Abstract
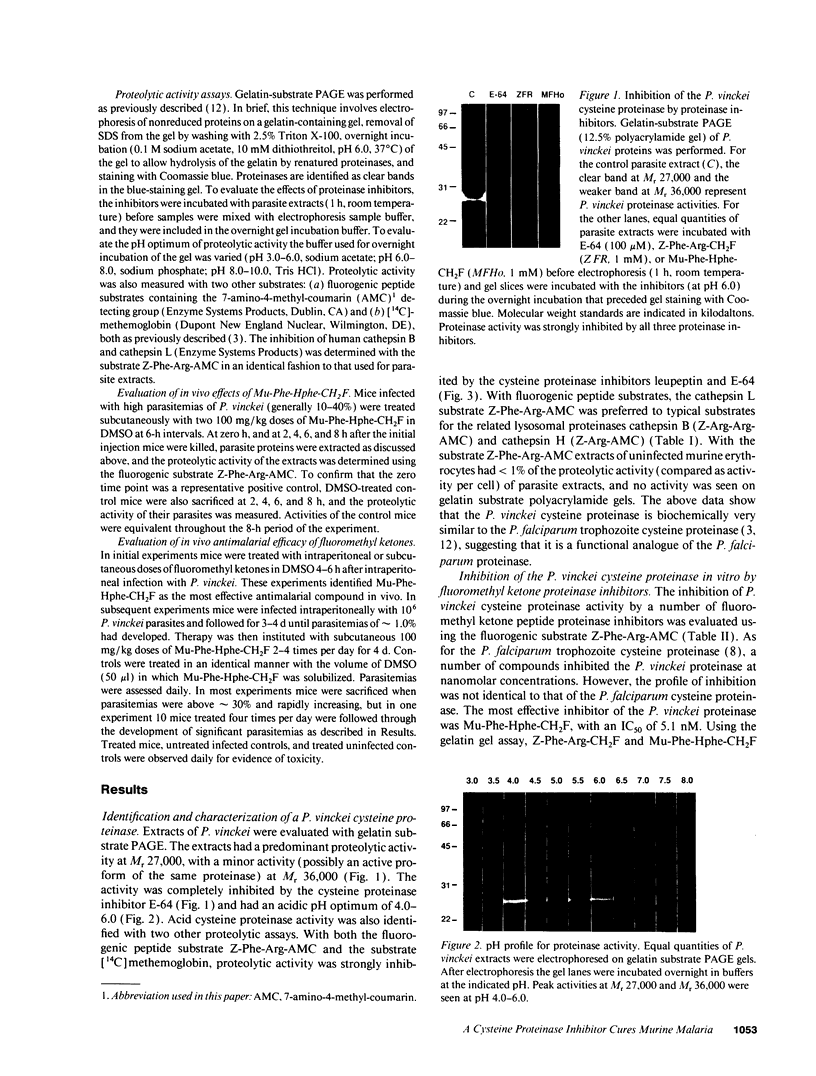
Intraerythrocytic malaria parasites degrade hemoglobin as a principal source of amino acids for parasite protein synthesis. We have previously identified a Plasmodium falciparum trophozoite cysteine proteinase as a putative hemoglobinase and shown that specific inhibitors of this proteinase block the hydrolysis of globin and the development of cultured parasites. We now show that the murine malaria parasite Plasmodium vinckei has an analogous cysteine proteinase with similar biochemical properties to the P. falciparum proteinase, including an acid pH optimum, a preference for the peptide proteolytic substrate benzyloxycarbonyl (Z)-Phe-Arg-7-amino-4-methylcoumarin, and nonomolar inhibition by seven peptide fluoromethyl ketone proteinase inhibitors. Thus, P. vinckei offers a model system for the in vivo testing of the antimalarial properties of cysteine proteinase inhibitors. One of the proteinase inhibitors studied, morpholine urea (Mu)-Phe-Homophenylalanine (HPhe)-CH2F strongly inhibited the P. vinckei cysteine proteinase in vitro and rapidly blocked parasite cysteine proteinase activity in vivo. When administered four times a day for 4 d to P. vinckei-infected mice, Mu-Phe-HPhe-CH2F elicited long-term cures in 80% of the treated animals. These results show that peptide proteinase inhibitors can be effective antimalarial compounds in vivo and suggest that the P. falciparum cysteine proteinase is a promising target for chemotherapy.
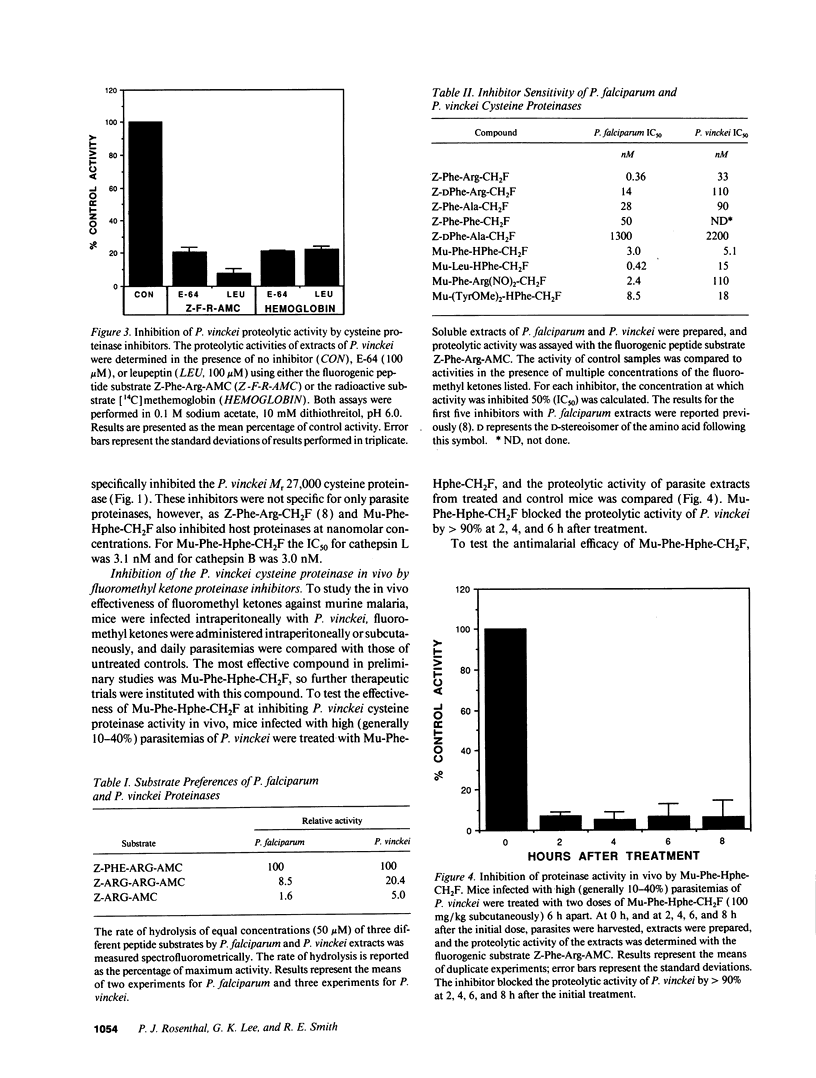
Full text
PDF
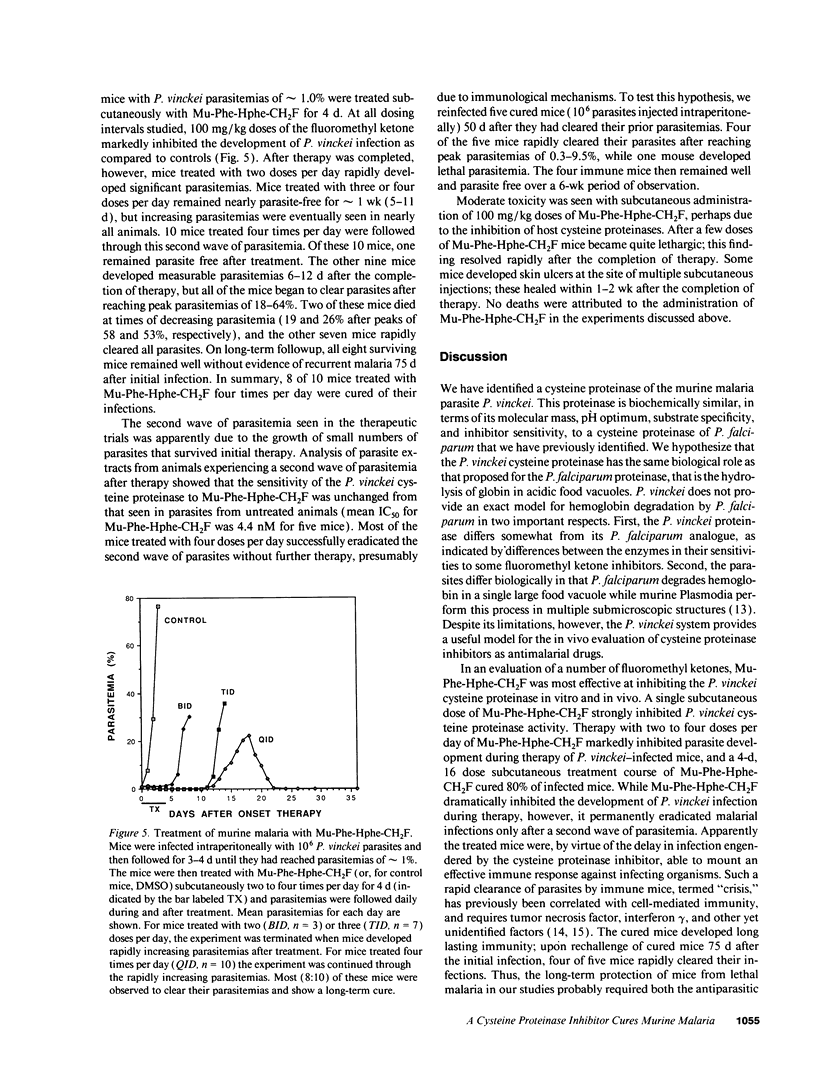

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Goldberg D. E., Slater A. F., Beavis R., Chait B., Cerami A., Henderson G. B. Hemoglobin degradation in the human malaria pathogen Plasmodium falciparum: a catabolic pathway initiated by a specific aspartic protease. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):961–969. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambros C., Vanderberg J. P. Synchronization of Plasmodium falciparum erythrocytic stages in culture. J Parasitol. 1979 Jun;65(3):418–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naotunne T. S., Karunaweera N. D., Del Giudice G., Kularatne M. U., Grau G. E., Carter R., Mendis K. N. Cytokines kill malaria parasites during infection crisis: extracellular complementary factors are essential. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):523–529. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. J., Kim K., McKerrow J. H., Leech J. H. Identification of three stage-specific proteinases of Plasmodium falciparum. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):816–821. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. J., McKerrow J. H., Aikawa M., Nagasawa H., Leech J. H. A malarial cysteine proteinase is necessary for hemoglobin degradation by Plasmodium falciparum. J Clin Invest. 1988 Nov;82(5):1560–1566. doi: 10.1172/JCI113766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. J., McKerrow J. H., Rasnick D., Leech J. H. Plasmodium falciparum: inhibitors of lysosomal cysteine proteinases inhibit a trophozoite proteinase and block parasite development. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Jun 15;35(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90120-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal P. J., Wollish W. S., Palmer J. T., Rasnick D. Antimalarial effects of peptide inhibitors of a Plasmodium falciparum cysteine proteinase. J Clin Invest. 1991 Nov;88(5):1467–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI115456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudzinska M. A., Trager W., Bray R. S. Pinocytotic uptake and the digestion of hemoglobin in malaria parasites. J Protozool. 1965 Nov;12(4):563–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1965.tb03256.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman I. W., Tanigoshi L. Purification of Plasmodium lophurae cathepsin D and its effects on erythrocyte membrane proteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Jul;8(3):207–226. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trager W., Jensen J. B. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science. 1976 Aug 20;193(4254):673–675. doi: 10.1126/science.781840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vander Jagt D. L., Hunsaker L. A., Campos N. M. Characterization of a hemoglobin-degrading, low molecular weight protease from Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Mar;18(3):389–400. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





