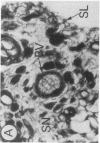
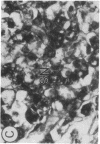
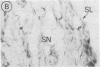
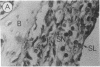
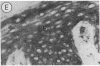
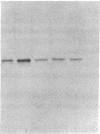
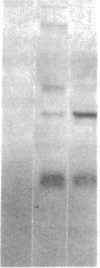
Abstract
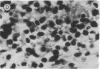
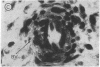
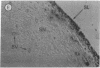
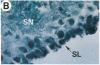
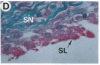
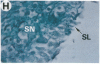
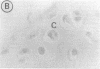
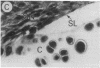
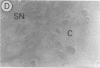
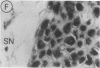
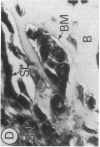
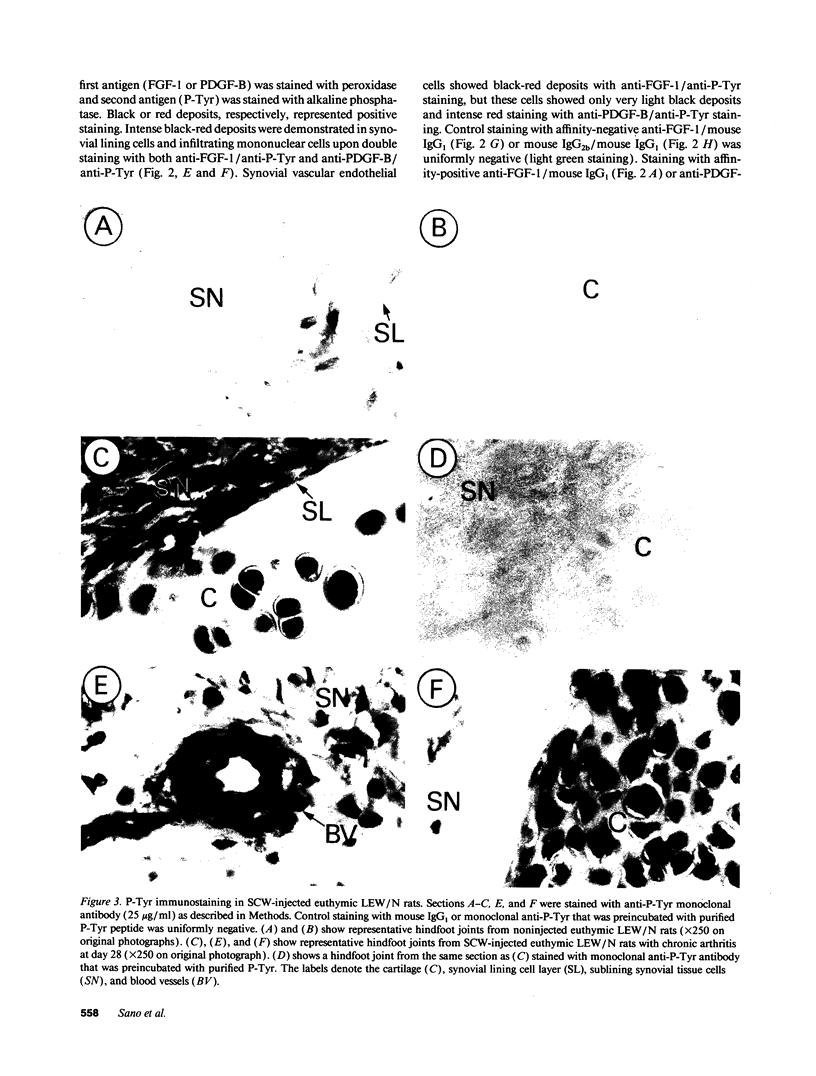
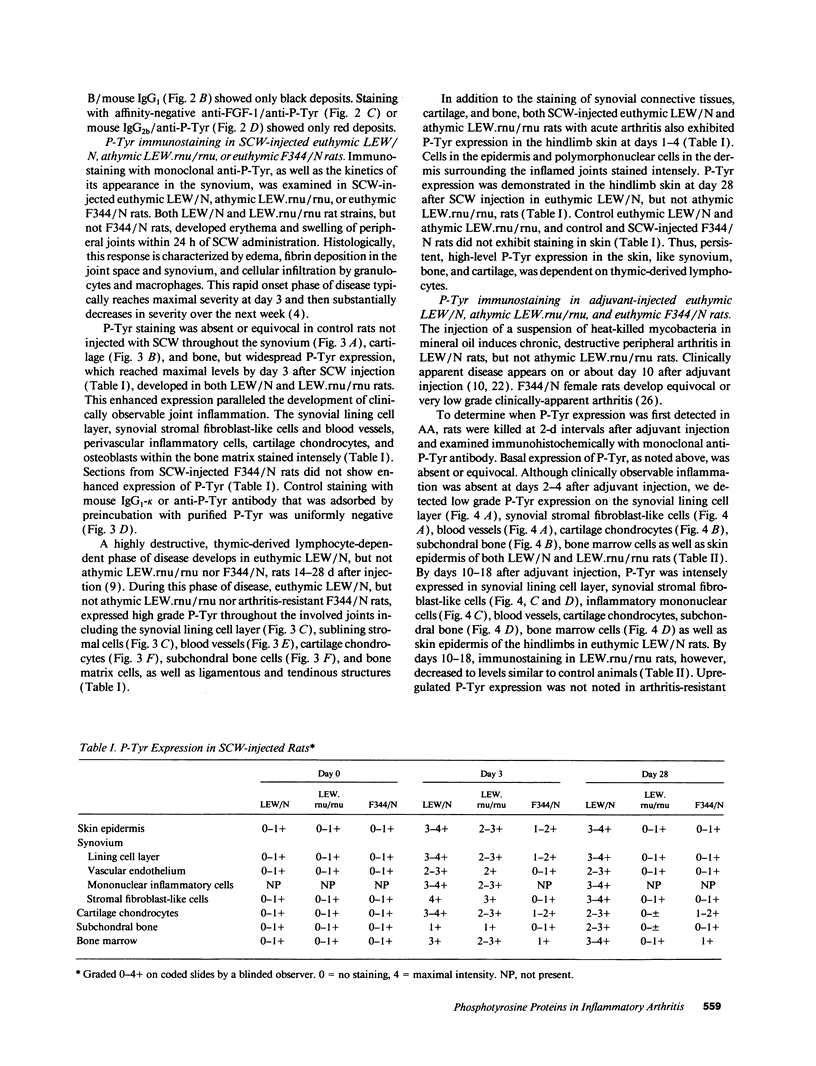
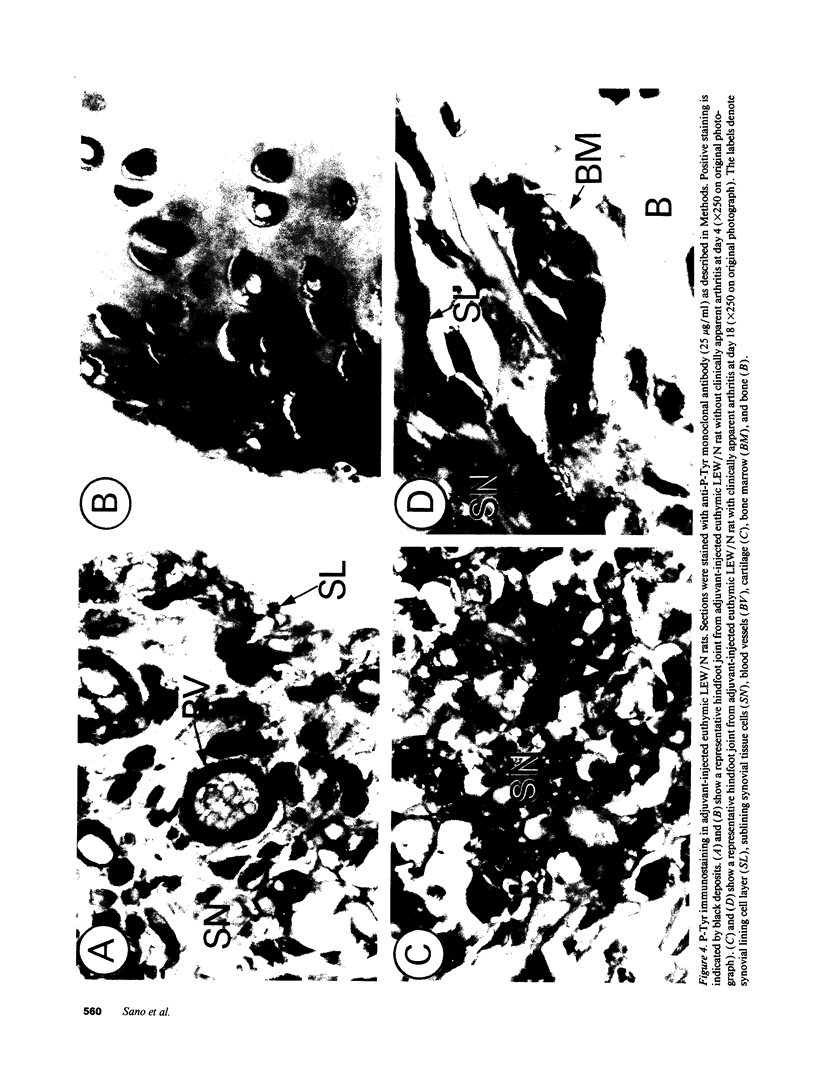
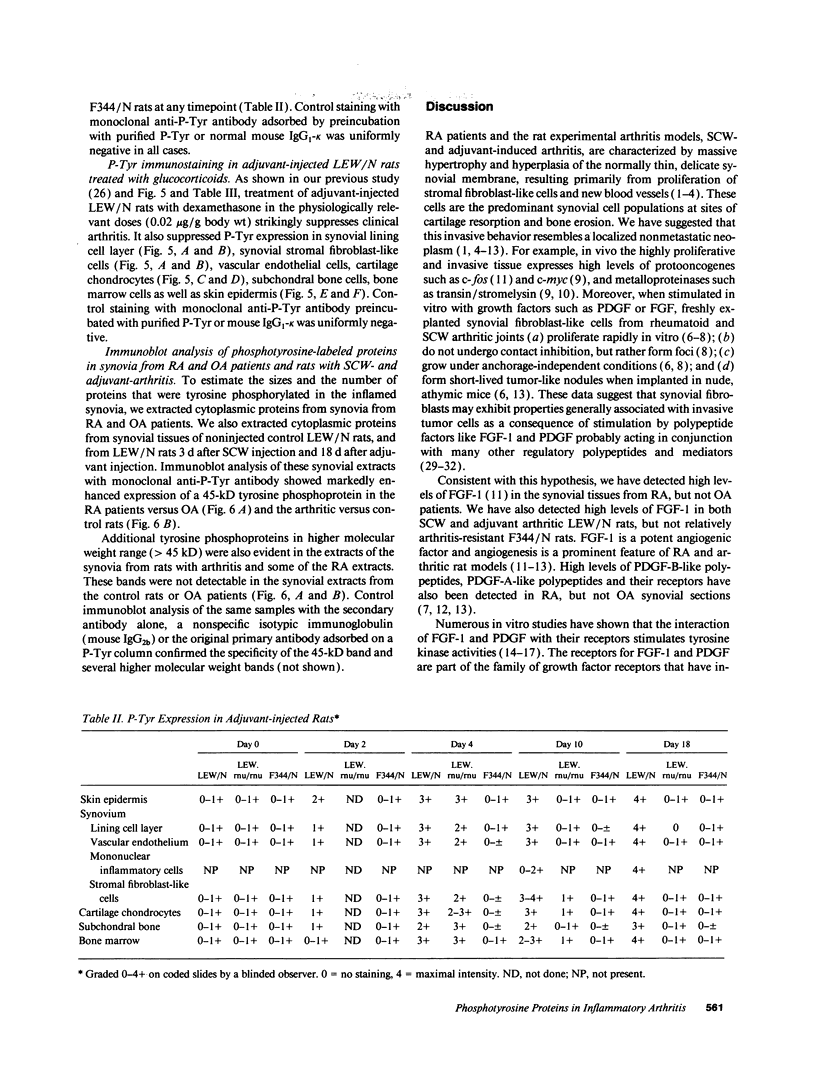
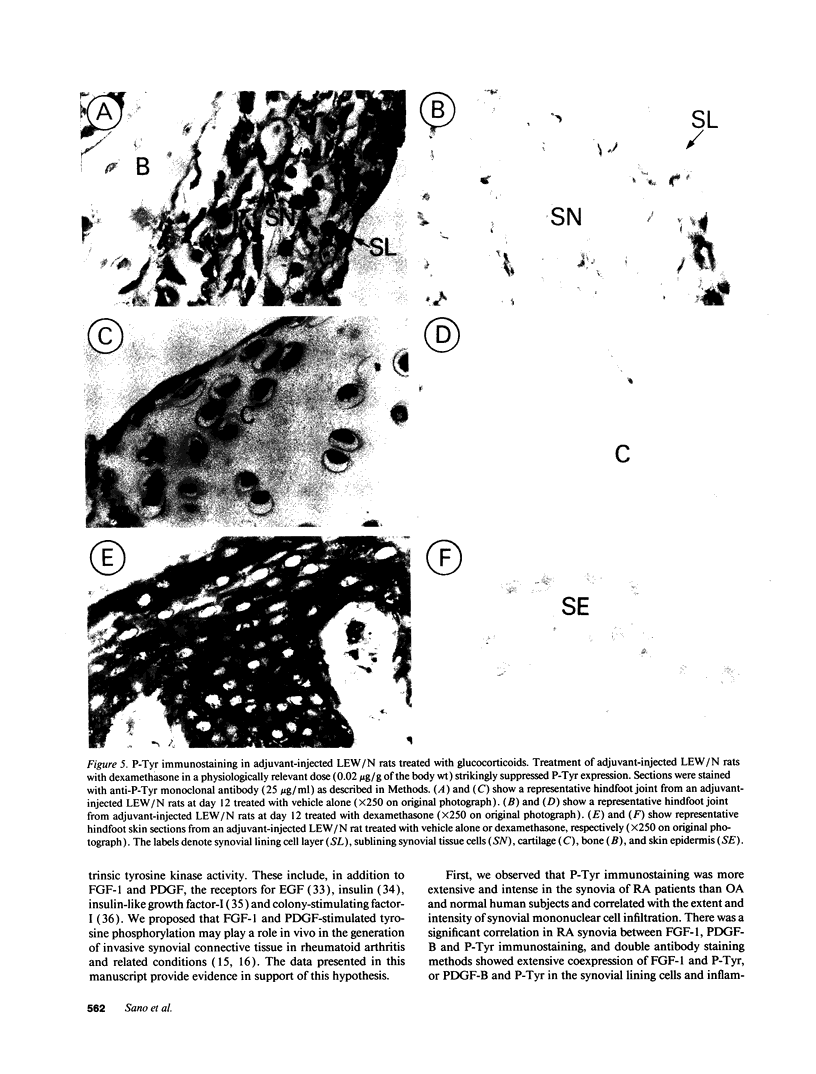
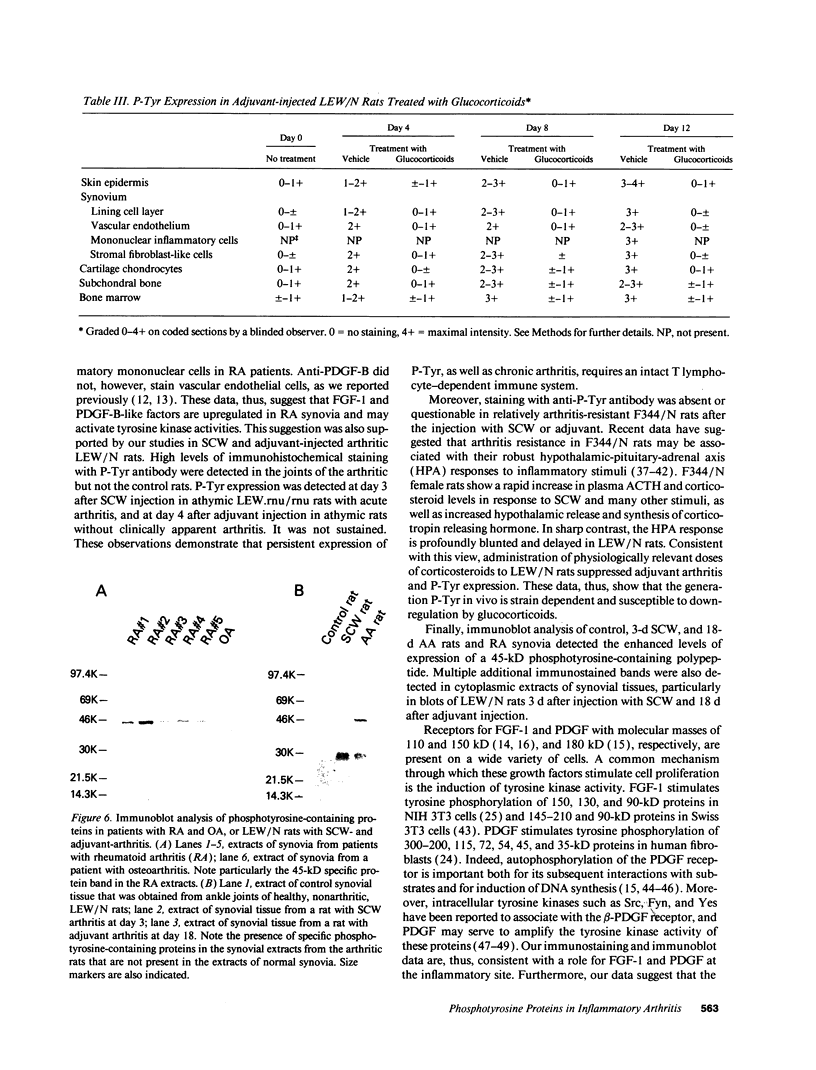
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-1 and PDGF-B-like factors have been implicated in the pathobiology of RA and animal models of this disease. Since the receptors for FGF-1 and PDGF are tyrosine kinases, we examined the expression of tyrosine phosphorylated proteins (phosphotyrosine, P-Tyr) in synovial tissues from patients with RA and osteoarthritis (OA), and rats with streptococcal cell wall (SCW) and adjuvant arthritis (AA). Synovia from patients with RA and LEW/N rats with SCW and AA arthritis, in contrast to controls, stained intensely with anti-P-Tyr antibody. The staining colocalized with PDGF-B and FGF-1 staining. Comparative immunoblot analysis showed markedly enhanced expression of a 45-kD P-Tyr protein in the inflamed synovia. Treatment with physiological concentrations of dexamethasone suppressed both arthritis and P-Tyr expression in AA. P-Tyr was only transiently expressed in athymic nude Lewis rats and was not detected in relatively arthritis-resistant F344/N rats. These data suggest that (a) FGF-1 and PDGF-B-like factors are upregulated and may induce tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in vivo in inflammatory joint diseases, (b) persistent high level P-Tyr expression is T lymphocyte dependent, correlates with disease severity, and is strain dependent in rats, (c) corticosteroids, in physiological concentrations, downregulate P-Tyr expression in these lesions.
Full text
PDF


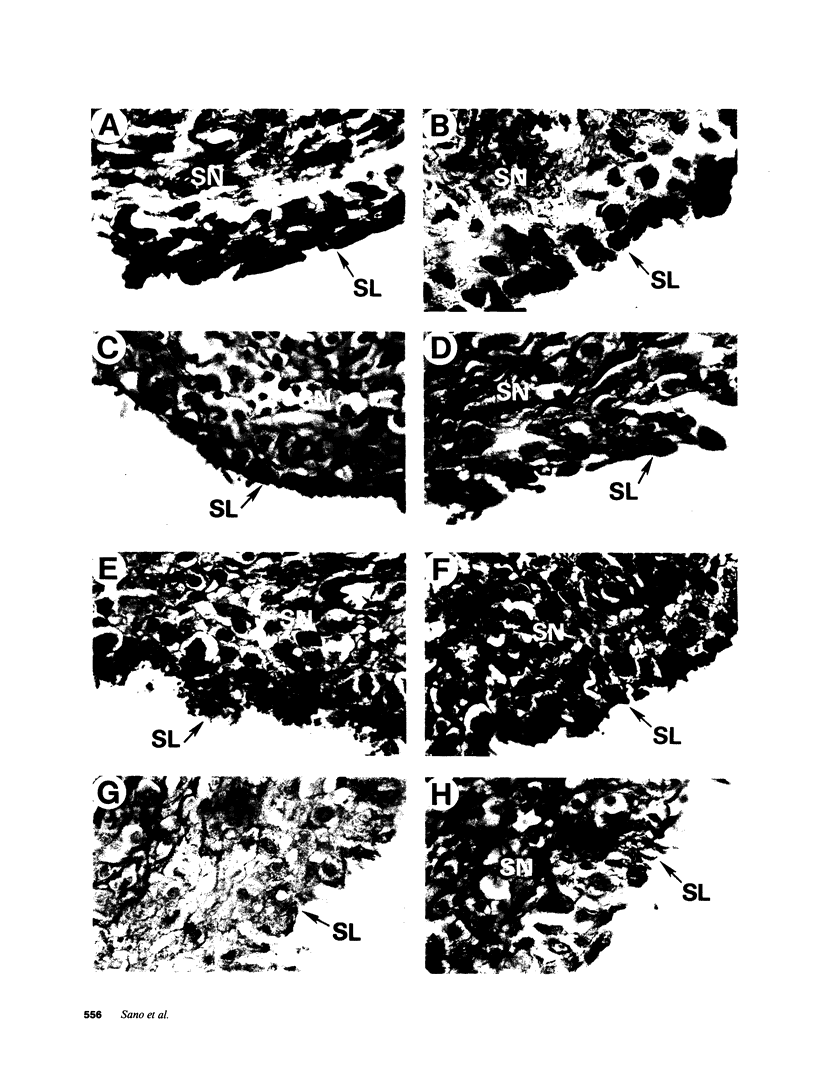



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksentijevich S., Whitfield H. J., Jr, Young W. S., 3rd, Wilder R. L., Chrousos G. P., Gold P. W., Sternberg E. M. Arthritis-susceptible Lewis rats fail to emerge from the stress hyporesponsive period. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1992 Jan 17;65(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(92)90014-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman R., Asch E., Bloch D., Bole G., Borenstein D., Brandt K., Christy W., Cooke T. D., Greenwald R., Hochberg M. Development of criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis. Classification of osteoarthritis of the knee. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee of the American Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):1039–1049. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley M., Woolley D. E. Chondroclasts and osteoclasts at subchondral sites of erosion in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Sep;27(9):968–975. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bromley M., Woolley D. E. Histopathology of the rheumatoid lesion. Identification of cell types at sites of cartilage erosion. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):857–863. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Ritchlin C., Winchester R., Cerami A. Constitutive production of inflammatory and mitogenic cytokines by rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):569–574. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess W. H., Maciag T. The heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factor family of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:575–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calogero A. E., Sternberg E. M., Bagdy G., Smith C., Bernardini R., Aksentijevich S., Wilder R. L., Gold P. W., Chrousos G. P. Neurotransmitter-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsiveness is defective in inflammatory disease-susceptible Lewis rats: in vivo and in vitro studies suggesting globally defective hypothalamic secretion of corticotropin-releasing hormone. Neuroendocrinology. 1992 May;55(5):600–608. doi: 10.1159/000126173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case J. P., Lafyatis R., Remmers E. F., Kumkumian G. K., Wilder R. L. Transin/stromelysin expression in rheumatoid synovium. A transformation-associated metalloproteinase secreted by phenotypically invasive synoviocytes. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1055–1064. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case J. P., Lorberboum-Galski H., Lafyatis R., FitzGerald D., Wilder R. L., Pastan I. Chimeric cytotoxin IL2-PE40 delays and mitigates adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):287–291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case J. P., Sano H., Lafyatis R., Remmers E. F., Kumkumian G. K., Wilder R. L. Transin/stromelysin expression in the synovium of rats with experimental erosive arthritis. In situ localization and kinetics of expression of the transformation-associated metalloproteinase in euthymic and athymic Lewis rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Dec;84(6):1731–1740. doi: 10.1172/JCI114356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Barr P. J., Cousens L. S., Fretto L. J., Williams L. T. Acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors stimulate tyrosine kinase activity in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):988–993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Heldin C. H. Use of an antiserum against phosphotyrosine for the identification of phosphorylated components in human fibroblasts stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 10;259(17):11145–11152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesel R., Burgess W. H., Maciag T. Heparin-binding growth factor 1 stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1857–1865. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haraoui B., Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Sporn M. B., Helfgott R. K., Brinckerhoff C. E. Dose-dependent suppression by the synthetic retinoid, 4-hydroxyphenyl retinamide, of streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(6):903–916. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Recent insights into the pathogenesis of the proliferative lesion in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jan-Feb;19(1):68–72. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huhn R. D., Posner M. R., Rayter S. I., Foulkes J. G., Frackelton A. R., Jr Cell lines and peripheral blood leukocytes derived from individuals with chronic myelogenous leukemia display virtually identical proteins phosphorylated on tyrosine residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4408–4412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C. A., Anderson D., Moran M. F., Ellis C., Pawson T. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):668–674. doi: 10.1126/science.1708916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafyatis R., Remmers E. F., Roberts A. B., Yocum D. E., Sporn M. B., Wilder R. L. Anchorage-independent growth of synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints. Stimulation by exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1267–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI114011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafyatis R., Thompson N. L., Remmers E. F., Flanders K. C., Roche N. S., Kim S. J., Case J. P., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B., Wilder R. L. Transforming growth factor-beta production by synovial tissues from rheumatoid patients and streptococcal cell wall arthritic rats. Studies on secretion by synovial fibroblast-like cells and immunohistologic localization. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1142–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorberboum-Galski H., Lafyatis R., Case J. P., FitzGerald D., Wilder R. L., Pastan I. Administration of IL-2-PE40 via osmotic pumps prevents adjuvant induced arthritis in rats. Improved therapeutic index of IL-2-PE40 administered by continuous infusion. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1991;13(2-3):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(91)90112-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The product of the protooncogene c-src is modified during the cellular response to platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7845–7849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Lafyatis R., Kumkumian G. K., Case J. P., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Wilder R. L. Cytokines and growth regulation of synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and rats with streptococcal cell wall arthritis. Growth Factors. 1990;2(2-3):179–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Sano H., Lafyatis R., Case J. P., Kumkumian G. K., Hla T., Maciag T., Wilder R. L. Production of platelet derived growth factor B chain (PDGF-B/c-sis) mRNA and immunoreactive PDGF B-like polypeptide by rheumatoid synovium: coexpression with heparin binding acidic fibroblast growth factor-1. J Rheumatol. 1991 Jan;18(1):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Sano H., Wilder R. L. Platelet-derived growth factors and heparin-binding (fibroblast) growth factors in the synovial tissue pathology of rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Dec;21(3):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(91)90009-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Forough R., Maier J. A., Case J. P., Jackson A., Engleka K., Maciag T., Wilder R. L. Detection of high levels of heparin binding growth factor-1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor) in inflammatory arthritic joints. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1417–1426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Hla T., Maier J. A., Crofford L. J., Case J. P., Maciag T., Wilder R. L. In vivo cyclooxygenase expression in synovial tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis and rats with adjuvant and streptococcal cell wall arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):97–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI115591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Rettenmier C. W., Sacca R., Roussel M. F., Look A. T., Stanley E. R. The c-fms proto-oncogene product is related to the receptor for the mononuclear phagocyte growth factor, CSF-1. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):665–676. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa S., Shiozawa K., Tanaka Y., Morimoto I., Uchihashi M., Fujita T., Hirohata K., Hirata Y., Imura S. Human epidermal growth factor for the stratification of synovial lining layer and neovascularisation in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Oct;48(10):820–828. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.10.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. C., Hauser E., Renaud N. K., Leff A., Aksentijevich S., Chrousos G. P., Wilder R. L., Gold P. W., Sternberg E. M. Increased hypothalamic [3H]flunitrazepam binding in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hyporesponsive Lewis rats. Brain Res. 1992 Jan 13;569(2):295–299. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90642-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Glowa J. R., Smith M. A., Calogero A. E., Listwak S. J., Aksentijevich S., Chrousos G. P., Wilder R. L., Gold P. W. Corticotropin releasing hormone related behavioral and neuroendocrine responses to stress in Lewis and Fischer rats. Brain Res. 1992 Jan 20;570(1-2):54–60. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90563-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Hill J. M., Chrousos G. P., Kamilaris T., Listwak S. J., Gold P. W., Wilder R. L. Inflammatory mediator-induced hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activation is defective in streptococcal cell wall arthritis-susceptible Lewis rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2374–2378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. M., Young W. S., 3rd, Bernardini R., Calogero A. E., Chrousos G. P., Gold P. W., Wilder R. L. A central nervous system defect in biosynthesis of corticotropin-releasing hormone is associated with susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis in Lewis rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4771–4775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Hansen C. Thymus-dependent and -independent regulation of Ia antigen expression in situ by cells in the synovium of rats with streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Differences in site and intensity of expression in euthymic, athymic, and cyclosporin A-treated LEW and F344 rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1160–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI112933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564–1570. doi: 10.1126/science.2538922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum D. E., Esparza L., Dubry S., Benjamin J. B., Volz R., Scuderi P. Characteristics of tumor necrosis factor production in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Immunol. 1989 Aug;122(1):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum D. E., Lafyatis R., Remmers E. F., Schumacher H. R., Wilder R. L. Hyperplastic synoviocytes from rats with streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis exhibit a transformed phenotype that is thymic-dependent and retinoid inhibitable. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):38–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]