Abstract
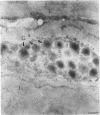
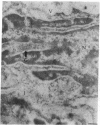
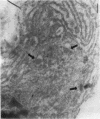
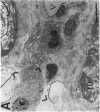
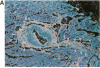
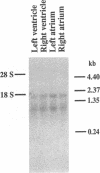
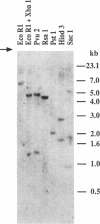
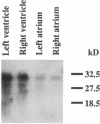
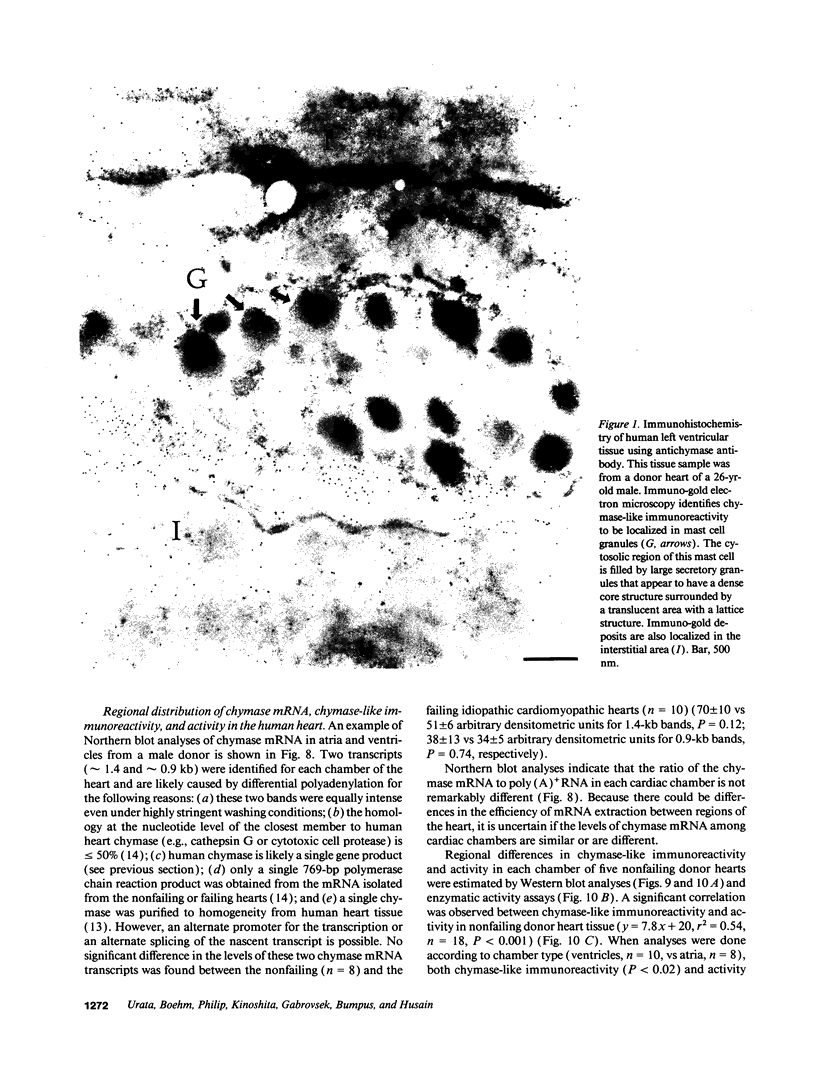
The human heart is a target organ for the octapeptide hormone, angiotensin II (Ang II). Recent studies suggest that the human heart contains a dual pathway of Ang II formation in which the major Ang II-forming enzymes are angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) and chymase. Human heart chymase has recently been purified and its cDNA and gene cloned. This cardiac serine proteinase is the most efficient and specific Ang II-forming enzyme described. To obtain insights into the cardiac sites of chymase-dependent Ang II formation, we examined the cellular localization and regional distribution of chymase in the human heart. Electron microscope immunocytochemistry using an anti-human chymase antibody showed the presence of chymase-like immunoreactivity in the cardiac interstitium and in cytosolic granules of mast cells, endothelial cells, and some mesenchymal interstitial cells. In the cardiac interstitium, chymase-like immunoreactivity is associated with the extracellular matrix. In situ hybridization studies further indicated that chymase mRNA is expressed in endothelial cells and in interstitial cells, including mast cells. Tissue chymase levels were determined by activity assays and by Western blot analyses. Chymase levels were approximately twofold higher in ventricles than in atria. There were no significant differences in chymase levels in ventricular tissues obtained from non-failing donor hearts, failing ischemic hearts, or hearts from patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. These findings suggest that a major site of chymase-dependent Ang II formation in the heart is the interstitium and that cardiac mast cells, mesenchymal interstitial cells, and endothelial cells are the cellular sites of synthesis and storage of chymase. In the human heart, because ACE levels are highest in the atria and chymase levels are highest in ventricles, it is likely that the relative contribution of ACE and chymase to cardiac Ang II formation varies with the cardiac chamber. Such differences may lead to differential suppression of cardiac Ang II levels during chronic ACE inhibitor therapy in patients with congestive heart failure.
Full text
PDF



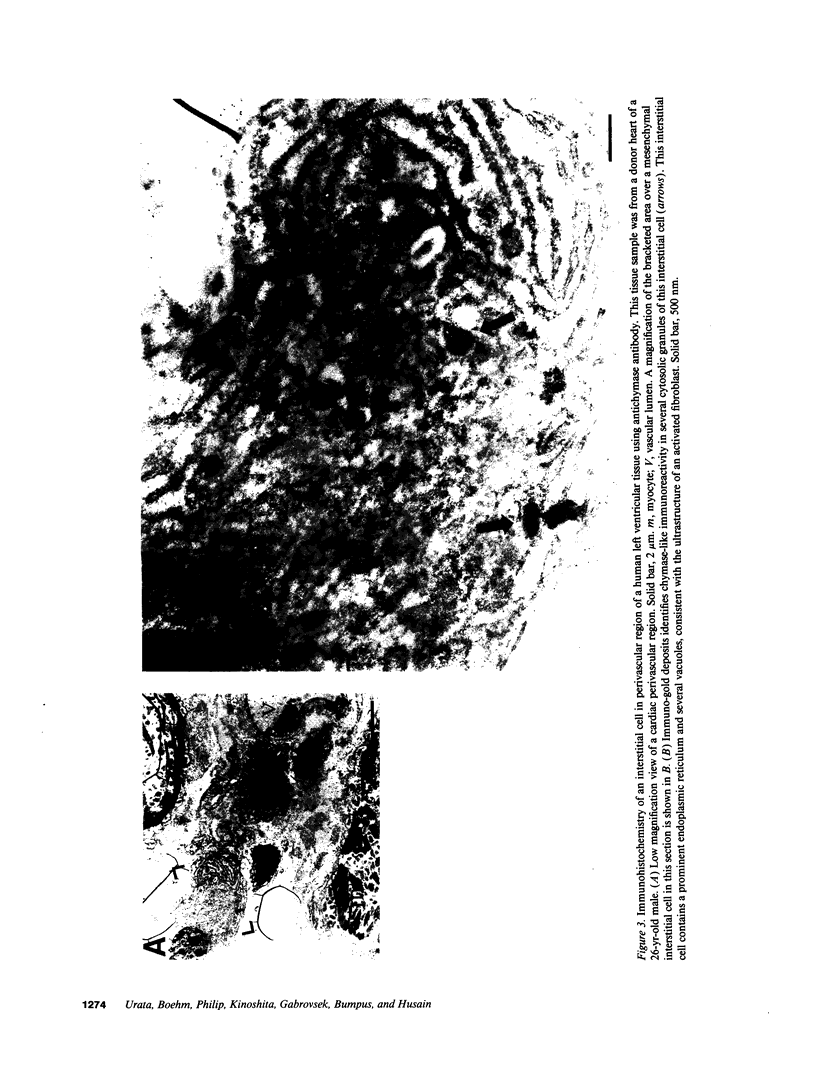

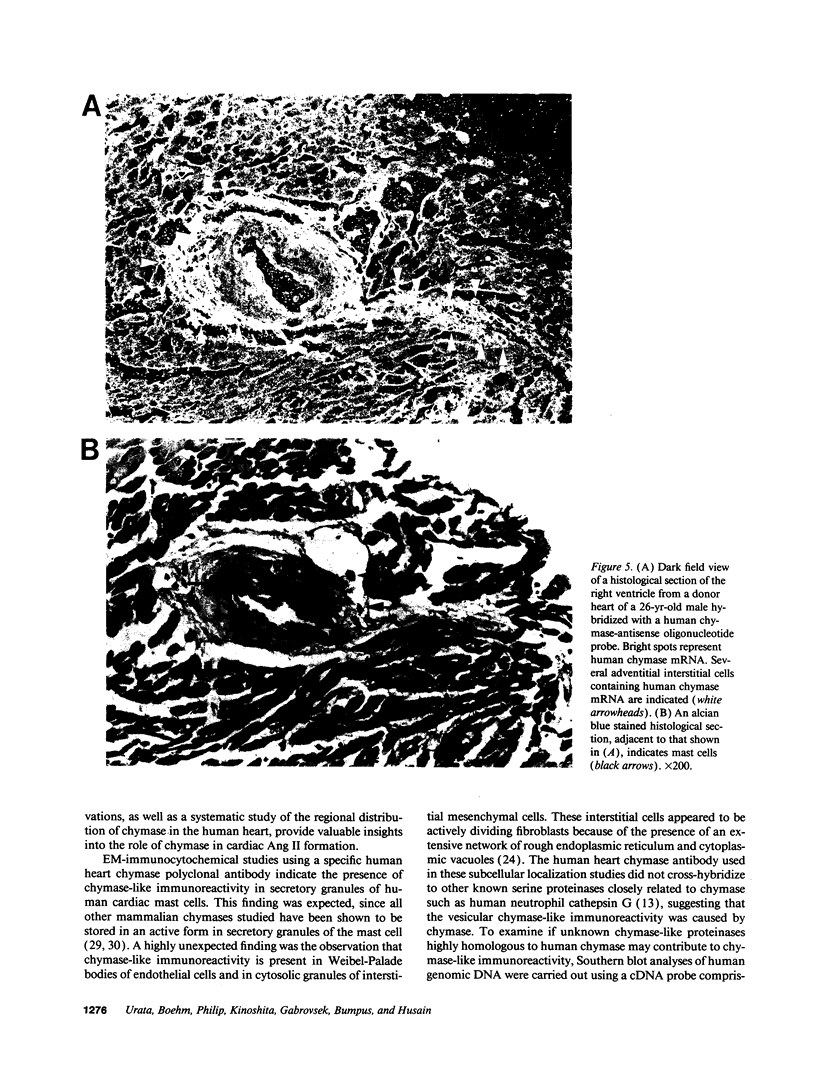
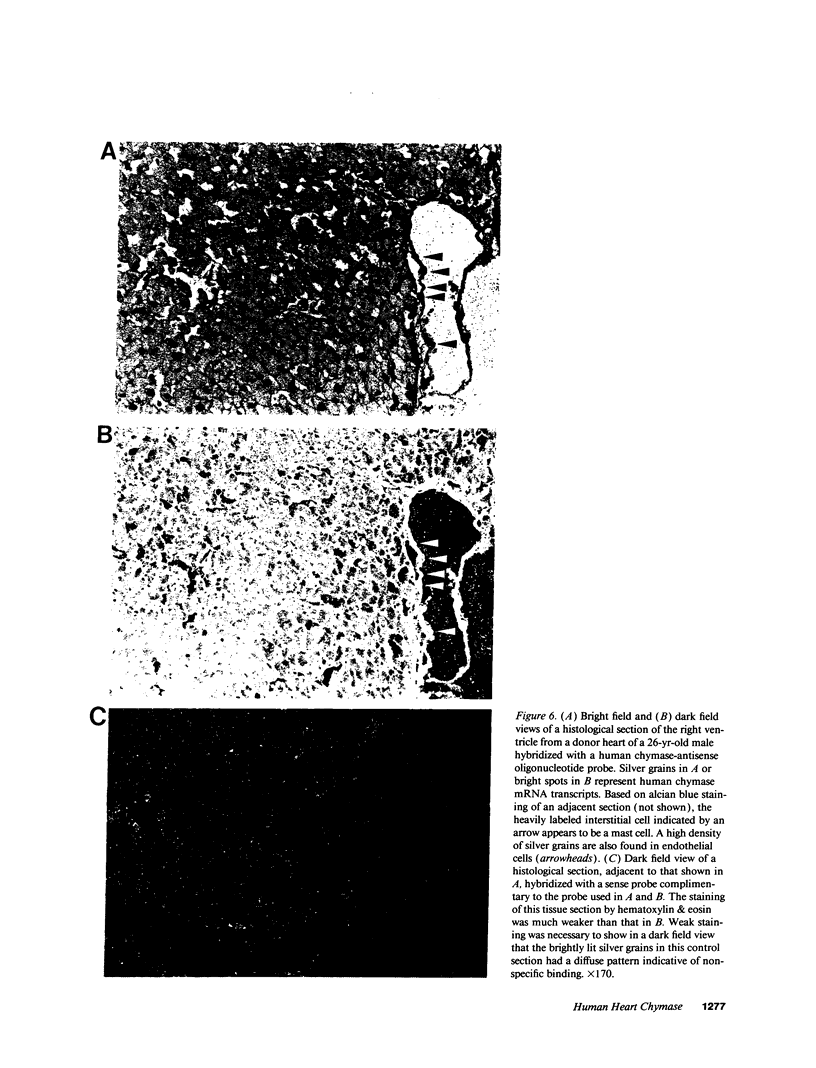

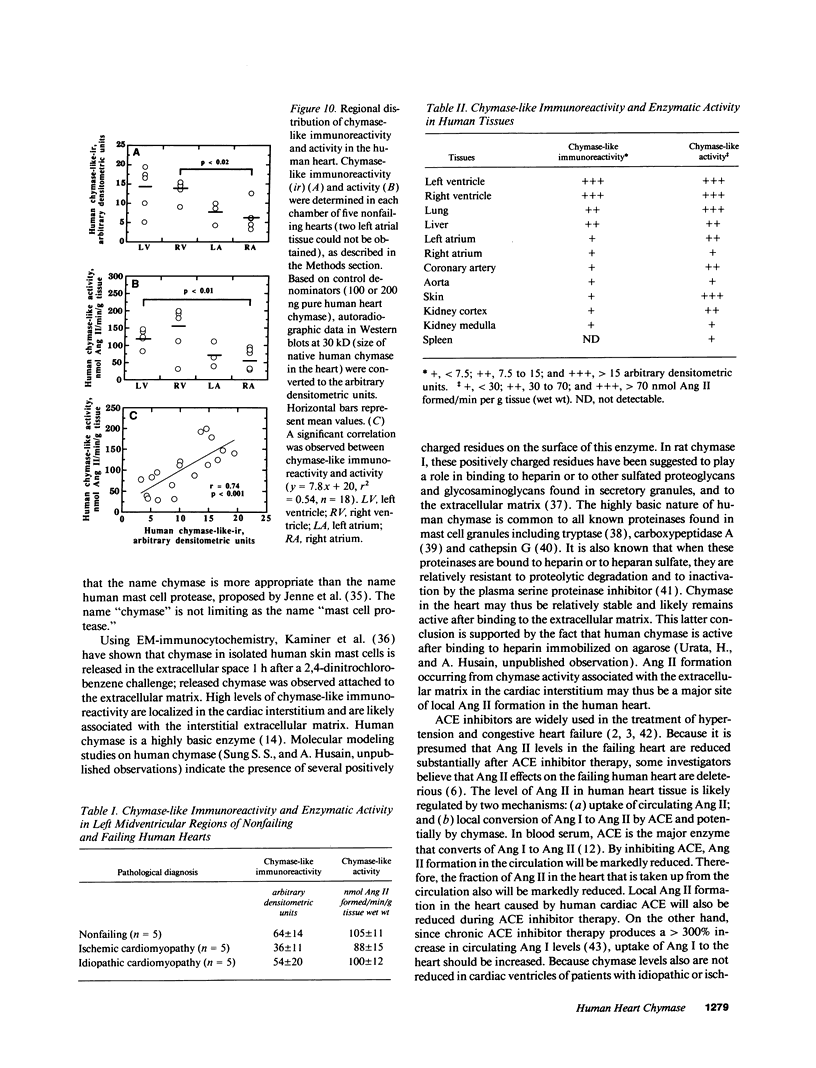


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aceto J. F., Baker K. M. [Sar1]angiotensin II receptor-mediated stimulation of protein synthesis in chick heart cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):H806–H813. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.3.H806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avraham S., Stevens R. L., Nicodemus C. F., Gartner M. C., Austen K. F., Weis J. H. Molecular cloning of a cDNA that encodes the peptide core of a mouse mast cell secretory granule proteoglycan and comparison with the analogous rat and human cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3763–3767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benfey P. N., Yin F. H., Leder P. Cloning of the mast cell protease, RMCP II. Evidence for cell-specific expression and a multi-gene family. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5377–5384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm K. D., Kelley M. F., Ilan J., Ilan J. The interleukin 2 gene is expressed in the syncytiotrophoblast of the human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):656–660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey G. H., Zerweck E. H., Vanderslice P. Structure, chromosomal assignment, and deduced amino acid sequence of a human gene for mast cell chymase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12956–12963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield J. P., el-Lati S., Thomas G., Church M. K. Dissociated human foreskin mast cells degranulate in response to anti-IgE and substance P. Lab Invest. 1990 Oct;63(4):502–510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. A., Chang M. S., Chiang B. N., Cheng K. K., Lin C. I. Electromechanical effects of angiotensin in human atrial tissues. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991 Apr;23(4):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(91)90172-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn J. N., Archibald D. G., Ziesche S., Franciosa J. A., Harston W. E., Tristani F. E., Dunkman W. B., Jacobs W., Francis G. S., Flohr K. H. Effect of vasodilator therapy on mortality in chronic congestive heart failure. Results of a Veterans Administration Cooperative Study. N Engl J Med. 1986 Jun 12;314(24):1547–1552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198606123142404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. S., Schechter N. M., Schwartz L. B. Ultrastructural analysis of maturing human T and TC mast cells in situ. Lab Invest. 1989 Jan;60(1):147–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. S., Schwartz L. B. Tryptase and chymase, markers of distinct types of human mast cells. Immunol Res. 1989;8(2):130–148. doi: 10.1007/BF02919075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouad F. M., El-Tobgi S., Tarazi R. C., Bravo E. L., Hart N. J., Shirey E. K., Lim J. Captopril in congestive heart failure resistant to other vasodilators. Eur Heart J. 1984 Jan;5(1):47–54. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommherz K. J., Faller B., Bieth J. G. Heparin strongly decreases the rate of inhibition of neutrophil elastase by alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15356–15362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S. M., Kaempfer C. E., Proud D., Schwartz L. B., Irani A. M., Wintroub B. U. Detection and partial characterization of a human mast cell carboxypeptidase. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2724–2729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch A. T., Talsness C. E., Schunkert H., Paul M., Dzau V. J. Tissue-specific activation of cardiac angiotensin converting enzyme in experimental heart failure. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):475–482. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D. E., Tschopp J. Angiotensin II-forming heart chymase is a mast-cell-specific enzyme. Biochem J. 1991 Jun 1;276(Pt 2):567–568. doi: 10.1042/bj2760567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminer M. S., Lavker R. M., Walsh L. J., Whitaker D., Zweiman B., Murphy G. F. Extracellular localization of human connective tissue mast cell granule contents. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Jun;96(6):857–863. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12475169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita A., Urata H., Bumpus F. M., Husain A. Multiple determinants for the high substrate specificity of an angiotensin II-forming chymase from the human heart. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19192–19197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff D., Pritzl P. Characterization of rat mast cell granule proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):554–563. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindpaintner K., Ganten D. The cardiac renin-angiotensin system. An appraisal of present experimental and clinical evidence. Circ Res. 1991 Apr;68(4):905–921. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moravec C. S., Schluchter M. D., Paranandi L., Czerska B., Stewart R. W., Rosenkranz E., Bond M. Inotropic effects of angiotensin II on human cardiac muscle in vitro. Circulation. 1990 Dec;82(6):1973–1984. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.6.1973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussberger J., Brunner D. B., Waeber B., Brunner H. R. Specific measurement of angiotensin metabolites and in vitro generated angiotensin II in plasma. Hypertension. 1986 Jun;8(6):476–482. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.8.6.476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okunishi H., Miyazaki M., Toda N. Evidence for a putatively new angiotensin II-generating enzyme in the vascular wall. J Hypertens. 1984 Jun;2(3):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peach M. J. Renin-angiotensin system: biochemistry and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev. 1977 Apr;57(2):313–370. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S. J., Woodbury R. G., Reynolds R. A., Matthews B. W., Neurath H. The structure of rat mast cell protease II at 1.9-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8097–8105. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvesen G., Farley D., Shuman J., Przybyla A., Reilly C., Travis J. Molecular cloning of human cathepsin G: structural similarity to mast cell and cytotoxic T lymphocyte proteinases. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 21;26(8):2289–2293. doi: 10.1021/bi00382a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayama S., Iozzo R. V., Lazarus G. S., Schechter N. M. Human skin chymotrypsin-like proteinase chymase. Subcellular localization to mast cell granules and interaction with heparin and other glycosaminoglycans. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6808–6815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Tryptase from human pulmonary mast cells. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11939–11943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafin W. E., Reynolds D. S., Rogelj S., Lane W. S., Conder G. A., Johnson S. S., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L. Identification and molecular cloning of a novel mouse mucosal mast cell serine protease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):423–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serafin W. E., Sullivan T. P., Conder G. A., Ebrahimi A., Marcham P., Johnson S. S., Austen K. F., Reynolds D. S. Cloning of the cDNA and gene for mouse mast cell protease 4. Demonstration of its late transcription in mast cell subclasses and analysis of its homology to subclass-specific neutral proteases of the mouse and rat. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1934–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turini G. A., Brunner H. R., Gribic M., Waeber B., Gavras H. Improvement of chronic congestive heart-failure by oral captopril. Lancet. 1979 Jun 9;1(8128):1213–1215. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)91897-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urata H., Healy B., Stewart R. W., Bumpus F. M., Husain A. Angiotensin II receptors in normal and failing human hearts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1989 Jul;69(1):54–66. doi: 10.1210/jcem-69-1-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urata H., Healy B., Stewart R. W., Bumpus F. M., Husain A. Angiotensin II-forming pathways in normal and failing human hearts. Circ Res. 1990 Apr;66(4):883–890. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.4.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urata H., Kinoshita A., Misono K. S., Bumpus F. M., Husain A. Identification of a highly specific chymase as the major angiotensin II-forming enzyme in the human heart. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22348–22357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urata H., Kinoshita A., Perez D. M., Misono K. S., Bumpus F. M., Graham R. M., Husain A. Cloning of the gene and cDNA for human heart chymase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17173–17179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber B., Gavras I., Brunner H. R., Cook C. A., Charocopos F., Gavras H. P. Prediction of sustained antihypertensive efficacy of chronic captopril therapy: relationships to immediate blood pressure response and control plasma renin activity. Am Heart J. 1982 Mar;103(3):384–390. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(82)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D. Cell biology of von Willebrand factor. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:217–246. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Olmsted J. B., Marder V. J. Immunolocalization of von Willebrand protein in Weibel-Palade bodies of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):355–360. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolosewick J. J., De Mey J., Meininger V. Ultrastructural localization of tubulin and actin in polyethylene glycol-embedded rat seminiferous epithelium by immunogold staining. Biol Cell. 1983;49(3):219–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Everitt M. T., Neurath H. Mast cell proteases. Methods Enzymol. 1981;80(Pt 100):588–609. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)80047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]