Abstract
A thrombin receptor (TR) demonstrating a unique activation mechanism has recently been isolated from a megakaryocytic (Dami) cell line. To further study determinants of peptide ligand-mediated activation phenomenon, we have isolated, cloned, and stably expressed the identical receptor from a human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) library. Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing a functional TR (CHO-TR), platelets, and HUVECs were then used to specifically characterize alpha-thrombin- and peptide ligand-induced activation responses using two different antibodies: anti-TR34-52 directed against a 20-amino acid peptide spanning the thrombin cleavage site, and anti-TR1-160 generated against the NH2-terminal 160 amino acids of the TR expressed as a chimeric protein in Escherichia coli. Activation-dependent responses to both alpha-thrombin (10 nM) and peptide ligand (20 microM) were studied using fura 2-loaded cells and microspectrofluorimetry. Whereas preincubation of CHO-TR with anti-TR34-52 abolished only alpha-thrombin-induced [Ca2+]i transients, preincubation with anti-TR1-160 abrogated both alpha-thrombin- and peptide ligand-induced responses. This latter inhibitory effect was dose dependent and similar for both agonists, with an EC50 of approximately 90 micrograms/ml. Anti-TR1-160 similarly abolished peptide ligand-induced [Ca2+]i transients in platelets and HUVECs, whereas qualitatively different responses characterized by delayed but sustained elevations in [Ca2+]i transients were evident using alpha-thrombin. Platelet aggregation to low concentrations of both ligands was nearly abolished by anti-TR1-160, although some shape change remained; anti-TR34-52 only inhibited alpha-thrombin-induced aggregation. These data establish that a critical recognition sequence for peptide ligand-mediated receptor activation is contained on the NH2-terminal portion of the receptor, upstream from the first transmembrane domain. Furthermore, alpha-thrombin-induced activation of HUVECs and platelets may be partially mediated by an alternative mechanism(s) or receptor(s).
Full text
PDF

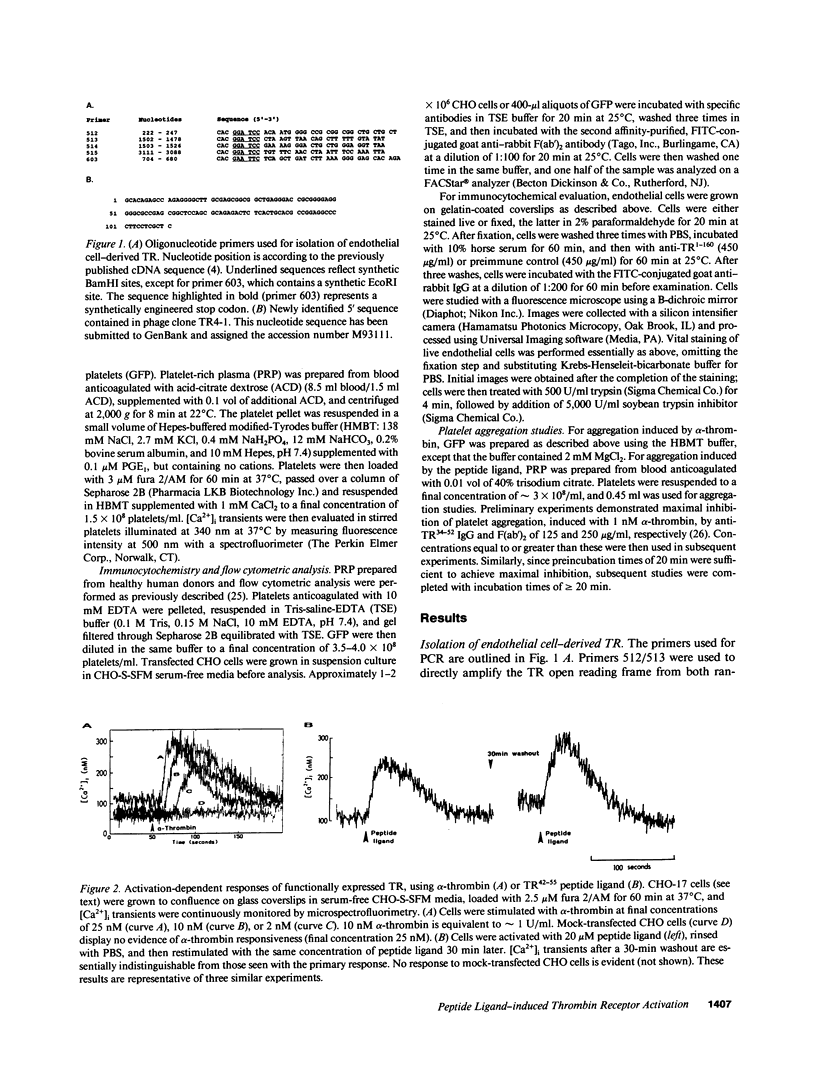
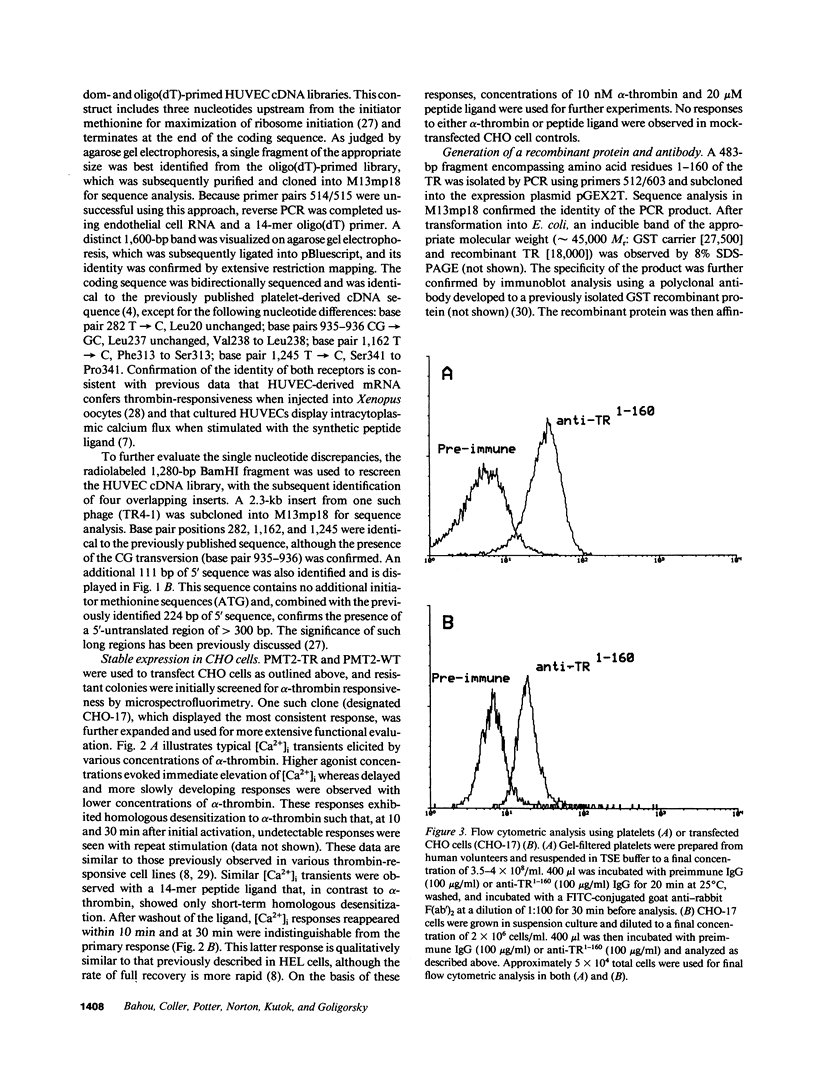

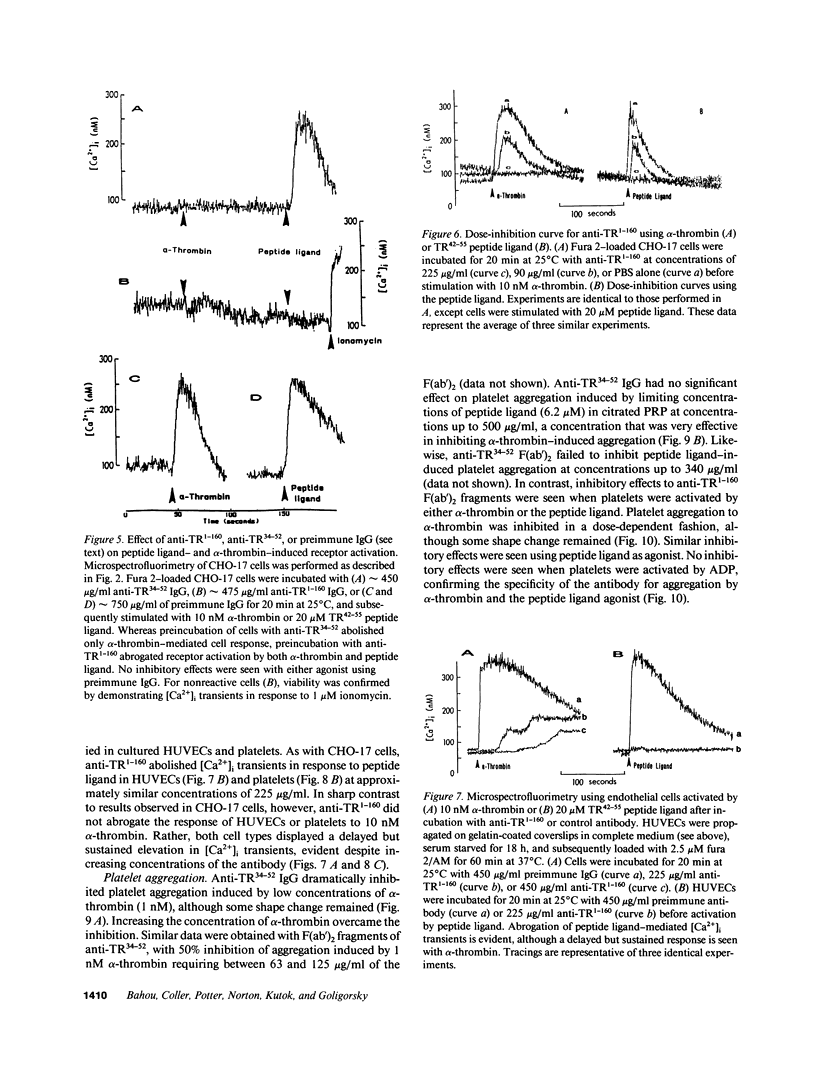
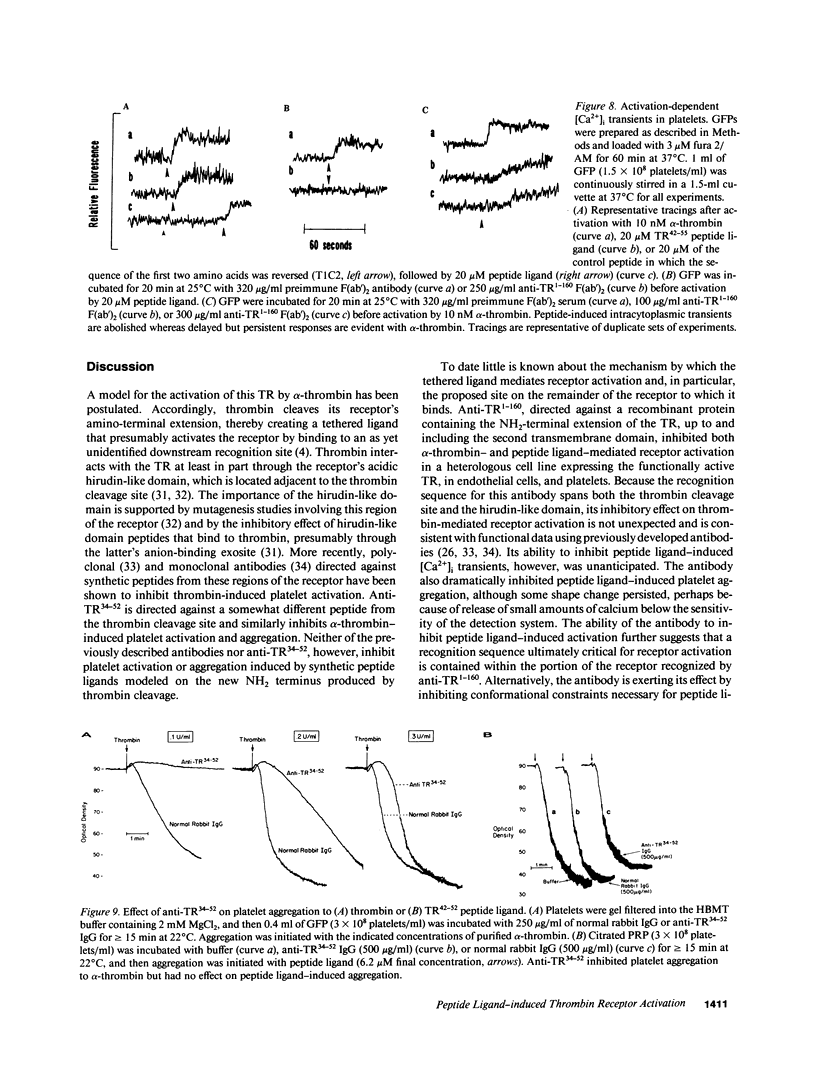
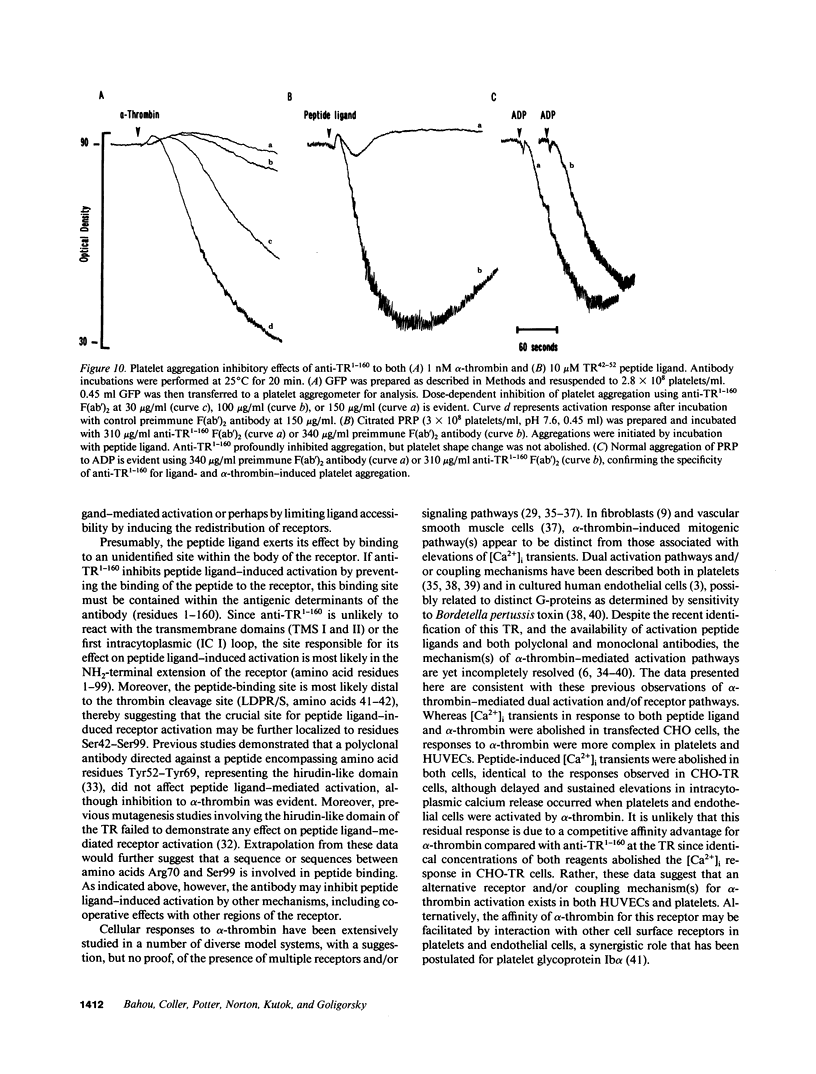

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahou W. F., Campbell A. D., Wicha M. S. cDNA cloning and molecular characterization of MSE55, a novel human serum constituent protein that displays bone marrow stromal/endothelial cell-specific expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13986–13992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahou W. F., Ginsburg D., Sikkink R., Litwiller R., Fass D. N. A monoclonal antibody to von Willebrand factor (vWF) inhibits factor VIII binding. Localization of its antigenic determinant to a nonadecapeptide at the amino terminus of the mature vWF polypeptide. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):56–61. doi: 10.1172/JCI114169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonthron D. T., Handin R. I., Kaufman R. J., Wasley L. C., Orr E. C., Mitsock L. M., Ewenstein B., Loscalzo J., Ginsburg D., Orkin S. H. Structure of pre-pro-von Willebrand factor and its expression in heterologous cells. Nature. 1986 Nov 20;324(6094):270–273. doi: 10.1038/324270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F. Homologous desensitization of HEL cell thrombin receptors. Distinguishable roles for proteolysis and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6044–6050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Laposata M., Banga H. S., Rittenhouse S. E. Regulation of the phosphoinositide hydrolysis pathway in thrombin-stimulated platelets by a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein. Evaluation of its contribution to platelet activation and comparisons with the adenylate cyclase inhibitory protein, Gi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16838–16847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Vassallo R. R., Jr, Belmonte E., Ahuja M., Cichowski K., Hoxie J. A. Structure and function of the human platelet thrombin receptor. Studies using monoclonal antibodies directed against a defined domain within the receptor N terminus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):13795–13798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. A., Capasso E. L. GTP gamma S increases thrombin-mediated inositol trisphosphate accumulation in permeabilized human endothelial cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 Oct;140(4):1121–1125. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/140.4.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambard J. C., Paris S., L'Allemain G., Pouysségur J. Two growth factor signalling pathways in fibroblasts distinguished by pertussis toxin. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):800–803. doi: 10.1038/326800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coller B. S., Beer J. H., Scudder L. E., Steinberg M. H. Collagen-platelet interactions: evidence for a direct interaction of collagen with platelet GPIa/IIa and an indirect interaction with platelet GPIIb/IIIa mediated by adhesive proteins. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):182–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco L., Mazzucato M., Masotti A., Fenton J. W., 2nd, Ruggeri Z. M. Function of glycoprotein Ib alpha in platelet activation induced by alpha-thrombin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23776–23783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenton J. W., 2nd Regulation of thrombin generation and functions. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1988 Jul;14(3):234–240. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Bonthron D. T., Donlon T. A., Bruns G. A., Latt S. A., Orkin S. H. Human von Willebrand factor (vWF): isolation of complementary DNA (cDNA) clones and chromosomal localization. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1401–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3874428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Konkle B. A., Gill J. C., Montgomery R. R., Bockenstedt P. L., Johnson T. A., Yang A. Y. Molecular basis of human von Willebrand disease: analysis of platelet von Willebrand factor mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3723–3727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goligorsky M. S., Menton D. N., Laszlo A., Lum H. Nature of thrombin-induced sustained increase in cytosolic calcium concentration in cultured endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16771–16775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. S., Sorisky A., Church W. R., Simons E. R., Rittenhouse S. E. "Thrombin" receptor-directed ligand accounts for activation by thrombin of platelet phospholipase C and accumulation of 3-phosphorylated phosphoinositides. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18435–18438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung D. T., Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Ishii K., Coughlin S. R. Cloned platelet thrombin receptor is necessary for thrombin-induced platelet activation. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1350–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI115721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Grulich J., Weksler B. B., Hampel G., Watanabe K. Correlation between thrombin-induced prostacyclin production and inositol trisphosphate and cytosolic free calcium levels in cultured human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8557–8565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamieson G. A. The activation of platelets by thrombin: a model for activation by high and moderate affinity receptor pathways. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1988;283:137–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. W., Vu T. K., Esmon C. T., Coughlin S. R. The region of the thrombin receptor resembling hirudin binds to thrombin and alters enzyme specificity. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):16977–16980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGowan E. B., Detwiler T. C. Modified platelet responses to thrombin. Evidence for two types of receptors or coupling mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngaiza J. R., Jaffe E. A. A 14 amino acid peptide derived from the amino terminus of the cleaved thrombin receptor elevates intracellular calcium and stimulates prostacyclin production in human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Sep 30;179(3):1656–1661. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91765-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberdisse E., Lapetina E. G. GDP beta S enhances the activation of phospholipase C caused by thrombin in human platelets: evidence for involvement of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 14;144(3):1188–1196. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipili-Synetos E., Gershengorn M. C., Jaffe E. A. Expression of functional thrombin receptors in xenopus oocytes injected with human endothelial cell mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 28;171(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90770-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler S. M., Goldenberg H. J., Michel I. M., Hunt J. T., Zavoico G. B. Multiple pathways of thrombin-induced platelet activation differentiated by desensitization and a thrombin exosite inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 16;181(2):636–643. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)91238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler S. M., Michel I. M., Fenton J. W., 2nd Involvement of the "tethered-ligand" receptor in thrombin inhibition of platelet adenylate cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1296–1302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91873-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassallo R. R., Jr, Kieber-Emmons T., Cichowski K., Brass L. F. Structure-function relationships in the activation of platelet thrombin receptors by receptor-derived peptides. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6081–6085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vouret-Craviari V., Van Obberghen-Schilling E., Rasmussen U. B., Pavirani A., Lecocq J. P., Pouysségur J. Synthetic alpha-thrombin receptor peptides activate G protein-coupled signaling pathways but are unable to induce mitogenesis. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):95–102. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Hung D. T., Charo I., Coughlin S. R. Domains specifying thrombin-receptor interaction. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):674–677. doi: 10.1038/353674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. H., Nuccitelli R. Inhibition of tyrosine phosphorylation prevents thrombin-induced mitogenesis, but not intracellular free calcium release, in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5608–5613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]