Abstract
Transmembrane transport of neutral amino acids in skeletal muscle is mediated by at least four different systems (system A, ASC, L, and Nm), and may be an important target for insulin's effects on amino acid and protein metabolism. We have measured net amino acid exchanges and fractional rates of inward (k(in), min-1) and outward (kout, min-1) transmembrane transport of 2-methylaminoisobutyric acid (MeAIB, a nonmetabolizable amino acid analogue, specific for system A amino acid transport) in forearm deep tissues (skeletal muscle), by combining the forearm perfusion technique and a novel dual tracer ([1-H3]-D-mannitol and 2-[1-14C]-methylaminoisobutyric acid) approach for measuring in vivo the activity of system A amino acid transport. Seven healthy lean subjects were studied. After a baseline period, insulin was infused into the brachial artery to achieve local physiologic hyperinsulinemia (76 +/- 8 microU/ml vs 6.4 +/- 1.6 microU/ml in the basal period, P < 0.01) without affecting systemic hormone and substrate concentrations. Insulin switched forearm amino acid exchange from a net output (-2,630 +/- 1,100 nmol/min per kig of forearm tissue) to a net uptake (1,610 +/- 600 nmol/min per kg, P < 0.01 vs baseline). Phenylalanine and tyrosine balances simultaneously shifted from a net output (-146 +/- 47 and -173 +/- 34 nmol/min per kg, respectively) to a zero balance (16.3 +/- 51 for phenylalanine and 15.5 +/- 14.3 nmol/min per kg for tyrosine, P < 0.01 vs baseline for both), showing that protein synthesis and breakdown were in equilibrium during hyperinsulinemia. Net negative balances of alanine, methionine, glycine, threonine and asparagine (typical substrates for system A amino acid transport) also were decreased by insulin, whereas serine (another substrate for system A transport) shifted from a zero balance to net uptake. Insulin increased k(in) of MeAIB from a basal value of 11.8.10(-2) +/- 1.7.10(-2).min-1 to 13.7.10(-2) +/- 2.2.10(-2).min-1 (P < 0.02 vs the postabsorptive value), whereas kout was unchanged. We conclude that physiologic hyperinsulinemia stimulates the activity of system A amino acid transport in human skeletal muscle, and that this effect may play a role in determining the overall concomitant response of muscle amino acid/protein metabolism to insulin.
Full text
PDF


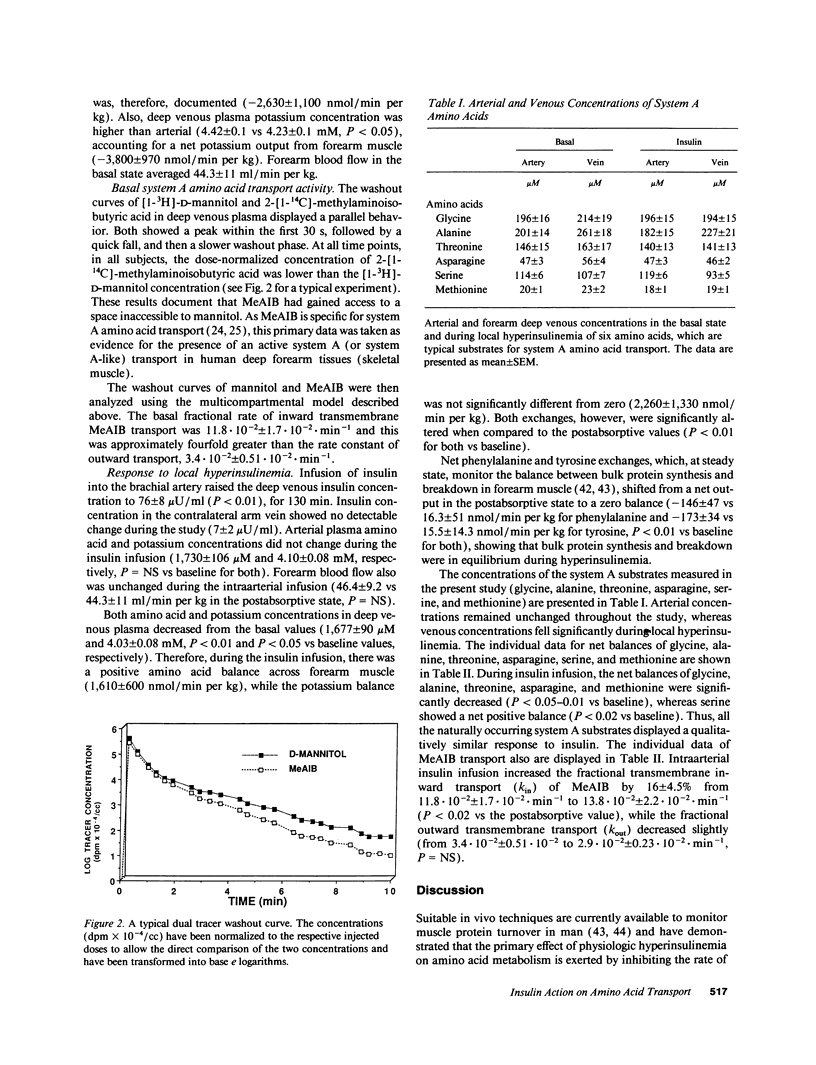
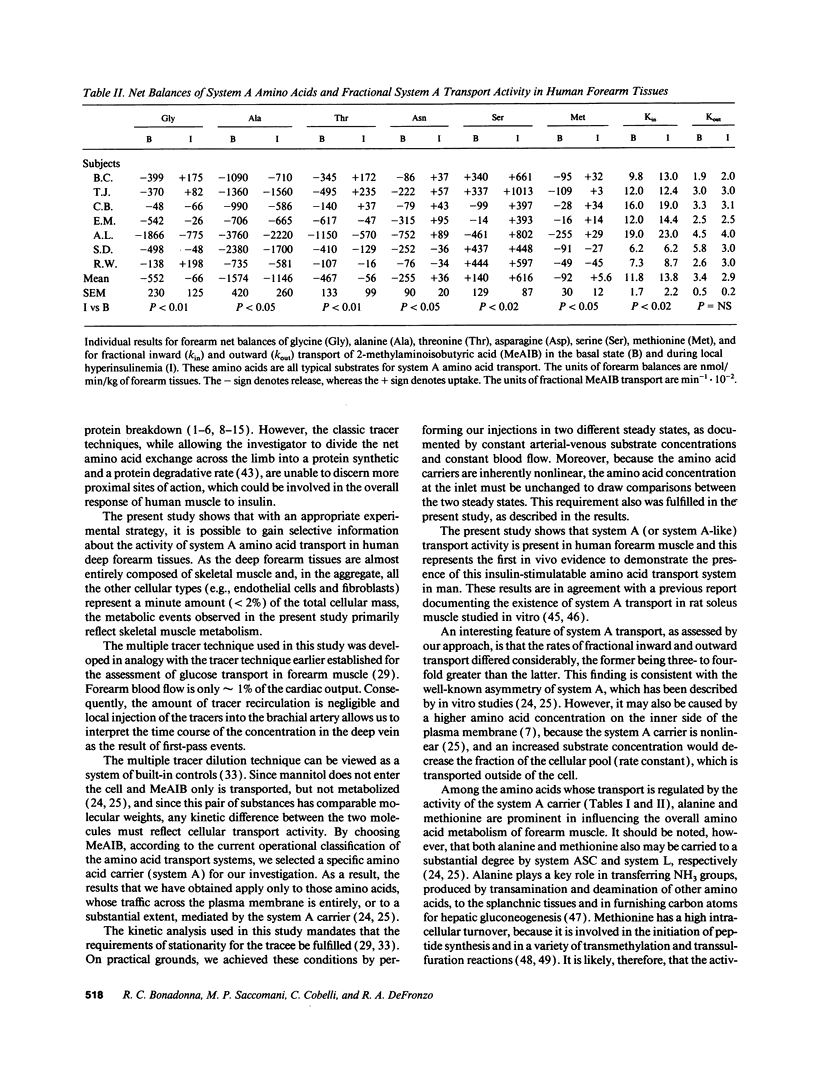



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRES R., BALTZAN M. A., CADER G., ZIERLER K. L. Effect of insulin on carbohydrate metabolism and on potassium in the forearm of man. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jan;41:108–115. doi: 10.1172/JCI104452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Airhart J., Arnold J. A., Stirewalt W. S., Low R. B. Insulin stimulation of protein synthesis in cultured skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):C81–C86. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1982.243.1.C81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. J., Gelfand R. A. The in vivo study of cardiac and skeletal muscle protein turnover. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1989 Mar;5(2):133–148. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. J., Revkin J. H., Young L. H., Zaret B. L., Jacob R., Gelfand R. A. An isotopic method for measurement of muscle protein synthesis and degradation in vivo. Biochem J. 1987 Jul 1;245(1):223–228. doi: 10.1042/bj2450223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennet W. M., Connacher A. A., Scrimgeour C. M., Jung R. T., Rennie M. J. Euglycemic hyperinsulinemia augments amino acid uptake by human leg tissues during hyperaminoacidemia. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):E185–E194. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.2.E185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennet W. M., Connacher A. A., Smith K., Jung R. T., Rennie M. J. Inability to stimulate skeletal muscle or whole body protein synthesis in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients by insulin-plus-glucose during amino acid infusion: studies of incorporation and turnover of tracer L-[1-13C]leucine. Diabetologia. 1990 Jan;33(1):43–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00586460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellino P., Luzi L., Simonson D. C., Haymond M., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of insulin and plasma amino acid concentrations on leucine metabolism in man. Role of substrate availability on estimates of whole body protein synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1784–1793. doi: 10.1172/JCI113272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N., Oxender D. L., Liang M., Vatz K. A. The use of N-methylation to direct route of mediated transport of amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3609–3616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H. N. Role of amino acid transport and countertransport in nutrition and metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jan;70(1):43–77. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T. Regulation of active Na+-K+ transport in skeletal muscle. Physiol Rev. 1986 Jul;66(3):542–580. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1986.66.3.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobelli C., Saccomani M. P., Ferrannini E., Defronzo R. A., Gelfand R., Bonadonna R. A compartmental model to quantitate in vivo glucose transport in the human forearm. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):E943–E958. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.6.E943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. D., Smith T. C. Energetics of Na+-dependent amino acid co-transport in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 12;897(1):5–13. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Feo P., Gaisano M. G., Haymond M. W. Differential effects of insulin deficiency on albumin and fibrinogen synthesis in humans. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):833–840. doi: 10.1172/JCI115384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prato S., DeFronzo R. A., Castellino P., Wahren J., Alvestrand A. Regulation of amino acid metabolism by epinephrine. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):E878–E887. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.5.E878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felig P., Pozefsky T., Marliss E., Cahill G. F., Jr Alanine: key role in gluconeogenesis. Science. 1970 Feb 13;167(3920):1003–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3920.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flakoll P. J., Kulaylat M., Frexes-Steed M., Hourani H., Brown L. L., Hill J. O., Abumrad N. N. Amino acids augment insulin's suppression of whole body proteolysis. Am J Physiol. 1989 Dec;257(6 Pt 1):E839–E847. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.6.E839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frexes-Steed M., Warner M. L., Bulus N., Flakoll P., Abumrad N. N. Role of insulin and branched-chain amino acids in regulating protein metabolism during fasting. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):E907–E917. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.6.E907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryburg D. A., Gelfand R. A., Barrett E. J. Growth hormone acutely stimulates forearm muscle protein synthesis in normal humans. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):E499–E504. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.3.E499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa N. K., Minaker K. L., Rowe J. W., Goodman M. N., Matthews D. E., Bier D. M., Young V. R. Insulin-mediated reduction of whole body protein breakdown. Dose-response effects on leucine metabolism in postabsorptive men. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2306–2311. doi: 10.1172/JCI112240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Fern M., Preedy V. R. The effect of insulin infusion and food intake on muscle protein synthesis in postabsorptive rats. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):669–676. doi: 10.1042/bj2100669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand R. A., Barrett E. J. Effect of physiologic hyperinsulinemia on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and breakdown in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI113033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundal H. S., Rennie M. J., Watt P. W. Characteristics of L-glutamine transport in perfused rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;393:283–305. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hundal H. S., Rennie M. J., Watt P. W. Characteristics of acidic, basic and neutral amino acid transport in the perfused rat hindlimb. J Physiol. 1989 Jan;408:93–114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Koehler J. O., Morgan H. E. Effect of insulin on protein synthesis in skeletal muscle of an isolated perfused preparation of rat hemicorpus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):816–820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Li J. B., Rannels S. R. Regulation by insulin of amino acid release and protein turnover in the perfused rat hemicorpus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1476–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball S. R., Jefferson L. S. Cellular mechanisms involved in the action of insulin on protein synthesis. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988 Dec;4(8):773–787. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610040806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louard R. J., Barrett E. J., Gelfand R. A. Effect of infused branched-chain amino acids on muscle and whole-body amino acid metabolism in man. Clin Sci (Lond) 1990 Nov;79(5):457–466. doi: 10.1042/cs0790457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundholm K., Edström S., Ekman L., Karlberg I., Walker P., Scherstén T. Protein degradation in human skeletal muscle tissue: the effect of insulin, leucine, amino acids and ions. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Mar;60(3):319–326. doi: 10.1042/cs0600319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANCHESTER K. L., YOUNG F. G. The effect of insulin on incorporation of amino acids into protein of normal rat diaphragm in vitro. Biochem J. 1958 Nov;70(3):353–358. doi: 10.1042/bj0700353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni B. J., Karapanos G., Mitch W. E. System A amino acid transport in incubated muscle: effects of insulin and acute uremia. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 2):F74–F80. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.1.F74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroni B. J., Karapanos G., Mitch W. E. System ASC and sodium-independent neutral amino acid transport in muscle of uremic rats. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 2):F81–F86. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1986.251.1.F81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall S., Monzon R. Amino acid regulation of insulin action in isolated adipocytes. Selective ability of amino acids to enhance both insulin sensitivity and maximal insulin responsiveness of the protein synthesis system. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2037–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali A., Buzzigoli G., Taddei S., Santoro D., Cerri M., Pedrinelli R., Ferrannini E. Effects of insulin on hemodynamics and metabolism in human forearm. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):490–500. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacy P. J., Nair K. S., Ford C., Halliday D. Failure of insulin infusion to stimulate fractional muscle protein synthesis in type I diabetic patients. Anabolic effect of insulin and decreased proteolysis. Diabetes. 1989 May;38(5):618–624. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.5.618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J. J., Beaufrere B., Koziet J., Desjeux J. F., Bier D. M., Young V. R., Lestradet H. Whole body de novo amino acid synthesis in type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes studied with stable isotope-labeled leucine, alanine, and glycine. Diabetes. 1985 Jan;34(1):67–73. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shangraw R. E., Stuart C. A., Prince M. J., Peters E. J., Wolfe R. R. Insulin responsiveness of protein metabolism in vivo following bedrest in humans. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 1):E548–E558. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.4.E548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotwell M. A., Kilberg M. S., Oxender D. L. The regulation of neutral amino acid transport in mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch K. J., Wagner D. A., Burke J. F., Young V. R. Quantitative study in vivo of methionine cycle in humans using [methyl-2H3]- and [1-13C]methionine. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):E322–E331. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.3.E322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storch K. J., Wagner D. A., Burke J. F., Young V. R. [1-13C; methyl-2H3]methionine kinetics in humans: methionine conservation and cystine sparing. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 1):E790–E798. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.5.E790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Inchiostro S., Biolo G., Trevisan R., Fantin G., Marescotti M. C., Iori E., Tiengo A., Crepaldi G. Differential effects of hyperinsulinemia and hyperaminoacidemia on leucine-carbon metabolism in vivo. Evidence for distinct mechanisms in regulation of net amino acid deposition. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1062–1069. doi: 10.1172/JCI112919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Inchiostro S., Biolo G., Vincenti E., Sabadin L. Effects of acute systemic hyperinsulinemia on forearm muscle proteolysis in healthy man. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):27–33. doi: 10.1172/JCI115287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Trevisan R., Inchiostro S., Biolo G., Nosadini R., De Kreutzenberg S. V., Duner E., Tiengo A., Crepaldi G. Dose-response curves of effects of insulin on leucine kinetics in humans. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):E334–E342. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.3.E334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umpleby A. M., Boroujerdi M. A., Brown P. M., Carson E. R., Sönksen P. H. The effect of metabolic control on leucine metabolism in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1986 Mar;29(3):131–141. doi: 10.1007/BF02427082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams I. H., Sugden P. H., Morgan H. E. Use of aromatic amino acids as monitors of protein turnover. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jun;240(6):E677–E681. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.240.6.E677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K. L. THEORY OF THE USE OF ARTERIOVENOUS CONCENTRATION DIFFERENCES FOR MEASURING METABOLISM IN STEADY AND NON-STEADY STATES. J Clin Invest. 1961 Dec;40(12):2111–2125. doi: 10.1172/JCI104437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K., Rogus E. M. Rapid hyperpolarization of rat skeletal muscle induced by insulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



