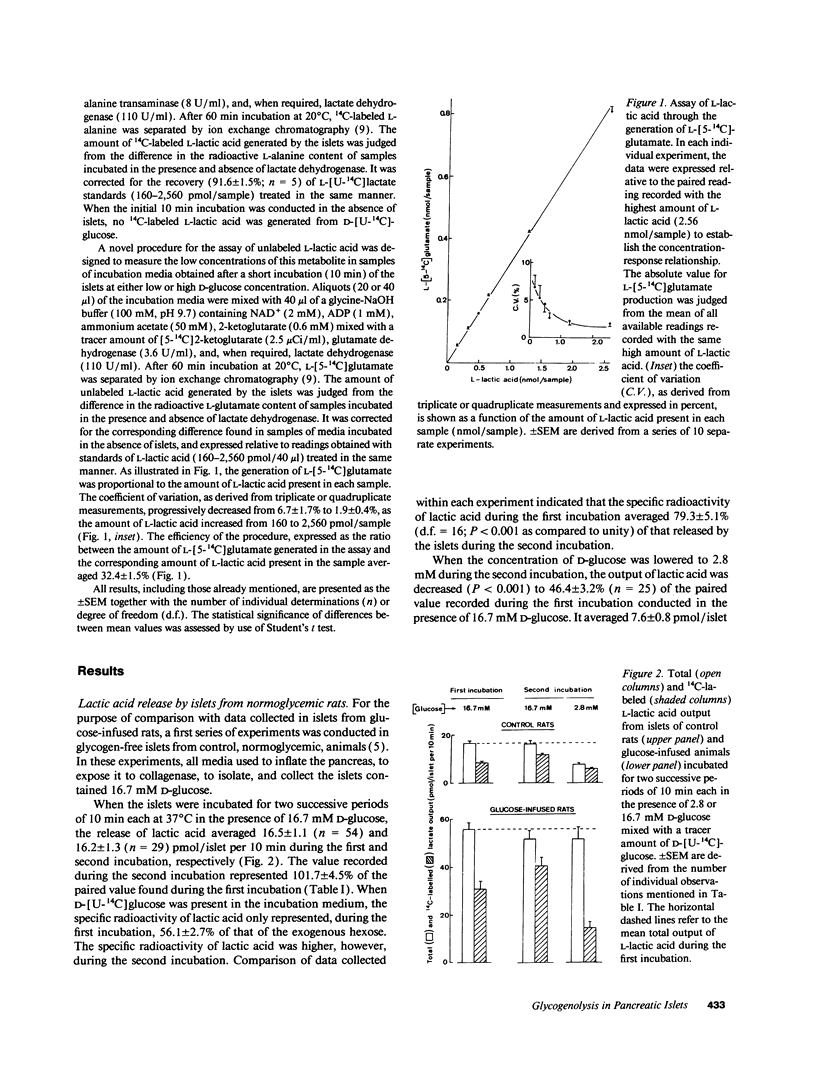
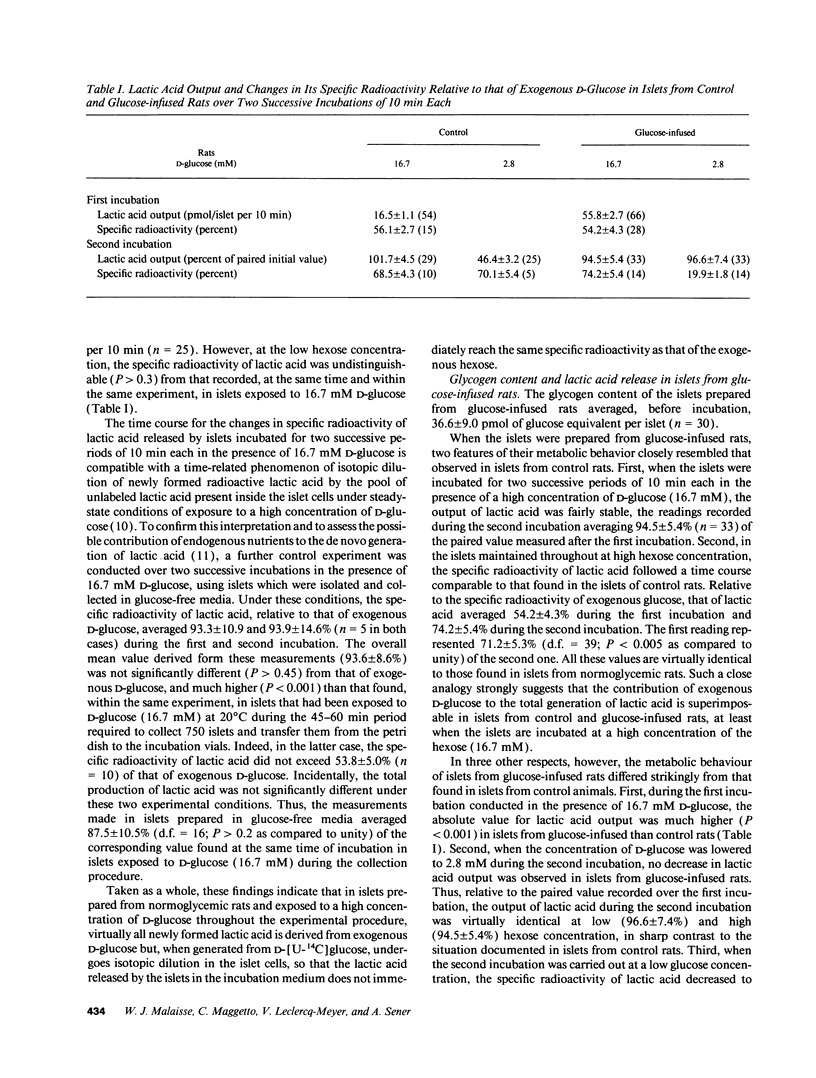
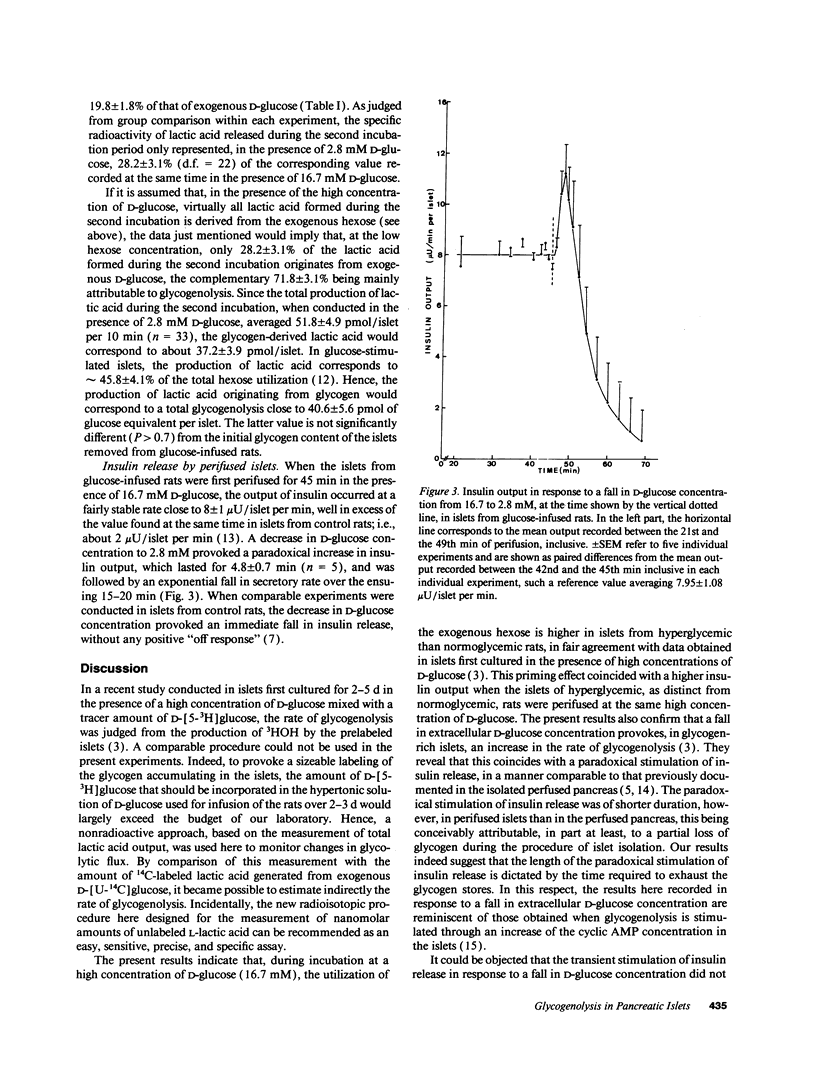
Abstract
When pancreatic islets isolated from rats infused for 48-72 h with a hypertonic solution of D-glucose were incubated for two successive periods of 10 min each, in the presence first of 16.7 mM and then 2.8 mM D-[U-14C]glucose, the total output of L-lactic acid during the second incubation was as high as that recorded during the first incubation, while the specific radioactivity of L-lactic acid dramatically decreased during the second incubation. In islets from normoglycemic rats, however, the total output of L-lactic acid decreased and its specific radioactivity modestly increased as the concentration of D-glucose was lowered from 16.7 to 2.8 mM. Such contrasting results indicate that in the glycogen-rich islets isolated from glucose-infused rats, the fall in extracellular D-glucose concentration was not accompanied by a parallel fall in glycolytic flux, the decreased utilization of exogenous D-[U-14C]glucose coinciding with stimulation of glycogenolysis. This unusual metabolic situation also coincided with a transient and paradoxical stimulation of insulin release in response to the decrease in extracellular D-glucose concentration. It is proposed, therefore, that the interference of glycogenolysis with glycolysis in pancreatic islets from glucose-infused rats participates in the paradoxical changes in insulin output which represent a typical feature of B-cell glucotoxicity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carpinelli A. R., Nogueira C. R., Machado U. F., Curi R., Malaisse W. J. Paradoxical inhibition of insulin release by D-glucose islets exposed to dopamine. Horm Metab Res. 1992 Sep;24(9):452–453. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomis R., Novials A., Coves M. J., Casamitjana R., Malaisse W. J. Suppression by insulin treatment of glucose-induced inhibition of insulin release in non-insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1989 Apr 1;6(3):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0168-8227(89)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in pancreatic islets: dissociation between calcium and insulin release. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:409–424. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herchuelz A., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Regulation of calcium fluxes in rat pancreatic islets: calcium extrusion by sodium-calcium countertransport. J Membr Biol. 1980 Nov 15;57(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01868981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laury M. C., Takao F., Bailbe D., Penicaud L., Portha B., Picon L., Ktorza A. Differential effects of prolonged hyperglycemia on in vivo and in vitro insulin secretion in rats. Endocrinology. 1991 May;128(5):2526–2533. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-5-2526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy J. L., Cooper H. E., Deal D. A., Weir G. C. Chronic hyperglycemia is associated with impaired glucose influence on insulin secretion. A study in normal rats using chronic in vivo glucose infusions. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):908–915. doi: 10.1172/JCI112389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J. Glucose-sensing by the pancreatic B-cell: the mitochondrial part. Int J Biochem. 1992 May;24(5):693–701. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(92)90002-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Malaisse-Lagae F., Mayhew D. A possible role for the adenylcyclase system in insulin secretion. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1724–1734. doi: 10.1172/JCI105663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Marynissen G., Sener A. Possible role of glycogen accumulation in B-cell glucotoxicity. Metabolism. 1992 Aug;41(8):814–819. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(92)90160-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Rasschaert J., Zähner D., Sener A. Hexose metabolism in pancreatic islets: the Pasteur effect. Diabetes Res. 1988 Feb;7(2):53–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A. Glucose-induced changes in cytosolic ATP content in pancreatic islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 18;927(2):190–195. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90134-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Koser M., Ravazzola M., Malaisse-Lagae F. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Insulin release due to glycogenolysis in glucose-deprived islets. Biochem J. 1977 May 15;164(2):447–454. doi: 10.1042/bj1640447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Levy J., Herchuelz A. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XXII. Qualitative and quantitative aspects of glycolysis in isolated islets. Acta Diabetol Lat. 1976 Sep-Dec;13(5-6):202–215. doi: 10.1007/BF02581118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J. The anomeric malaise: a manifestation of B-cell glucotoxicity. Horm Metab Res. 1991 Jul;23(7):307–311. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1003684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marynissen G., Leclercq-Meyer V., Sener A., Malaisse W. J. Perturbation of pancreatic islet function in glucose-infused rats. Metabolism. 1990 Jan;39(1):87–95. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovira A., Garrote F. J., Valverde I., Malaisse W. J. Anomeric specificity of glucose-induced insulin release in normal and diabetic subjects. Diabetes Res. 1987 Jul;5(3):119–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Levy J., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. Does glycolysis control calcium transport in the B-cell? Biochem J. 1976 Jun 15;156(3):521–525. doi: 10.1042/bj1560521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sener A., Malaisse W. J. A sensitive radioisotopic method for the measurement of NAD(P)H: its application to the assay of metabolites and enzymatic activities. Anal Biochem. 1990 May 1;186(2):236–242. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90073-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



