Abstract
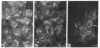
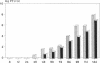
Marburg and Ebola virus, members of the family Filoviridae, cause a severe hemorrhagic disease in humans and primates. The disease is characterized as a pantropic virus infection often resulting in a fulminating shock associated with hemorrhage, and death. All known histological and pathophysiological parameters of the disease are not sufficient to explain the devastating symptoms. Previous studies suggested a nonspecific destruction of the endothelium as a possible mechanism. Concerning the important regulatory functions of the endothelium (blood pressure, anti-thrombogenicity, homeostasis), we examined Marburg virus replication in primary cultures of human endothelial cells and organ cultures of human umbilical cord veins. We show here that Marburg virus replicates in endothelial cells almost as well as in monkey kidney cells commonly used for virus propagation. Our data support the concept that the destruction of endothelial cells resulting from Marburg virus replication is a possible mechanism responsible for the hemorrhagic disease and the shock syndrome typical of this infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker S., Feldmann H., Will C., Slenczka W. Evidence for occurrence of filovirus antibodies in humans and imported monkeys: do subclinical filovirus infections occur worldwide? Med Microbiol Immunol. 1992;181(1):43–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00193395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C. The Malpighi lecture. From 'Porositates carnis' to cellular microcirculation. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1987;6(2):101–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott L. H., Kiley M. P., McCormick J. B. Descriptive analysis of Ebola virus proteins. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann H., Mühlberger E., Randolf A., Will C., Kiley M. P., Sanchez A., Klenk H. D. Marburg virus, a filovirus: messenger RNAs, gene order, and regulatory elements of the replication cycle. Virus Res. 1992 Jun;24(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann H., Will C., Schikore M., Slenczka W., Klenk H. D. Glycosylation and oligomerization of the spike protein of Marburg virus. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90680-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher-Hoch S. P., Platt G. S., Neild G. H., Southee T., Baskerville A., Raymond R. T., Lloyd G., Simpson D. I. Pathophysiology of shock and hemorrhage in a fulminating viral infection (Ebola). J Infect Dis. 1985 Nov;152(5):887–894. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.5.887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gear J. S., Cassel G. A., Gear A. J., Trappler B., Clausen L., Meyers A. M., Kew M. C., Bothwell T. H., Sher R., Miller G. B. Outbreake of Marburg virus disease in Johannesburg. Br Med J. 1975 Nov 29;4(5995):489–493. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5995.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., De los Santos R. P., Hoyer J. R. Antihemophilic factor antigen. Localization in endothelial cells by immunofluorescent microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2737–2744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishak K. G., Walker D. H., Coetzer J. A., Gardner J. J., Gorelkin L. Viral hemorrhagic fevers with hepatic involvement: pathologic aspects with clinical correlations. Prog Liver Dis. 1982;7:495–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahrling P. B., Geisbert T. W., Dalgard D. W., Johnson E. D., Ksiazek T. G., Hall W. C., Peters C. J. Preliminary report: isolation of Ebola virus from monkeys imported to USA. Lancet. 1990 Mar 3;335(8688):502–505. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90737-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. M., Lange J. V., Webb P. A., Murphy F. A. Isolation and partial characterisation of a new virus causing acute haemorrhagic fever in Zaire. Lancet. 1977 Mar 12;1(8011):569–571. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92000-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley M. P., Bowen E. T., Eddy G. A., Isaäcson M., Johnson K. M., McCormick J. B., Murphy F. A., Pattyn S. R., Peters D., Prozesky O. W. Filoviridae: a taxonomic home for Marburg and Ebola viruses? Intervirology. 1982;18(1-2):24–32. doi: 10.1159/000149300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiley M. P., Cox N. J., Elliott L. H., Sanchez A., DeFries R., Buchmeier M. J., Richman D. D., McCormick J. B. Physicochemical properties of Marburg virus: evidence for three distinct virus strains and their relationship to Ebola virus. J Gen Virol. 1988 Aug;69(Pt 8):1957–1967. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-8-1957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E. Studies on inflammation. 1. The effect of histamine and serotonin on vascular permeability: an electron microscopic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:571–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel C. C. Capillary permeability and how it may change. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:1–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlberger E., Sanchez A., Randolf A., Will C., Kiley M. P., Klenk H. D., Feldmann H. The nucleotide sequence of the L gene of Marburg virus, a filovirus: homologies with paramyxoviruses and rhabdoviruses. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):534–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90456-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez A., Kiley M. P., Klenk H. D., Feldmann H. Sequence analysis of the Marburg virus nucleoprotein gene: comparison to Ebola virus and other non-segmented negative-strand RNA viruses. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):347–357. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittler H. J., Wilke A., Gress T., Suttorp N., Drenckhahn D. Role of actin and myosin in the control of paracellular permeability in pig, rat and human vascular endothelium. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:379–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. E., Simpson D. I., Bowen E. T., Zlotnik I. Fatal human disease from vervet monkeys. Lancet. 1967 Nov 25;2(7526):1119–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90621-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Johnson B. K., Isaacson M., Swanapoel R., Johnson K. M., Killey M., Bagshawe A., Siongok T., Keruga W. K. Marburg-virus disease in Kenya. Lancet. 1982 Apr 10;1(8276):816–820. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91871-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trump B. F., Valigorsky J. M., Jones R. T., Mergner W. J., Garcia J. H., Cowley R. A. The application of electron microscopy and cellular biochemistry to the autopsy. Observations on cellular changes in human shock. Hum Pathol. 1975 Jul;6(4):499–516. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(75)80068-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner D. D., Olmsted J. B., Marder V. J. Immunolocalization of von Willebrand protein in Weibel-Palade bodies of human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):355–360. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong M. K., Gotlieb A. I. The reorganization of microfilaments, centrosomes, and microtubules during in vitro small wound reendothelialization. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1777–1783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]