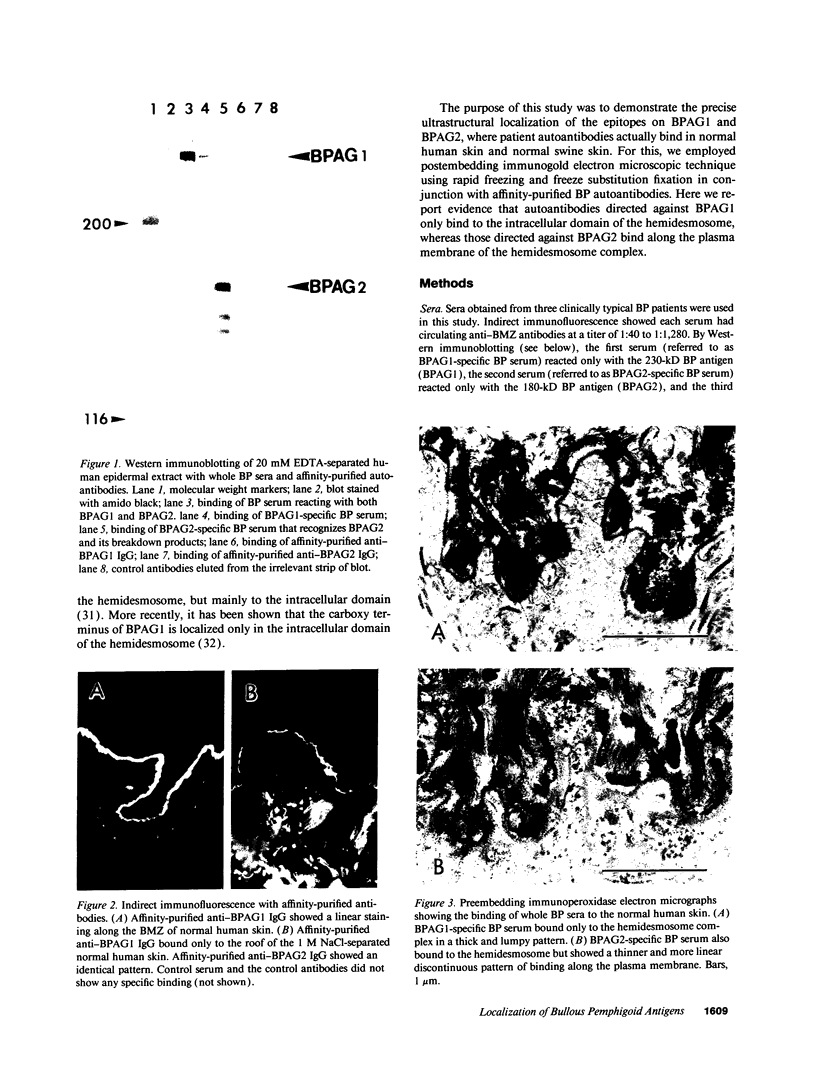
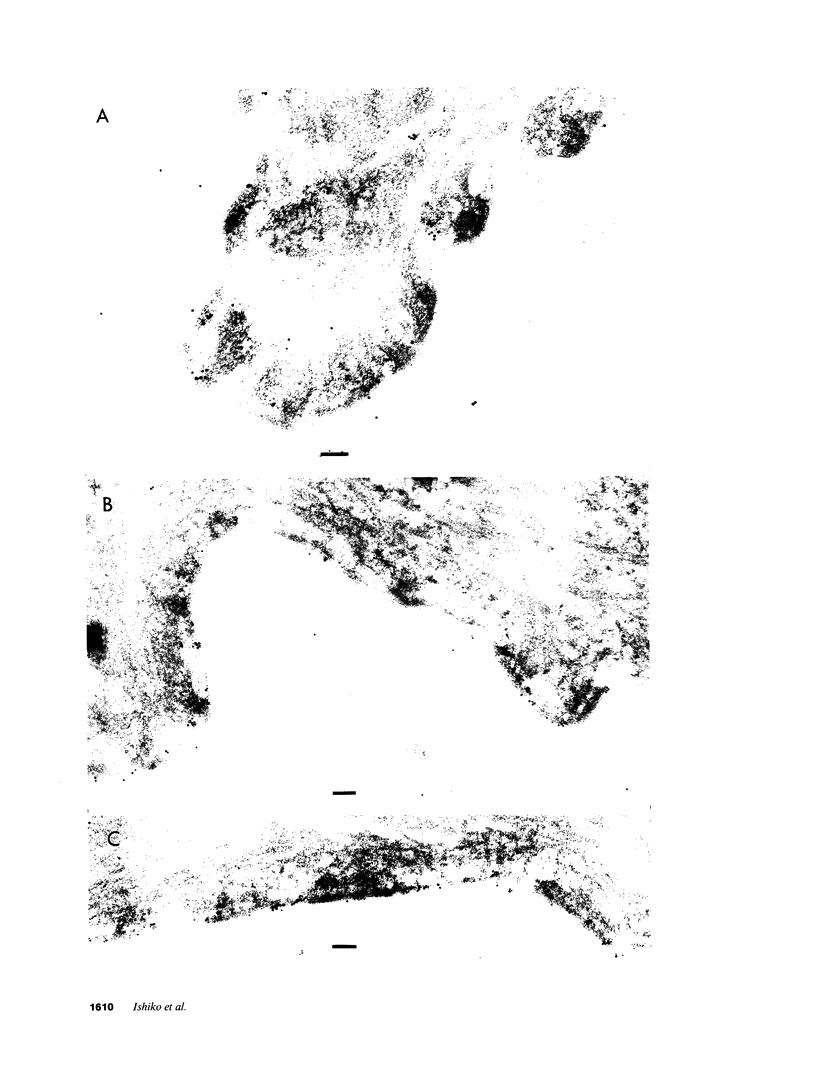
Abstract
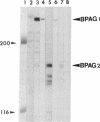
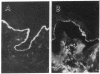
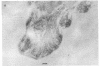
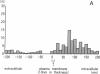
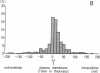
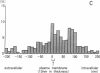
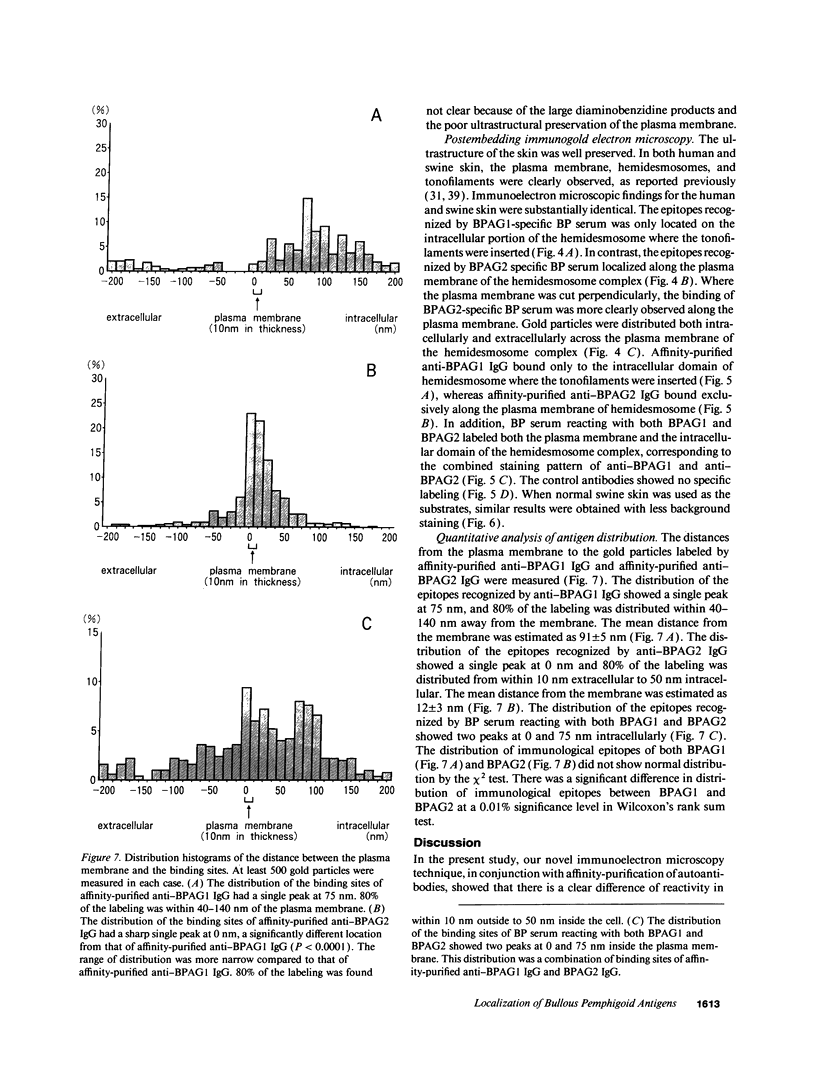
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a blistering skin disease in which autoantibodies develop to hemidesmosomal components of the epidermal basement membrane zone, including two major antigenic proteins of the 230-kD antigen (BPAG1) and the 180-kD antigen (BPAG2). The present study demonstrated the precise ultrastructural localization of the epitopes for autoantibodies against BPAG1 and BPAG2 in normal skin. Autoantibodies against either BPAG1 or BPAG2 were affinity-purified using nitrocellulose membrane, which was blotted with SDS-PAGE-fractionated antigens from human epidermal extract as the immunoabsorbent. Postembedding, immunogold electron microscopy was performed after skin was processed by rapid freezing and freeze substitution fixation without chemical fixatives. Purified autoantibodies against BPAG1 bound only to the intracellular domain of the hemidesmosome, and 80% of the gold labeling was within 40-140 nm from the plasma membrane (mean distance 91 nm inside). In contrast, the autoantibodies against BPAG2 bound along the plasma membrane of the hemidesmosome, and 80% of the gold labeling was within 10 nm outside to 50 nm inside the cells (mean distance 12 nm inside). These results suggest that the autoantibodies against BPAG1 and BPAG2 react with the epitopes localizing in distinct regions of the hemidesmosome complex, and may play different roles in the blister formation in patients with BP.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amagai M., Hashimoto T., Tajima S., Inokuchi Y., Shimizu N., Saito M., Miki K., Nishikawa T. Partial cDNA cloning of the 230-kD mouse bullous pemphigoid antigen by use of a human monoclonal anti-basement membrane zone antibody. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Sep;95(3):252–259. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12484863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anhalt G. J., Bahn C. F., Labib R. S., Voorhees J. J., Sugar A., Diaz L. A. Pathogenic effects of bullous pemphigoid autoantibodies on rabbit corneal epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1097–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI110333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTNER E. H., JORDON R. E. DEMONSTRATION OF SKIN ANTIBODIES IN SERA OF PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS PATIENTS BY INDIRECT IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:505–510. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Calvanico N. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr, Jordon R. E. Bullous pemphigoid antigen: isolation from normal human skin. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):455–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Patel H., Calvanico N. J. Bullous pemphigoid antigen. II. Isolation from the urine of a patient. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):605–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Ratrie H., 3rd, Saunders W. S., Futamura S., Squiquera H. L., Anhalt G. J., Giudice G. J. Isolation of a human epidermal cDNA corresponding to the 180-kD autoantigen recognized by bullous pemphigoid and herpes gestationis sera. Immunolocalization of this protein to the hemidesmosome. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1088–1094. doi: 10.1172/JCI114812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon W. R., Briggaman R. A., Inman A. O., 3rd, Queen L. L., Wheeler C. E. Differentiating anti-lamina lucida and anti-sublamina densa anti-BMZ antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence on 1.0 M sodium chloride-separated skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Feb;82(2):139–144. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice G. J., Emery D. J., Diaz L. A. Cloning and primary structural analysis of the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen BP180. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Sep;99(3):243–250. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12616580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice G. J., Squiquera H. L., Elias P. M., Diaz L. A. Identification of two collagen domains within the bullous pemphigoid autoantigen, BP180. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):734–738. doi: 10.1172/JCI115054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. J., Parry D. A., Steinert P. M., Virata M. L., Wagner R. M., Angst B. D., Nilles L. A. Structure of the human desmoplakins. Implications for function in the desmosomal plaque. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2603–2612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grekin P. M., Levy G. N., King A. J., Diaz L. A. Some biochemical properties of pemphigoid antigen bound to the surface of dissociated epidermal basal cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):190–192. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holubar K., Wolff K., Konrad K., Beutner E. H. Ultrastructural localization of immunoglobulins in bullous pemphigoid skin. Employment of a new peroxidase-antiperoxidase multistep method. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Apr;64(4):220–227. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12510658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson S. B., Riddelle K. S., Jones J. C. Cytoplasmic domain of the 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigen, a hemidesmosomal component: molecular and cell biologic characterization. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Sep;99(3):264–270. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12616615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiguchi Y., Imamura S. Discrepancy between the localization of in vivo bound immunoglobulins in the skin and in vitro binding sites of circulating anti-BMZ antibodies in bullous pemphigoid: immunoelectron microscopic studies. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Dec;87(6):715–719. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12456694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments and the initiation of desmosome assembly. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):506–517. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Kurpakus M. A., Cooper H. M., Quaranta V. A function for the integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell Regul. 1991 Jun;2(6):427–438. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.6.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatte D. H., Kurpakus M. A., Grelling K. A., Jones J. C. Immunochemical characterization of three components of the hemidesmosome and their expression in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3377–3390. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labib R. S., Anhalt G. J., Patel H. P., Mutasim D. F., Diaz L. A. Molecular heterogeneity of the bullous pemphigoid antigens as detected by immunoblotting. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 15;136(4):1231–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li K., Guidice G. J., Tamai K., Do H. C., Sawamura D., Diaz L. A., Uitto J. Cloning of partial cDNA for mouse 180-kDa bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG2), a highly conserved collagenous protein of the cutaneous basement membrane zone. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Sep;99(3):258–263. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12616611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer L. J., Taylor T. B., Kadunce D. P., Zone J. J. Two groups of bullous pemphigoid antigens are identified by affinity-purified antibodies. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 May;94(5):611–616. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K., Mattey D., Measures H., Hopkins C., Garrod D. Localisation of the protein and glycoprotein components of bovine nasal epithelial desmosomes by immunoelectron microscopy. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):885–889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutasim D. F., Morrison L. H., Takahashi Y., Labib R. S., Skouge J., Diaz L. A., Anhalt G. J. Definition of bullous pemphigoid antibody binding to intracellular and extracellular antigen associated with hemidesmosomes. J Invest Dermatol. 1989 Feb;92(2):225–230. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12276753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutasim D. F., Takahashi Y., Labib R. S., Anhalt G. J., Patel H. P., Diaz L. A. A pool of bullous pemphigoid antigen(s) is intracellular and associated with the basal cell cytoskeleton-hemidesmosome complex. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jan;84(1):47–53. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12274684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Morioka S., Ogawa H. The pathogenic mechanisms of blister formation in bullous pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Nov;79(5):303–306. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12500082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T., Kurihara S., Harada T., Hatano H. Binding of bullous pemphigoid antibodies to basal cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jun;74(6):389–391. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12544466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnier M., Vaigot P., Michel S., Prunieras M. Localization of bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPA) in isolated human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Sep;85(3):187–190. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12276656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robledo M. A., Kim S. C., Korman N. J., Stanley J. R., Labib R. S., Futamura S., Anhalt G. J. Studies of the relationship of the 230-kD and 180-kD bullous pemphigoid antigens. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Jun;94(6):793–797. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12874652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sams W. M., Jr, Gammon W. R. Mechanism of lesion production in pemphigus and pemphigoid. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1982 Apr;6(4 Pt 1):431–452. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(82)70036-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura D., Li K., Chu M. L., Uitto J. Human bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG1). Amino acid sequences deduced from cloned cDNAs predict biologically important peptide segments and protein domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17784–17790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Hayakawa K., Nishikawa T. A comparative immunoelectron microscopic study of typical and atypical cases of pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 1988 Dec;119(6):717–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1988.tb03493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Ishida-Yamamoto A., Eady R. A. The use of silver-enhanced 1-nm gold probes for light and electron microscopic localization of intra- and extracellular antigens in skin. J Histochem Cytochem. 1992 Jun;40(6):883–888. doi: 10.1177/40.6.1375240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., McDonald J. N., Kennedy A. R., Eady R. A. Demonstration of intra- and extracellular localization of bullous pemphigoid antigen using cryofixation and freeze substitution for postembedding immunoelectron microscopy. Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281(7):443–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00510078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Fisher P. A. Identification, developmental regulation, and response to heat shock of two antigenically related forms of a major nuclear envelope protein in Drosophila embryos: application of an improved method for affinity purification of antibodies using polypeptides immobilized on nitrocellulose blots. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):20–28. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Calafat J., Janssen H., Daams H., van der Raaij-Helmer L. M., Falcioni R., Kennel S. J., Aplin J. D., Baker J., Loizidou M. Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):907–917. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Yuspa S. H., Shevach E. M., Katz S. I. Characterization of bullous pemphigoid antigen: a unique basement membrane protein of stratified squamous epithelia. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Woodley D. T., Katz S. I. Identification and partial characterization of pemphigoid antigen extracted from normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jan;82(1):108–111. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugi T., Hashimoto T., Hibi T., Nishikawa T. Production of human monoclonal anti-basement membrane zone (BMZ) antibodies from a patient with bullous pemphigoid (BP) by Epstein-Barr virus transformation. Analyses of the heterogeneity of anti-BMZ antibodies in BP sera using them. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1050–1055. doi: 10.1172/JCI114266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Hashimoto T., Amagai M., Shimizu N., Ikeguchi N., Tsubata T., Hasegawa A., Miki K., Nishikawa T. Characterization of bullous pemphigoid antibodies by use of recombinant bullous pemphigoid antigen proteins. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):725–728. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12484223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Korman N. J., Shimizu H., Eady R. A., Klaus-Kovtun V., Cehrs K., Stanley J. R. Production of rabbit antibodies against carboxy-terminal epitopes encoded by bullous pemphigoid cDNA. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 May;94(5):617–623. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12876200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Parry D. A., Klaus-Kovtun V., Steinert P. M., Stanley J. R. Comparison of molecularly cloned bullous pemphigoid antigen to desmoplakin I confirms that they define a new family of cell adhesion junction plaque proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 5;266(19):12555–12559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westgate G. E., Weaver A. C., Couchman J. R. Bullous pemphigoid antigen localization suggests an intracellular association with hemidesmosomes. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Mar;84(3):218–224. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12265229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki Y., Nishikawa T. Ultrastructural localization of in vitro binding sites of circulating anti-basement membrane zone antibodies in bullous pemphigoid. Acta Derm Venereol. 1983;63(6):501–506. doi: 10.2340/00015555463501506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]