Abstract
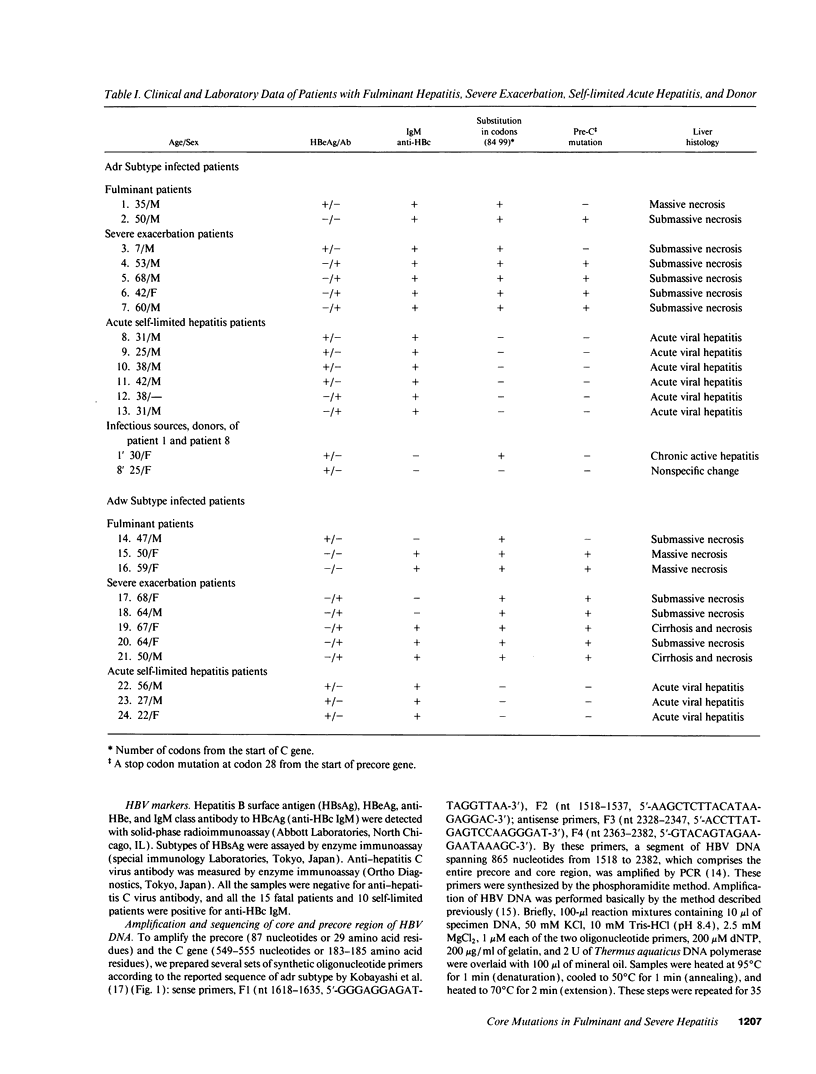
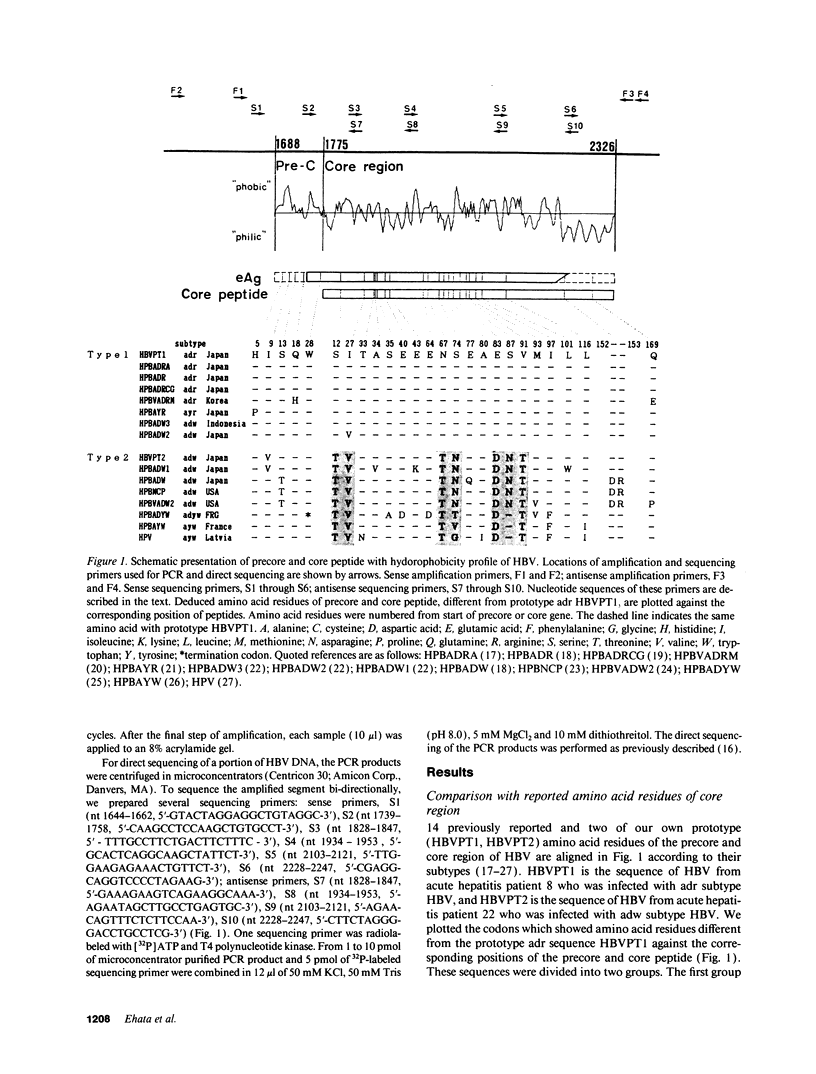
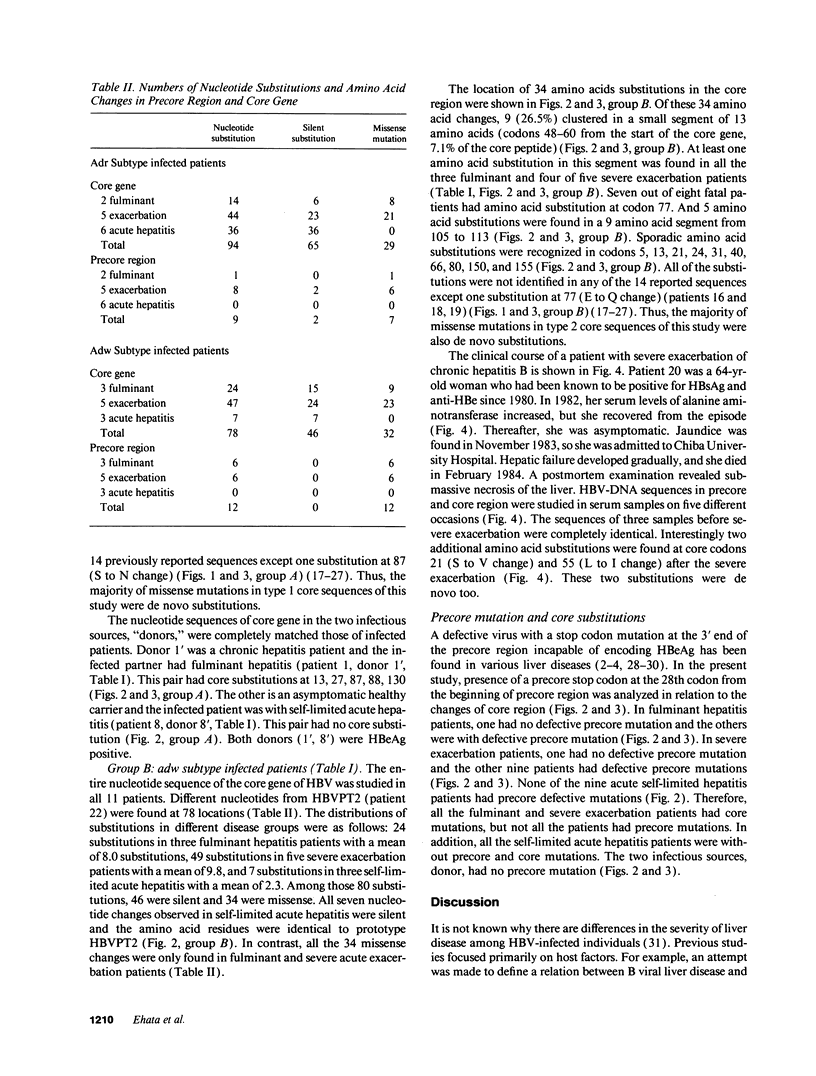
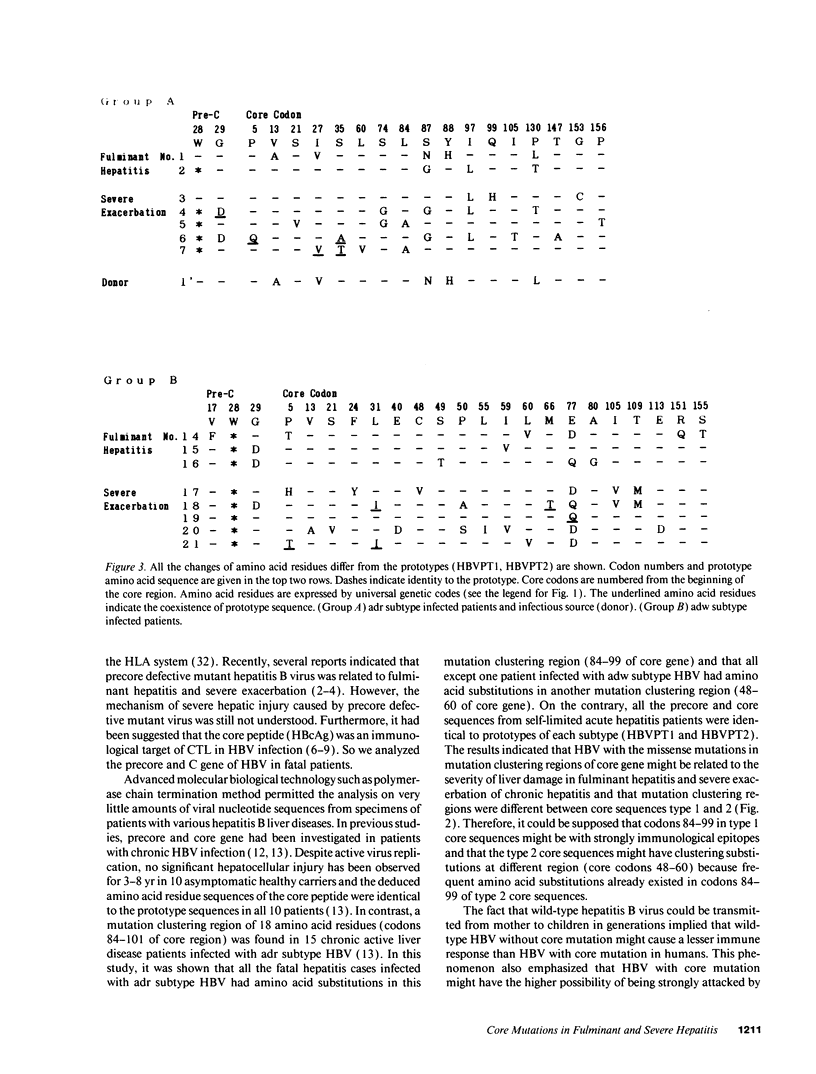
Infection with hepatitis B virus leads to a wide spectrum of liver injury, including self-limited acute hepatitis, fulminant hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with progression to cirrhosis or acute exacerbation to liver failure, as well as an asymptomatic chronic carrier state. Several studies have suggested that the hepatitis B core antigen could be an immunological target of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. To investigate the reason why the extreme immunological attack occurred in fulminant hepatitis and severe exacerbation patients, the entire precore and core region of hepatitis B virus DNA was sequenced in 24 subjects (5 fulminant, 10 severe fatal exacerbation, and 9 self-limited acute hepatitis patients). No significant change in the nucleotide sequence and deduced amino acid residue was noted in the nine self-limited acute hepatitis patients. In contrast, clustering changes in a small segment of 16 amino acids (codon 84-99 from the start of the core gene) in all seven adr subtype infected fulminant and severe exacerbation patients was found. A different segment with clustering substitutions (codon 48-60) was also found in seven of eight adw subtype infected fulminant and severe exacerbation patients. Of the 15 patients, 2 lacked precore stop mutation which was previously reported to be associated with fulminant hepatitis. These data suggest that these core regions with mutations may play an important role in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B viral disease, and such mutations are related to severe liver damage.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akahane Y., Yamanaka T., Suzuki H., Sugai Y., Tsuda F., Yotsumoto S., Omi S., Okamoto H., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Chronic active hepatitis with hepatitis B virus DNA and antibody against e antigen in the serum. Disturbed synthesis and secretion of e antigen from hepatocytes due to a point mutation in the precore region. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):1113–1119. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90632-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichko V., Pushko P., Dreilina D., Pumpen P., Gren E. Subtype ayw variant of hepatitis B virus. DNA primary structure analysis. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jun 3;185(1):208–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80771-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Jacyna M. R., Hadziyannis S., Karayiannis P., McGarvey M. J., Makris A., Thomas H. C. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet. 1989 Sep 9;2(8663):588–591. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S., Vogel R., Ye W., Blume M., Lee S., Hung P. The core gene of hepatitis B virus; subtype adw2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8188–8188. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Chisari F. V. Immunological aspects of hepatitis B virus infection. Am J Med Sci. 1975 Sep-Oct;270(2):212–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehata T., Omata M., Yokosuka O., Hosoda K., Ohto M. Amino acid residues of core region of hepatitis B virus. Asymptomatic carriers versus patients with liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1991 May-Jun;6(3):292–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.1991.tb01481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehata T., Omata M., Yokosuka O., Hosoda K., Ohto M. Variations in codons 84-101 in the core nucleotide sequence correlate with hepatocellular injury in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):332–338. doi: 10.1172/JCI115581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari C., Penna A., Giuberti T., Tong M. J., Ribera E., Fiaccadori F., Chisari F. V. Intrahepatic, nucleocapsid antigen-specific T cells in chronic active hepatitis B. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 15;139(6):2050–2058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillis W. D., Hillis A., Bias W. B., Walker W. G. Associations of hepatitis B surface antigenemia with HLA locus B specificities. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jun 9;296(23):1310–1314. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197706092962302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H. Chronic type B hepatitis. Gastroenterology. 1983 Feb;84(2):422–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi M., Koike K. Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatitis B virus DNA of subtype adr and its conserved gene organization. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka Y., Takase K., Kojima M., Shimizu M., Inoue K., Yoshiba M., Tanaka S., Akahane Y., Okamoto H., Tsuda F. Fulminant hepatitis B: induction by hepatitis B virus mutants defective in the precore region and incapable of encoding e antigen. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):1087–1094. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90286-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang T. J., Hasegawa K., Rimon N., Wands J. R., Ben-Porath E. A hepatitis B virus mutant associated with an epidemic of fulminant hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1705–1709. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Hughes J. L., Houghten R., McLachlan A., Jones J. E. Functional identification of agretopic and epitopic residues within an HBcAg T cell determinant. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3141–3147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Imai M., Shimozaki M., Hoshi Y., Iizuka H., Gotanda T., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned hepatitis B virus genome, subtype ayr: comparison with genomes of the other three subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2305–2314. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Sakugawa H., Sastrosoewignjo R. I., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2575–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Yotsumoto S., Akahane Y., Yamanaka T., Miyazaki Y., Sugai Y., Tsuda F., Tanaka T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Hepatitis B viruses with precore region defects prevail in persistently infected hosts along with seroconversion to the antibody against e antigen. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1298–1303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1298-1303.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omata M., Ehata T., Yokosuka O., Hosoda K., Ohto M. Mutations in the precore region of hepatitis B virus DNA in patients with fulminant and severe hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1699–1704. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rho H. M., Kim K., Hyun S. W., Kim Y. S. The nucleotide sequence and reading frames of a mutant hepatitis B virus subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2124–2124. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rötzschke O., Falk K., Deres K., Schild H., Norda M., Metzger J., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Isolation and analysis of naturally processed viral peptides as recognized by cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):252–254. doi: 10.1038/348252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Masiarz F. R., Rutter W. J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tada M., Omata M., Ohto M. Analysis of ras gene mutations in human hepatic malignant tumors by polymerase chain reaction and direct sequencing. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 15;50(4):1121–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Machida A., Funatsu G., Nomura M., Usuda S., Aoyagi S., Tachibana K., Miyamoto H., Imai M., Nakamura T. Immunochemical structure of hepatitis B e antigen in the serum. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2903–2907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiollais P., Pourcel C., Dejean A. The hepatitis B virus. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):489–495. doi: 10.1038/317489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uy A., Bruss V., Gerlich W. H., Köchel H. G., Thomssen R. Precore sequence of hepatitis B virus inducing e antigen and membrane association of the viral core protein. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):89–96. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bleek G. M., Nathenson S. G. Isolation of an endogenously processed immunodominant viral peptide from the class I H-2Kb molecule. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):213–216. doi: 10.1038/348213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vento S., Hegarty J. E., Alberti A., O'Brien C. J., Alexander G. J., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. T lymphocyte sensitization to HBcAg and T cell-mediated unresponsiveness to HBsAg in hepatitis B virus-related chronic liver disease. Hepatology. 1985 Mar-Apr;5(2):192–197. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokosuka O., Omata M., Hosoda K., Tada M., Ehata T., Ohto M. Detection and direct sequencing of hepatitis B virus genome by DNA amplification method. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):175–181. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90598-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





