance is referred to as 12C[benzene].
Cultivation of P. putida ML2
P. putida ML2 (German Collection of Microorganisms and Cell Cultures, Braunschweig, Germany) was cultivated under aerobic conditions in the DSMK mineral medium number 457. The medium was modified by adding 1 ml/L of trace element solution SL-10 (medium number 320). Benzene was added to the bacterial cultures as the sole carbon and energy source. The cultivation conditions followed specifications described previously (16). The carbon atom labeling approach involved replacement of unlabeled benzene by labeled [13C6]benzene. To achieve predefined levels of heavy isotope incorporation, different ratios of labeled substrate were used. The following substrate ratios (13C6:12C6-labeled benzene, v/v) were selected: (a) 12C natural abundance benzene (referred as 0 atom %); (b) 1:9 (10 atom %); (c) 1:4 (25 atom %); (d) 1:1 (50 atom %); and (e) completely labeled [13C6]benzene (100 atom % incorporation of heavy isotopes).
Sample Preparation for 1-D Gel Electrophoresis
P. putida ML2 was harvested at the stationary growth phase by centrifugation for 10 min at 15,500 × g (Laboratory Centrifuge 3K30; Sigma, Osterode, Germany). For protein conservation, cell pellets were treated with phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Proteins were extracted, processed (17), and quantified (18). For 1-D analysis, 50 μg of extracted protein were precipitated with 20% trichloroacetic acid (v/v). Trichloroacetic acid was removed by washing the protein pellet twice with 80% ice-cold acetone. Acetone-treated samples were centrifuged (13,000 × g for 10 min) and the resulting pellet was air-dried. SDS-PAGE (19) was performed using the Laemmli buffer system (20) and a 12% acrylamide separating gel. After separation, protein bands were stained with the use of colloidal Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 (21) (Roth, Kassel, Germany) (data not shown). Trypsin digestion was performed as described previously (16).
Identification of Proteins by Nano-LC-LTQ Orbitrap-MS/MS
The tryptic peptide measurements from the digested bands of the 1-D gel were performed on a Dionex Ultimate 3000 nano-LC system (Sunnyvale, CA) connected to a linear quadrupole ion trap (LTQ Orbitrap) mass spectrometer equipped with a nano-electrospray ionization source. For the liquid chromatography separation, we used an Acclaim PepMap 100 (C18, 3 μm, 100 Å; Dionex) capillary column of 12-cm bed length. The flow rate used for the nano column was 300 nL/min, and the solvent gradient used was 7% solvent B to 50% solvent B in 60 min. Solvent A was 0.1% formic acid, whereas solvent B was aqueous 90% acetonitrile in 0.1% formic acid. The mass spectrometer was set in the data-dependent mode to switch automatically between Orbitrap MS and LTQ-MS/MS acquisition. Survey full-scan MS spectra (from m/z 300 to 2,000) were acquired in the Orbitrap with resolution R = 60,000 at m/z 400 (after accumulation to a target of 106 charges in the LTQ). This method allowed sequential isolation of the most intense ions, up to six, depending on signal intensity, for fragmentation on the linear ion trap using collision-induced dissociation at a target value of 105 charges. For accurate mass measurements, the lock mass option was enabled in the MS mode and the polydimethyl cyclosiloxane ions generated in the electrospray process from the ambient air were used for internal recalibration during the analysis (22). Target ions already selected for MS/MS were dynamically excluded for 60 s. The general mass spectrometry conditions were as follows: 1.5-kV electrospray voltage, no sheath, and auxiliary gas flow. The ion selection threshold was 500 counts for MS/MS; an activation Q-value of 0.25 and activation time of 30 ms were also applied for MS/MS. Raw data were processed using Thermo Proteome Discoverer® software (version 1.0 build 43) to generate Mascot generic files. Finally, a database search was carried out by tandem mass spectrometry ion search algorithms from the Mascot house server (version 2.2.1) by database comparison (23) against all Proteobacteria entries from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBInr database 2008-04-24), with 5-ppm tolerance for the precursor and 0.8 Da for MS/MS fragments. Further, trypsin with a maximum of two missed cleavages was selected, and variable modifications, such as methionine oxidation and carbamidomethylation of cysteine, were allowed. Peptides were considered to be identified by Mascot when a probability < 0.05 (probability-based ion scores threshold >40) was achieved. In addition, proteins were considered to be identified if at least three peptides were identified (supplemental Table 1).
Calculation of 13C Incorporation Levels of Experimentally Derived Peptides
We used a peptide database of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (initially containing >9 × 104 tryptic peptide sequences with lengths of 2–40 amino acids) as a reference (24). In the first step, we reduced the data set to 90,637 detectable tryptic peptide sequences fitting the analytical windows of common high-resolution mass spectrometers. Next, the molecular weights for the theoretical, fully labeled peptides were calculated by replacing every 12C of each amino acid with the heavier 13C mass. After peptide mass grouping, a k-means clustering approach was used to plot the peptide masses against their digital residuals. Because user data often contain fewer measurement points, standard linear curve fitting was not applicable. We therefore applied the robust linear fitting procedure using M-estimators because they gave more reliable results with better isotope incorporation rate estimates. An M-estimator is a generalizing maximum likelihood estimation used for calculation of the slope (“M” stands for “maximum likelihood type” (25). A robust linear regression line accounting for all data points was used to evaluate the incorporation efficiency. The slope inferred from the experimental data was set in relation to the minimum and maximum slopes of the 13C peptides to obtain the incorporation level. For convenience, an R-script was written in which peak lists from selected signals can be used.
To apply the calculation method, the atomic peptide composition of 22 known proteins from P. putida ML2 derived from a single 1-D gel band (apparent molecular mass of around 45 kDa) was calculated (Isotope Pattern; Bruker Daltonics, Billerica, MA) with respect to all substrate ratios and was used to calculate the heavy carbon incorporation levels. To avoid inefficiencies in the incorporation calculation, sulfur-containing peptides were not taken into account. Numbers of carbon atoms were used to predict incorporation-dependent mass distances between 12C-monoisotopic and 13C-containing protein molecules. To calculate the 13C peptide incorporation levels, the highest m/z peak of the isotope clusters were deconvoluted and transferred to a simple text file to be analyzed further using the R-script. A robust linear regression line accounting for all data points was used to evaluate the incorporation efficiency and was analyzed with regard to the minimal and maximal incorporation of 13C.
To verify the estimated values of incorporation, we performed a second calculation using a widely applied method (26) based on the isotopic distribution, and a Perl script was developed (10). Here, for a given isotopomer, the incorporation efficiency is defined as the percentage of incorporated 13C atoms in relation to the total number of carbon atoms in the compound with natural isotope abundance (approximately 1.01 atom % 13C) (27).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Experimental Application of the HDPR to Determine 13C Peptide Incorporation
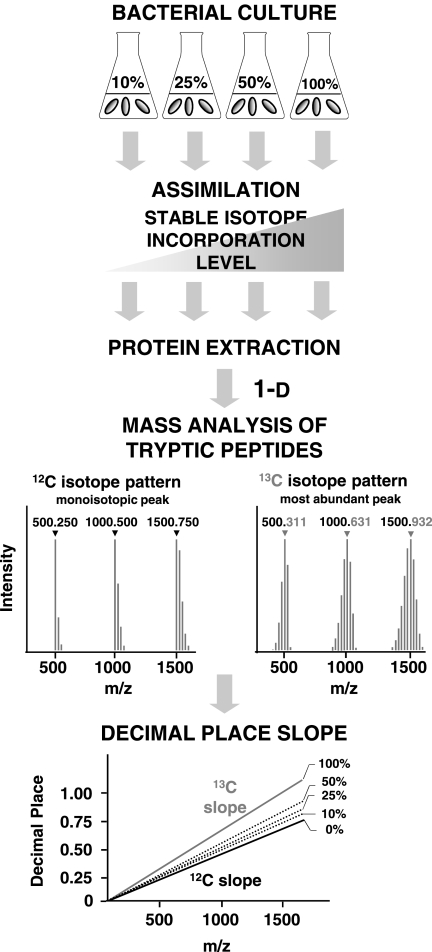
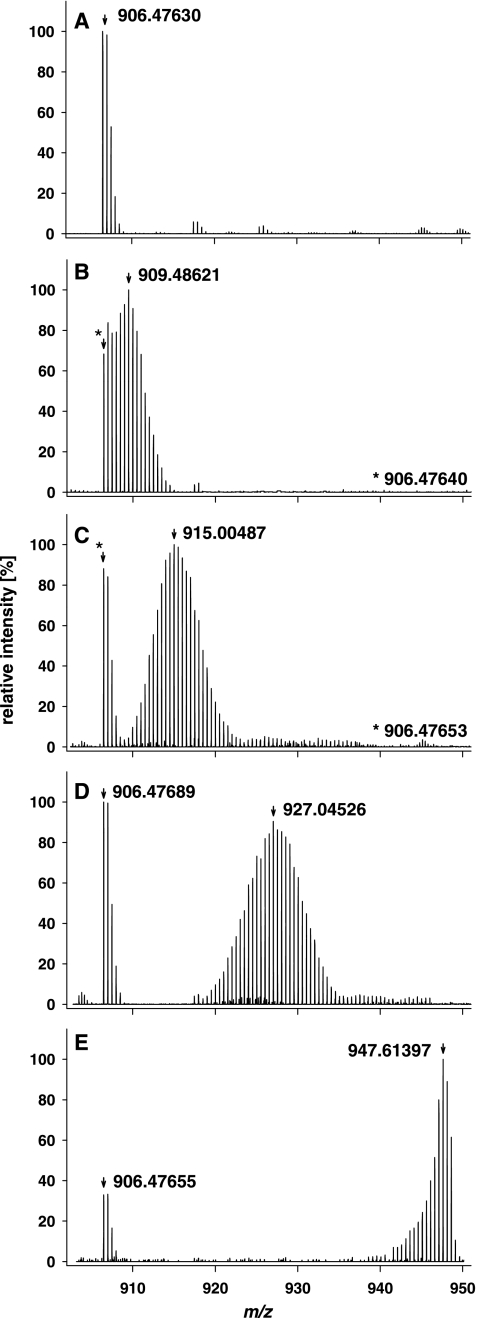
To determine the 13C peptide incorporation level using the peptide decimal place slope method, P. putida ML2 was grown in the presence of different [13C6:12C6]benzene ratios. The protein extracts were subjected to SDS-PAGE, in-gel digested, and measured by nano-LC LTQ Orbitrap-MS. For protein identification by MS/MS, the remaining 12C peptides from proteins of the bacterial culture grown in [13C6]benzene were analyzed as described in the experimental setup (Fig. 1). During the peptide mass analysis with LC-MS, the 13C peptides were eluted at the same time as unlabeled peptides displaying atypical isotopic distributions. Therefore, in one MS spectrum, the isotopic pattern of the natural isotope abundance (12C) and the 13C-labeled species are clearly distinguishable. For example, one peptide from the benzene 1,2 dioxygenase system ferredoxin-NAD(+) reductase subunit protein was taken and evaluated with respect to the various substrate ratios to illustrate the differential isotopic pattern between 12C and 13C peptides (Fig. 2). As expected, the heavy isotopomers shifted to a higher mass range because of the incorporation of heavy labeled carbon into the proteins. The assumed experimental incorporation levels of 13C carbon atoms are as follows: 0 atom % (Fig. 2A); 10 atom % (Fig. 2B); 25 atom % (Fig. 2C); 50 atom % (Fig. 2D); and 100 atom % (Fig. 2E). Particularly at the 10 atom % incorporation level (Fig. 2B), the newly metabolized heavy isotopes interfered with the natural isotopomers. However, the highest 13C peak was easily distinguishable, and the incorporation calculation for the highest isotopic masses of labeled tryptic peptides was considered. At 25 atom % 13C and higher incorporation levels, the 12C and 13C isotopomers were completely separated. To calculate the incorporation level, 100 peptide masses were deconvoluted and their monoisotopic masses were calculated (supplemental Table 1).
Fig. 1.
The experimental design for determining the 13C incorporation level in peptides by its decimal place slope. In our study, P. putida ML2 was grown in the presence of [13C6]benzene (sole energy and carbon source) and, as a control, in the presence of [12C6]benzene. Subsequently, the proteins were extracted and subjected to 1-D gel electrophoresis and tryptic in-gel digestion, and the peptides were analyzed by nano-LC LTQ Orbitrap-MS. The difference in the isotopic pattern between the 12C/13C peptides allowed for the calculation of 13C incorporation levels for various labeled contents, using the highest intensity 13C peak and the decimal place slope script.
Fig. 2.
Averaged MS-spectra of one peptide from the benzene-1,2 dioxygenase ferredoxin-NAD(+) reductase subunit protein (P. putida KT2440) measured by nano-LC LTQ Orbitrap-MS to demonstrate the differential isotopic pattern of 12C peptides and 13C-labeled peptides during the incorporation of different substrate ratios. The measured peptide with the sequence GIFAVGDVATWPLHSGGK has a mass charge of +2 and is also listed in supplemental Table 1. At all substrate ratios, the isotopomers changed from the natural monoisotopic mass of 906.476 (A) because of the incorporation of heavy isotopes. The highest 13C peak in the 10 atom % labeling experiment (B) with [MH+H]+2 was 909.48621. The highest 13C peak in the 25 atom % labeling experiment (C) with [MH+H]+2 was 915.00487. C, The highest 13C peak in the 25 atom % labeling experiment was [MH+H]+2 915.00487. D, the highest 13C peak in the 50 atom % labeling experiment was [MH+H]+2 927.04526. E, the highest 13C peak in the 100 atom % 13C labeling experiment was [MH+H]+2 947.61397.
Calculation of Incorporation levels by the HDPR
To calculate the slope for the function of the decimal places with respect to the peptide mass, an in silico tryptic digest of all predicted proteins of M. tuberculosis H37Rv was performed, and the masses obtained were plotted with respect to their decimal places as described elsewhere (24). The uniform slope has its origin in similar distributions of carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) in each of the peptides, independent of their lengths (28). The slight scattering is the result of different elemental compositions of the amino acid residues. For instance, peptides containing sulfur result in a lower slope than those that do not contain sulfur, which may also have an impact on data scattering (supplemental Fig. 1). Using a y-intercept point of zero, a 100% atom 12C slope of approximately 0.00051 was achieved. The decimal place slope for 100 atom % 13C incorporation was revealed to be 0.00063. These regression functions were used for calculation of the 13C peptide incorporation. The use of high-resolution and high-mass-accuracy mass spectrometers that provide <1 ppm precision allowed us to calculate each peptide mass to five decimal places.
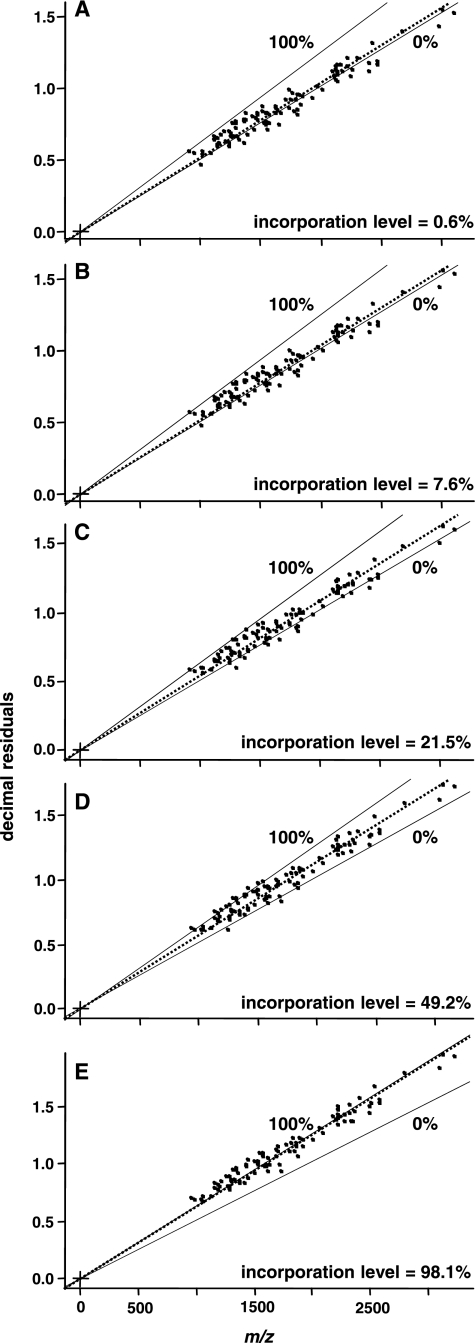
To calculate the incorporation levels of five different substrates with predefined amounts of 13C, the slopes for our experimental data sets were considered with respect to the predicted limits (Fig. 3: A, 0.6 atom %; B, 7.6 atom %; C, 21.5 atom %; D, 49.2 atom %; and E, 98.1 atom %). As a result, our experimentally calculated 13C peptide incorporation deviated between 0.6 atom % (A) and −3.5 atom % (C) in relation to our assumed 13C substrate content. Compared with other methods, the decimal place slope calculation is carried out independent of knowledge about a peptide sequence and can therefore be obtained by automated calculation based only upon the information given in the decimal places of tryptic peptides. Thus, the algorithm can be used to calculate the amount of mass added by isotopic labeling and used to correct the peptide mass for determining protein identity; it is even possible to draw quantitative conclusions by comparison with the unlabeled peptide. Furthermore, in studies investigating substrate use, for example, such an analysis method would allow researchers to omit the 12C control experiments because identification and determination can be done using a single sample. In addition to these advantages in the field of microbial ecology, the accuracy of this technique is comparable with that of algorithms taking into account the complete isotopic envelope (7). For example, we tested the calculation given by Snijders et al. (26) with a peptide of the benzene-1,2 dioxygenase system ferredoxin-NAD(+) reductase subunit protein (P. putida KT2440). The differential isotopic pattern of 12C peptides and 13C-labeled peptides during the incorporation of different substrate ratios are shown in Fig. 2. As a result, the calculations of the measured peptide with the amino acid sequence GIFAVGDVATWPLHSGGK were as follows: (a) 1.7, (b) 8.4, (c) 21.2, (d) 49.2, and (e) 97.1 atom %. Comparing the accuracy of both approaches, the maximum deviation calculated by our method was 3.5 atom %; that for the for the method given by Snijders was 3.8 atom %, indicating that the decimal place incorporation method is quite precise.
Fig. 3.
Practical data set of P. putida ML2 peptides measured by nano-LC LTQ Orbitrap-MS. In each case, exactly 100 peptide masses (highest intensity peak) from 22 different proteins were plotted according to their exact mass and decimal place. The slope of the regression line passing through the data points was calculated by means of an R-script, resulting in the given figures (A–E) for the different substrate ratios (0, 10, 25, 50, and 100 atom %). For example, the experimental incorporation level of 7.6 atom % (B) was calculated based upon the 12C (0.000512) and 13C slope (0.000632) for the 10 atom % labeling experiment.
A greater level of accuracy can be achieved only by either isotope ratio MS (28), which is capable of detecting natural abundances (0.001 atom %) or by halogen in situ hybridization-secondary ion mass spectroscopy technology (29), also capable of detecting natural abundance, but is mostly used in a less sensitive mode leading to an accuracy of 0.01 atom %. However, both techniques are available in very few laboratories worldwide and access to these techniques is limited.
Possible Use of the Carbon-Centered Approach in the Analysis of Other Molecule Classes
Before the incorporation of stable isotopes into proteins was introduced into microbial ecological studies, so-called stable isotope probing was widely used for investigating the structure and function of microbial communities on the basis of the incorporation of 13C into DNA and RNA (30). Using these approaches, the heavy (labeled) and the light (unlabeled) molecules were separated before analysis by density gradient centrifugation, resulting in limited resolution. The subsequent analysis by isotope ratio mass spectrometry allowed for the identification of isotopically labeled substrate mineralization and, in combination with the nucleotide sequence, the identification of the metabolically active microbial species (31). A procedure analogous to the HDPR could also be applied to refine RNA/DNA-based labeling approaches. The stable atom composition of nucleotides enables one to define a two-fifteenths decimal place rule corresponding to the HDPR for proteins. It has been observed for DNA and RNA molecules that the first decimal place of a mass is nearly two-fifteenths of the first digit for mass values between 1,000 and 4,000 Da (supplemental Fig. 2). Because of the different elemental compositions of DNA/RNA and proteins, the DNA/RNA slope gently increases over the mass range. However, the large distance between the two slopes of DNA/RNA (12C and 13C) facilitates an accurate quantitative detection of 13C incorporation. Following the methodology presented here, the measurement of 100 polynucleotides could also be used for determination of the level of 13C incorporation. If it were possible to specifically isolate segments of RNA or DNA from a microbial community metabolizing an isotopically labeled substrate (by using a nucleotide probe in a stable isotope probing experiment, for example), then mass spectrometry analysis could be used to determine the amount of incorporation for the metabolized 13C. Because the application of the decimal place rule depends upon the minute differences between 12C and 13C, we examined other components of biomolecules in detail and found that the amount of the differences for 15N, 34S/36S, and 31P are similar to or larger than those for 13C but are negative and would therefore result in a negative slope. The data are summarized in Table I, and it is especially clear that 15N could be used for an analogous experimental design.
Table I. Summarized data of possible uses of stable isotopes in the analysis of other molecule classes.
A detailed analysis of other components of biomolecules, especially 14N/15N and 34S/36S stable isotope pairs, is given. The relative differences between the light and heavy slopes are similar to or larger than those for 12C/13C but are negative and would therefore result in a negative slope. Nonetheless, it is especially clear that 15N could be used for an analogous study design.
| Stable isotopes | Mr | ΔMr | ΔMr − 1 (except S, 4) | Slope direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12C | 12.000000 | 1.003355 | 0.003355 | Positive |
| 13C | 13.003355 | |||
| 14N | 14.003074 | 0.997035 | −0.002965 | Negative |
| 15N | 15.000109 | |||
| 32S | 31.972071 | 3.995010 | −0.004990 | Negative |
| 36S | 35.967081 |
CONCLUSION
Here we present a method for calculation of 13C incorporation levels into peptides by making complete use of the information acquired by modern high-resolution mass spectrometry. Compared with existing methods, calculation by the decimal place slope method has the advantage of being independent from the peptide sequence and can therefore be important for organisms with unknown genomes. The decimal place slope can be automatically calculated, thereby significantly reducing analysis time and increasing reliability and reproducibility. The slopes can be calculated using high-precision mass spectrometry data obtained from simple shotgun approaches or one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis peptide mass fingerprints. The accuracy of the calculated incorporation level is directly proportional to the number of peptides used for the analysis and requires the use of more than 100 peptide masses to achieve a precision greater than a ± 5 atom % deviation for levels of 13C incorporation. The automatic determination of incorporation levels in dynamic metabolic labeling experiments facilitates the opportunity to apply qualitative proteomics to the field of microbial ecology on a broader scale. Furthermore, the method demonstrated here may also be extended to the calculation of the labeling efficiency for a large range of biomolecules used in ecological studies, including RNA and DNA.
Acknowledgments
We thank Christine Schumann, Sylvia Els, Stephanie Hinke, and Christian Koehler (The Biotechnology Centre of Oslo) for excellent technical assistance and support with data evaluation and Peter Germain and Brandon Emory Morris for critical reading of the manuscript.
* This work was supported, in whole or in part, by the European Union (European Commission, Marie Curie Contract No. MTKD-CT 2006-042758) and by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft Priority Programme 1319.
 This article contains supplemental Figs. 1 and 2 and supplemental Table 1.
This article contains supplemental Figs. 1 and 2 and supplemental Table 1.
1 The abbreviations used are:
- SIP
- stable isotope probing
- 1-D
- one dimensional
- HDPR
- half decimal place rule
- LC
- liquid chromatography
- LTQ
- linear trap quadrupole
- MS
- mass spectrometry
- MS/MS
- tandem mass spectrometry.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bantscheff M., Schirle M., Sweetman G., Rick J., Kuster B. (2007) Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: a critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem 389, 1017–1031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Friedrich M. W. (2006) Stable-isotope probing of DNA: insights into the function of uncultivated microorganisms from isotopically labeled metagenomes. Curr. Opin. Biotech 17, 59–66 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Manefield M., Whiteley A. S., Griffiths R. I., Bailey M. J. (2002) RNA stable isotope probing, a novel means of linking microbial community function to phylogeny. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 68, 5367–5373 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jehmlich N., Schmidt F., von Bergen M., Richnow H. H., Vogt C. (2008) Protein-based stable isotope probing (Protein-SIP) reveals active species within anoxic mixed cultures. ISME J 2, 1122–1133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ong S. E., Blagoev B., Kratchmarova I., Kristensen D. B., Steen H., Pandey A., Mann M. (2002) Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture, SILAC, as a simple and accurate approach to expression proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1, 376–386 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Huttlin E. L., Hegeman A. D., Harms A. C., Sussman M. R. (2007) Comparison of full versus partial metabolic labeling for quantitative proteomics analysis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 6, 860–881 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.McIlwain S., Page D., Huttlin E. L., Sussman M. R. (2007) Using dynamic programming to create isotopic distribution maps from mass spectra. Bioinformatics 23, i328–36 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Salzmann M., Pervushin K., Wider G., Senn H., Wuethrich K. (2000) NMR Assignment and secondary structure determination of an octameric 110 kDa protein using TROSY in triple resonance experiments. J. Am. Chem. Soc 122, 7543–7548 [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhao Q., Frederick R., Seder K., Thao S., Sreenath H., Peterson F., Volkman B. F., Markley J. L., Fox B. G. (2004) Production in two-liter beverage bottles of proteins for NMR structure determination labeled with either 15N- or 13C-15N. Compar. Funct. Genom 5, 87–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Choudhary K., Spicer V. L., Donald L. J., Duckworth H. W., Ens W., Loewen P. C., Standing K. G. (2006) Method for estimating the isotopic distributions of metabolically labeled proteins by MALDI-TOFMS: Application to NMR samples. Anal. Chem 78, 5419–5423 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Snijders A. P. L., de Vos M. G. J., Wright P. C. (2005) Novel approach for peptide quantitation and sequencing based on N-15 and C-13 metabolic labeling. J. Proteome Res 4, 578–585 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yergey J. A. (1983) A general-approach to calculating isotopic distributions for mass-spectrometry. Int. J. Mass. Spectrom 52, 337–349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gay S., Binz P. A., Hochstrasser D. F., Appel R. D. (1999) Modeling peptide mass fingerprinting data using the atomic composition of peptides. Electrophoresis 20, 3527–3534 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Karty J. A., Ireland M. M., Brun Y. V., Reilly J. P. (2002) Artifacts and unassigned masses encountered in peptide mass mapping. J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci 782, 363–383 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Schmidt F., Schmid M., Mattow J., Facius A., Pleissner K. P., Jungblut P. R. (2003) Iterative data analysis is the key for exhaustive analysis of peptide mass fingerprints from proteins separated by two-dimensional electrophoresis. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 14, 943–956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jehmlich N., Schmidt F., Hartwich M., von Bergen M., Richnow H. H., Vogt C. (2008) Incorporation of carbon and nitrogen atoms into proteins measured by protein-based stable isotope probing (Protein-SIP). Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom 22, 2889–2897 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Benndorf D., Thiersch M., Loffhagen N., Kunath C., Harms H. (2006) Pseudomonas putida KT2440 responds specifically to chlorophenoxy herbicides and their initial metabolites. Proteomics 6, 3319–3329 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bradford M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem 72, 248–254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Schagger H., Aquila H., von Jagow G. (1988) Coomassie blue sodium dodecyl-sulfate polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis for direct visualization of polypeptides during electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem 173, 201–205 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Laemmli U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Neuhoff V., Arold N., Taube D., Ehrhardt W. (1988) Improved staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels including isoelectric focusing gels with clear background at nanogram sensitivity using Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 and R-250. Electrophoresis 9, 255–262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Olsen J. V., de Godoy L. M., Li G., Macek B., Mortensen P., Pesch R., Makarov A., Lange O., Horning S., Mann M. (2005) Parts per million mass accuracy on an Orbitrap mass spectrometer via lock mass injection into a C-trap. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4, 2010–2021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Perkins D. N., Pappin D. J., Creasy D. M., Cottrell J. S. (1999) Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 20, 3551–3567 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mattow J., Schmidt F., Hohenwarter W., Siejak F., Schaible U. E., Kaufmann S. H. (2004) Protein identification and tracking in two-dimensional electrophoretic gels by minimal protein identifiers. Proteomics 4, 2927–2941 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Huber P. J. (ed.) (2004) Robust Statistics, p. 43, Wiley-VCH, New York [Google Scholar]
- 26.Snijders A. P. L., de Koning B., Wright P. C. (2005) Perturbation and interpretation of nitrogen isotope distribution patterns in proteomics. J. Proteome Res 4, 2185–2191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Valkenborg D., Jansen I., Burzykowski T. (2008) A model-based method for the prediction of the isotopic distribution of peptides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 19, 703–712 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Heinzle E., Yuan Y., Kumar S., Wittmann C., Gehre M., Richnow H. H., Wehrung P., Adam P., Albrecht P. (2008) Analysis of 13C labeling enrichment in microbial culture applying metabolic tracer experiments using gas chromatography-combustion-isotope ratio mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem 380, 202–210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Musat N., Halm H., Winterholler B., Hoppe P., Peduzzi S., Hillion F., Horreard F., Amann R., Jorgensen B. B., Kuypers M. M. (2008) A single-cell view on the ecophysiology of anaerobic phototrophic bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 105, 17861–17866 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Neufeld J. D., Dumont M. G., Vohra J., Murrell J. C. (2007) Methodological considerations for the use of stable isotope probing in microbial ecology. Microb. Ecol 53, 435–442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Webster G., Watt L. C., Rinna J., Fry J. C., Evershed R. P., Parkes R. J., Weightman A. J. (2006) A comparison of stable-isotope probing of DNA and phospholipid fatty acids to study prokaryotic functional diversity in sulfate-reducing marine sediment enrichment slurries. Environ. Microbiol 8, 1575–1589 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]