Abstract
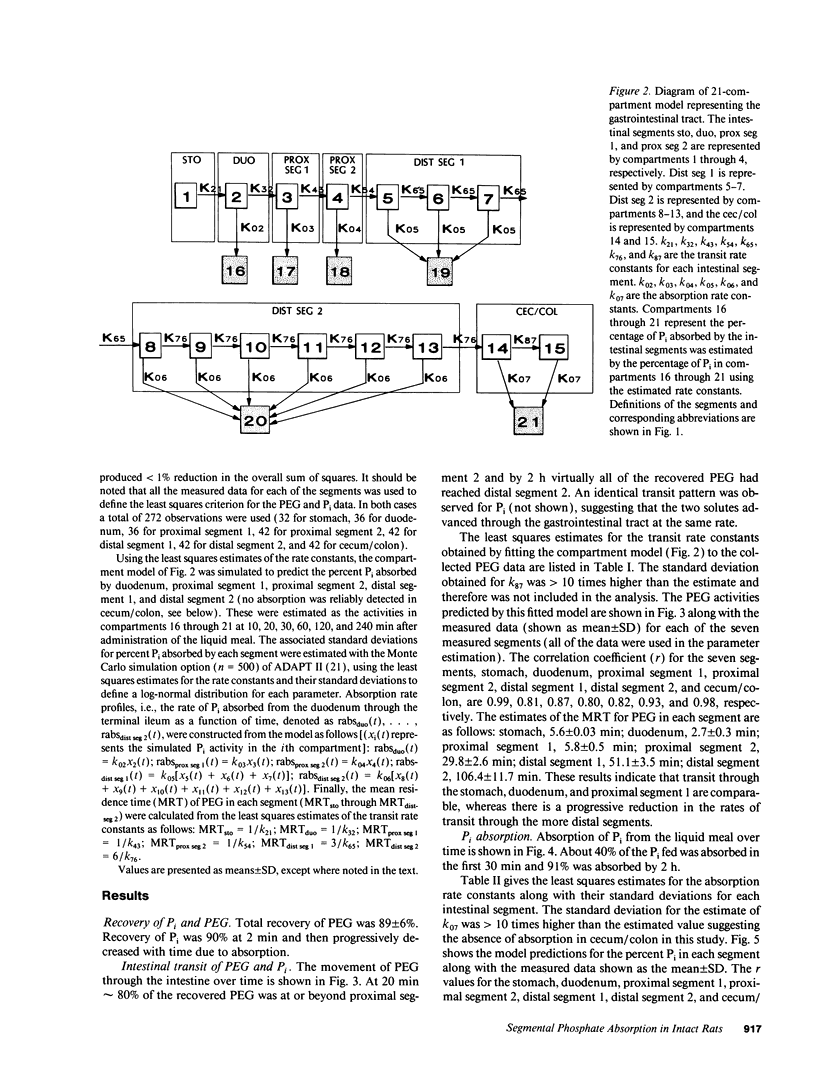
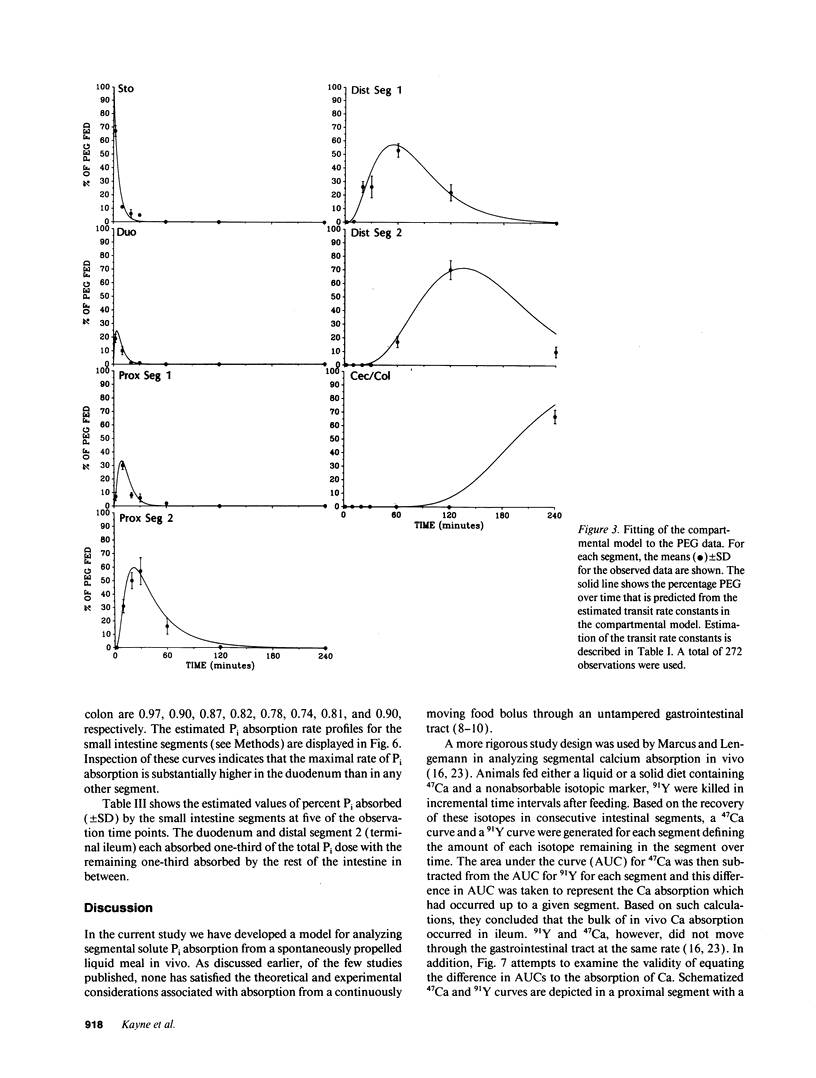
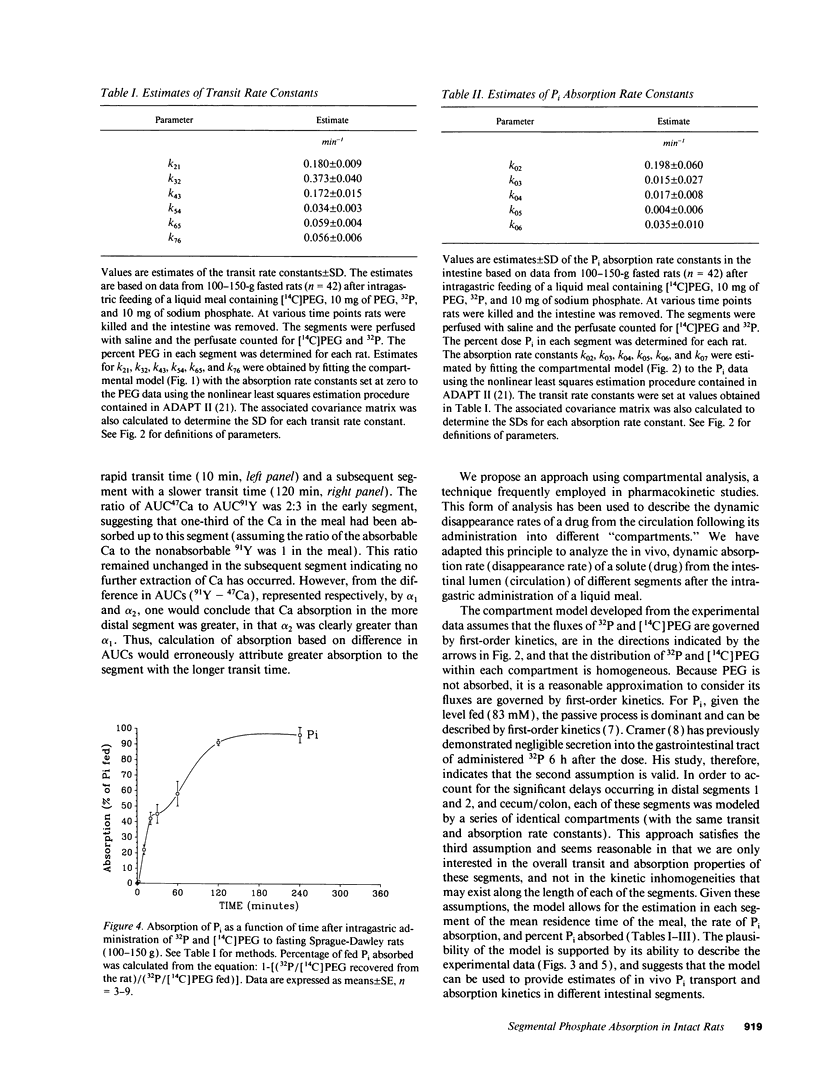
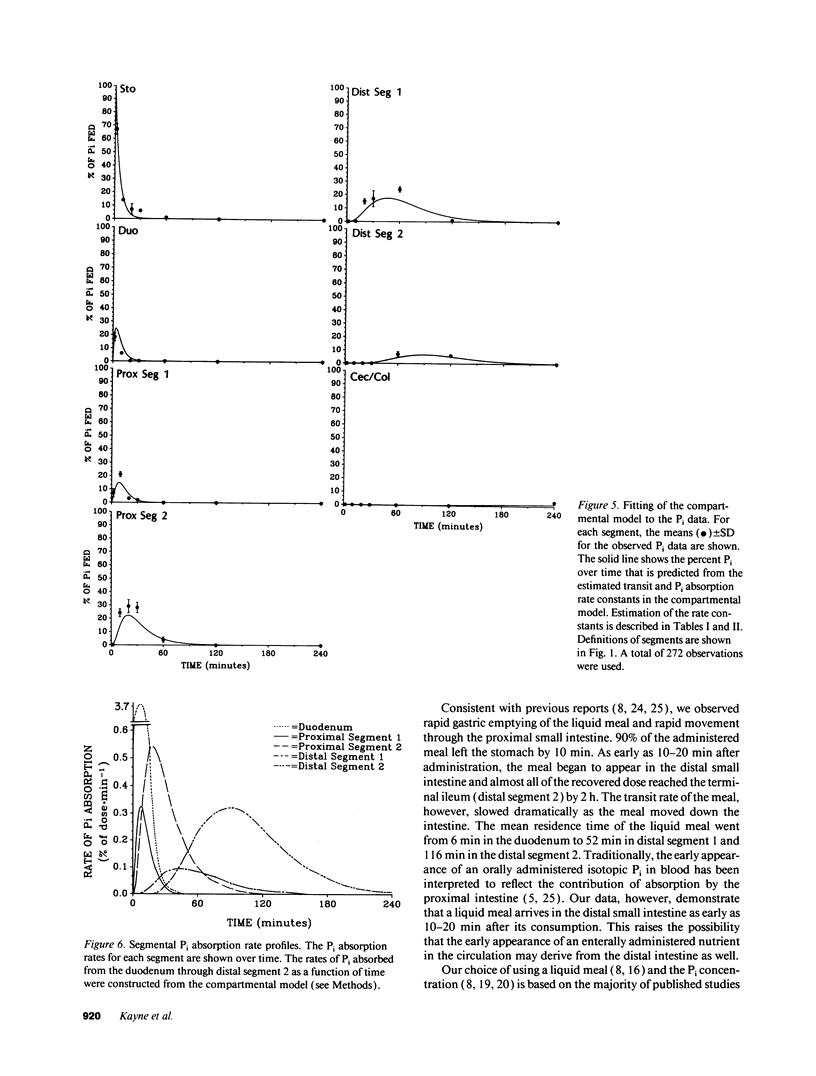
Available information supports the dominance of the proximal intestine in inorganic phosphate (Pi) absorption. However, there is no strategy for analyzing segmental Pi absorption from a spontaneously propelled meal in an intact animal. We propose a solution using compartmental analysis. After intragastric administration of a 32P-labeled Pi liquid meal containing a nonabsorbable marker, [14C]polyethylene glycol (PEG), rats were killed at 2, 10, 20, 30, 60, 120, and 240 min. The gastrointestinal tract was removed and divided into seven segments, from which 32P and [14C]PEG were recovered. Data was expressed as a percentage of the dose fed, i.e., (32P[in segment] divided by 32P[fed]) and [14C]PEG[in segment] divided by [14C]PEG[fed]), respectively. A compartmental model was constructed and the rate constants for intersegmental transit and segmental absorption were estimated. The "goodness of fit" between the simulated model and the actual data indicates the estimated rate constants reflect in vivo events. The duodenum, with the highest transit and absorption rates, accounted for a third of the total absorption. However, the terminal ileum, with a lower absorption rate but a longer transit time, absorbed an equal amount of Pi. This approach allows the analysis of the mechanism and the regulation of Pi absorption under more authentic in vivo conditions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CRAMER C. F. In vivo measurement of radiophosphorus and radiostrontium absorption in rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Feb;100(2):364–367. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAMER C. F. Progress and rate of absorption of radiophosphorus through the intestinal tract of rats. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1961 Mar;39:499–503. doi: 10.1139/o61-048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caniggia A., Gennari C., Bencini M., Palazzuoli V. Intestinal absorption of radio phosphate in osteomalacia before and after vitamin D treatment. Calcif Tissue Res. 1968;2(3):299–300. doi: 10.1007/BF02279218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condon J. R., Nassim J. R., Rutter A. Defective intestinal phosphate absorption in familial and non-familial hypophosphataemia. Br Med J. 1970 Jul 18;3(5715):138–141. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5715.138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freel R. W., Hatch M., Earnest D. L., Goldner A. M. Role of tight-junctional pathways in bile salt-induced increases in colonic permeability. Am J Physiol. 1983 Dec;245(6):G816–G823. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.6.G816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ S., BAR A. ABSORPTION OF CALCIUM AND PHOSPHORUS ALONG THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF THE LAYING FOWL AS INFLUENCED BY DIETARY CALCIUM AND EGG SHELL FORMATION. J Nutr. 1965 Aug;86:433–438. doi: 10.1093/jn/86.4.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz S., Bar A. The sites of calcium and phosphate absorption in the chick. Poult Sci. 1970 Jan;49(1):324–325. doi: 10.3382/ps.0490324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landaw E. M., DiStefano J. J., 3rd Multiexponential, multicompartmental, and noncompartmental modeling. II. Data analysis and statistical considerations. Am J Physiol. 1984 May;246(5 Pt 2):R665–R677. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1984.246.5.R665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. B., Walling M. W., Brautbar N. Intestinal phosphate absorption: influence of vitamin D and non-vitamin D factors. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):G369–G373. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.3.G369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. B., Walling M. W., Corry D. B. Phosphate transport across rat jejunum: influence of sodium, pH, and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jul;251(1 Pt 1):G90–G95. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.1.G90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. B., Walling M. W., Gafter U., Silis V., Coburn J. W. Calcium and inorganic phosphate transport in rat colon: dissociated response to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1326–1331. doi: 10.1172/JCI109796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS C. S., LENGEMANN F. W. Absorption of Ca45 and Sr85 from solid and liquid food at various levels of the alimentary tract of the rat. J Nutr. 1962 Jun;77:155–160. doi: 10.1093/jn/77.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS C. S., LENGEMANN F. W. Use of radioyttrium to study food movement in the small intestine of the rat. J Nutr. 1962 Feb;76:179–182. doi: 10.1093/jn/76.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malagelada J. R., Robertson J. S., Brown M. L., Remington M., Duenes J. A., Thomforde G. M., Carryer P. W. Intestinal transit of solid and liquid components of a meal in health. Gastroenterology. 1984 Dec;87(6):1255–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer J. H., Mayer E. A., Jehn D., Gu Y., Fink A. S., Fried M. Gastric processing and emptying of fat. Gastroenterology. 1986 May;90(5 Pt 1):1176–1187. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. L., Schedl H. P., Bouska J., Phillips S. F. Food restriction and recovery of nonabsorbed indicators from the small intestine of the rat. Digestion. 1987;38(2):83–89. doi: 10.1159/000199576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nellans H. N., Kimberg D. V. Anomalous calcium secretion in rat ileum: role of paracellular pathway. Am J Physiol. 1979 Apr;236(4):E473–E481. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.236.4.E473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaysen R. Studies upon the mode of action of vitamin D: The absorption of phosphates from isolated loops of the small intestine in the rat. Biochem J. 1937 Jul;31(7):1086–1088. doi: 10.1042/bj0311086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulakos L., Kent T. H. Gastric emptying and small intestinal propulsion in fed and fasted rats. Gastroenterology. 1973 May;64(5):962–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling M. W. Intestinal Ca and phosphate transport: differential responses to vitamin D3 metabolites. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):E488–E494. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.6.E488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman R. H., Taylor A. N. Intestinal absorption of phosphate in the chick: effect of vitamin D and other parameters. J Nutr. 1973 Apr;103(4):586–599. doi: 10.1093/jn/103.4.586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




