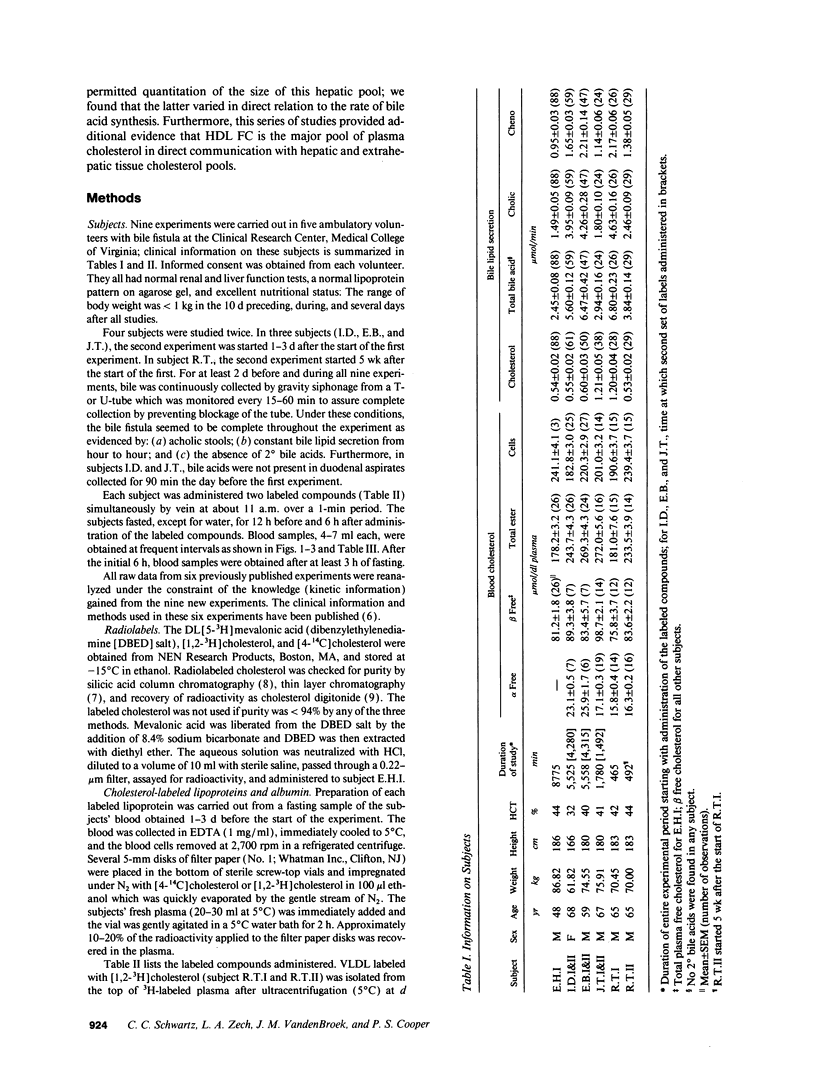
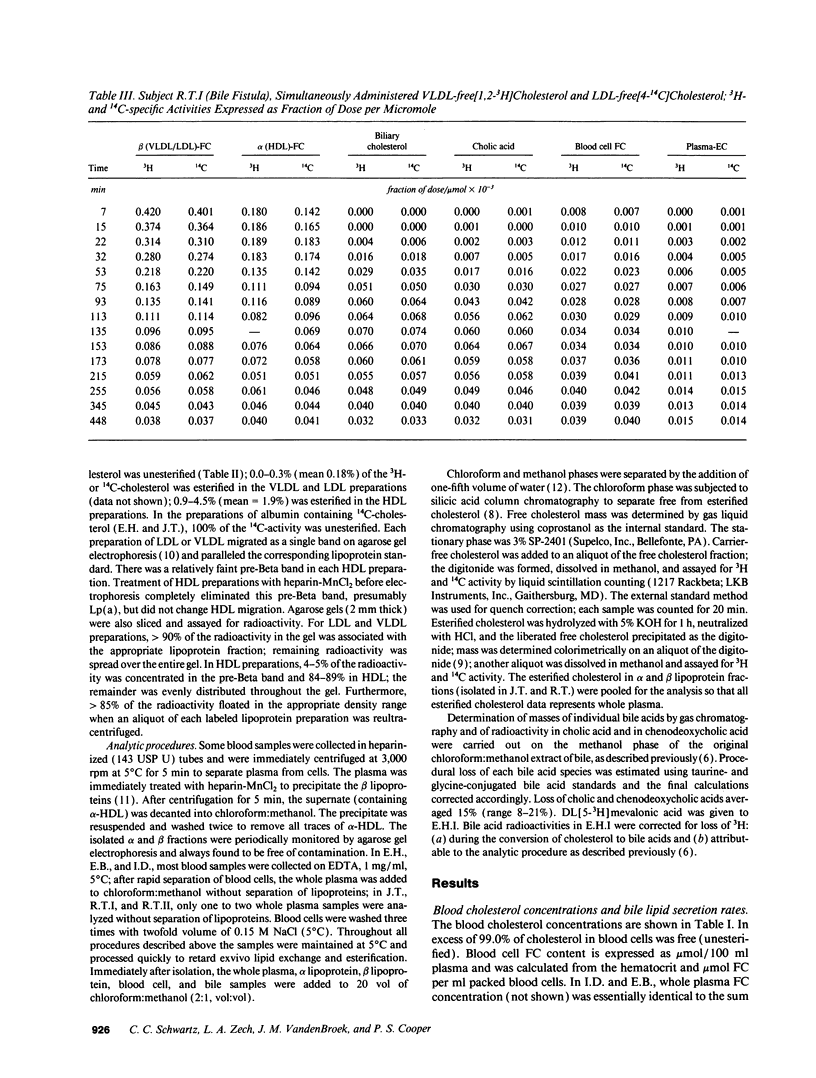
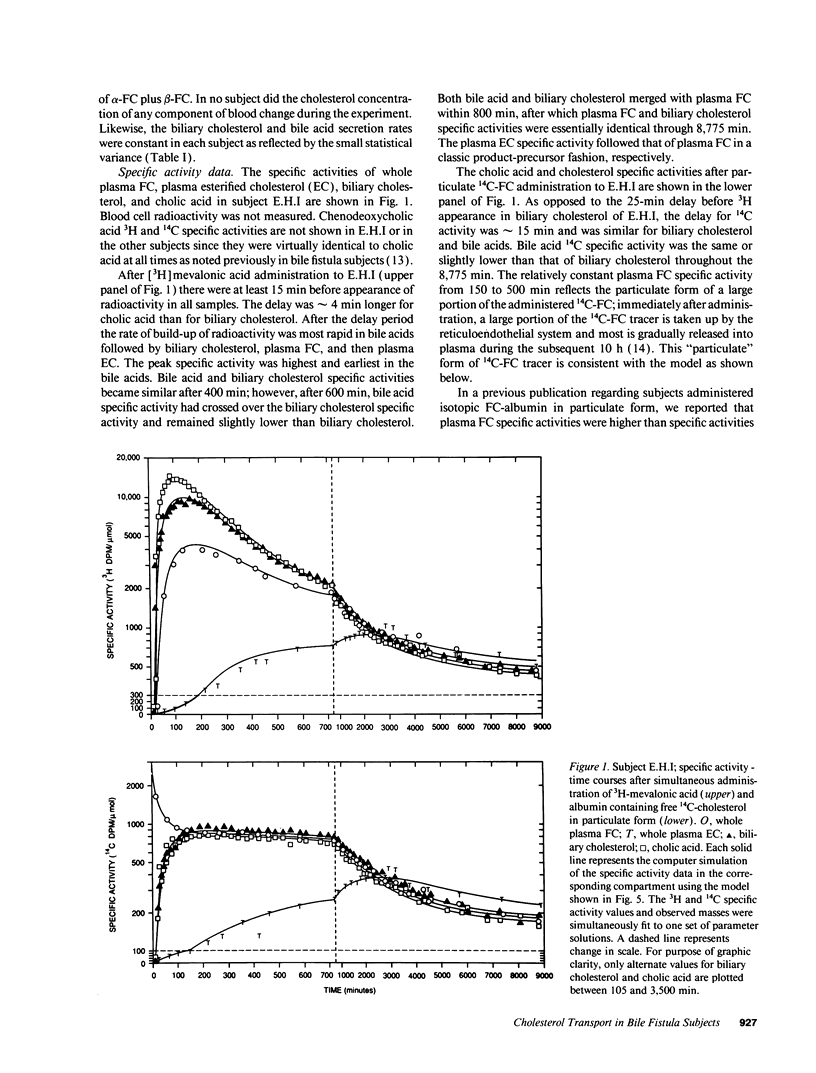
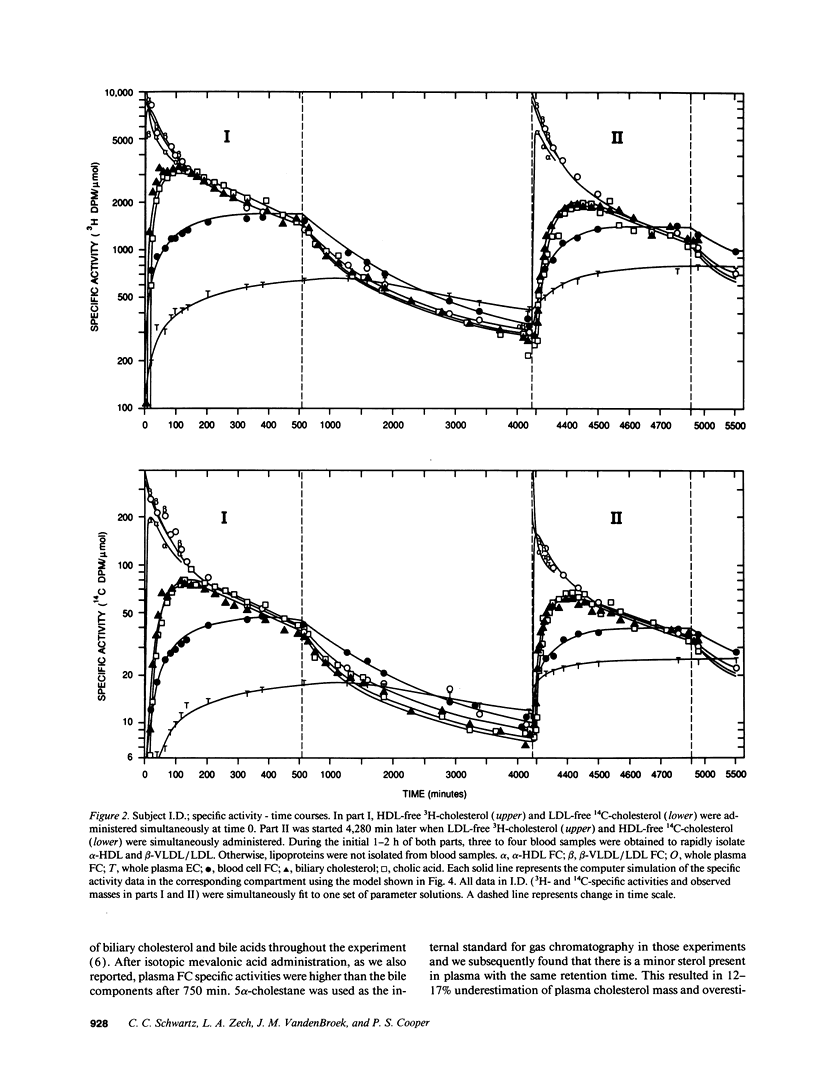
Abstract
Our aim was to identify and quantitate cholesterol pools and transport pathways in blood and liver. By studying bile fistula subjects, using several types of isotopic preparations, simultaneous labeling of separate cholesterol pools and sampling all components of blood and bile at frequent intervals, we developed a comprehensive multicompartmental model for cholesterol within the rapidly miscible pool. Data in six components (bile acids, esterified cholesterol in whole plasma, and free cholesterol in blood cells, bile, alpha lipoproteins, and beta lipoproteins) were modeled simultaneously with the SAAM program. The analysis revealed extensive exchange of free cholesterol between HDL and liver, blood cells, and other tissues. There was net free cholesterol transport from HDL to the liver in most subjects. The major organ that removed esterified cholesterol from blood was the liver. A large portion (4,211 mumol) of total hepatic cholesterol comprised a pool that turned over rapidly (t1/2 of 72 min) by exchanging mainly with plasma HDL and was the major source of bile acids and biliary cholesterol. Only 6% of hepatic newly synthesized cholesterol was used directly for bile acid synthesis: the analysis showed that 94% of newly synthesized cholesterol was partitioned into the large hepatic pool (putative plasma membrane free cholesterol) which exchanged rapidly with plasma lipoproteins. Bile acid synthetic rate correlated directly with the size of the large hepatic pool. In conclusion, hepatic and blood cholesterol pools and transports have been quantitated. HDL plays a central role in free cholesterol exchange/transport between all tissues and plasma. In humans, the metabolically active pool comprises a large portion of total hepatic cholesterol that, in part, regulates bile acid synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björkhem I., Akerlund J. E. Studies on the link between HMG-CoA reductase and cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase in rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1988 Feb;29(2):136–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Levy R. I., Eisenberg S., Hall M., 3rd, Goebel R. H., Berman M. High density lipoprotein metabolism in man. J Clin Invest. 1977 Oct;60(4):795–807. doi: 10.1172/JCI108833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein M., Scholnick H. R. Lipoprotein-polyanion-metal interactions. Adv Lipid Res. 1973;11(0):67–108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. High density lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1984 Oct;25(10):1017–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD H., Jr, SWELL L., SCHOOLS P. E., Jr, TREADWELL C. R. Dynamic aspects of cholesterol metabolism in different areas of the aorta and other tissues in man and their relationship to atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1960 Oct;22:547–558. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.22.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francone O. L., Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Distribution of cell-derived cholesterol among plasma lipoproteins: a comparison of three techniques. J Lipid Res. 1990 Dec;31(12):2195–2200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD R. G., LEROY G. V., OKITA G. T., KABARA J. J., KEEGAN P., BERGENSTAL D. M. The use of C14-labeled acetate to study cholesterol metabolism in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Sep;46(3):372–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Noble R. P., Dell R. B. Three-pool model of the long-term turnover of plasma cholesterol in man. J Lipid Res. 1973 Mar;14(2):178–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLMAN L., ROSENFELD R. S., EIDINOFF M. L., FUKUSHIMA D. K., GALLAGHER T. F., WANG C. I., ADLERSBERG D. Isotopic studies of plasma cholesterol of endogenous and exogenous origins. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jan;34(1):48–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI103062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J., AHRENS E. H., Jr The separation of complex lipide mixtures by the use of silicic acid chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1958 Aug;233(2):311–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek D. F., Andersson S., Slaughter C. A., Russell D. W. Cloning and regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase, the rate-limiting enzyme in bile acid biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8190–8197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. J., Bamberger M. J., Latta R. A., Rapp P. E., Phillips M. C., Rothblat G. H. The bidirectional flux of cholesterol between cells and lipoproteins. Effects of phospholipid depletion of high density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5766–5776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KURLAND G. S., LUCAS J. L., FREEDBERG A. S. The metabolism of intravenously infused C14-labeled cholesterol in euthyroidism and myxedema. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Apr;57:574–585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Ramos B. V. Analysis of the distribution of cholesterol in the intact cell. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15130–15134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y., Steck T. L. Cholesterol-rich intracellular membranes: a precursor to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15592–15597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange Y. Tracking cell cholesterol with cholesterol oxidase. J Lipid Res. 1992 Mar;33(3):315–321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer T., Strober W., Levy R. I. The metabolism of low density lipoprotein in familial type II hyperlipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1528–1536. doi: 10.1172/JCI106949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson A., Zilversmit D. B. Fate of intravenously administered particulate and lipoprotein cholesterol in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1972 Jan;13(1):32–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble R. P. Electrophoretic separation of plasma lipoproteins in agarose gel. J Lipid Res. 1968 Nov;9(6):693–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERRY W. M., WEBB M. A revision of the Schoenheimer-Sperry method for cholesterol determination. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel P., Perl W. Long-term decay of serum cholesterol radioactivity: body cholesterol metabolism in normals and in patients with hyperlipoproteinemia and atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):346–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI106243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. C., Berman M., Vlahcevic Z. R., Halloran L. G., Gregory D. H., Swell L. Multicompartmental analysis of cholesterol metabolism in man. Characterization of the hepatic bile acid and biliary cholesterol precursor sites. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):408–423. doi: 10.1172/JCI108952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. C., Berman M., Vlahcevic Z. R., Swell L. Multicompartmental analysis of cholesterol metabolism in man. Quantitative kinetic evaluation of precursor sources and turnover of high density lipoprotein cholesterol esters. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):863–876. doi: 10.1172/JCI110683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. C., Halloran L. G., Vlahcevic Z. R., Gregory D. H., Swell L. Preferential utilization of free cholesterol from high-density lipoproteins for biliary cholesterol secretion in man. Science. 1978 Apr 7;200(4337):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.204996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. C., Vlahcevic Z. R., Berman M., Meadows J. G., Nisman R. M., Swell L. Central role of high density lipoprotein in plasma free cholesterol metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):105–116. doi: 10.1172/JCI110582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz C. C., Vlahcevic Z. R., Halloran L. G., Nisman R., Swell L. Evidence for a common hepatic cholesterol precursor site for cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid synthesis in man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Nov;156(2):261–264. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. R., Dell R. B., Noble R. P., Goodman D. S. Parameters of the three-pool model of the turnover of plasma cholesterol in normal and hyperlipidemic humans. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):137–148. doi: 10.1172/JCI108253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbani L., Simoni R. D. Cholesterol and vesicular stomatitis virus G protein take separate routes from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1919–1923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



