Abstract
Background
Smoking remains the primary preventable cause of death and illness in the U.S. Effective, convenient treatment programs are needed to reduce smoking prevalence.
Purpose
This study compared the effectiveness of three modalities of a behavioral smoking-cessation program in smokers using varenicline.
Methods
Current treatment seeking smokers (n=1202) were recruited from a large healthcare organization between October 2006 and October 2007. Eligible participants were randomized to one of three smoking-cessation interventions: web-based counseling (n=401), proactive telephone-based counseling (PTC; n=402), or combined PTC and web counseling (n=399). All participants received a standard 12-week FDA-approved course of varenicline. Self-report determined the primary outcomes (7-day point prevalent abstinence at 3- and 6-month follow-up), the number of days varenicline was taken, and treatment-related symptoms. Behavioral measures determined utilization of both the web- and phone-based counseling.
Results
Intent-to-treat analyses revealed relatively high percentages of abstinence at 3 months (38.9%, 48.5%, 43.4%) and at 6 months (30.7%, 34.3%, 33.8%) for the web, PTC, and PTC web groups, respectively. The PTC group had a significantly higher percentage of abstinence than the web group at 3 months, OR=1.48, 95% CI 1.12–1.96, but no between-group differences in abstinence outcomes were seen at 6 months.
Conclusions
Phone counseling had greater treatment advantage for early cessation and appeared to increase medication adherence, but the absence of differences at 6 months suggests that any of the interventions hold promise when used in conjunction with varenicline.
Introduction
Proactive telephone counseling (PTC) is a popular mode of delivery of behavioral counseling for smoking cessation. Its advantages include convenience and interpersonal contact, and its effectiveness is well-documented.1, 2 Delivery of health information and behavioral counseling for smoking cessation via web-based platforms is also becoming increasingly available, and several real-world evaluations of online cessation services3–5 and randomized trials of web-based services6–10 have been reported. Most of these studies demonstrate web-based delivery is effective.6, 9, 10 The combination of PTC and web-based delivery could result in better abstinence outcomes than either delivery method alone. For example, PTC could be reinforced and supplemented by content on the web which is available to smokers at any time. Information entered by the smoker online and sections visited could help tailor future counseling interactions. However, prior research has not examined the potential synergy of combining PTC and web-based treatment.
At the time the present study was being designed, varenicline (aka, Chantix), an α4β2 partial agonist that reduces the effects of withdrawal while also temporarily reducing the reinforcing effects of nicotine through stimulation of the dopaminergic reward pathway, had just been approved by the FDA. Evidence in support of varenicline’s efficacy is derived entirely from Phase II11–13 and standard duration Phase III14–18 randomized placebo-controlled trials that also provided concomitant face-to-face behavioral counseling. Compared to placebo, varenicline resulted in a significantly higher biochemically confirmed abstinence percentage at 6 months (33.2% vs 13.8 for placebo) following cessation.2 The extent to which varenicline is effective under more real-world (i.e., less-controlled) conditions or in conjunction with counseling delivered via PTC or the web remains to be determined.
The primary objective of this randomized investigation was to determine the relative effectiveness of a widely used and empirically supported smoking-cessation program19–21 delivered three ways in a real-world setting: as standard PTC, via a newly developed web-based mode of delivery translated from the existing PTC program, and as a combined PTC- and web-based program. Because it offers both interpersonal contact and greater availability, it was hypothesized that the combined PTC- and web-based condition would result in the highest percentage of abstinence at 6-month follow-up and that the web condition would result in a 6-month abstinence percentage that was equivalent to that observed for the PTC condition. Given recent concerns about potential side effects among people taking varenicline,22 a secondary aim was to report on symptoms and other events reported by participants in each of the three treatment groups. Also provided are data on the effectiveness of varenicline when paired with various behavioral treatment programs and offered in a real-world setting.
Methods
Setting and Participants
Group Health, headquartered in Seattle, WA, is a consumer-governed nonprofit healthcare organization that serves approximately 600,000 residents of Washington and Idaho. All protocols were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Boards of Group Health, SRI International, and Free & Clear, Inc., as well as by a study Data and Safety Monitoring Board.
Participants were recruited from October 2006 to October 2007 through health plan magazine advertisements, employee mailings, physician referrals, and through Free & Clear’s Quit For Life® Program. Smokers were eligible if they: were aged ≥18 years; smoked at least 10 cigarettes per day over the past year and 5 cigarettes per day within the past week; had dependable telephone and Internet access and comfort using the Internet; were eligible for smoking-cessation services under current health plan coverage, and were medically appropriate for varenicline use.
Exclusion Criteria
Because participants did not see a study physician in person and received their prescription medication by mail, the exclusion criteria were more conservative than what is recommended in the varenicline prescribing information.2 Individuals were excluded from participation for any of the following: current/planned pregnancy or breast feeding; self-report of poor health, severe chronic heart disease or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; on dialysis or with certain kidney disease; current treatment for or self-report of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or mania; high-frequency alcohol use over the past 6 months (more than two drinks per day almost every day) and/or binge drinking two or more times in the last month, current use of bupropion, NRT, investigational or recreational/street drugs, or cimetidine, metformin, phenformin, pindolol or procainamide (drugs that could potentially interfere with renal clearance of varenicline23).
Screening, Intake, and Follow-up Surveys
Eligible volunteers were interviewed by phone at intake to assess smoking history including the Fagerström Test for Nicotine Dependence24; quitting history; motivation to quit; psychosocial characteristics including: (1) items from the Perceived Stress Scale,25 (2) depression history assessed using an item reflecting the two hallmark symptoms of major depression described in the DSM-IV,26 and, (3) current depressive symptoms assessed using a brief measure derived from the Hopkins Symptom Checklist;27 and demographics. Telephone follow-up surveys were conducted by non-intervention study staff approximately 3 and 6 months after the target quit date to collect information on quit attempts, smoking, and medication use. At 3 months, participants were also asked if during the past month they experienced any of a number of symptoms including probable medication side effects (obtained from the Chantix prescribing information) and nicotine abstinence effects.28 For each symptom experienced the participant rated its severity on a 5-point scale as follows: 1=very mild, 2=mild, 3=moderate, 4=severe, and 5=very severe.
Randomization and Interventions
Participants were randomized to treatment at the end of the Intake Survey. Group assignment was randomly allocated using an automated algorithm built into the study database. No restrictions such as stratification or blocking were employed as part of the randomization process, and participants and study staff were not blinded to treatment assignment.
Behavioral Intervention
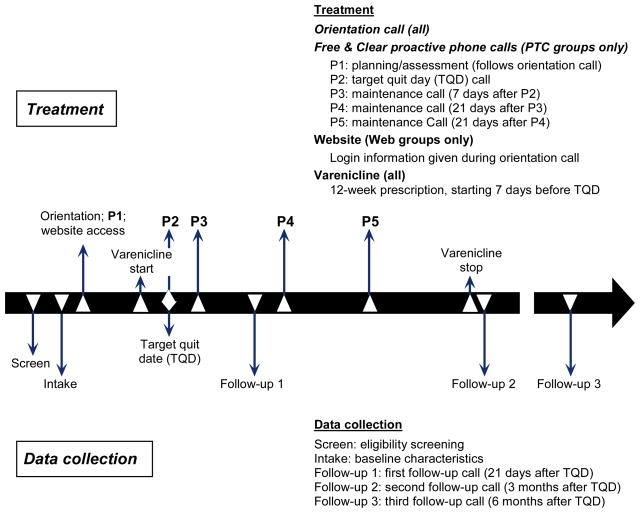
The three behavioral interventions were delivered by Free & Clear. The PTC condition was the original Free & Clear Quit For Life® program19–21, 29–31 and the web and PTC–web components were developed to replicate the principles and components of the PTC-based Quit For Life® program. Once screened and randomized, all participants received a 5- to 10-minute orientation call, printed Quit Guides and access to a toll-free in-bound support line for ad hoc calls. Other services varied by intervention group. PTC participants received up to five one-on-one proactive phone counseling sessions initiated by a Free & Clear tobacco treatment counselor (see Figure 1). Participants in the web-based condition had access to the online program which contained standardized content and interactive tools. PTC–web participants received access to both programs, and the counselors had access to information participants entered online.
Figure 1.
Timeline of study activities
PTC, proactive telephone-based counseling
The proactive counseling calls provided practical expert support to help participants develop problem-solving and coping skills, secure social support, and design a plan for successful cessation and long-term abstinence. Calls were scheduled at times convenient for the participant and at relapse-sensitive intervals. Counselors used Motivational Interviewing techniques to elicit each participant’s agenda for the call. The web-based intervention contained interactive tools modified from those used in the PTC intervention. Tailored content was based on where the participant was in the quit process. Key features included an interactive quit plan, educational content in an online library, a quit calendar, cost calculator and progress tracker, a tool to email to friends and family for support, and active discussion forums to interact with other members. During the PTC–web proactive calls, the treatment counselor encouraged participants to use the website for additional information and social support and to track the number of cigarettes smoked per day. For PTC–web participants, the treatment counselors were able to see Quit Status, last login, and last use of the discussion forums. The website contained numerous interactive sections and all items were covered by treatment counselors during the calls.
Medication
Participants in all three treatment groups received a prescription for a 12-week supply of varenicline, to be taken according to recommended guidelines2 starting 1 week prior to the quit date. In addition to material packaged with the medication, Free & Clear sent information about medication use with the printed Quit Guides. Treatment counselors encouraged and answered all questions about the medication, and Free & Clear had a detailed process for managing any symptoms reported to them by the participants.
Utilization Measures
Utilization of behavioral programs was summarized into two global measures: number of contacts (phone calls completed plus website logins), and total minutes (sum of minutes spent on the phone and the website). Phone minutes included all minutes spent on proactive and ad hoc telephone calls, and website minutes were collected automatically via a web activity tracker. To remove the influence of a few very large outliers, total contacts and contact duration were truncated based on visual inspection of the data by the study biostatistician. These truncated values fell between the 95th and 99th percentiles for each measure. Utilization of medication is summarized as proportion of pills taken during the treatment phase (a 5-point scale from 1=“none” to 5=“all”) as well as by the total number of days varenicline was taken.
Outcome Measures
Abstinence was defined as the self-report of no smoking, not even a puff, within the past 7 or 30 days (i.e., 7- and 30-day point prevalent abstinence). Using an intention-to-treat approach, individuals who were not reached for follow-up were considered to be smoking.
Sample Size Estimates
Based on prior experience with Free & Clear PTC in this population, it was assumed that the PTC-only treatment would be 32.3% abstinent at follow-up. Having 400 participants per treatment arm would provide 80% power to distinguish a difference in abstinence percentage at follow-up between the PTC-only and the web or the combined PTC–web groups of roughly 9.9% (i.e., up to 42.2% or down to 23.1%).
Statistical Analysis
Overall group differences on pretreatment characteristics and treatment utilization were examined using ANOVA (continuous variables) or the chi-square test of equality of distributions (categoric variables). Pairwise comparisons between treatments on utilization variables were conducted while adjusting for multiple comparisons via the HSD Tukey procedure. Logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the relationship of mode of counseling (web, PTC, PTC–web) to smoking outcome at each follow-up point, both with and without relevant covariates (see Table 1). For analysis of intake predictors of abstinence at 3 and 6 months, only those variables with P-values less than 0.25 in an initial full model with all intake predictors were included in the models shown in Table 5.
Table 1.
Intake characteristics of the sample overall and by treatment group
| Characteristic | Overall n=1202 | Web n=401 | PTC n=402 | PTC Web n=399 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | ||||
| Age in years (M) | 47.3 | 47.1 | 47.0 | 47.9 |
| Gender (% female) | 66.9 | 66.8 | 65.2 | 68.7 |
| Race (% white) | 89.7† | 91.7 | 87.9 | 89.4 |
| Years of formal schooling (M) | 14.0 | 14.0 | 14.0 | 14.1 |
| Marital status (% married) | 63.7 | 66.4 | 63.7 | 61.0 |
| BMI (kg/m2; M) | 27.8 | 27.9 | 27.7 | 27.7 |
| Smoking history | ||||
| Cigarettes per day (M) | 19.7 | 19.8 | 19.5 | 19.8 |
| FTNDa (M) | 4.9 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 5.0 |
| Other smokers in home (% yes) | 44.1 | 47.4 | 41.5 | 43.4 |
| Quitting history | ||||
| Quit attempt past year (% yes) | 48.3 | 46.3 | 49.9 | 48.6 |
| Longest previous quit of >6 months (% yes) | 36.7 | 36.7 | 35.1 | 38.2 |
| Previous use of NRTb (% yes) | 82.5 | 80.8 | 83.6 | 83.2 |
| Previous use of bupropion (% yes) | 48.4 | 49.0 | 47.9 | 48.5 |
| Motivational | ||||
| Motivated to quit (% extremely) | 69.0 | 66.5 | 70.2 | 70.2 |
| Confident in success (% extremely) | 35.5 | 34.5 | 36.9 | 35.0 |
| Psychosocial | ||||
| Perceived Stress | 7.6 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 7.5 |
| Depression Scale | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Ever suffer from depression (% yes)* | 56.2 | 57.5 | 59.9 | 51.0 |
| % of family ever depressed (M) | 19.1 | 19.3 | 19.5 | 18.3 |
| % of family ever smoked (M) | 52.0 | 52.8 | 51.1 | 52.1 |
The three treatment groups were similar on all characteristics listed except Ever suffer from depression (χ2 (2) =6.7, P =.04).
FTND=Fagerström Test of Nicotine Dependence;
NRT=nicotine replacement therapy.
Remaining racial categories include American Indian/Alaska Native (0.9%), Asian (1.0%), black (3.7%), Pacific Islander (1.0%), and “more than one race” (3.7%). N=13 (1.0%) declined to state their race.
Table 5.
Predictors of 7-day point prevalence abstinence at 3 and 6 months
| 3 Months |
6 Months |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | P-value | OR (95% CI) | P-value | OR | 95% CI | |
| Demographic | ||||||
| Older age (years)* | 0.0438 | 1.13 (1.00, 1.27) | 0.1476 | 1.10 | 0.97, 1.24 | |
| Male gender | 0.4388 | 1.10 | 0.86, 1.42 | 0.1341 | 1.22 | 0.94, 1.59 |
| More years of formal schooling* | 0.0060 | 1.18 | 1.05, 1.33 | 0.0991 | 1.11 | 0.98, 1.26 |
| Smoking history | ||||||
| Lower FTND* | 0.0011 | 1.23 | 1.08, 1.39 | 0.0018 | 1.23 | 1.08, 1.39 |
| No other smokers in home | – | – | – | 0.2456 | 1.16 | 0.90, 1.49 |
| Previous use of bupropion | – | – | – | 0.1667 | 1.19 | 0.93, 1.53 |
| Quitting history | ||||||
| Previous quit attempt > 6 months | 0.0084 | 1.39 | 1.09, 1.78 | 0.0156 | 1.37 | 1.06, 1.77 |
| Quit attempt 24-hour past year | 0.1468 | 1.19 | 0.94, 1.51 | – | – | – |
| Motivational | ||||||
| Higher motivation to quit* | 0.0030 | 1.20 | 1.06, 1.36 | 0.0176 | 1.17 | 1.03, 1.34 |
| Psychosocial | ||||||
| Lower Perceived Stress* | 0.1167 | 1.10 | 0.98, 1.25 | 0.0180 | 1.17 | 1.03, 1.34 |
Note: Only one of two variables with high bivariate intercorrelations were selected for inclusion (for example, cigarettes smoked per day and FTND, r = 0.69). In order to maximize the number of cases available to be included in the models to predict treatment outcome, multiple imputation65–66 was used to replace each missing value with a set of plausible values. The multiply imputed data sets were then analyzed by using standard procedures.
ORs for continuous variables reflect a change of 1 SD. FTND= Fagerström Test of Nicotine Dependence
Results
Eligibility
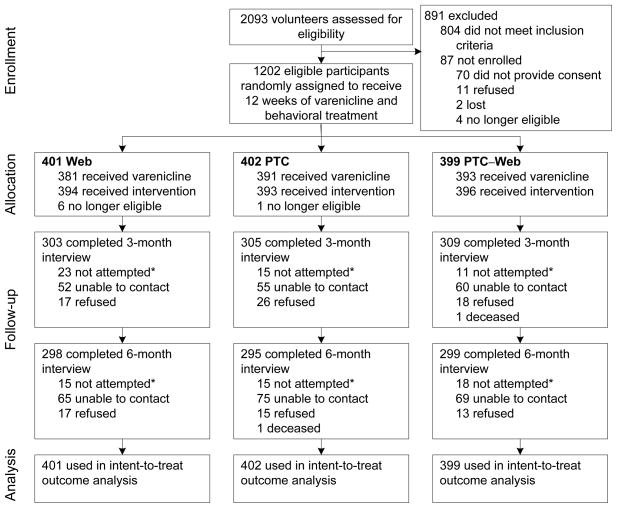
A total of 2,093 screening interviews were conducted. The 2,093 screened volunteers were, on average, aged 47.5 (±11.5) years, smoked 20.6 (±8.9) cigarettes per day in the past year, and were 64.6% female. Overall, 804 (31.2%) volunteers were excluded from participation in this study, with the most common reasons being computer-related (lack of Internet or e-mail access; 20% of 804) followed by too few cigarettes smoked per day (14%), excessive daily alcohol use or binge drinking (14%), current use of a contraindicated medication (recreational or prescribed; 13%), the lack of proper coverage under the volunteer’s insurance plan (12%) and ineligibility for smoking-cessation services (12%). While eligible volunteers were similar to those who were excluded with respect to number of cigarettes smoked per day at screening (20.9 vs 20.3), eligible volunteers were younger (46.8 vs 48.8 years, P < .0001) and more likely to be female (66.9% vs 60.9%, P = .006).
Participant Characteristics
Consent was received and intake surveys completed for 1,202 volunteers (93.3% of all eligible to participate; see Figure 2). The characteristics of the resulting sample overall and by treatment group are shown in Table 1.
Figure 2.
Participant disposition
Note: After treatment assignment, some participants did not participate in the behavioral interventions. A few who had participated did not set a target date to quit smoking, one of the required steps to initiate the varenicline prescription.
* Not attempted: Because the timing for interviews was based on the target quit date, no attempt was made to contact participants at 3 months if they had not set a quit date (n=33). Other participants were not attempted for interviews if they had requested no further participation (n=16 at 3 months, n=48 at 6 months) or had passed away (n=1 at each time point).
PTC, proactive telephone-based counseling
Follow-up
A total of 917 (76.3%) were reached for the 3-month interview and 892 (74.2%) were reached for the 6-month interview. There were no differences in participation percentages among the three treatment groups at either time point.
Treatment Utilization
Pairwise comparisons revealed that the total number of contacts varied significantly across treatment groups (see Table 2) with the PTC–web group having a higher average number than either of the other two treatments (vs web, P < .05, vs PTC, P < .05). Total contact duration in minutes was significantly lower for the PTC and web groups than for the PTC–web group (vs web, P < .05; vs PTC, P < .05). The PTC group reported a significantly larger number of days taken varenicline than did the other two groups (vs web, P < .05; vs PTC–web, P < .05) and a significantly higher proportion of pills taken than did the web group (P = .02).
Table 2.
Utilization by treatment group
| Characteristic | Web n=401 | PTC n=402 | PTC Web n=399 | Overall comparison P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Behavioral treatment | ||||
| Number of contacts, M (SD) | 5.2a (5.0) | 4.1b (1.7) | 6.6c (4.4) | <.0001 |
| Contact duration in minutes, M (SD) | 67.9a (68.2) | 67.5a (29.9) | 100.2 (62.6) | <.0001 |
| Medication | ||||
| Number of days varenicline taken, M (SD) | 60.0b (35.7) | 67.7 (31.2) | 61.5b (32.7) | <.007 |
| Number of pills taken (% “most” or “all”) | 71.2a | 79.1b | 73.8ab | ns |
Pairwise comparisons: means that have no superscript in common are significantly different from each other (Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference, P<0.05), superscripts generated at http://www.jerrydallal.com/LHSP/similar_prog.htm
Number of contacts=Total completed phone calls+web logins
Contact duration=Total minutes spent on the phone or on the website
Participants did use the option to call in for support across the three treatment conditions. There were no differences among the three treatment groups regarding the number (percentage) who made one or more of these ad hoc calls: web: 128 (32.1%), PTC: 126 (31.4%), PTC–web: 144 (36.1%). For those who made these calls, the average number made was similar across the groups: web: 1.6, PTC 1.4, and PTC–web 1.6.
At the 3-month interview a total of 582 participants (64%) indicated they were not taking the medication. Participants could endorse any number of reasons for stopping which included experience of treatment-related symptoms (39%), running out of pills (33%), feeling they did not need it (24%), feeling it was not working (8%), and “other” (26%). There were no group differences for no longer taking the medication or reasons for stopping.
Point Prevalence Outcomes
Intention-to-treat analyses revealed relatively high percentages of 7-day point prevalence abstinence at 3 and 6 months (see Table 3). Pairwise comparisons revealed that the PTC group had a significantly higher abstinence percentage than the web group at 3 months, OR=1.48, 95% CI 1.12–1.96, but no group differences were seen at 6 months. A similar pattern was seen for 30-day point prevalence abstinence.
Table 3.
Seven and 30-day point prevalence abstinence at 3 and 6 months by treatment group
| Follow-up point | 7-Day Point Prevalence Abstinence, % | OR (95% CI) for comparison to web | OR (95% CI) for comparison to PTC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 months | |||
| Web | 38.9 | ||
| PTC | 48.5 | 1.48 (1.12, 1.96)* | |
| PTC–web | 43.4 | 1.20 (0.91, 1.59) | 0.81 (0.62, 1.07) |
| 6 months | |||
| Web | 30.7 | ||
| PTC | 34.3 | 1.18 (0.86, 1.56) | |
| PTC–web | 33.8 | 1.16 (0.88, 1.59) | 0.98 (0.73, 1.31) |
| 30-Day Point Prevalence Abstinence, % | OR (95% CI) for comparison to web | OR (95% CI) for comparison to PTC | |
| 3 months | |||
| Web | 32.7 | ||
| PTC | 42.0 | 1.50 (1.12, 1.99)* | |
| PTC–web | 39.1 | 1.32 (0.99, 1.77) | 0.88 (0.67, 1.17) |
| 6 months | |||
| Web | 27.4 | ||
| PTC | 30.6 | 1.17 (0.86, 1.58) | |
| PTC–web | 30.3 | 1.15 (0.85, 1.56) | 0.99 (0.73, 1.33) |
P < 0.05.
Reported Symptoms
The percentages of people surveyed at 3 months who experienced any of the listed symptoms are shown in Table 4. The most frequently reported symptom across all participants was the desire to smoke, which was also the most likely to be rated as higher in intensity.
Table 4.
Overall symptom experience at 3 months (%)a
| Symptom | None | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probable side effects | ||||
| Nausea | 64.8 | 16.2 | 12.2 | 6.7 |
| Vomiting | 92.5 | 3.7 | 2.1 | 1.7 |
| Constipation | 73.5 | 12.3 | 10.2 | 4.0 |
| Flatulence | 52.5 | 20.1 | 20.5 | 6.9 |
| Change in dreaming | 62.5 | 12.0 | 15.5 | 10.0 |
| Change in taste perception | 62.3 | 14.2 | 18.3 | 5.1 |
| Probable abstinence effects | ||||
| Difficulty sleeping | 59.5 | 14.3 | 18.2 | 8.0 |
| Change in appetite | 65.4 | 11.9 | 16.8 | 5.9 |
| Desire to smoke | 26.1 | 28.7 | 26.7 | 18.4 |
| Difficulty concentrating | 75.7 | 13.0 | 8.8 | 2.5 |
| Tension/agitation | 61.1 | 19.9 | 16.3 | 2.8 |
| Irritability/anger | 63.1 | 18.3 | 14.5 | 4.1 |
| Depression | 74.8 | 14.8 | 8.5 | 2.0 |
| Confusion | 86.8 | 8.4 | 4.1 | 0.8 |
| Anxiety | 69.4 | 15.5 | 12.2 | 2.9 |
Note: Because the study design did not include a drug placebo condition, drug and abstinence side effects are considered “probable.”
Participants who did not experience a symptom were given the rating of “none”. For display simplicity, “very mild” and “mild” categories were combined, as were the “severe” and “very severe” categories.
An examination of mean symptom severity ratings by type of counseling was also conducted in two groups: those who reported not smoking but still taking varenicline at the time of the 3-month interview (for probable side effects; n= 227) and those who reported not smoking but no longer taking varenicline (for probable abstinence effects; n= 296). Type of behavioral counseling did not significantly influence mean severity ratings of the six probable drug side effects. Of the nine probable abstinence effects, only one was associated with form of counseling (change in appetite) with the PTC–web group reporting significantly higher average severity ratings than the web groups (P < 0.05; data not shown).
Predictors of Abstinence at 3 and 6 Months
Table 5 presents results of the analysis of prediction of subsequent abstinence at 3 and 6 months by intake characteristics. Variables that were associated with abstinence at 3 months only included older age, and more years of formal education. Lower levels of stress were associated with decreased risk for smoking at 6 months but not at 3 months. Variables that were consistently predictive of abstinence at both 3 and 6 months included having had a previous quit attempt that was longer than 6 months, lower levels of nicotine dependence, and a higher level of motivation to quit.
Discussion
While it was hypothesized that the PTC–web group would experience better 6-month outcomes by virtue of the synergy between the two components, an additive benefit of allowing participants access to online resources 24 hours a day, 7 days a week was not observed. The fact that the web and PTC groups experienced equivalent 6-month outcomes was consistent with expectation. A plausible explanation for the lack of significant differences among the three treatment groups at 6 months is that the content and treatment philosophy of all three behavioral programs were similar. The web and PTC–web programs were designed to be comparable to the PTC program in order to determine whether mode of delivery influenced treatment outcomes.
The PTC program provided several of the proven aspects recommended by the PHS guidelines: social support, practical advice and support, and assistance with planning and developing problem solving and coping skills. The reported percentages of abstinence for all three forms of the behavioral treatment–varenicline combination were roughly three times higher than the 13.1% point estimate provided in Fiore et al. for PTC alone2 and are consistent with the self-reported percentage seen in a previous study of a behavioral treatment–bupropion combination in this setting (32.3%).21
The 3-month point prevalence abstinence percentage for the PTC condition (48.5%) is consistent with that reported by two Phase III trials (50.3%),14, 15 and the 6-month point prevalence abstinence outcomes for all treatment groups fall within the 95% CI for the abstinence percentage estimated from currently available data relevant to varenicline’s biochemically confirmed efficacy (28.9% – 37.8%).2 Based on these observed abstinence outcomes it is concluded that the percentages observed in the varenicline Phase III clinical trials are generalizable to real-world behavioral treatment settings under less-controlled conditions.
Gastrointestinal disturbances and abnormal dreams were the most likely symptoms to be rated as moderate or severe at the 3-month interview, similar to the proportion of study participants reporting side effects in the efficacy trials. Overall, the type of behavioral counseling was not associated with severity ratings for any of the symptoms assessed in the present study. A previous analysis showed that change in the severity of these symptoms also did not differ as a function of a self-reported depression history.32
In the present study, there were nine (0.8%) serious adverse effects reported to the FDA, but none was considered likely to be causally related to varenicline use with the exception of a moderate allergic event that did not require medical attention. An individual with an extensive psychiatric history undisclosed at study entry had a brief psychiatric hospitalization. There were two cardiac deaths that occurred in participants with pre-existing cardiac disease and risk factors. For both the cardiac deaths and the psychiatric hospitalization, a potentiating role of varenicline was considered unlikely.
Potential limitations of the study include its reliance on self-report for medication adherence and smoking outcomes. Because this open-label study was conducted in a real-world setting and utilized telephone and mailed interactions between study participants and project staff, more intensive monitoring was not feasible. The finding that utilization of treatment regimens varied across treatment groups will need to be confirmed in subsequent studies. The absence of biochemical confirmation may have resulted in an overestimation of the true abstinence percentage; however previous analyses suggest that the amount of underreporting of smoking in a large field trial of this type may be minimal.20, 33–35 Moreover, all interventions examined in this trial can be described as being of “low intensity.” There were no in-person visits and, at most, participants received five proactive call attempts. There were no guarantees that the participants would take these calls or to be fully engaged in treatment. In addition, the self-reported smoking status used to document outcomes was provided by the participants to the Group Health Survey Research Program, an organization that is independent of the interventions provided by Free & Clear. For these reasons, it is felt that the inherent demand of the assessment context would have had only minimal impact on the over-reporting of abstinence.
The lack of a no-medication control group limits the ability to draw conclusions about the effectiveness of these behavioral treatments without medication or to determine the true range of symptoms associated with varenicline use or nicotine withdrawal. In addition, the systematic screening of all probable treatment-related symptoms endorsed at each follow-up is different than the method used to assess side effects in a standard clinical trial, and could result in greater frequencies of some side effects than previously reported.
While these results are consistent with those seen in the original Phase III clinical trials the reader should remain cautious to not overgeneralize. The individuals recruited for this trial were highly motivated and were offered behavioral support. While the observed abstinence outcomes are closer to those expected in real-world applications similar to that seen in managed care, they are likely to be higher still than those seen in the general population for whom varenicline is prescribed for smoking cessation but no concomitant behavioral support is provided.
Conclusion
The present study reveals two important issues in nicotine addiction treatment. First, that there were no differences in abstinence outcomes at 6 months suggests that any of the three programs offered here hold promise as alternative interventions in combination with varenicline. Second, this study provides important data regarding the use of varenicline in real-world settings and is responsive to the need for community-based trials involving varenicline.36, 37 Use of varenicline in a real-world setting, with less stringent eligibility criteria and less clinical follow-up than in the Phase III trials, still results in substantial abstinence outcomes when paired with behavioral intervention.
Acknowledgments
All authors had full access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
The authors wish to acknowledge the following individuals who contributed substantially to this project: Gaye Courtney, Lisa Nguyen, Shahab Kahn and Martha Agreda for their efforts in screening and enrolling the participants in this study; Sallie Dacey, M.D for consultation on eligibility issues and medical chart review as needed; Jennifer Cinnamon for her diligent care and monitoring of trial participants and general assistance with myriad essential tasks throughout the study; Julia Anderson and KatieRose Oliver for their hard work and patience in managing the collection of the follow-up data; Ken Wassum, who was instrumental in developing protocols for varenicline treatment support and health event reporting; Jenny Hapgood for managing the development of the website; and Abigail Halperin, M.D. for support of health event reporting and investigation. The authors also wish to acknowledge the consultative assistance of Drs. Ray Niaura, Caryn Lerman, and Neal Benowitz, who served on the study’s data and safety monitoring board.
This study was funded by the National Cancer Institute (grant # R01CA071358) and is registered at Clinicaltrials.gov (NCT00301145). Varenicline and nominal support for recruiting participants was provided by Pfizer, Inc. Neither entity had any role in the study design, the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in the writing of the report, or in the decision to submit the report for publication. Portions of this paper were presented to the annual meeting of the Society for Behavioral Medicine, Montreal, April 24, 2009.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Disclosures
SMZ owns stock in Free & Clear, Inc.; and GES received financial support from Pfizer to attend a 1-day advisory meeting in 2008, and a small grant from Pfizer to support recruitment and study intake. No other financial disclosures were reported by the authors of this paper.
References
- 1.Stead LF, Perera R, Lancaster T. Telephone counseling for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2006;3:CD002850. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002850.pub2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fiore MC, Jaén CR, Baker TB, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline. Rockville, MD: USDHHS. Public Health Service; May, 2008. Treating Tobacco Use and Dependence: 2008 Update. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cobb NK, Graham AL, Bock BC, Papandonatos G, Abrams DB. Initial evaluation of a real-world Internet smoking cessation system. Nicotine Tob Res. 2005;7(2):207–16. doi: 10.1080/14622200500055319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Graham AL, Cobb NK, Raymond L, Sill S, Young J. Effectiveness of an Internet-based worksite smoking cessation intervention at 12 months. J Occup Environ Med. 2007;49(8):821–8. doi: 10.1097/JOM.0b013e3180d09e6f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Saul JE, Schillo BA, Evered S, Luxenberg MG, Kavanaugh A, Cobb N, et al. Impact of a statewide Internet-based tobacco cessation intervention. J Med Internet Res. 2007;9(3):e28. doi: 10.2196/jmir.9.4.e28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Etter JF. Comparing the efficacy of two Internet-based, computer-tailored smoking cessation programs: a randomized trial. J Med Internet Res. 2005;7(1):e2. doi: 10.2196/jmir.7.1.e2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Japuntich SJ, Zehner ME, Smith SS, Jorenby DE, Valdez JA, Fiore MC, et al. Smoking cessation via the Internet: a randomized clinical trial of an Internet intervention as adjuvant treatment in a smoking cessation intervention. Nicotine Tob Res. 2006;8 (Suppl 1):S59–67. doi: 10.1080/14622200601047900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pike KJ, Rabius V, McAlister A, Geiger A. American Cancer Society’s QuitLink: randomized trial of Internet assistance. Nicotine Tob Res. 2007;9(3):415–20. doi: 10.1080/14622200701188877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Strecher VJ, McClure JB, Alexander GL, Chakraborty B, Nair VN, Konkel JM, et al. Web-based smoking-cessation programs: results of a randomized trial. Am J Prev Med. 2008;34(5):373–81. doi: 10.1016/j.amepre.2007.12.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Strecher VJ, Shiffman S, West R. Randomized controlled trial of a web-based computer-tailored smoking cessation program as a supplement to nicotine patch therapy. Addiction. 2005;100(5):682–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2005.01093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nides M, Oncken C, Gonzales D, Rennard S, Watsky EJ, Anziano R, et al. Smoking cessation with varenicline, a selective alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor partial agonist: results from a 7-week, randomized, placebo- and bupropion-controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(15):1561–8. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.15.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Oncken C, Gonzales D, Nides M, Rennard S, Watsky E, Billing CB, et al. Efficacy and safety of the novel selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, varenicline, for smoking cessation. Arch Intern Med. 2006;166(15):1571–7. doi: 10.1001/archinte.166.15.1571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Niaura R, Hays JT, Jorenby DE, Leone FT, Pappas JE, Reeves KR, et al. The efficacy and safety of varenicline for smoking cessation using a flexible dosing strategy in adult smokers: a randomized controlled trial. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008 doi: 10.1185/03007990802177523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gonzales D, Rennard SI, Nides M, Oncken C, Azoulay S, Billing CB, et al. Varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, vs sustained-release bupropion and placebo for smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;296(1):47–55. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jorenby DE, Hays JT, Rigotti NA, Azoulay S, Watsky EJ, Williams KE, et al. Efficacy of varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, vs placebo or sustained-release bupropion for smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;296(1):56–63. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nakamura M, Oshima A, Fujimoto Y, Maruyama N, Ishibashi T, Reeves KR. Efficacy and tolerability of varenicline, an alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, in a 12-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose–response study with 40-week follow-up for smoking cessation in Japanese smokers. Clin Ther. 2007;29(6):1040–56. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.06.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tsai ST, Cho HJ, Cheng HS, Kim CH, Hsueh KC, Billing CB, Jr, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of varenicline, a selective alpha4beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, as a new therapy for smoking cessation in Asian smokers. Clin Ther. 2007;29(6):1027–39. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tonstad S, Tonnesen P, Hajek P, Williams KE, Billing CB, Reeves KR. Effect of maintenance therapy with varenicline on smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006;296(1):64–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.296.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hollis JF, McAfee TA, Fellows JL, Zbikowski SM, Stark M, Riedlinger K. The effectiveness and cost effectiveness of telephone counselling and the nicotine patch in a state tobacco quitline. Tob Control. 2007;16 (Suppl 1):i53–9. doi: 10.1136/tc.2006.019794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Orleans CT, Schoenbach VJ, Wagner EH, Quade D, Salmon MA, Pearson DC, et al. Self-help quit smoking interventions: effects of self-help materials, social support instructions, and telephone counseling. J Consult Clin Psychol. 1991;59(3):439–48. doi: 10.1037//0022-006x.59.3.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Swan GE, McAfee T, Curry SJ, Jack LM, Javitz H, Dacey S, et al. Effectiveness of bupropion sustained release for smoking cessation in a health care setting: a randomized trial. Arch Intern Med. 2003;163(19):2337–44. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.19.2337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Public Health Advisory: Important Information on Chantix (varenicline) 2008 January 10 2009]; Available from: http://www.fda.gov/cder/drug/advisory/varenicline.htm.
- 23.Leabman MK, Huang CC, Stryke D, Johns SJ, Kawamoto M, Ferrin TE, et al. PharmGKB update: I. Genetic variants of the organic cation transporter 2 (OCT2, SLC22A2) Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55(3):399. doi: 10.1124/pr.55.3.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Heatherton TF, Kozlowski LT, Frecker RC, Fagerstrom KO. The Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire. Br J Addict. 1991;86(9):1119–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.1991.tb01879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cohen S, Lichtenstein E. Perceived stress, quitting smoking, and smoking relapse. Health Psychol. 1990;9(4):466–78. doi: 10.1037//0278-6133.9.4.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.American Psychological Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Derogatis LR, Lipman RS, Rickels K, Uhlenhuth EH, Covi L. The Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL): a self-report symptom inventory. Behav Sci. 1974;19(1):1–15. doi: 10.1002/bs.3830190102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ward MM, Swan GE, Jack LM. Self-reported abstinence effects in the first month after smoking cessation. Addict Behav. 2001;26(3):311–27. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4603(00)00107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Curry SJ, Grothaus LC, McAfee T, Pabiniak C. Use and cost effectiveness of smoking-cessation services under four insurance plans in a health maintenance organization. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(10):673–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199809033391006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.El-Bastawissi A, McAfee T, Zbikowski SM, Hollis J, Stark M, Wassum K, et al. The uninsured and Medicaid Oregon tobacco user experience in a real-world, phone-based cessation programme. Tob Control. 2003;12(1):45–51. doi: 10.1136/tc.12.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ringen K, Anderson N, McAfee T, Zbikowski SM, Fales D. Smoking cessation in a blue-collar population: results from an evidence-based pilot program. Am J Ind Med. 2002;42(5):367–77. doi: 10.1002/ajim.10129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McClure JB, Swan GE, Jack L, Catz SL, Zbikowski SM, McAfee TA, et al. Mood, side-effects and smoking outcomes among persons with and without probable lifetime depression taking varenicline. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(5):563–9. doi: 10.1007/s11606-009-0926-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Glasgow RE, Mullooly JP, Vogt TM, Stevens VJ, Lichtenstein E, Hollis JF, et al. Biochemical validation of smoking status: pros, cons, and data from four low-intensity intervention trials. Addict Behav. 1993;18(5):511–27. doi: 10.1016/0306-4603(93)90068-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Patrick DL, Cheadle A, Thompson DC, Diehr P, Koepsell T, Kinne S. The validity of self-reported smoking: a review and meta-analysis. Am J Public Health. 1994;84(7):1086–93. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.7.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.SRNT Subcommittee on Biochemical Verification. Biochemical verification of tobacco use and cessation. Nicotine Tob Res. 2002;4(2):149–59. doi: 10.1080/14622200210123581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cahill K, Stead LF, Lancaster T. Nicotine receptor partial agonists for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008;(3):CD006103. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006103.pub3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Schroeder SA, Sox HC. Trials that matter: varenicline: a designer drug to help smokers quit. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145(10):784–5. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-145-10-200611210-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]