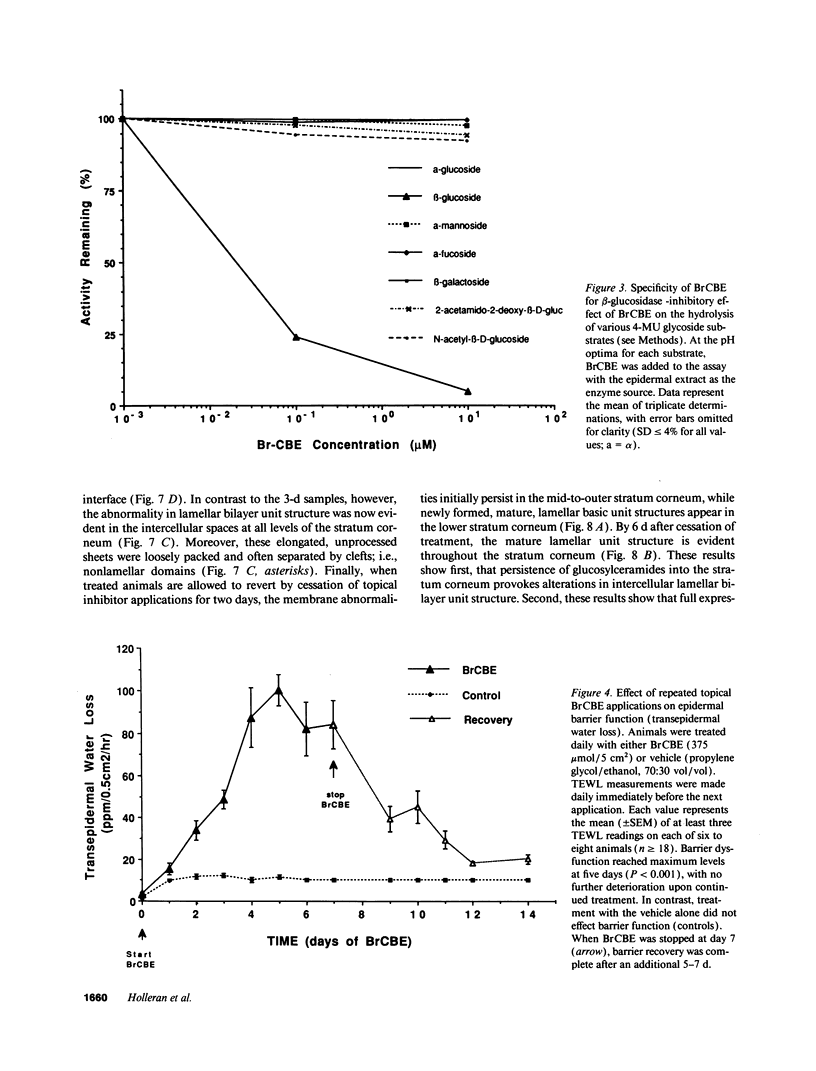
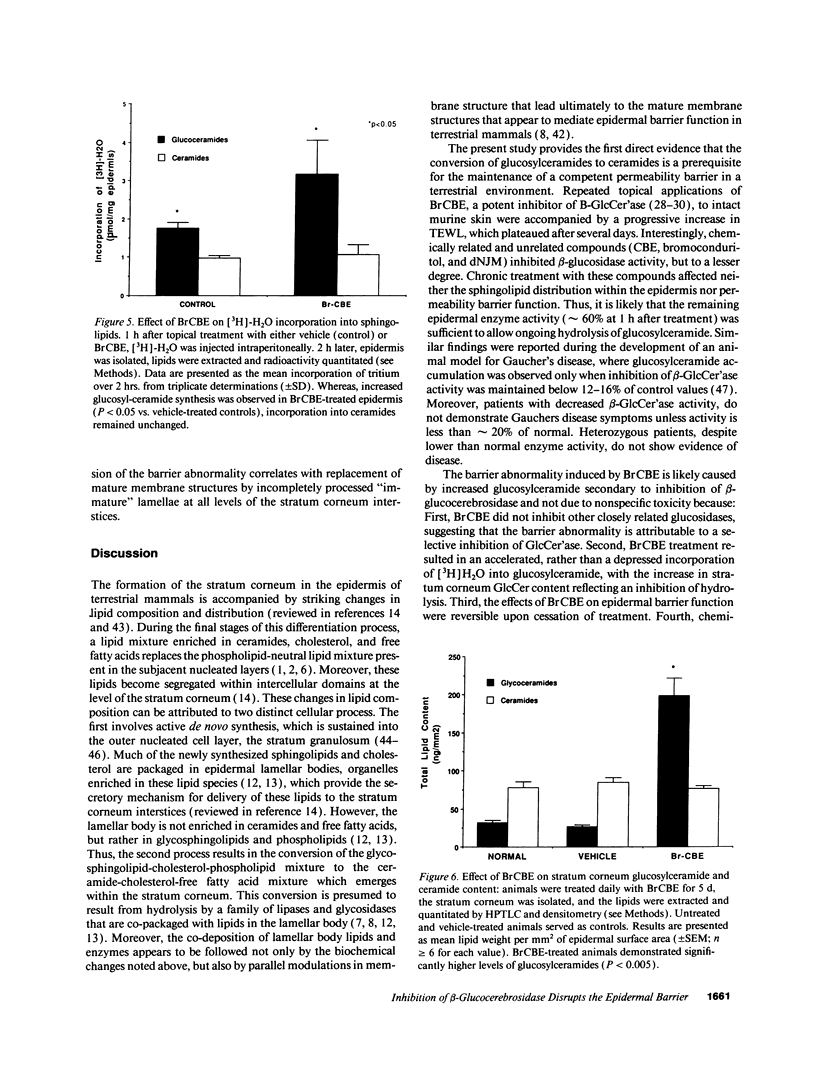
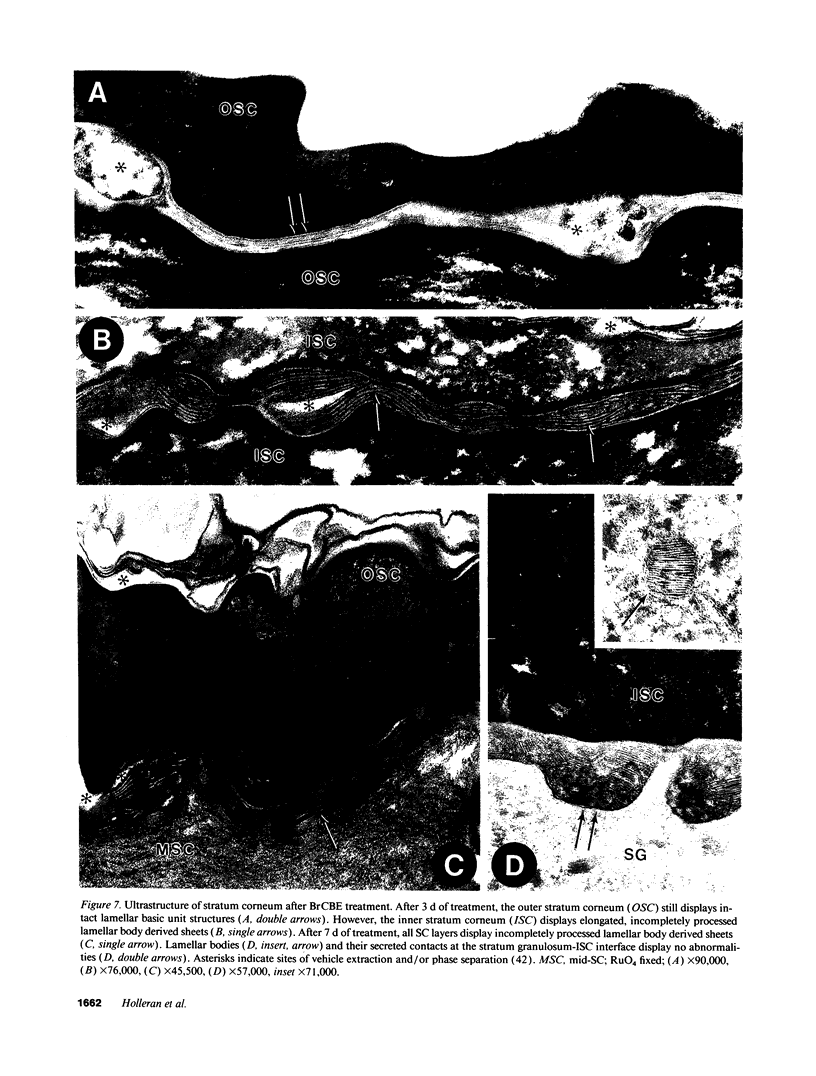
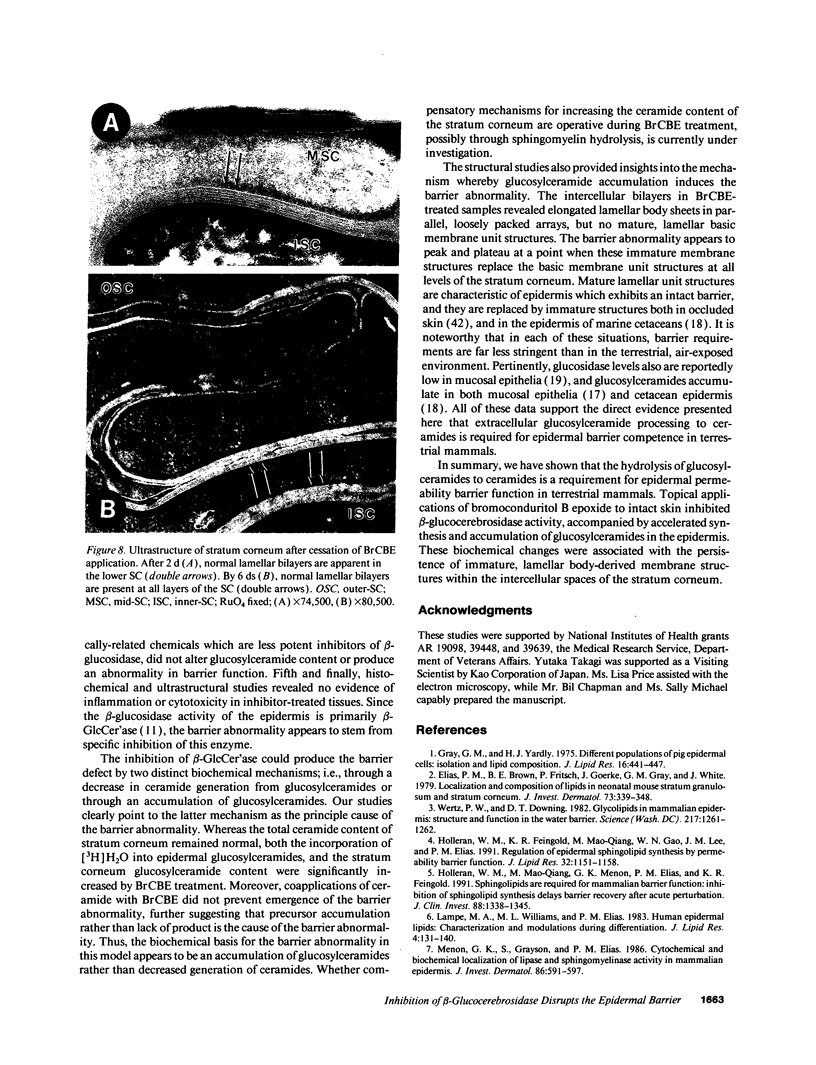
Abstract
The interstices of the mammalian stratum corneum contain lipids in a system of continuous membrane bilayers critical for the epidermal permeability barrier. During the transition from inner to outer stratum corneum, the content of polar lipids including glucosylceramides, decreases while ceramide content increases. We investigated whether inhibition of glucosylceramide hydrolysis would alter epidermal permeability barrier function. Daily topical applications of bromoconduritol B epoxide (BrCBE) to intact murine skin selectively inhibited beta-glucocerebrosidase, increased glucosylceramide content of stratum corneum with ceramide content remaining largely unchanged, and caused a progressive, reversible decrease in barrier function. Histochemistry of inhibitor-treated epidermis revealed persistence of periodic acid-Schiff-positive staining in stratum corneum cell membranes, consistent with retention of hexose moieties. Electron microscopy of inhibitor-treated samples revealed no evidence of toxicity or changes in the epidermal lipid delivery system. However, immature membrane structures persisted in the intercellular spaces throughout the stratum corneum, with reappearance of mature membrane structures progressing outward from the lower stratum corneum upon termination of BrCBE. Finally, the induced barrier abnormality was not reversed by coapplications of ceramide. These data demonstrate that glucosylceramide hydrolysis is important in the formation of the epidermal permeability barrier, and suggest that accumulation of glucosylceramides in stratum corneum intercellular membrane domains leads to abnormal barrier function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Wertz P. W., Squier C. A. Comparison of glycosidase activities in epidermis, palatal epithelium and buccal epithelium. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1991;100(1):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(91)90096-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F., Wertz P. W., Squier C. A. Comparison of glycosidase activities in epidermis, palatal epithelium and buccal epithelium. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1991;100(1):137–139. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(91)90096-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinur T., Osiecki K. M., Legler G., Gatt S., Desnick R. J., Grabowski G. A. Human acid beta-glucosidase: isolation and amino acid sequence of a peptide containing the catalytic site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1660–1664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Brown B. E., Fritsch P., Goerke J., Gray G. M., White R. J. Localization and composition of lipids in neonatal mouse stratum granulosum and stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Nov;73(5):339–348. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12550377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Menon G. K., Grayson S., Brown B. E. Membrane structural alterations in murine stratum corneum: relationship to the localization of polar lipids and phospholipases. J Invest Dermatol. 1988 Jul;91(1):3–10. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12463279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Menon G. K. Structural and lipid biochemical correlates of the epidermal permeability barrier. Adv Lipid Res. 1991;24:1–26. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024924-4.50005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Williams M. L., Maloney M. E., Bonifas J. A., Brown B. E., Grayson S., Epstein E. H., Jr Stratum corneum lipids in disorders of cornification. Steroid sulfatase and cholesterol sulfate in normal desquamation and the pathogenesis of recessive X-linked ichthyosis. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1414–1421. doi: 10.1172/JCI111552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Brown B. E., Lear S. R., Moser A. H., Elias P. M. Localization of de novo sterologenesis in mammalian skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Oct;81(4):365–369. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12519974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freinkel R. K., Traczyk T. N. Lipid composition and acid hydrolase content of lamellar granules of fetal rat epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Oct;85(4):295–298. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12276831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg M. F., Cotlier E., Fichenscher L. G., Kenyon K., Enat R., Borowsky S. A. Macular cherry-red spot, corneal clouding, and beta-galactosidase deficiency. Clinical, biochemical, and electron microscopic study of a new autosomal recessive storage disease. Arch Intern Med. 1971 Sep;128(3):387–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. M., Yardley H. J. Different populations of pig epidermal cells: isolation and lipid composition. J Lipid Res. 1975 Nov;16(6):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grayson S., Johnson-Winegar A. G., Wintroub B. U., Isseroff R. R., Epstein E. H., Jr, Elias P. M. Lamellar body-enriched fractions from neonatal mice: preparative techniques and partial characterization. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Oct;85(4):289–294. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12276826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubauer G., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Transepidermal water loss: the signal for recovery of barrier structure and function. J Lipid Res. 1989 Mar;30(3):323–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubauer G., Feingold K. R., Elias P. M. Relationship of epidermal lipogenesis to cutaneous barrier function. J Lipid Res. 1987 Jun;28(6):746–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Feingold K. R., Man M. Q., Gao W. N., Lee J. M., Elias P. M. Regulation of epidermal sphingolipid synthesis by permeability barrier function. J Lipid Res. 1991 Jul;32(7):1151–1158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M. Lipid modulators of epidermal proliferation and differentiation. Adv Lipid Res. 1991;24:119–139. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024924-4.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Man M. Q., Gao W. N., Menon G. K., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Sphingolipids are required for mammalian epidermal barrier function. Inhibition of sphingolipid synthesis delays barrier recovery after acute perturbation. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1338–1345. doi: 10.1172/JCI115439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleran W. M., Takagi Y., Imokawa G., Jackson S., Lee J. M., Elias P. M. beta-Glucocerebrosidase activity in murine epidermis: characterization and localization in relation to differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1992 Aug;33(8):1201–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou S. Y., Mitra A. K., White S. H., Menon G. K., Ghadially R., Elias P. M. Membrane structures in normal and essential fatty acid-deficient stratum corneum: characterization by ruthenium tetroxide staining and x-ray diffraction. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Feb;96(2):215–223. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12461361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampe M. A., Williams M. L., Elias P. M. Human epidermal lipids: characterization and modulations during differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):131–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Bieberich E. Active site directed inhibition of a cytosolic beta-glucosidase from calf liver by bromoconduritol B epoxide and bromoconduritol F. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Jan;260(1):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90467-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G. Glucosidases. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:368–381. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legler G., Liedtke H. Glucosylceramidase from calf spleen. Characterization of its active site with 4-n-alkylumbelliferyl beta-glucosides and N-alkyl derivatives of 1-deoxynojirimycin. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1985 Dec;366(12):1113–1122. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1985.366.2.1113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison K. C., Swartzendruber D. C., Wertz P. W., Downing D. T. Presence of intact intercellular lipid lamellae in the upper layers of the stratum corneum. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jun;88(6):714–718. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Feingold K. R., Mao-Qiang M., Schaude M., Elias P. M. Structural basis for the barrier abnormality following inhibition of HMG CoA reductase in murine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1992 Feb;98(2):209–219. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12555880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Feingold K. R., Moser A. H., Brown B. E., Elias P. M. De novo sterologenesis in the skin. II. Regulation by cutaneous barrier requirements. J Lipid Res. 1985 Apr;26(4):418–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Grayson S., Brown B. E., Elias P. M. Lipokeratinocytes of the epidermis of a cetacean (Phocena phocena). Histochemistry, ultrastructure, and lipid composition. Cell Tissue Res. 1986;244(2):385–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00219214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon G. K., Grayson S., Elias P. M. Cytochemical and biochemical localization of lipase and sphingomyelinase activity in mammalian epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 May;86(5):591–597. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12355263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier P. D., van den Hurk J. J. Lysosomal hydrolases of the epidermis. 6. Changes in disease. Br J Dermatol. 1976 Sep;95(3):271–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1976.tb07014.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mier P. D., van den Hurk J. J. Lysosomal hydrolases of the epidermis. I. Glycosidases. Br J Dermatol. 1975 Jul;93(1):1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb06468.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monger D. J., Williams M. L., Feingold K. R., Brown B. E., Elias P. M. Localization of sites of lipid biosynthesis in mammalian epidermis. J Lipid Res. 1988 May;29(5):603–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemanic M. K., Whitehead J. S., Elias P. M. Alterations in membrane sugars during epidermal differentiation: visualization with lectins and role of glycosidases. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jul;31(7):887–897. doi: 10.1177/31.7.6854004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemanic M. K., Whitehead J. S., Elias P. M. Alterations in membrane sugars during epidermal differentiation: visualization with lectins and role of glycosidases. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jul;31(7):887–897. doi: 10.1177/31.7.6854004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockerman P. A. Acid hydrolases in human skin. Acta Derm Venereol. 1969;49(2):139–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okawara A., Halprin K. M., Taylor J. R., Levine V. Acid hydrolases in the human epidermis. Br J Dermatol. 1972 Nov;87(5):450–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponec M., Weerheim A., Kempenaar J., Mommaas A. M., Nugteren D. H. Lipid composition of cultured human keratinocytes in relation to their differentiation. J Lipid Res. 1988 Jul;29(7):949–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proksch E., Elias P. M., Feingold K. R. Localization and regulation of epidermal 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase activity by barrier requirements. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 24;1083(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90126-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Squier C. A., Cox P. S., Wertz P. W., Downing D. T. The lipid composition of porcine epidermis and oral epithelium. Arch Oral Biol. 1986;31(11):741–747. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(86)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens M. C., Bernatsky A., Burachinsky V., Legler G., Kanfer J. N. The Gaucher mouse: differential action of conduritol B epoxide and reversibility of its effects. J Neurochem. 1978 May;30(5):1023–1027. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb12395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz P. W., Downing D. T. Beta-glucosidase activity in porcine epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 6;1001(2):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz P. W., Downing D. T. Glycolipids in mammalian epidermis: structure and function in the water barrier. Science. 1982 Sep 24;217(4566):1261–1262. doi: 10.1126/science.7112128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K., Schreiner E. Epidermal lysosomes. Electron microscopic-cytochemical studies. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Mar;101(3):276–286. doi: 10.1001/archderm.101.3.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley H. J., Summerly R. Lipid composition and metabolism in normal and diseased epidermis. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;13(2):357–383. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90006-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]