Abstract
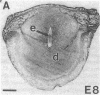
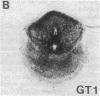
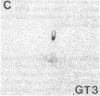
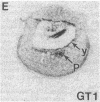
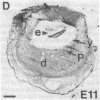
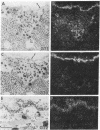
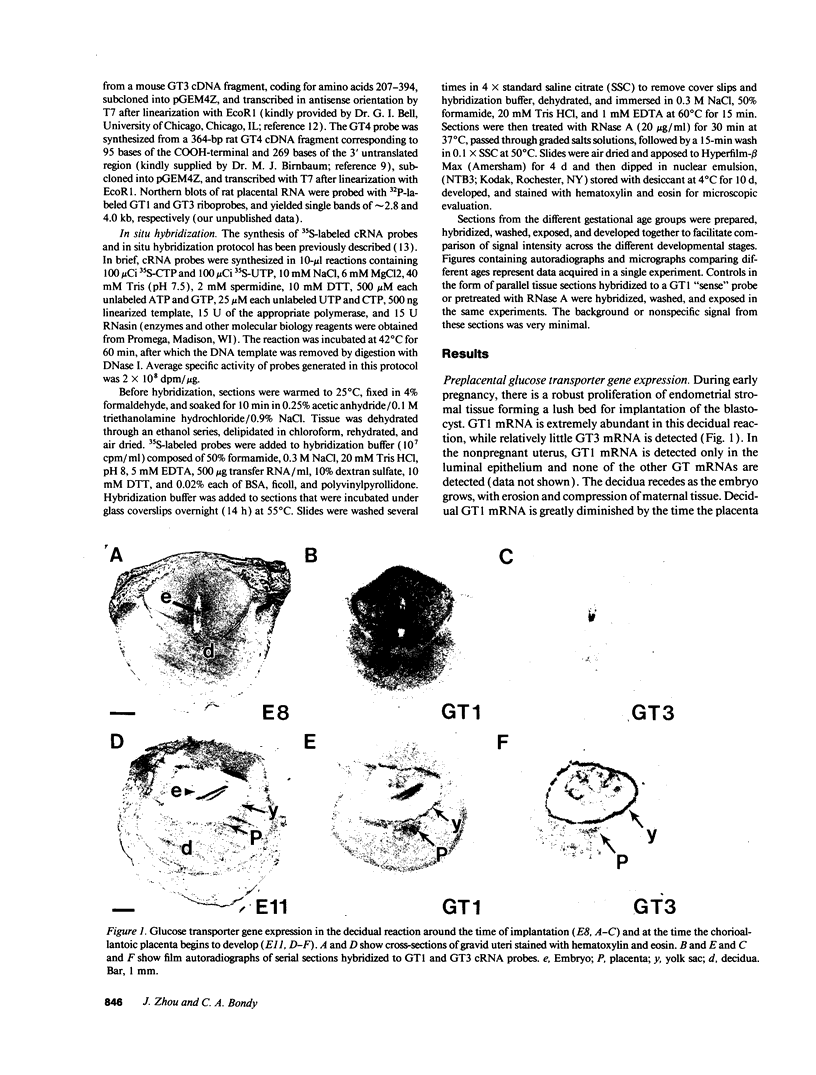
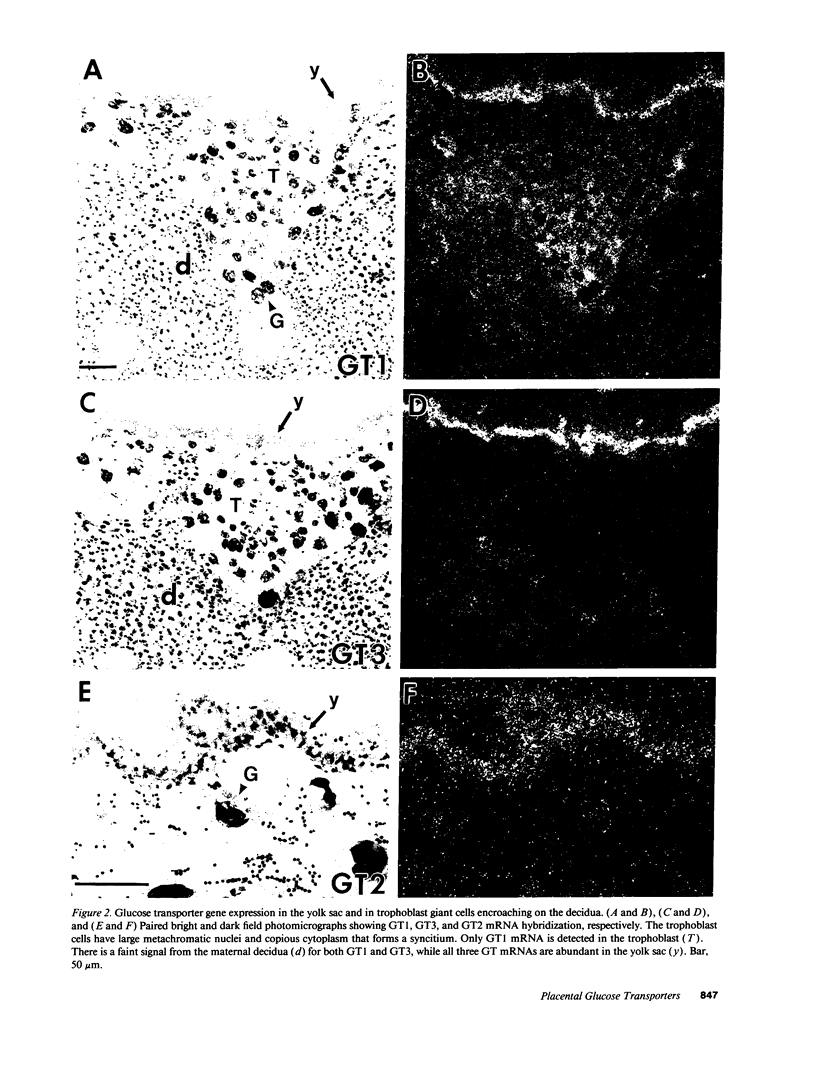
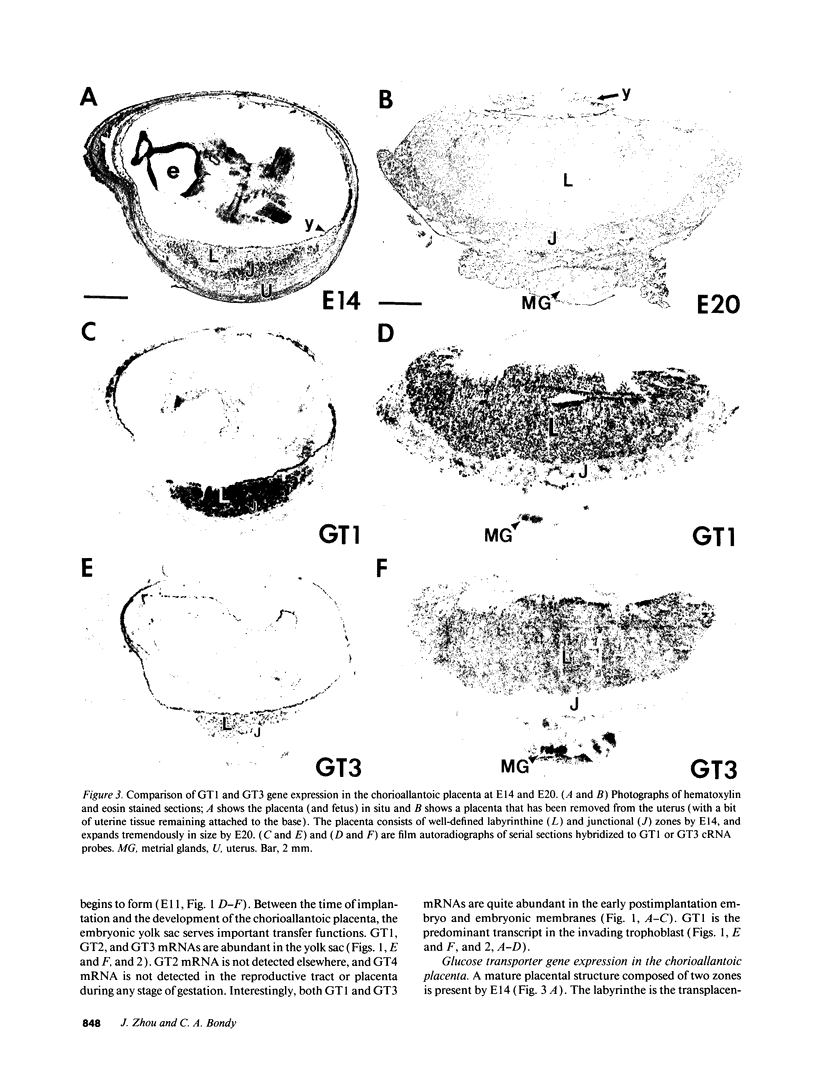
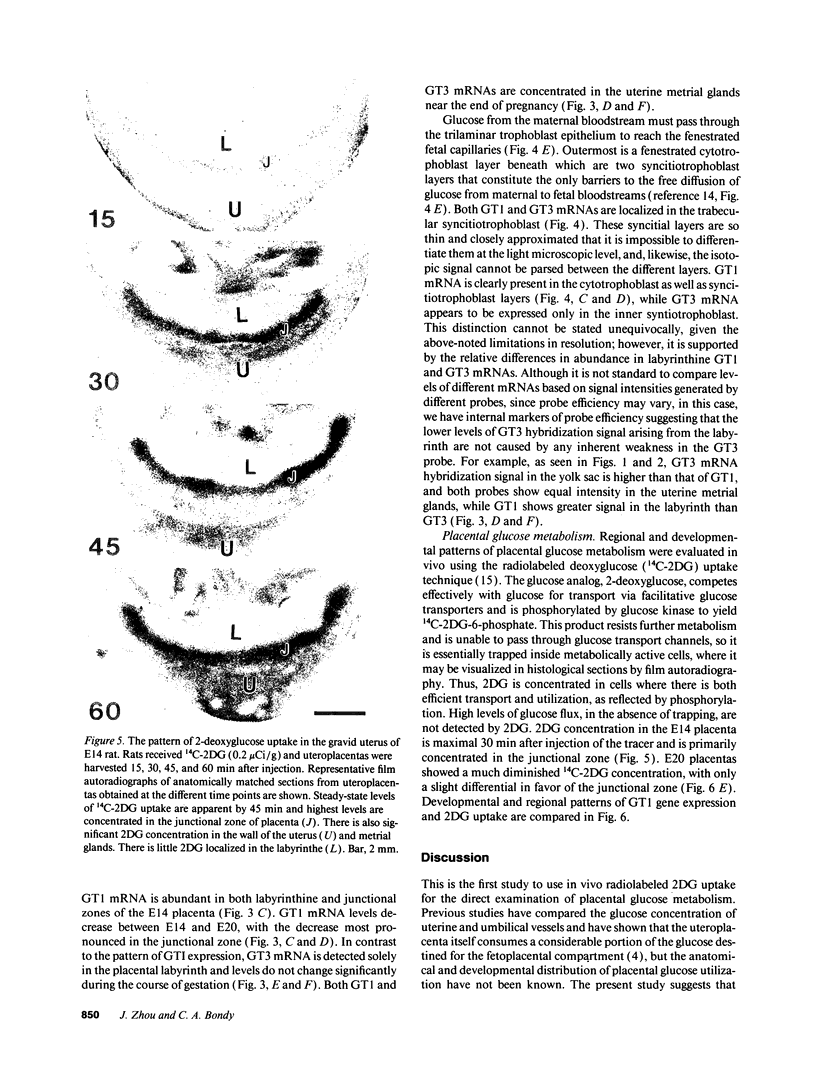
In situ hybridization was used to evaluate patterns of gene expression for glucose transporters 1-4 (GT1-4) in the rat uteroplacenta from the time of implantation through term, and in vivo regional placental glucose metabolism was measured by 14C-labeled 2-deoxyglucose uptake. GT1 mRNA was highly abundant and GT3 was barely detected in the postimplantation decidual reaction. GT1 and 3 mRNAs were colocalized in the labyrinthine syncitiotrophoblast layer of the chorioallantoic placenta, which forms the membranous barrier between maternal and fetal circulations. The level of labyrinthine GT3 mRNA showed no change from midgestation through term; however, the volume of the labyrinth and hence total GT 3 gene expression increased greatly during this period. Labyrinthine GT1 mRNA levels, in contrast, showed significant diminution near term. GT1 mRNA was also localized in the placental growth plate, or junctional zone, where it was most abundant during the period of rapid placental growth and was decreased at term. Placental glucose metabolism, as reflected by steady-state 2-deoxyglucose uptake, was highest in the junctional zone during the rapid growth phase during midgestation, and decreased significantly at term, in parallel with GT1 gene expression. These findings suggest that GT1 is responsible for supplying glucose for use as a placental fuel and that GT3 is important for glucose transfer to the embryo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battaglia F. C., Meschia G. Principal substrates of fetal metabolism. Physiol Rev. 1978 Apr;58(2):499–527. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.2.499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A. Transient IGF-I gene expression during the maturation of functionally related central projection neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3442–3455. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Hausman A. M., Ifkovits C. A., Buse J. B., Gould G. W., Burant C. F., Bell G. I. Human intestinal glucose transporter expression and localization of GLUT5. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C795–C800. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Glasser S. R. Histological and fine structural observations on the placenta of the rat. Acta Anat (Basel) 1968;69(4):542–608. doi: 10.1159/000143100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould G. W., Thomas H. M., Jess T. J., Bell G. I. Expression of human glucose transporters in Xenopus oocytes: kinetic characterization and substrate specificities of the erythrocyte, liver, and brain isoforms. Biochemistry. 1991 May 28;30(21):5139–5145. doi: 10.1021/bi00235a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay W. W., Jr, Sparks J. W., Wilkening R. B., Battaglia F. C., Meschia G. Fetal glucose uptake and utilization as functions of maternal glucose concentration. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):E237–E242. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.246.3.E237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingermann R. L. Control of placental glucose transfer. Placenta. 1987 Nov-Dec;8(6):557–571. doi: 10.1016/0143-4004(87)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. W., Smith C. H. Glucose transport across the basal plasma membrane of human placental syncytiotrophoblast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 26;815(1):44–50. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90472-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones C. T. Control of glucose metabolism in the perinatal period. J Dev Physiol. 1991 Feb;15(2):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B. Facilitative glucose transporters: regulatory mechanisms and dysregulation in diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1992 May;89(5):1367–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI115724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasanicki M. A., Pilch P. F. Regulation of glucose-transporter function. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):219–227. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M. Family of glucose-transporter genes. Implications for glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Diabetes. 1990 Jan;39(1):6–11. doi: 10.2337/diacare.39.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagamatsu S., Kornhauser J. M., Burant C. F., Seino S., Mayo K. E., Bell G. I. Glucose transporter expression in brain. cDNA sequence of mouse GLUT3, the brain facilitative glucose transporter isoform, and identification of sites of expression by in situ hybridization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):467–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. M., Smith R. M., Jarett L. Nonuniform distribution and grouping of insulin receptors on the surface of human placental syncytial trophoblast. Diabetes. 1978 May;27(5):530–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posner B. I. Insulin receptors in human and animal placental tissue. Diabetes. 1974 Mar;23(3):209–217. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L. Localization of functional activity in the central nervous system by measurement of glucose utilization with radioactive deoxyglucose. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1981;1(1):7–36. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1981.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F. Molecular physiology of glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):209–218. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]