Abstract
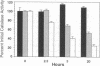
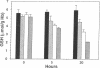
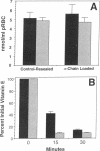
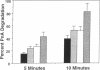
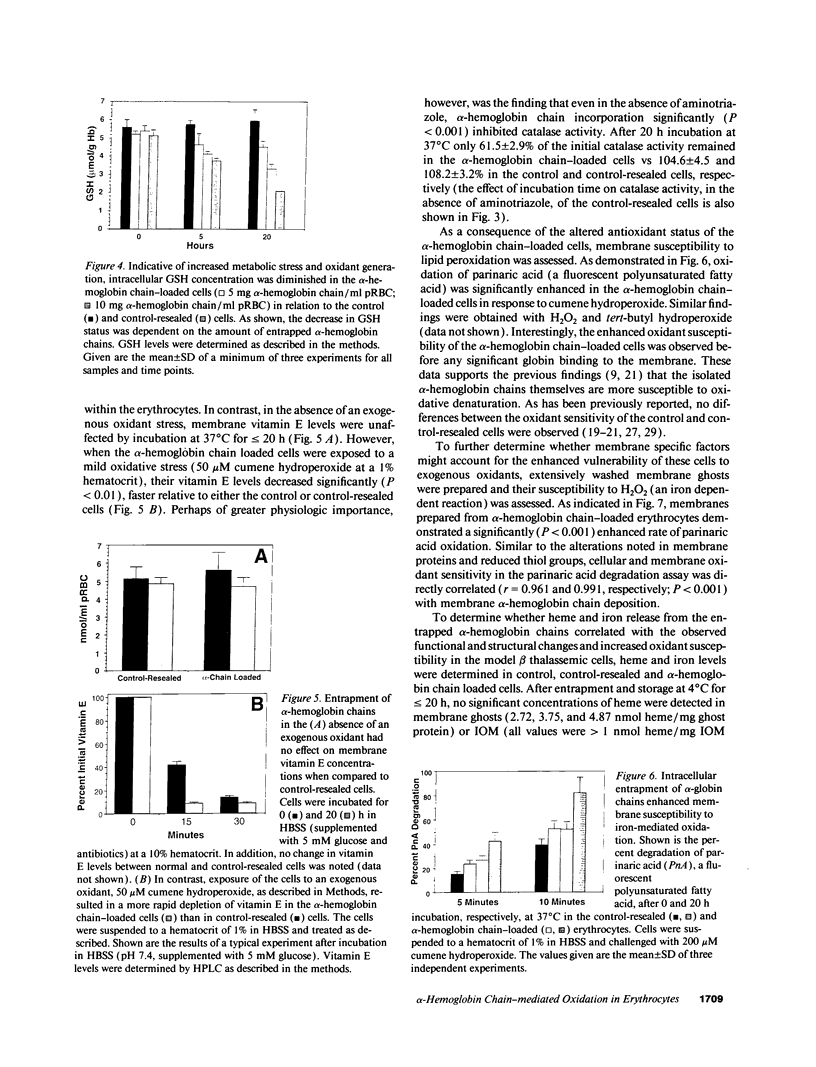
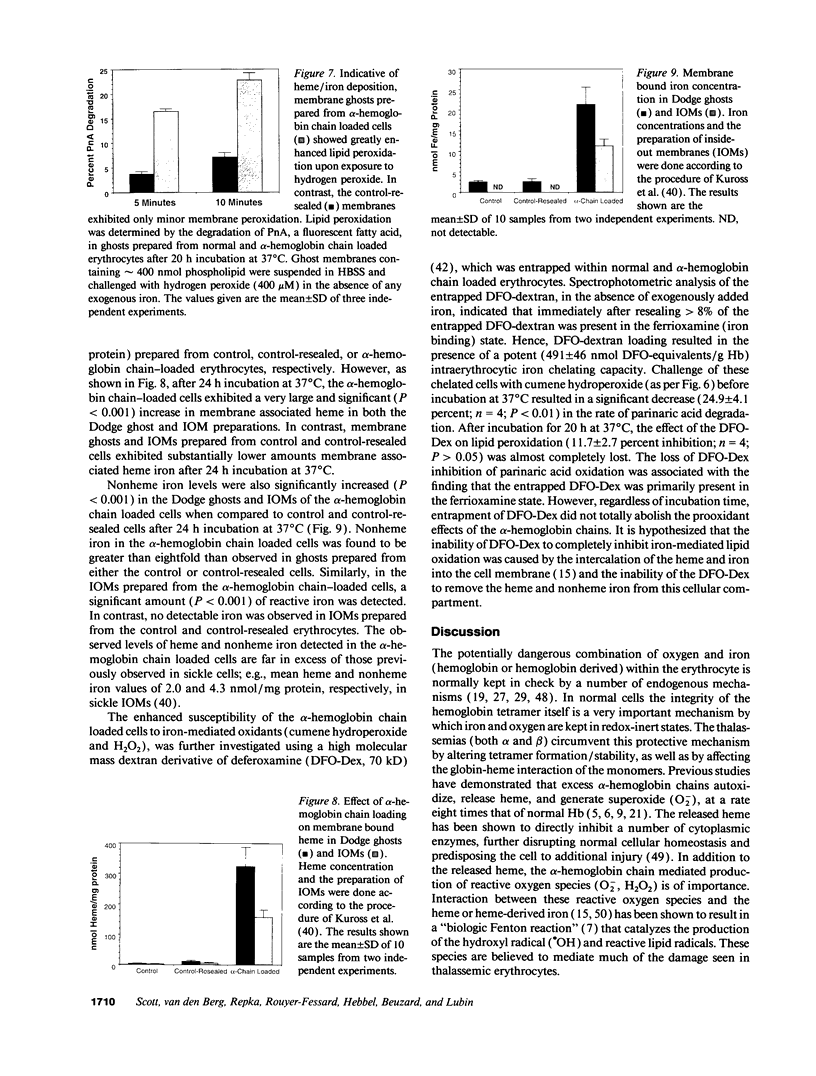
While red cells from individuals with beta thalassemias are characterized by evidence of elevated in vivo oxidation, it has not been possible to directly examine the relationship between excess alpha-hemoglobin chains and the observed oxidant damage. To investigate the oxidative effects of unpaired alpha-hemoglobin chains, purified alpha-hemoglobin chains were entrapped within normal erythrocytes. These "model" beta-thalassemic cells generated significantly (P < 0.001) greater amounts of methemoglobin and intracellular hydrogen peroxide than did control cells. This resulted in significant time-dependent decreases in the protein concentrations and reduced thiol content of spectrin and ankyrin. These abnormalities correlated with the rate of alpha-hemoglobin chain autoxidation and appearance of membrane-bound globin. In addition, alpha-hemoglobin chain loading resulted in a direct decrease (38.5%) in catalase activity. In the absence of exogenous oxidants, membrane peroxidation and vitamin E levels were unaltered. However, when challenged with an external oxidant, lipid peroxidation and vitamin E oxidation were significantly (P < 0.001) enhanced in the alpha-hemoglobin chain-loaded cells. Membrane bound heme and iron were also significantly elevated (P < 0.001) in the alpha-hemoglobin chain-loaded cells and lipid peroxidation could be partially inhibited by entrapment of an iron chelator. In contrast, chemical inhibition of cellular catalase activity enhanced the detrimental effects of entrapped alpha-hemoglobin chains. In summary, entrapment of purified alpha-hemoglobin chains within normal erythrocytes significantly enhanced cellular oxidant stress and resulted in pathological changes characteristic of thalassemic cells in vivo. This model provides a means by which the pathophysiological effects of excess alpha-hemoglobin chains can be examined.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham E. C., Reese A., Stallings M., Huisman T. H. Separation of human hemoglobins by DEAE-cellulose chromatography using glycine-KCN-NaC1 developers. Hemoglobin. 1976;1(1):27–44. doi: 10.3109/03630267609031020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn H. F., Jandl J. H. Exchange of heme among hemoglobins and between hemoglobin and albumin. J Biol Chem. 1968 Feb 10;243(3):465–475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttriss J. L., Diplock A. T. High-performance liquid chromatography methods for vitamin E in tissues. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:131–138. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G., HOCHSTEIN P. GENERATION OF HYDROGEN PEROXIDE IN ERYTHROCYTES BY HEMOLYTIC AGENTS. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:895–900. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorléac E., Morlé L., Gentilhomme O., Jaccoud P., Baudonnet C., Delaunay J. Thalassemia-like abnormalities of the red cell membrane in hemoglobin E trait and disease. Am J Hematol. 1984 Apr;16(3):207–217. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830160302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerli G. C., Beretta L., Bianchi M., Pellegatta A., Agostoni A. Erythrocyte superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase activities in beta-thalassaemia (major and minor). Scand J Haematol. 1980 Jul;25(1):87–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1981.tb01370.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallaway P. E., Eaton J. W., Panter S. S., Hedlund B. E. Modulation of deferoxamine toxicity and clearance by covalent attachment to biocompatible polymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10108–10112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi W., Leb L., Piotrowski J., Fortier N., Snyder L. M. Increased sensitivity of isolated alpha subunits of normal human hemoglobin to oxidative damage and crosslinkage with spectrin. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Jul;102(1):46–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Shifter A., Rachmilewitz E. A. Cross-linking of red blood cell membrane proteins induced by oxidative stress in beta thalassemia. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jan 15;85(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80470-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazian H. H., Jr, Boehm C. D. Molecular basis and prenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuross S. A., Hebbel R. P. Nonheme iron in sickle erythrocyte membranes: association with phospholipids and potential role in lipid peroxidation. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1278–1285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuross S. A., Rank B. H., Hebbel R. P. Excess heme in sickle erythrocyte inside-out membranes: possible role in thiol oxidation. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):876–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers F. A., van den Berg J. J., Schalkwijk C., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A. Parinaric acid as a sensitive fluorescent probe for the determination of lipid peroxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Sep 25;921(2):266–274. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy-Viard K., Rouyer-Fessard P., Beuzard Y. Improvement of mouse beta-thalassemia by recombinant human erythropoietin. Blood. 1991 Sep 15;78(6):1596–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIASH E., NOVOGRODSKY A., SCHEJTER A. Irreversible reaction of 3-amino-1:2:4-triazole and related inhibitors with the protein of catalase. Biochem J. 1960 Feb;74:339–348. doi: 10.1042/bj0740339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puppo A., Halliwell B. Formation of hydroxyl radicals from hydrogen peroxide in the presence of iron. Is haemoglobin a biological Fenton reagent? Biochem J. 1988 Jan 1;249(1):185–190. doi: 10.1042/bj2490185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON A. R., ROBSON M., HARRISON A. P., ZUELZER W. W. A new technique for differentiation of hemoglobin. J Lab Clin Med. 1957 Nov;50(5):745–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz E. A., Shohet S. B., Lubin B. H. Lipid membrane peroxidation in beta-thalassemia major. Blood. 1976 Mar;47(3):495–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rank B. H., Carlsson J., Hebbel R. P. Abnormal redox status of membrane-protein thiols in sickle erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1531–1537. doi: 10.1172/JCI111857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouyer-Fessard P., Garel M. C., Domenget C., Guetarni D., Bachir D., Colonna P., Beuzard Y. A study of membrane protein defects and alpha hemoglobin chains of red blood cells in human beta thalassemia. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19092–19098. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Magarian C., Borun T. W. Resolution of hemoglobin subunits by electrophoresis in acid urea polyacrylamide gels containing Triton X-100. Anal Biochem. 1978 Apr;85(2):506–518. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadrzadeh S. M., Graf E., Panter S. S., Hallaway P. E., Eaton J. W. Hemoglobin. A biologic fenton reagent. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14354–14356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Eaton J. W., Kuypers F. A., Chiu D. T., Lubin B. H. Enhancement of erythrocyte superoxide dismutase activity: effects on cellular oxidant defense. Blood. 1989 Nov 15;74(7):2542–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Kuypers F. A., Butikofer P., Bookchin R. M., Ortiz O. E., Lubin B. H. Effect of osmotic lysis and resealing on red cell structure and function. J Lab Clin Med. 1990 Apr;115(4):470–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Lubin B. H., Zuo L., Kuypers F. A. Erythrocyte defense against hydrogen peroxide: preeminent importance of catalase. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Jul;118(1):7–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Ranz A., Kuypers F. A., Lubin B. H., Meshnick S. R. Parasite uptake of desferroxamine: a prerequisite for antimalarial activity. Br J Haematol. 1990 Aug;75(4):598–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Rouyer-Fessard P., Ba M. S., Lubin B. H., Beuzard Y. Alpha- and beta-haemoglobin chain induced changes in normal erythrocyte deformability: comparison to beta thalassaemia intermedia and Hb H disease. Br J Haematol. 1992 Apr;80(4):519–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1992.tb04567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Rouyer-Fessard P., Lubin B. H., Beuzard Y. Entrapment of purified alpha-hemoglobin chains in normal erythrocytes. A model for beta thalassemia. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17953–17959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Zuo L., Lubin B. H., Chiu D. T. NADPH, not glutathione, status modulates oxidant sensitivity in normal and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-deficient erythrocytes. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):2059–2064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinar E., Rachmilewitz E. A., Lux S. E. Differing erythrocyte membrane skeletal protein defects in alpha and beta thalassemia. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):404–410. doi: 10.1172/JCI113898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinar E., Shalev O., Rachmilewitz E. A., Schrier S. L. Erythrocyte membrane skeleton abnormalities in severe beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):158–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar L. A., Hudson B. S., Simoni R. D. Conjugated polyene fatty acids as fluorescent probes: synthetic phospholipid membrane studies. Biochemistry. 1977 Mar 8;16(5):819–828. doi: 10.1021/bi00624a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stump D. D., Roth E. F., Jr, Gilbert H. S. Simultaneous determination by high-performance liquid chromatography of tocopherol isomers, alpha-tocopheryl quinone, and cholesterol in red blood cells and plasma. J Chromatogr. 1984 Mar 9;306:371–376. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80901-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg J. J., Kuypers F. A., Qju J. H., Chiu D., Lubin B., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A. The use of cis-parinaric acid to determine lipid peroxidation in human erythrocyte membranes. Comparison of normal and sickle erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 15;944(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90313-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vatanavicharn S., Anuwatanakulchai M., Yenchitsomanus P., Siddhikol C. Relationship of serum vitamin E, erythrocyte nonheme iron, and malonyldialdehyde (lipid membrane peroxidation product) in thalassemia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1987;23(5A):207–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vigi V., Volpato S., Gaburro D., Conconi F., Bargellesi A., Pontremoli S. The correlation between red-cell survival and excess of alpha-globin synthesis in beta-thalassemia. Br J Haematol. 1969 Jan-Feb;16(1):25–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherall D. J., Clegg J. B. Thalassemia revisited. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):7–9. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winterbourn C. C. Oxidative reactions of hemoglobin. Methods Enzymol. 1990;186:265–272. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)86118-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerez C. R., Hseih J. W., Tanaka K. R. Inhibition of red blood cell enzymes by hemin: a mechanism for hemolysis in hemoglobinopathies. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1987;100:329–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van KAMPEN E., ZIJLSTRA W. G. Standardization of hemoglobinometry. II. The hemiglobincyanide method. Clin Chim Acta. 1961 Jul;6:538–544. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(61)90145-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg J. J., Kuypers F. A., Lubin B. H., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A. Direct and continuous measurement of hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress on the membrane of intact erythrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 1991;11(3):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(91)90121-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg J. J., Kuypers F. A., Roelofsen B., Op den Kamp J. A. The cooperative action of vitamins E and C in the protection against peroxidation of parinaric acid in human erythrocyte membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1990 Mar;53(4):309–320. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(90)90028-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]