Abstract
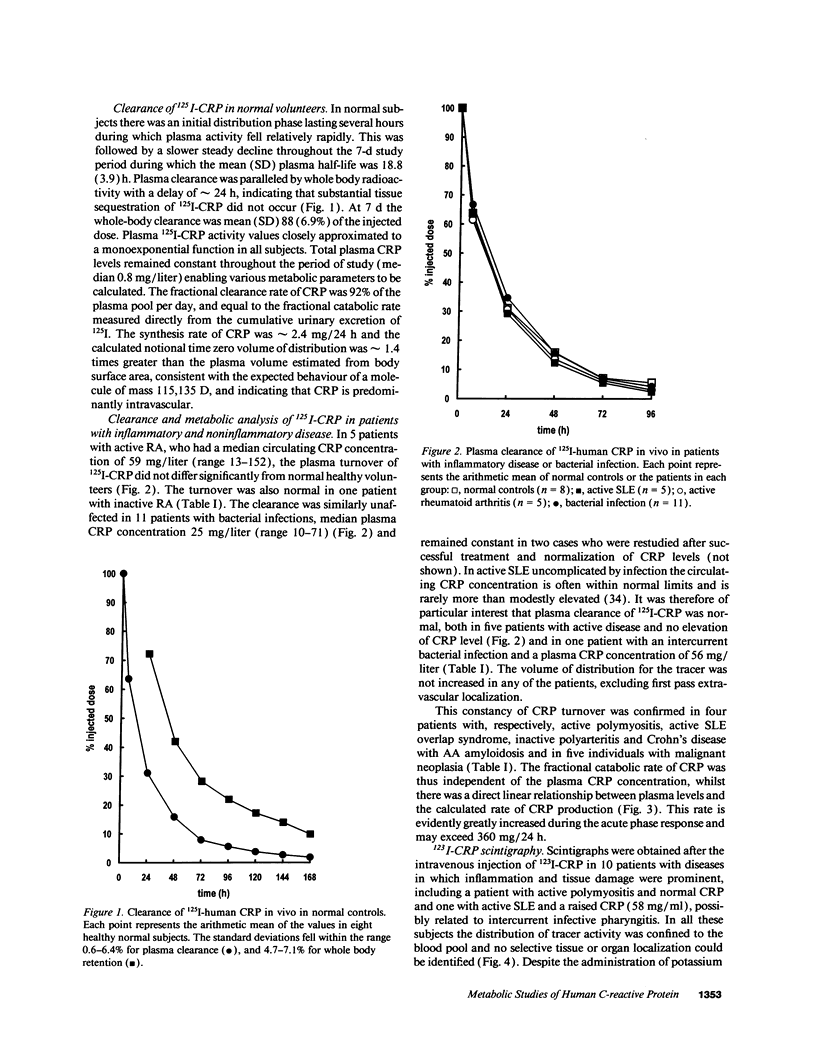
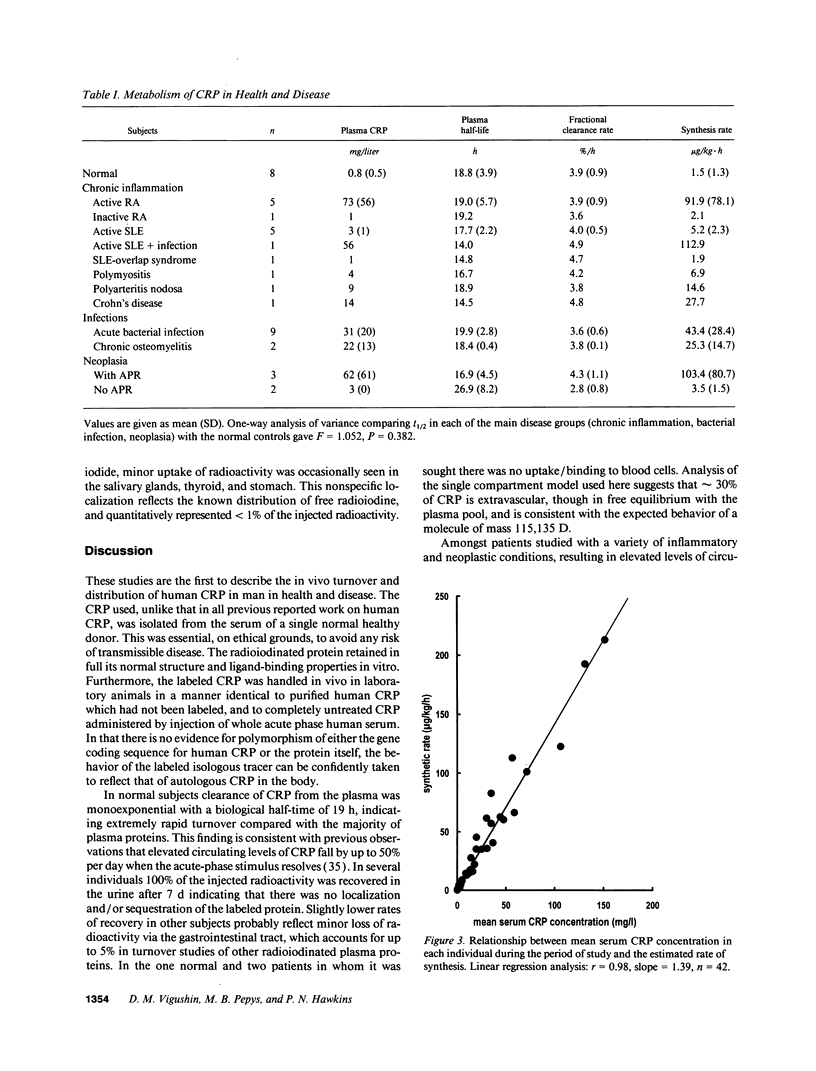
Plasma and whole-body turnover studies of human C-reactive protein (CRP), isolated from a single normal healthy donor and labeled with 125I, were undertaken in 8 healthy control subjects and 35 hospitalized patients including cases of rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, infections, and neoplasia. Plasma clearance of 125I-CRP closely approximated to a monoexponential function and was similar in the control and all patient groups. There was no evidence for accelerated clearance or catabolism of CRP in any of the diseases studied. The 19-h half-life was more rapid than that of most human plasma proteins studied previously, and the fractional catabolic rate was independent of the plasma CRP concentration. The synthesis rate of CRP is thus the only significant determinant of its plasma level, confirming the validity of serum CRP measurement as an objective index of disease activity in disorders associated with an acute-phase response. Approximately 90% of injected radioactivity was recovered in the urine after 7 d, and scintigraphic imaging studies with 123I-labeled CRP in 10 patients with different focal pathology showed no significant localization of tracer. The functions of CRP are thus likely to be effected predominantly in the fluid phase rather than by major deposition at sites of tissue damage or inflammation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltz M. L., Rowe I. F., Pepys M. B. In vivo turnover studies of C-reactive protein. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Jan;59(1):243–250. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchta R., Gennaro R., Pontet M., Fridkin M., Romeo D. C-reactive protein decreases protein phosphorylation in stimulated human neutrophils. FEBS Lett. 1988 Sep 12;237(1-2):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler P. J., Tennent G. A., Pepys M. B. Pentraxin-chromatin interactions: serum amyloid P component specifically displaces H1-type histones and solubilizes native long chromatin. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):13–18. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelladurai M., Macintyre S. S., Kushner I. In vivo studies of serum C-reactive protein turnover in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):604–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI110806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox M. L., Rudd A. G., Gallimore R., Hodkinson H. M., Pepys M. B. Real-time measurement of serum C-reactive protein in the management of infection in the elderly. Age Ageing. 1986 Sep;15(5):257–266. doi: 10.1093/ageing/15.5.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Isolation of human C-reactive protein and serum amyloid P component. J Immunol Methods. 1982;50(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Beer F. C., Shine B., Pepys M. B. Radiometric ligand binding assay for C-reactive protein. Complexed C-reactive protein is not detectable in acute phase serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Oct;50(1):231–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W. C-reactive protein reacts with the U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2553–2559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Marnell L., Zlock L. R., Burlingame R. W. Analysis of the binding of C-reactive protein to chromatin subunits. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1220–1225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Clos T. W., Mold C., Paterson P. Y., Alroy J., Gewurz H. Localization of C-reactive protein in inflammatory lesions of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):565–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan E. A., Dyck R. F., Maton P. N., Hodgson H. J., Chadwick V. S., Petrie A., Pepys M. B. Serum levels of C-reactive protein in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;12(4):351–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1982.tb02244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filep J. G., Hermán F., Kelemen E., Földes-Filep E. C-reactive protein inhibits binding of platelet-activating factor to human platelets. Thromb Res. 1991 Feb 15;61(4):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(91)90655-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filep J., Földes-Filep E. Effects of C-reactive protein on human neutrophil granulocytes challenged with N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine and platelet-activating factor. Life Sci. 1989;44(8):517–524. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(89)90613-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin J. D., Gitlin J. I., Gitlin D. Localizing of C-reactive protein in synovium of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Nov-Dec;20(8):1491–1499. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Lavender J. P., Pepys M. B. Evaluation of systemic amyloidosis by scintigraphy with 123I-labeled serum amyloid P component. N Engl J Med. 1990 Aug 23;323(8):508–513. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199008233230803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Myers M. J., Epenetos A. A., Caspi D., Pepys M. B. Specific localization and imaging of amyloid deposits in vivo using 123I-labeled serum amyloid P component. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):903–913. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. N., Myers M. J., Lavender J. P., Pepys M. B. Diagnostic radionuclide imaging of amyloid: biological targeting by circulating human serum amyloid P component. Lancet. 1988 Jun 25;1(8600):1413–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich P. C., Castell J. V., Andus T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J. 1990 Feb 1;265(3):621–636. doi: 10.1042/bj2650621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute phase protein. I. An immunohistochemical method for the localization of Cx-reactive protein in rabbits. Association with necrosis in local inflammatory lesions. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:961–974. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER I., RAKITA L., KAPLAN M. H. Studies of acute-phase protein. II. Localization of Cx-reactive protein in heart in induced myocardial infarction in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:286–292. doi: 10.1172/JCI104715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kew R. R., Hyers T. M., Webster R. O. Human C-reactive protein inhibits neutrophil chemotaxis in vitro: possible implications for the adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Mar;115(3):339–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick J. M., Volanakis J. E. Molecular genetics, structure, and function of C-reactive protein. Immunol Res. 1991;10(1):43–53. doi: 10.1007/BF02918166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei K. J., Liu T., Zon G., Soravia E., Liu T. Y., Goldman N. D. Genomic DNA sequence for human C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13377–13383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather S. J., Ward B. G. High efficiency iodination of monoclonal antibodies for radiotherapy. J Nucl Med. 1987 Jun;28(6):1034–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Martin L. S., Cort S. P., Mozen M., Heldebrant C. M., Evatt B. L. Thermal inactivation of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome virus, human T lymphotropic virus-III/lymphadenopathy-associated virus, with special reference to antihemophilic factor. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):875–877. doi: 10.1172/JCI112045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mold C., Nakayama S., Holzer T. J., Gewurz H., Du Clos T. W. C-reactive protein is protective against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1703–1708. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama S., Gewurz H., Holzer T., Du Clos T. W., Mold C. The role of the spleen in the protective effect of C-reactive protein in Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Nov;54(2):319–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama S., Mold C., Gewurz H., du Clos T. W. Opsonic properties of C-reactive protein in vivo. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2435–2438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira E. B., Gotschlich E. C., Liu T. Y. Primary structure of human C-reactive protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3148–3151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish W. E. Studies on vasculitis. VII. C-reactive protein as a substance perpetuating chronic vasculitis. Occurrence in lesions and concentrations in sera. Clin Allergy. 1976 Nov;6(6):543–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1976.tb01939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Butler P. J. Serum amyloid P component is the major calcium-dependent specific DNA binding protein of the serum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Oct 14;148(1):308–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91111-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. C-reactive protein fifty years on. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):653–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91565-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Lanham J. G., De Beer F. C. C-reactive protein in SLE. Clin Rheum Dis. 1982 Apr;8(1):91–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Rowe I. F., Baltz M. L. C-reactive protein: binding to lipids and lipoproteins. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1985;27:83–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontet M., Engler R., Jayle M. F. One step preparation of both human C-reactive protein and CIt. FEBS Lett. 1978 Apr 15;88(2):172–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. D., Vance R. P. C-reactive protein immunohistochemical localization in normal and atherosclerotic human aortas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1987 Mar;111(3):265–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robey F. A., Jones K. D., Tanaka T., Liu T. Y. Binding of C-reactive protein to chromatin and nucleosome core particles. A possible physiological role of C-reactive protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):7311–7316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues M. M., Robey P. G. C-reactive protein in human lattice corneal dystrophy. Curr Eye Res. 1982;2(10):721–724. doi: 10.3109/02713688209020002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe I. F., Baltz M. L., Soutar A. K., Pepys M. B. In vivo turnover studies of C-reactive protein and lipoproteins in the rabbit. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Oct;58(1):245–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe I. F., Walker L. N., Bowyer D. E., Soutar A. K., Smith L. C., Pepys M. B. Immunohistochemical studies of C-reactive protein and apolipoprotein B in inflammatory and arterial lesions. J Pathol. 1985 Mar;145(3):241–249. doi: 10.1002/path.1711450305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shephard E. G., Beer S. M., Anderson R., Strachan A. F., Nel A. E., de Beer F. C. Generation of biologically active C-reactive protein peptides by a neutral protease on the membrane of phorbol myristate acetate-stimulated neutrophils. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2974–2981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine B., de Beer F. C., Pepys M. B. Solid phase radioimmunoassays for human C-reactive protein. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 Nov 25;117(1):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke I. D., de Beer F. C., Donnelly J. P., Catovsky D., Goldman J. M., Galton D. A., Pepys M. B. Serum C-reactive protein levels in the management of infection in acute leukaemia. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1984 Mar;20(3):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(84)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigo C. Effect of C-reactive protein on platelet-activating factor-induced platelet aggregation and membrane stabilization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3418–3422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E. Complement activation by C-reactive protein complexes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;389:235–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb22140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volanakis J. E., Wirtz K. W. Interaction of C-reactive protein with artificial phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):155–157. doi: 10.1038/281155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasunna A., Whitelaw A., Gallimore R., Hawkins P. N., Pepys M. B. C-reactive protein and bacterial infection in preterm infants. Eur J Pediatr. 1990 Mar;149(6):424–427. doi: 10.1007/BF02009664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo P., Korenberg J. R., Whitehead A. S. Characterization of genomic and complementary DNA sequence of human C-reactive protein, and comparison with the complementary DNA sequence of serum amyloid P component. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):13384–13388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yother J., Volanakis J. E., Briles D. E. Human C-reactive protein is protective against fatal Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in mice. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2374–2376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Beer F. C., Soutar A. K., Baltz M. L., Trayner I. M., Feinstein A., Pepys M. B. Low density lipoprotein and very low density lipoprotein are selectively bound by aggregated C-reactive protein. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):230–242. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]