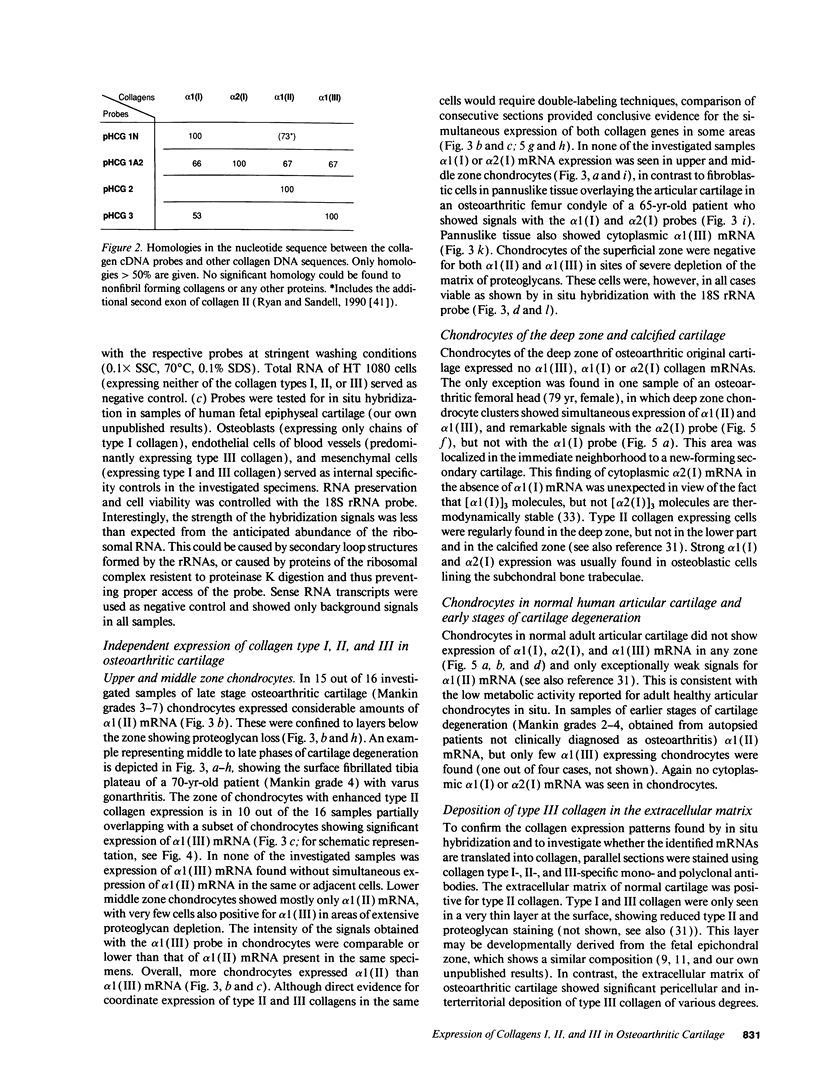
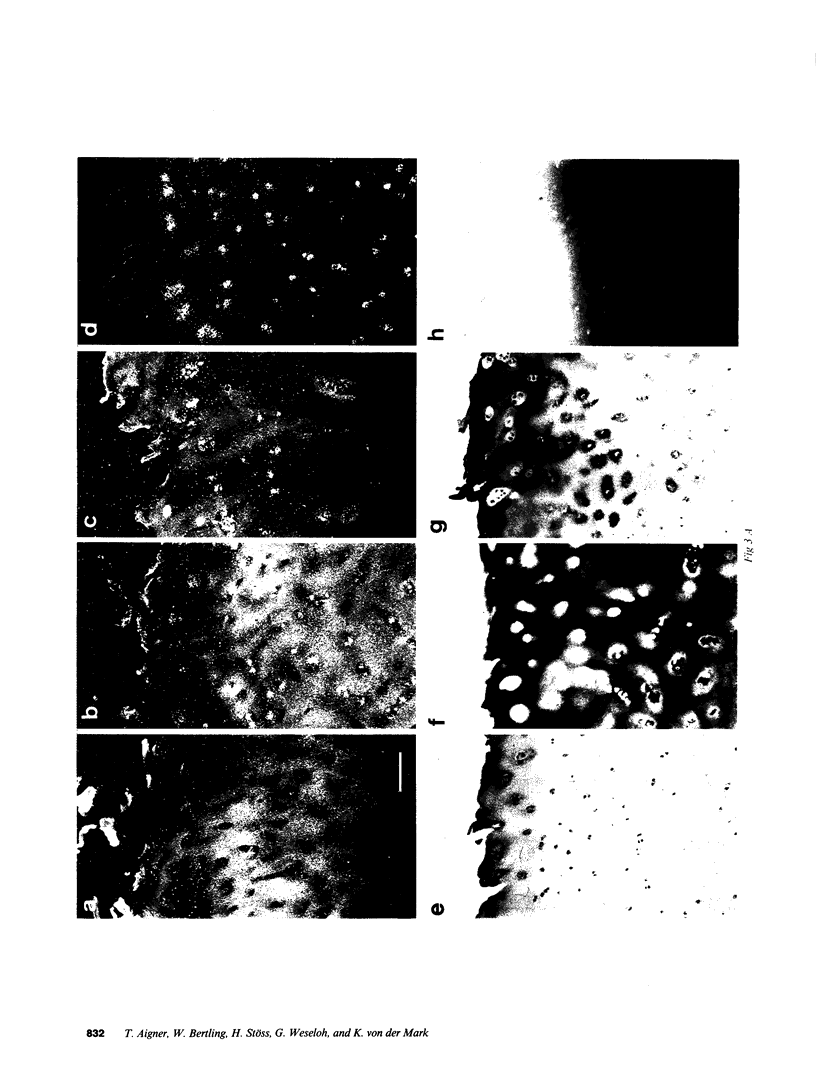
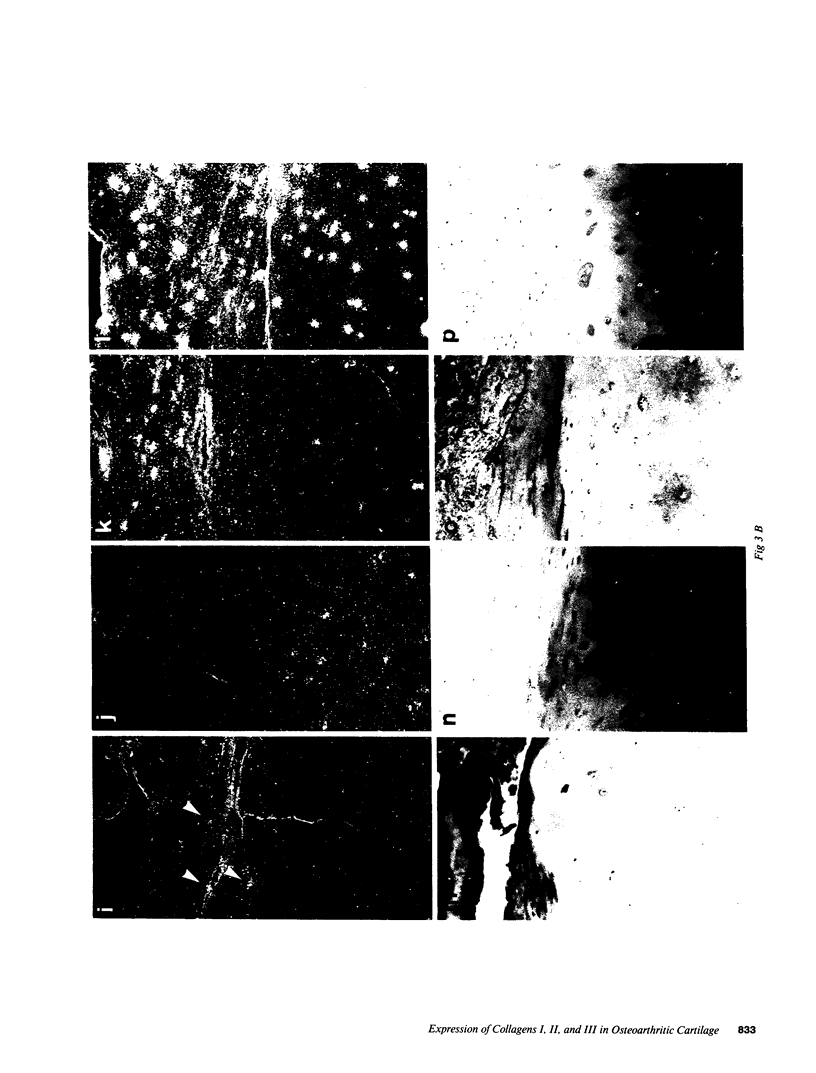
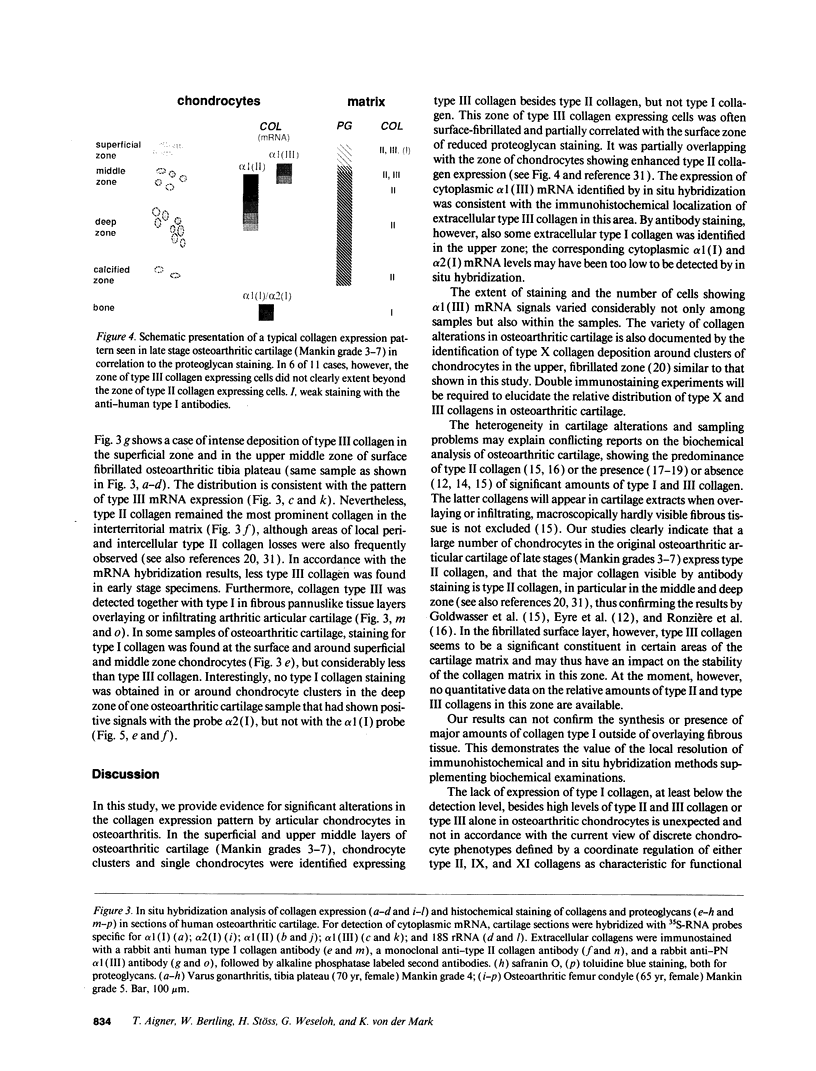
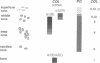Abstract
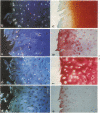
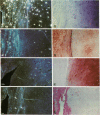
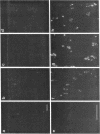
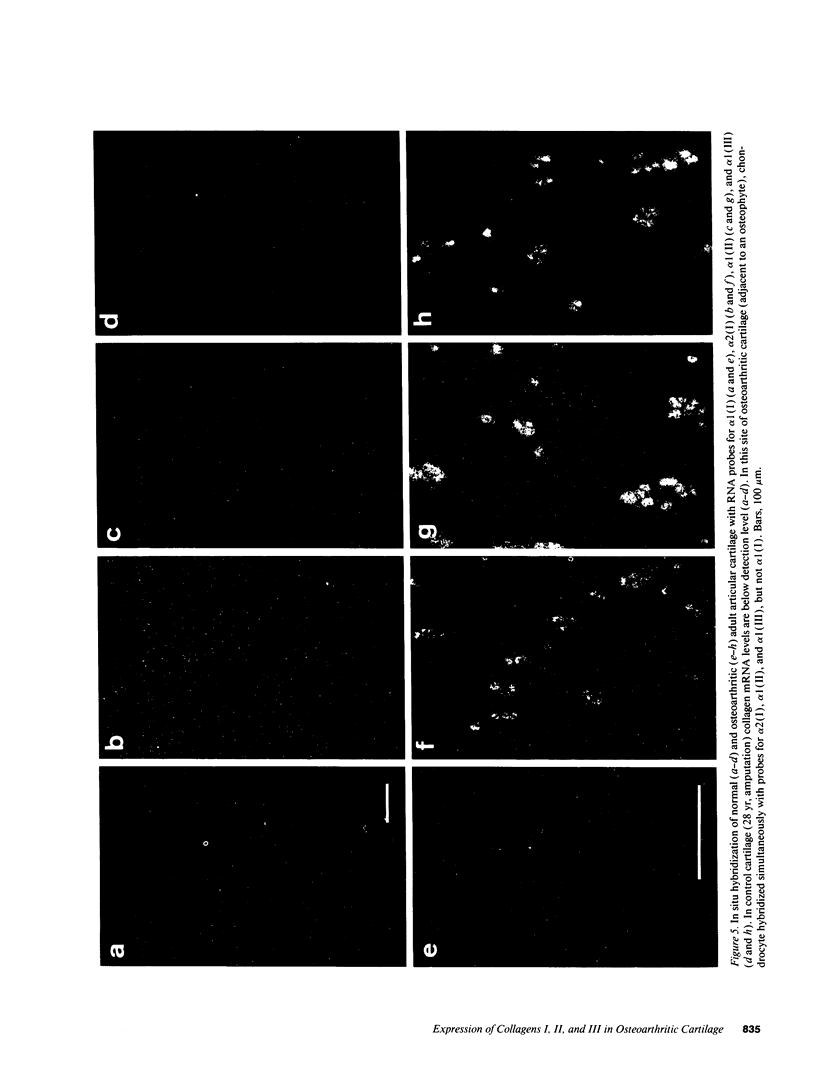
Normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage was investigated by in situ hybridization for expression patterns of the fibrillar collagens type I, II, and III to evaluate phenotypic changes of articular chondrocytes related to the disease. In 11 out of 20 samples, a defined subset of chondrocytes in the superficial and upper middle zone of osteoarthritic cartilage showed significant levels of cytoplasmic alpha 1 (III) mRNA, whereas strong signals of alpha 1 (II) mRNA were found in the upper and lower middle zone, partially overlapping with the zone of alpha 1 (III) mRNA-expressing cells. The extent of type II and III collagen expression depended on the integrity of the extracellular matrix surrounding the chondrocytes, and the location within the articular cartilage. No alpha 1 (I) mRNA was detectable in osteoarthritic original articular cartilage. The alpha 1 (I) probe did, however, reveal signals in pannus-like tissue, osteophytes, and bone cells. In normal articular cartilage, no detectable levels of cytoplasmic mRNA for alpha 1(I), alpha 2 (I), or alpha 1 (III) were seen. Using specific mono- and polyclonal antibodies, we found deposition of type III collagen but hardly any of type I collagen in the superficial zone of osteoarthritic cartilage that is consistent with the in situ hybridization results. These results indicate a phenotypic alteration in a defined subset of chondrocytes in conditions of diseased cartilage, expressing and synthesizing collagen type III independently from type I collagen, but in part simultaneously with type II collagen.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam M., Deyl Z. Altered expression of collagen phenotype in osteoarthrosis. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Sep 15;133(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aigner T., Stöss H., Weseloh G., Zeiler G., von der Mark K. Activation of collagen type II expression in osteoarthritic and rheumatoid cartilage. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1992;62(6):337–345. doi: 10.1007/BF02899701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V. D., Weiss I. M., Adams S. L. Cartilage-specific 5' end of chick alpha 2(I) collagen mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8402–8409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benya P. D., Padilla S. R., Nimni M. E. Independent regulation of collagen types by chondrocytes during the loss of differentiated function in culture. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1313–1321. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard M. P., Myers J. C., Chu M. L., Ramirez F., Eikenberry E. F., Prockop D. J. Structure of a cDNA for the pro alpha 2 chain of human type I procollagen. Comparison with chick cDNA for pro alpha 2(I) identifies structurally conserved features of the protein and the gene. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 1;22(5):1139–1145. doi: 10.1021/bi00274a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elima K., Vuorio T., Vuorio E. Determination of the single polyadenylation site of the human pro alpha 1(II) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9499–9504. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., McDevitt C. A., Billingham M. E., Muir H. Biosynthesis of collagen and other matrix proteins by articular cartilage in experimental osteoarthrosis. Biochem J. 1980 Jun 15;188(3):823–837. doi: 10.1042/bj1880823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Wu J. J., Woods P. E. The cartilage collagens: structural and metabolic studies. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1991 Feb;27:49–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Timpl R., Tuderman L., Raisher L., Wiestner M., Perlish J. S., Graves P. N. Ultrastructural identification of extension aminopropeptides of type I and III collagens in human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7360–7364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floman Y., Eyre D. R., Glimcher M. J. Induction of osteoarthrosis in the rabbit knee joint: biochemical studies on the articular cartilage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1980 Mar-Apr;(147):278–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S., Müller P. K., Lemmen C., Remberger K., Matzen K., Kühn K. Immunohistological study on collagen in cartilage-bone metamorphosis and degenerative osteoarthrosis. Klin Wochenschr. 1976 Oct 15;54(20):969–976. doi: 10.1007/BF01468947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring M. B., Birkhead J., Sandell L. J., Kimura T., Krane S. M. Interleukin 1 suppresses expression of cartilage-specific types II and IX collagens and increases types I and III collagens in human chondrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1988 Dec;82(6):2026–2037. doi: 10.1172/JCI113823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldwasser M., Astley T., van der Rest M., Glorieux F. H. Analysis of the type of collagen present in osteoarthritic human cartilage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1982 Jul;(167):296–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Soellner C., Scholz I. Characterization of a cloned ribosomal fragment from mouse which contains the 18S coding region and adjacent spacer sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1351–1369. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Ninomiya Y., Parsons J., Hayashi K., Olsen B. R., Trelstad R. L. Differential localization of mRNAs of collagen types I and II in chick fibroblasts, chondrocytes, and corneal cells by in situ hybridization using cDNA probes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2302–2309. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. J., Harper E. Quantitation of types I and III collagens in human tissue samples and cell culture by cyanogen bromide peptide analysis. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;141(1):83–93. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90429-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Rubin K., Klareskog L., Larsson E., Wigzell H. Characterization of the antibody response in mice with type II collagen-induced arthritis, using monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):400–410. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layman D. L., Epstein E. H., Jr, Dodson R. F., Titus J. L. Biosynthesis of type I and III collagens by cultured smooth muscle cells from human aorta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):671–675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Toole B. P., Trelstad R. L. Temporal and spatial transitions in collagen types during embryonic chick limb development. Dev Biol. 1973 Dec;35(2):232–239. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippiello L., Hall D., Mankin H. J. Collagen synthesis in normal and osteoarthritic human cartilage. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):593–600. doi: 10.1172/JCI108676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mankin H. J., Dorfman H., Lippiello L., Zarins A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Apr;53(3):523–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R. Cartilage collagens. What is their function, and are they involved in articular disease? Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Mar;32(3):241–246. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., Elrod B. W., Mayne P. M., Sanderson R. D., Linsenmayer T. F. Changes in the synthesis of minor cartilage collagens after growth of chick chondrocytes in 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine or to senescence. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Mar;151(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90366-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayne R., Vail M. S., Mayne P. M., Miller E. J. Changes in type of collagen synthesized as clones of chick chondrocytes grow and eventually lose division capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1674–1678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimni M., Deshmukh K. Differences in collagen metabolism between normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Science. 1973 Aug 24;181(4101):751–752. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4101.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowack H., Gay S., Wick G., Becker U., Timpl R. Preparation and use in immunohistology of antibodies specific for type I and type III collagen and procollagen. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(1-2):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronzière M. C., Ricard-Blum S., Tiollier J., Hartmann D. J., Garrone R., Herbage D. Comparative analysis of collagens solubilized from human foetal, and normal and osteoarthritic adult articular cartilage, with emphasis on type VI collagen. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 19;1038(2):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(90)90209-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg L. Chemical basis for the histological use of safranin O in the study of articular cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1971 Jan;53(1):69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan M. C., Sandell L. J. Differential expression of a cysteine-rich domain in the amino-terminal propeptide of type II (cartilage) procollagen by alternative splicing of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10334–10339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg M., Mäkelä J. K., Multimäki P., Vuorio T., Vuorio E. Construction of a human pro alpha 1(III) collagen cDNA clone and localization of type III collagen expression in human fetal tissues. Matrix. 1989 Mar;9(2):82–91. doi: 10.1016/s0934-8832(89)80025-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg M., Vuorio E. Localization of types I, II, and III collagen mRNAs in developing human skeletal tissues by in situ hybridization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1077–1084. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Popp R. G., Linsenmayer T. F. Hypertrophic cartilage matrix. Type X collagen, supramolecular assembly, and calcification. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;580:64–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17918.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkocz C., Kühn K. The formation of triple-helical collagen molecules from alpha-1 or alpha-2 polypeptide chains. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):454–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., Gauss V., von der Mark H., Müller P. Relationship between cell shape and type of collagen synthesised as chondrocytes lose their cartilage phenotype in culture. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):531–532. doi: 10.1038/267531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., Kirsch T., Nerlich A., Kuss A., Weseloh G., Glückert K., Stöss H. Type X collagen synthesis in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Indication of chondrocyte hypertrophy. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Jul;35(7):806–811. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H., Gay S. Study of differential collagen synthesis during development of the chick embryo by immunofluroescence. II. Localization of type I and type II collagen during long bone development. Dev Biol. 1976 Oct 15;53(2):153–170. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(76)90220-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H. Immunological and biochemical studies of collagen type transition during in vitro chrondrogenesis of chick limb mesodermal cells. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):736–747. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Mark K., von der Mark H. The role of three genetically distinct collagen types in endochondral ossification and calcification of cartilage. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1977 Nov;59-B(4):458–464. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.59B4.72756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]