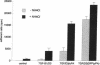Abstract
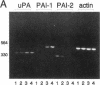
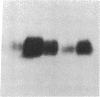
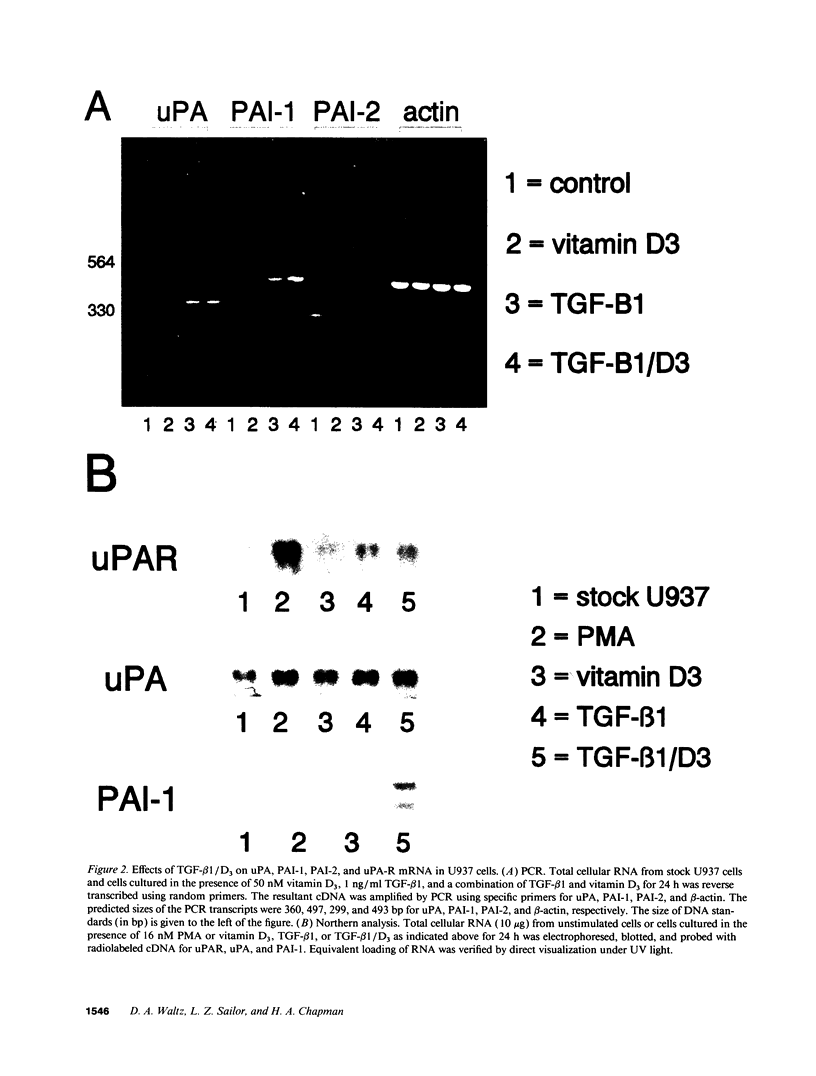
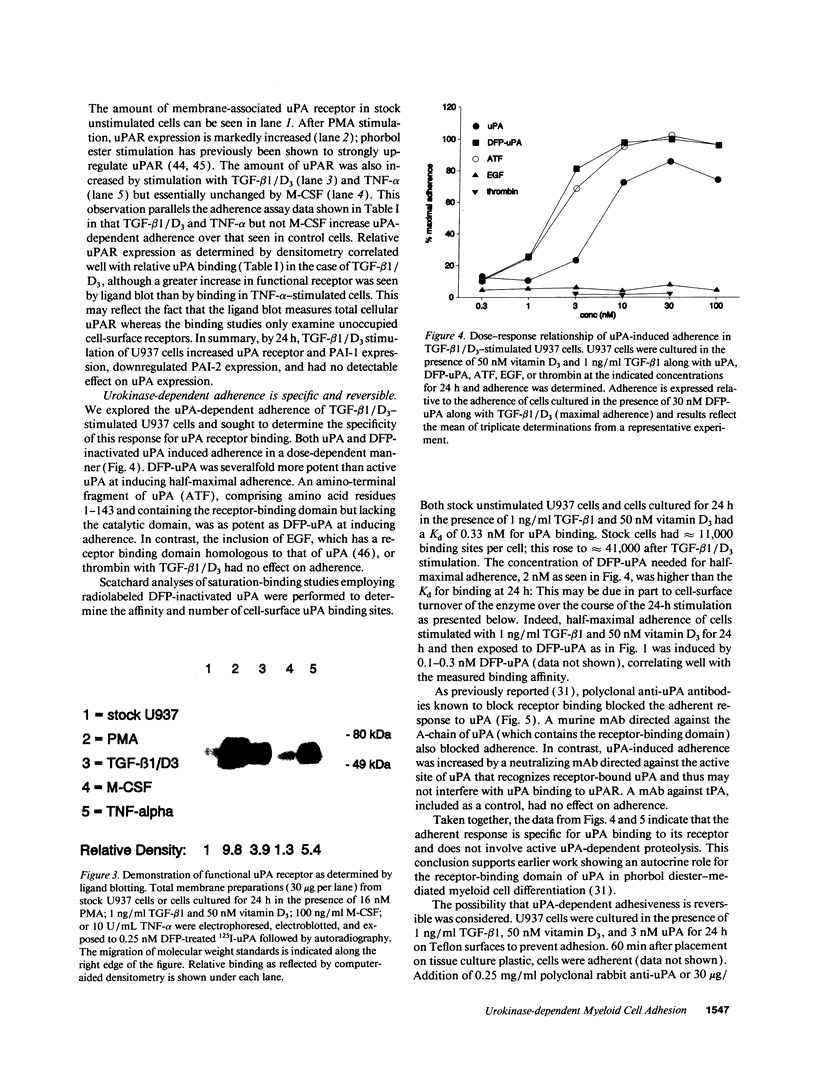
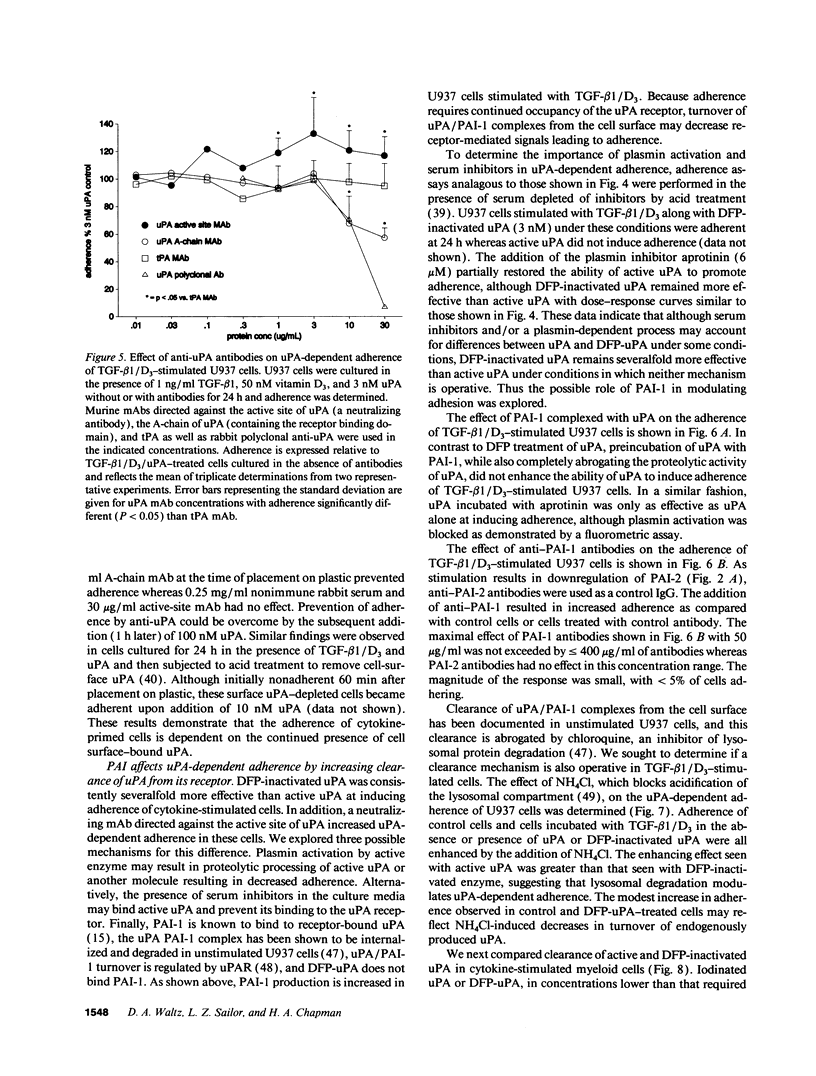
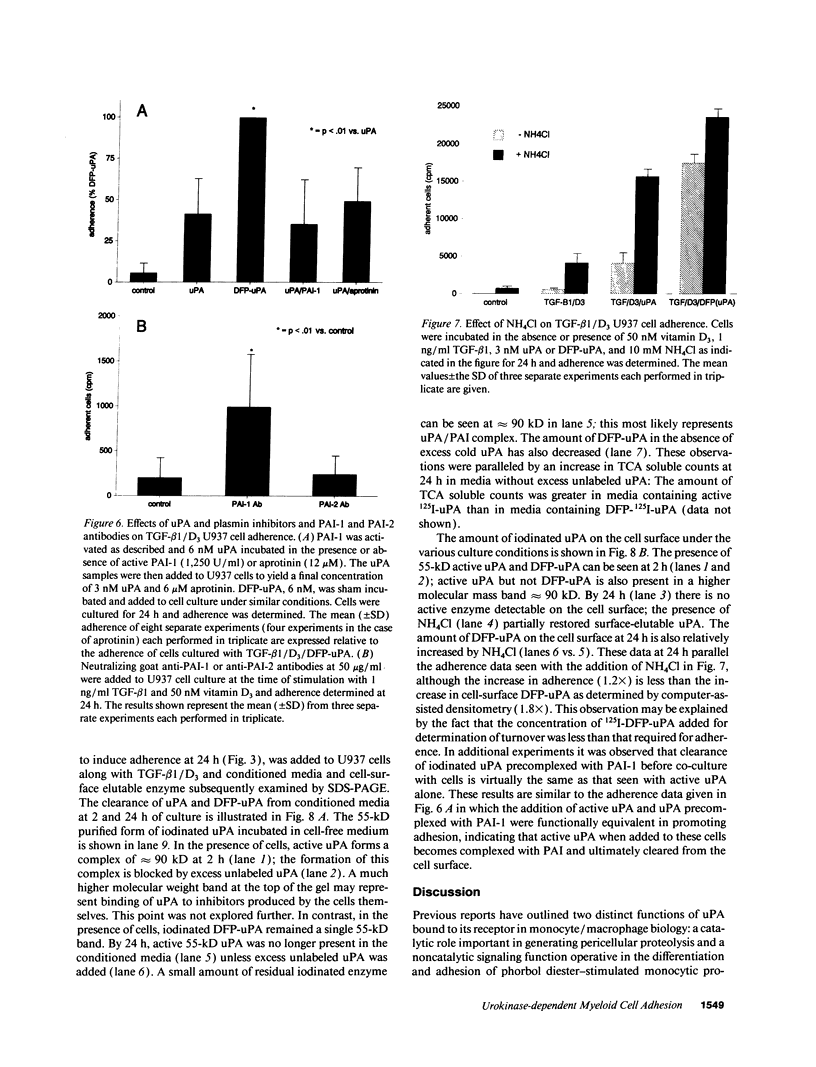
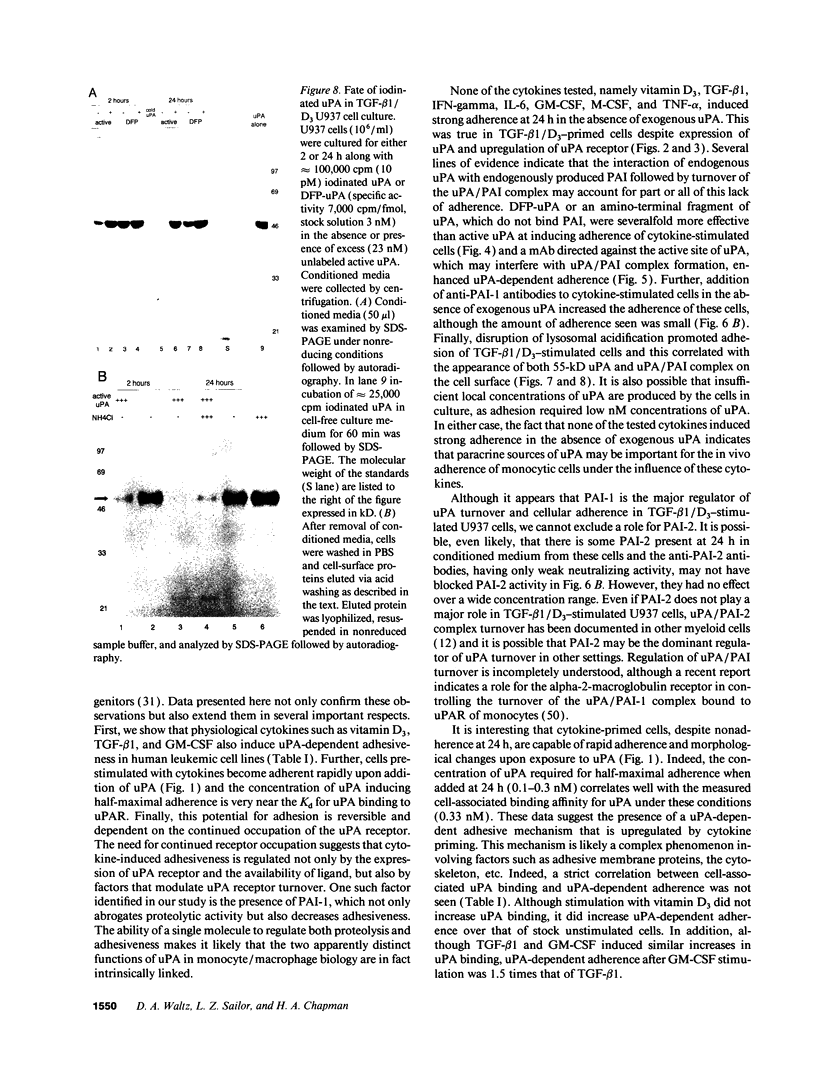
Differentiation of monocytic precursors often results in adhesive properties thought to be important in migration. In this study, the influence of cytokines, known to induce macrophage differentiation, on the adhesiveness of the monocytic cell line U937 was examined in vitro. Despite development of a macrophage morphology, < 5% of cytokine-stimulated U937 cells were adherent at 24 h. Addition of 1-10 nM urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) induced adherence in the presence of transforming growth factor type beta-1, 1,25-(OH)2 vitamin D3, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor, or tumor necrosis factor alpha. uPA-dependent adhesiveness was reversible after 24 h of stimulation with cytokines and uPA as adherence was prevented by the subsequent addition of anti-uPA antibodies. Adherence induced by diisopropylfluorophosphate-inactivated uPA was severalfold greater than that seen with active uPA. This difference was largely due to cell-surface turnover of active uPA complexed with plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI). These data indicate that cytokines prime monocyte progenitors for uPA receptor-mediated signals leading to adherence, continued uPA receptor occupancy is required for adherence, and PAI decreases adherence by promoting clearance of uPA/PAI complexes. Thus the interaction of uPA and PAI at the cell surface, known to affect extracellular matrix proteolysis and hence myeloid cell migration, also regulates adhesion. The coordinated regulation of these two uPA functions by PAI may enhance the migratory potential of monocytic cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alessi M. C., Declerck P. J., De Mol M., Nelles L., Collen D. Purification and characterization of natural and recombinant human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1). Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):531–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alving B. M., Krishnamurti C., Liu Y. P., Lucas D. L., Wright D. G. Stimulated production of urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 by the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line HL-60. Thromb Res. 1988 Jul 15;51(2):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amento E. P., Bhalla A. K., Kurnick J. T., Kradin R. L., Clemens T. L., Holick S. A., Holick M. F., Krane S. M. 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces maturation of the human monocyte cell line U937, and, in association with a factor from human T lymphocytes, augments production of the monokine, mononuclear cell factor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):731–739. doi: 10.1172/JCI111266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. C., Springer T. A. Leukocyte adhesion deficiency: an inherited defect in the Mac-1, LFA-1, and p150,95 glycoproteins. Annu Rev Med. 1987;38:175–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.38.020187.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appella E., Robinson E. A., Ullrich S. J., Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Cassani G., Blasi F. The receptor-binding sequence of urokinase. A biological function for the growth-factor module of proteases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4437–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertozzi P., Astedt B., Zenzius L., Lynch K., LeMaire F., Zapol W., Chapman H. A., Jr Depressed bronchoalveolar urokinase activity in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990 Mar 29;322(13):890–897. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199003293221304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Bertozzi P., Sailor L. Z., Nusrat A. R. Alveolar macrophage urokinase receptors localize enzyme activity to the cell surface. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):L432–L438. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.259.6.L432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman H. A., Yang X. L., Sailor L. Z., Sugarbaker D. J. Developmental expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 by human alveolar macrophages. Possible role in lung injury. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3398–3405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Andreasen P., Ragno P., Mayer M., Danø K., Blasi F. Accessibility of receptor-bound urokinase to type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4828–4832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Wun T. C., Blasi F. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S., Aldrich T. H., Valenzuela D. M., Wong V. V., Furth M. E., Squinto S. P., Yancopoulos G. D. The receptor for ciliary neurotrophic factor. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.1648265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Wun T. C., Behrendt N., Rønne E., Danø K. Inhibition of receptor-bound urokinase by plasminogen-activator inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9904–9908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble J. R., Elliott M. J., Jaipargas E., Lopez A. F., Vadas M. A. Regulation of human monocyte adherence by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7169–7173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Reich E. A study of proteases and protease-inhibitor complexes in biological fluids. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):223–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyetko M. R., Webb A. C., Sitrin R. G. Modulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor-2 expression by U-937 mononuclear phagocytes. Effects of 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and phorbol ester. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2693–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P., Ralph P. Human leukemic models of myelomonocytic development: a review of the HL-60 and U937 cell lines. J Leukoc Biol. 1985 Apr;37(4):407–422. doi: 10.1002/jlb.37.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmberg L., Bladh B., Astedt B. Purification of urokinase by affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 12;445(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90174-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsey S. M., Makin H. L., Macey M. G., Newland A. C. Gamma interferon augments functional and phenotypic characteristics of vitamin D3-induced monocytoid differentiation in the U937 human leukaemic cell line. Leuk Res. 1990;14(11-12):1027–1033. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(90)90116-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Binder B. R., Remold H. G. Matrix-bound plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 inhibits the invasion of human monocytes into interstitial tissue. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1518–1522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Nong Y. H., Remold H. G. IFN-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and urokinase regulate the expression of urokinase receptors on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4229–4234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Remold H. G. Endogenous receptor-bound urokinase mediates tissue invasion of human monocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2634–2639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Remold H. G. Functional characteristics of receptor-bound urokinase on human monocytes: catalytic efficiency and susceptibility to inactivation by plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1396–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauffenburger D. A. Models for receptor-mediated cell phenomena: adhesion and migration. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:387–414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Rønne E., Roldan A. L., Behrendt N., Rømer J., Blasi F., Danø K. Urokinase receptor mRNA level and gene transcription are strongly and rapidly increased by phorbol myristate acetate in human monocyte-like U937 cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5177–5181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert M., Herrmann F., Koeffler H. P. Expression and regulation of myeloid-specific genes in normal and leukemic myeloid cells. Blood. 1991 Mar 1;77(5):909–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaura C., Onozaki K., Akiyama Y., Taniyama T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T., Suda T. Recombinant human interleukin 6 (B-cell stimulatory factor 2) is a potent inducer of differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells (M1). FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 4;234(1):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa M., Harada N., Soma G., Yoshida T. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 modulates the effect of 1 alpha, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on leukemic cells. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1990 Jul;26(7):682–690. doi: 10.1007/BF02624424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munger J. S., Shi G. P., Mark E. A., Chin D. T., Gerard C., Chapman H. A. A serine esterase released by human alveolar macrophages is closely related to liver microsomal carboxylesterases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18832–18838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen L. S., Kellerman G. M., Behrendt N., Picone R., Danø K., Blasi F. A 55,000-60,000 Mr receptor protein for urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Identification in human tumor cell lines and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2358–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusrat A. R., Chapman H. A., Jr An autocrine role for urokinase in phorbol ester-mediated differentiation of myeloid cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):1091–1097. doi: 10.1172/JCI115070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Petersen C. M., Møller B., Jensen P. H., Moestrup S. K., Holtet T. L., Etzerodt M., Thøgersen H. C., Munch M., Andreasen P. A. Purified alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/LDL receptor-related protein binds urokinase.plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complex. Evidence that the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor mediates cellular degradation of urokinase receptor-bound complexes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14543–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma S., Poole B. Fluorescence probe measurement of the intralysosomal pH in living cells and the perturbation of pH by various agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson D., Pöllänen J., Høyer-Hansen G., Rønne E., Sakaguchi K., Wun T. C., Appella E., Danø K., Blasi F. Internalization of the urokinase-plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complex is mediated by the urokinase receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9129–9133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Jensen A. L., Blasi F., Danø K. Cellular receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Carboxyl-terminal processing and membrane anchoring by glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1926–1933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D. E., Plescia J., Miles L. A. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2411–2420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polla B. S., Healy A. M., Amento E. P., Krane S. M. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 maintains adherence of human monocytes and protects them from thermal injury. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1332–1339. doi: 10.1172/JCI112438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby W. F., Shen L., Ball E. D., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Differentiation of a human monocytic cell line by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol): a morphologic, phenotypic, and functional analysis. Blood. 1984 Nov;64(5):1110–1115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A., Pöllänen J., Stephens R., Andreasen P., Mayer M., Danø K., Gailit J., Ruoslahti E. Interaction of plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI-1) with vitronectin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6339–6343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Kupfer A. The directed migration of eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:337–365. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanová I., Horejsí V., Ansotegui I. J., Knapp W., Stockinger H. GPI-anchored cell-surface molecules complexed to protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1991 Nov 15;254(5034):1016–1019. doi: 10.1126/science.1719635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Tacchetti C., Cubellis M. V., Corti A., Hearing V. J., Cassani G., Appella E., Blasi F. Autocrine saturation of pro-urokinase receptors on human A431 cells. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90782-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga T., Hibi M., Hirata Y., Yamasaki K., Yasukawa K., Matsuda T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Interleukin-6 triggers the association of its receptor with a possible signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90438-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J., Dano K., Kellerman G. M., Reich E. Fibrinolysis associated with oncogenic transformation. Partial purification and characterization of the cell factor, a plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 10;249(13):4295–4305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaheri A., Stephens R. W., Salonen E. M., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H. Plasminogen activation at the cell surface-matrix interface. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90038-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Dayer J. M., Wohlwend A., Belin D. Concomitant secretion of prourokinase and of a plasminogen activator-specific inhibitor by cultured human monocytes-macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1653–1668. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Larrick J. W. Receptor-mediated monocytoid differentiation of human promyelocytic cells by tumor necrosis factor: synergistic actions with interferon-gamma and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Blood. 1987 Oct;70(4):994–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. A., Lowe L. D., Clark S. C. Comparison of the effects of IL-3, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, and macrophage colony-stimulating factor in supporting monocyte differentiation in culture. Analysis of macrophage antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):607–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Schreiber R. D. Up-regulation of gamma interferon receptors on the human monocytic cell line U937 by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Sep;44(3):187–191. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.3.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Surprenant Y. M., Tang J. Synergistic effect of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on the differentiation of the human monocytic cell line U937. Blood. 1988 Mar;71(3):619–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R. Current view on the mononuclear phagocyte system. Immunobiology. 1982 Apr;161(3-4):178–185. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(82)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]