Abstract
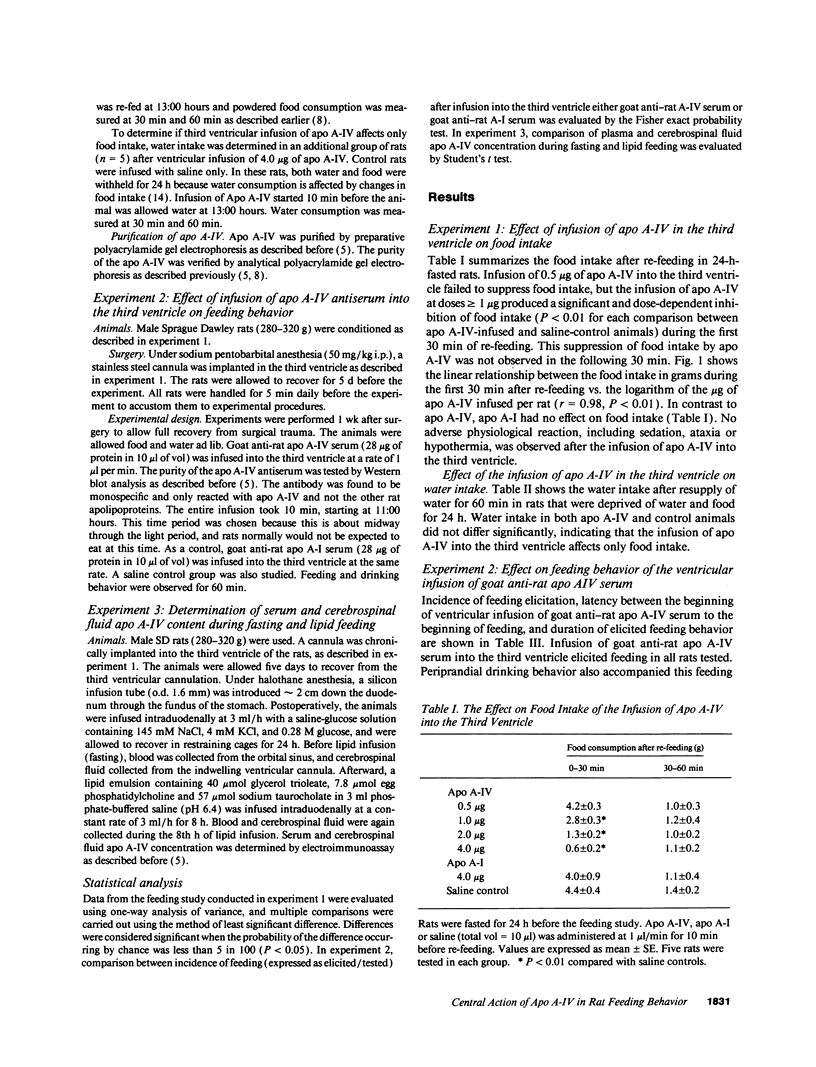
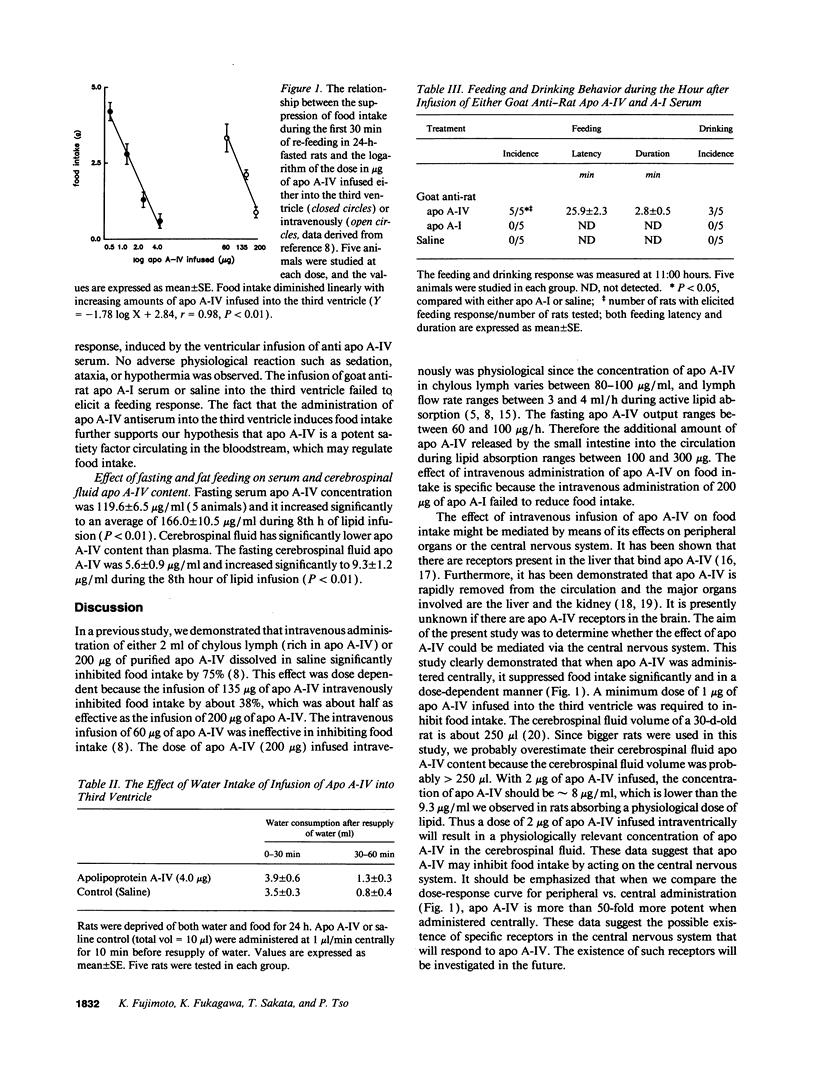
The aim of this experiment was to investigate whether the anorectic effect of apolipoprotein A-IV (apo A-IV) after lipid feeding is mediated via the central nervous system. Infusion of 0.5 micrograms of apo A-IV into the third ventricle failed to suppress food intake. Higher doses (1 micrograms or higher) of apo A-IV infused into the third ventricle inhibited food intake in a dose-dependent manner. In contrast, when apo A-I was infused into the third ventricle it had no effect on food intake. To further test the hypothesis that apo A-IV is an important factor controlling food intake, we administered goat anti-rat apo A-IV serum into the third ventricle of rats that were allowed food and water and lib. In all rats tested, this treatment resulted in enhanced food intake. In contrast, infusion of goat anti-rat apo A-IV serum failed to elicit such a response. Lastly, we determined the apo A-IV concentration in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid before and during active lipid absorption. Apo A-IV concentration in cerebrospinal fluid was about 1/20 that of plasma. Both serum and cerebrospinal fluid apo A-IV increased markedly as a result of feeding of lipid. In conclusion, we propose that apo A-IV may act centrally to control food intake.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apfelbaum T. F., Davidson N. O., Glickman R. M. Apolipoprotein A-IV synthesis in rat intestine: regulation by dietary triglyceride. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):G662–G666. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1987.252.5.G662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass N. H., Lundborg P. Postnatal development of bulk flow in the cerebrospinal fluid system of the albino rat: clearance of carboxyl-( 14 C)inulin after intrathecal infusion. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 30;52:323–332. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90668-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., Elshourbagy N., Taylor J. M., Gordon J. I. Rat apolipoprotein A-IV contains 13 tandem repetitions of a 22-amino acid segment with amphipathic helical potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray G. A., York D. A., Fisler J. S. Experimental obesity: a homeostatic failure due to defective nutrient stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Vitam Horm. 1989;45:1–125. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60393-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallinga-Thie G. M., Van 't Hooft F. M., Van Tol A. Tissue sites of degradation of high density lipoprotein apolipoprotein A-IV in rats. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 May-Jun;6(3):277–284. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorin E., Gorder N. L., Benson D. M., Gotto A. M., Jr Apolipoprotein A-IV. A determinant for binding and uptake of high density lipoproteins by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15714–15718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Boguski M. S., Liao W. S., Jefferson L. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Expression of rat apolipoprotein A-IV and A-I genes: mRNA induction during development and in response to glucocorticoids and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto K., Sakata T., Ookuma K., Kurokawa M., Yamatodani A., Wada H. Hypothalamic histamine modulates adaptive behavior of rats at high environmental temperature. Experientia. 1990 Mar 15;46(3):283–285. doi: 10.1007/BF01951767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukagawa K., Sakata T., Yoshimatsu H., Fujimoto K., Shiraishi T. Disruption of light-dark cycle of feeding and drinking behavior, and ambulatory activity induced by development of obesity in the Zucker rat. Int J Obes. 1988;12(5):481–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Crump W. L., 3rd, Gotto A. M., Jr Binding of apoA-IV-phospholipid complexes to plasma membranes of rat liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 29;139(1):122–128. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Crump W. L., 3rd, Musanti R., Sherrill B. C., Gotto A. M., Jr Metabolism of apolipoprotein A-IV in rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 6;1006(1):26–34. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90319-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths E. C., Kelly J. A. Mechanisms of inactivation of hypothalamic regulatory hormones. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Apr;14(1):3–17. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambrook J. M., Morgan B. A., Rance M. J., Smith C. F. Mode of deactivation of the enkephalins by rat and human plasma and rat brain homogenates. Nature. 1976 Aug 26;262(5571):782–783. doi: 10.1038/262782a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Nutting D. F., Fujimoto K., Cardelli J. A., Black D., Tso P. Transport of lipid and apolipoproteins A-I and A-IV in intestinal lymph of the rat. J Lipid Res. 1990 Sep;31(9):1613–1625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause B. R., Sloop C. H., Castle C. K., Roheim P. S. Mesenteric lymph apolipoproteins in control and ethinyl estradiol-treated rats: a model for studying apolipoproteins of intestinal origin. J Lipid Res. 1981 May;22(4):610–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novin D., Rogers R. C., Hermann G. Visceral afferent and efferent connections in the brain. Diabetologia. 1981 Mar;20 (Suppl):331–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oomura Y., Yoshimatsu H. Neural network of glucose monitoring system. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1984 May-Jun;10(3-4):359–372. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(84)90033-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata T., Fukushima M., Tsutsui K., Arase K., Fujimoto K. Theophylline disrupts diurnal rhythms of humoral factors with loss of meal cyclicity. Physiol Behav. 1982 Apr;28(4):641–647. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(82)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman J. R., Weinberg R. B. Serum apolipoprotein A-IV and lipoprotein cholesterol in patients undergoing total parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology. 1988 Aug;95(2):394–401. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90496-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaney J. B., Braithwaite F., Eder H. A. Characterization of the apolipoproteins of rat plasma lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1977 Jan 25;16(2):271–278. doi: 10.1021/bi00621a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso P., Buch K. L., Balint J. A., Rodgers J. B. Maximal lymphatic triglyceride transport rate from the rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1982 Apr;242(4):G408–G415. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.242.4.G408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso P. Gastrointestinal digestion and absorption of lipid. Adv Lipid Res. 1985;21:143–186. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024921-3.50011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



