Abstract
Blood low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and triglyceride levels are risk factors for cardiovascular disease. To dissect the polygenic basis of these traits, we conducted genome-wide association screens in 19,840 individuals and replication in up to 20,623 individuals. We identified 30 distinct loci associated with lipoprotein concentrations (each with P < 5 × 10-8), including 11 loci that reached genome-wide significance for the first time. The 11 newly defined loci include common variants associated with LDL cholesterol near ABCG8, MAFB, HNF1A and TIMD4; with HDL cholesterol near ANGPTL4, FADS1-FADS2-FADS3, HNF4A, LCAT, PLTP and TTC39B; and with triglycerides near AMAC1L2, FADS1-FADS2-FADS3 and PLTP. The proportion of individuals exceeding clinical cut points for high LDL cholesterol, low HDL cholesterol and high triglycerides varied according to an allelic dosage score (P < 10-15 for each trend). These results suggest that the cumulative effect of multiple common variants contributes to polygenic dyslipidemia.
Recent genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have localized common DNA sequence variants that contribute to many human phenotypes1. The success of this approach has been particularly notable for blood lipoprotein levels. We and others recently reported that at least 19 genetic loci harbor common DNA sequence variants associated with blood LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and/or triglycerides2-6. Those loci consist of genes previously shown to affect lipoprotein metabolism in humans, as well as eight loci that were newly reported at the time. However, each variant conferred a modest effect, and together, the variants explained only a small fraction (~5%) of interindividual variability in lipoprotein levels. These observations suggested that additional loci harboring lipid-associated DNA sequence variants could be identified with larger samples and improved statistical power for gene discovery.
RESULTS
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies
We conducted a meta-analysis of seven GWASs of blood lipoprotein and lipid phenotypes, and we conducted follow-up replication analyses for up to five additional studies (Table 1; see Supplementary Fig. 1 online for study design). The Framingham Heart Study (FHS), a prospective epidemiologic cohort established in 1948, represents the largest stage 1 sample7. Among the three generations of FHS participants who have been enrolled, we focused on second- and third-generation participants with fasting blood lipid phenotypes8,9. The power of the sample was indicated by the observation that for each of eight SNPs recently associated with lipid levels (near SORT1 for LDL cholesterol; MMAB-MVK and GALNT2 for HDL cholesterol; and GCKR, TRIB1, MLXIPL, NCAN and ANGPTL3 for triglycerides), association results in the FHS confirmed our earlier reports (P < 0.05; Supplementary Table 1 online)3,4. Replication consisted of the same allele at the same SNP associated in the same direction.
Table 1. Study design and participant characteristics.
| Design | Stage 1 GWASs | Stage 2 replication studies | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study | FHSa | LOLIPOP | SUVIMAX | InCHIANTI | DGI | FUSION | SardiNIA | MDC-CCb | FINRISK97b | FUSION Stage 2b | METSIMb | ISISb |
| n | 7,423 | 1,050 | 1,551 | 1,132 | 2,626 | 1,874 | 4,184 | 5,519 | 7,940 | 2,224 | 3,764 | 2,497 |
| Ascertainment scheme |
Community-based cohort |
Community-based cohort |
Community-based cohort |
Community-based cohort |
Cases, type 2 diabetes; controls, diabetes free |
Cases, type 2 diabetes; controls, diabetes free |
Community-based cohort |
Community-based cohort |
Population-based cohort |
Cases, type 2 diabetes; controls, diabetes free |
Community-based cohort |
Cases, myocardial infarction; controls, myocardial infarction free |
| Genotyping platform | Affymetrix 5.0, supplemental 50K | Affymetrix 5.0c | Illumina 317K | Illumina 550K | Affymetrix 5.0 | Illumina 317K | Affymetrix 5.0 | Sequenom, TaqMan | Sequenom | Sequenom | Sequenom | TaqMan |
| No. directly genotyped SNPs | 432,815 | 374,773 | 294,882 | 484,115 | 398,878 | 304,581 | 356,359 | 66 | 60 | 52 | 52 | 45 |
| No. imputed SNPs | 2,435,180 | 2,451,793 | 2,490,255 | 2,461,089 | 2,361,966 | 2,477,862 | 2,252,558 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Country of origind | US | UK | France | Italy | Sweden, Finland | Finland | Italy | Sweden | Finland | Finland | Finland | UK |
| Fasting lipids | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yese | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Nof |
| Mean age, years | 38 ± 10 | 52 ± 10 | 50 ± 6 | 68 ± 16 | 62 ± 11 | 61 ± 10 | 43 ± 17 | 58 ± 6 | 50 ± 13 | 59 ± 8 | 59 ± 6 | 50 ± 9 |
| Female gender, % | 53 | 18 | 62 | 56 | 51 | 45 | 56 | 59 | 50 | 40 | 0 | 38 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dl |
193 ± 37 | 215 ± 40 | 221 ± 31 | 213 ± 40 | 227 ± 44 | 223 ± 41 | 208 ± 42 | 239 ± 42 | 214 ± 21 | 226 ± 45 | 215 ± 37 | 225 ± 45 |
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dl |
119 ± 34 | 135 ± 34 | 137 ± 32 | 132 ± 35 | 151 ± 40 | 142 ± 36 | 127 ± 36 | 161 ± 38 | 135 ± 36 | 131 ± 35 | 138 ± 32 | 137 ± 37 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dl |
53 ± 15 | 53 ± 14 | 64 ± 15 | 56 ± 15 | 50 ± 13 | 53 ± 16 | 64 ± 15 | 53 ± 14 | 54 ± 14 | 55 ± 16 | 58 ± 16 | 47 ± 13 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dl |
107 ± 91 | 143 ± 119 | 91 ± 39 | 123 ± 75 | 146 ± 104 | 145 ± 91 | 86 ± 60 | 122 ± 71 | 133 ± 93 | 137 ± 80 | 127 ± 99 | 162 ± 115g |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 26.0 ± 5.0 | 27.6 ± 5.1 | 23.6 ± 3.2 | 27.1 ± 4.2 | 27.6 ± 4.2 | 28.3 ± 4.5 | 25.0 ± 4.7 | 25.8 ± 3.9 | 26.7 ± 4.5 | 28.5 ± 5.0 | 27.0 ± 4.1 | 25.6 ± 4.1 |
| Individuals with diabetes mellitus, % | 2.4 | 7.9 | 0.8 | 7.8 | 49.3 | 41.3 | 2.3 | 8.4 | 3.5 | 43.5 | 11.6 | 3.6 |
Values with ‘±’ are means ± s.d. To convert values for cholesterol to mM, multiply by 0.02586. To convert values for triglycerides to mM, multiply by 0.01129. Body mass index is weight (kg) divided by square of height (m).
Participant characteristics from baseline examination of second and third generations (1971-1975 and 2001-2005, respectively) are provided.
Total number of individuals with phenotype and at least one successful genotype is presented. Exact number of individuals for each SNP varied from the number presented because of exclusions and genotyping failures.
627 individuals were genotyped using Affymetrix 5.0, and 423 using a customized genome-wide array designed and genotyped by Perlegen Sciences.
All individuals studied were of self-reported European ancestry.
In FINRISK97, individuals were instructed to fast for at least 4 h, with mean fasting time of 6 ± 4 h.
Blood samples were nonfasting. For cases, LDL and HDL cholesterol were directly measured and analyzed; triglycerides were not analyzed. For controls free of myocardial infarction, all three lipid phenotypes were directly measured on nonfasting samples.
Triglyceride values are based only on controls free of myocardial infarction.
To the FHS data for 7,423 individuals, we added GWAS data for 3,733 individuals of European ancestry from the London Life Sciences Prospective Population Cohort (LOLIPOP), Supplémentation en Vitamines et Minéraux Antioxydants (SUVIMAX) and Invecchiare in Chianti (InCHIANTI) studies (Supplementary Methods online) and 8,684 individuals from our previous studies of the Diabetes Genetics Initiative (DGI)2,3, Finland-United States Investigation of NIDDM Genetics (FUSION)4 and SardiNIA Study of Aging (SardiNIA)4 samples, to bring the total stage 1 sample size to 19,840 individuals (Supplementary Fig. 1).
We used genotyped SNPs from each study and phased chromosomes from the HapMap sample of Utah residents with ancestry from northern and western Europe (CEU) to impute autosomal SNPs with minor allele frequency >1%. A total of ~2.6 million SNPs that were directly genotyped or imputed were tested for association with lipoprotein traits. Association statistics for each marker from each of the seven studies were combined using a weighted z statistic-based meta-analysis4. Genomic control parameters for the meta-analysis of the stage 1 studies were low, at 1.03 for LDL cholesterol, 1.04 for HDL cholesterol and 1.03 for triglycerides, suggesting little residual confounding caused by population stratification or unmodeled relatedness.
In the meta-analysis of seven stage 1 studies, 25 unique loci harbored variants associated with LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol or triglycerides at a significance level of P < 5 × 10-8 (corresponding to P < 0.05 after adjusting for ~1 million independent tests, the estimated GWAS multiple testing burden in individuals of European ancestry10). To evaluate these and other less significantly associated SNPs from stage 1, we genotyped SNPs in a maximum of 20,623 individuals from five stage 2 studies: Malmö Diet and Cancer Study (MDC)11, FINRISK97 (ref. 12), FUSION stage 2 (ref. 13), Metabolic Syndrome in Men (METSIM) and International Study of Infarct Survival (ISIS)14 (Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. 1). These SNPs were selected to focus on loci that had not previously been associated with our lipoprotein phenotypes (see Methods).
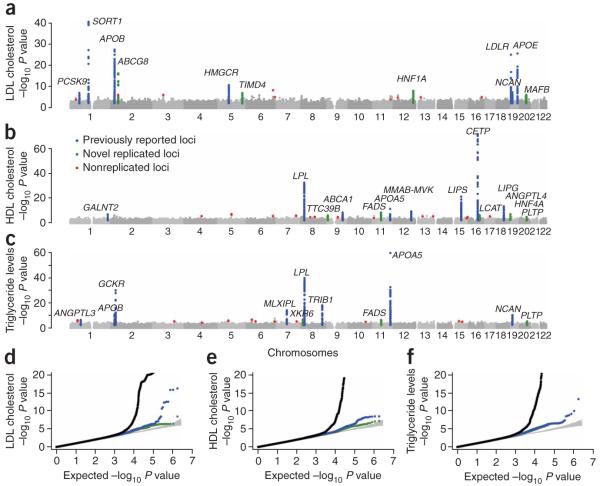
In the analysis including stage 1 and stage 2 studies, SNPs at 30 loci were convincingly associated (P < 5 × 10-8) with LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol or triglycerides, including 11 loci that reached genome-wide significance for the first time (Table 2 and Fig. 1). Each of the loci reached P < 1 × 10-5 in stage 1 and P < 0.05 in stage 2 (Supplementary Table 2 online). The 11 loci definitively identified in this study included genes whose function in humans has previously been studied (ABCG8 (ref. 15); ANGPTL4 (ref. 16); FADS1-FADS2-FADS3 (ref. 17); HNF4A18; LCAT19; PLTP20; and HNF1A (ref. 21)) and genes whose function in humans is poorly understood (TTC39B, TIMD4-HAVCR1, XKR6, AMAC1L2 and MAFB; Fig. 2).
Table 2. Genetic loci where common polymorphisms are associated with blood lipoprotein concentrations.
| FHS effect size estimatesa |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Chr. | SNP | P for combined stage 1 + 2 association | Combined stage 1 + 2 sample size | Associated interval size, kb (no. of genes within interval) | Gene(s) of interest within or near associated interval | Major allele, minor allele (MAF) | Effect size for minor allele (s.e.m.)b |
| Newly identified common SNPsd | ||||||||
| LDL | 2p21 | rs6544713 | 2 × 10-20 | 23,456 | 52 (2) | ABCG8 | C, T (0.32)c | 0.15 (0.02) |
| LDL | 5q23 | rs1501908 | 1 × 10-11 | 27,280 | 153 (2) | TIMD4-HAVCR1 | C, G (0.37) | -0.07 (0.02) |
| LDL | 20q12 | rs6102059 | 4 × 10-9 | 28,895 | 104 (0) | MAFB | C, T (0.32)c | -0.06 (0.02) |
| LDL | 12q24 | rs2650000 | 2 × 10-8 | 39,340 | 112 (3) | HNF1A | C, A (0.36) | 0.07 (0.02) |
| HDL | 11q12 | rs174547 | 2 × 10-12 | 40,330 | 84 (5) | FADS1-FADS2-FADS3 | T, C (0.33) | -0.09 (0.02) |
| HDL | 16q22 | rs2271293 | 9 × 10-13 | 31,946 | 620 (25) | LCAT | G, A (0.11) | 0.07 (0.03) |
| HDL | 9p22 | rs471364 | 3 × 10-10 | 40,414 | 55 (1) | TTC39B | T, C (0.12) | -0.08 (0.03) |
| HDL | 20q13 | rs1800961 | 8 × 10-10 | 30,714 | 24 (1) | HNF4A | C, T (0.03) | -0.19 (0.05) |
| HDL | 20q13 | rs7679 | 4 × 10-9 | 40,248 | 141 (5) | PLTP | T, C (0.19) | -0.07 (0.02) |
| HDL | 19p13 | rs2967605 | 1 × 10-8 | 35,151 | 155 (5) | ANGPTL4 | C, T (0.16)c | -0.12 (0.04) |
| TG | 11q12 | rs174547 | 2 × 10-14 | 38,846 | 84 (5) | FADS1-FADS2-FADS3 | T, C (0.33) | 0.06 (0.02) |
| TG | 20q13 | rs7679 | 7 × 10-11 | 38,561 | 141 (5) | PLTP | T, C (0.19) | 0.07 (0.02) |
| TG | 8p23 | rs7819412 | 3 × 10-8 | 33,336 | 550 (4) | XKR6-AMAC1L2 | A, G (0.48) | -0.04 (0.02) |
| Loci with definitive prior association evidence | ||||||||
| LDL | 1p13 | rs12740374 | 2 × 10-42 | 19,648 | 85 (4) | CELSR2, PSRC1, SORT1 | G, T (0.21)c | -0.23 (0.02) |
| LDL | 2p24 | rs515135 | 5 × 10-29 | 19,648 | 214 (1) | APOB | C, T (0.20)c | -0.16 (0.02) |
| LDL | 19q13 | rs4420638 | 4 × 10-27 | 11,881 | 79 (4) | APOE-APOC1-APOC4-APOC2 | A, G (0.16)c | 0.29 (0.06) |
| LDL | 19p13 | rs6511720 | 2 × 10-26 | 19,648 | 30 (1) | LDLR | G, T (0.10)c | -0.26 (0.04) |
| LDL | 5q13 | rs3846663 | 8 × 10-12 | 19,648 | 476 (4) | HMGCR | C, T (0.38) | 0.07 (0.02) |
| LDL | 19p13 | rs10401969 | 2 × 10-8 | 19,648 | 503 (18) | NCAN, CILP2, PBX4 | T, C (0.06)c | -0.05 (0.04) |
| LDL | 1p32 | rs11206510 | 4 × 10-8 | 19,629 | 16 (1) | PCSK9 | T, C (0.19) | -0.09 (0.02) |
| HDL | 16q13 | rs173539 | 4 × 10-75 | 19,794 | 36 (1) | CETP | C, T (0.32)c | 0.25 (0.02) |
| HDL | 8p21 | rs12678919 | 2 × 10-34 | 19,794 | 126 (1) | LPL | A, G (0.10)c | 0.23 (0.03) |
| HDL | 15q22 | rs10468017 | 8 × 10-23 | 19,794 | 47 (0) | LIPC | C, T (0.30)c | 0.10 (0.02) |
| HDL | 18q21 | rs4939883 | 7 × 10-15 | 19,785 | 128 (1) | LIPG | C, T (0.17) | -0.14 (0.02) |
| HDL | 11q23 | rs964184 | 1 × 10-12 | 19,794 | 138 (3) | APOA1-APOC3-APOA4-APOA5 | C, G (0.14)c | -0.17 (0.03) |
| HDL | 12q24 | rs2338104 | 1 × 10-10 | 19,793 | 315 (5) | MMAB, MVK | G, C (0.45) | -0.07 (0.02) |
| HDL | 9q31 | rs1883025 | 1 × 10-9 | 19,371 | 48 (1) | ABCA1 | C, T (0.26)c | -0.08 (0.02) |
| HDL | 1q42 | rs4846914 | 4 × 10-8 | 19,794 | 53 (1) | GALNT2 | A, G (0.40) | -0.05 (0.02) |
| TG | 11q23 | rs964184 | 4 × 10-62 | 19,840 | 138 (3) | APOA1-APOC3-APOA4-APOA5 | C, G (0.14)c | 0.30 (0.03) |
| TG | 8p21 | rs12678919 | 2 × 10-41 | 19,840 | 126 (1) | LPL | A, G (0.10)c | -0.25 (0.03) |
| TG | 2p23 | rs1260326 | 2 × 10-31 | 19,840 | 465 (22) | GCKR | C, T (0.45)c | 0.12 (0.02) |
| TG | 8q24 | rs2954029 | 3 × 10-19 | 19,840 | 35 (0) | TRIB1 | A, T (0.44)c | -0.11 (0.02) |
| TG | 7q11 | rs714052 | 3 × 10-15 | 19,840 | 254 (5) | MLXIPL | A, G (0.12)c | -0.16 (0.03) |
| TG | 2p24 | rs7557067 | 9 × 10-12 | 19,840 | 149 (1) | APOB | A, G (0.22)c | -0.08 (0.02) |
| TG | 19p13 | rs17216525 | 4 × 10-11 | 19,840 | 448 (15) | NCAN, CILP2, PBX4 | C, T (0.07)c | -0.11 (0.03) |
| TG | 1p31 | rs10889353 | 3 × 10-7 | 19,834 | 305 (3) | ANGPTL3 | A, C (0.33)c | -0.05 (0.02) |
Chr., chromosome; MAF, minor allele frequency.
Effect size and direction from the FHS, the largest of the stage 1 studies, are presented for illustrative purposes. Alleles for the SNP on the forward strand of the human genome reference sequence (NCBI build 36.2) are shown, and the minor allele at each SNP was modeled.
Effect size shown is β-coefficient, which represents change in lipid levels measured in s.d. units (in a sex-stratified analysis after adjustment for age, age2 and ten ancestry-informative principal components) per copy of the allele modeled.
Results for these SNPs are derived from imputed SNP data.
For five of these loci (TIMD4-HAVCR1, MAFB, FADS1-FADS2-FADS3, TTC39B and XKR6-AMAC1L2), there is no prior statistical evidence for association with blood lipoprotein concentrations. For the remaining six, there is at least some modest statistical evidence for common SNPs. For these six loci, we provide definitive evidence for common SNPs.
Figure 1.
Summary of genome-wide association results for LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and triglycerides from stage 1. (a-c) Chromosome number versus -log10 P values for LDL cholesterol (a), HDL cholesterol (b) and triglycerides (c). Green, 11 newly identified loci; blue, previously reported loci; gray, loci not subjected to follow-up; red, loci that did not replicate. (d) Quantile-quantile plot for test statistics, with observed association P values plotted as a function of expected P values. Black line, all test statistics; blue line, 19 previously reported loci excluded; green line, 11 loci confirmed in this study also excluded; gray area, 90% confidence region from a null distribution of P values (generated from 100 simulations). Blue and green lines are superimposed for triglycerides.
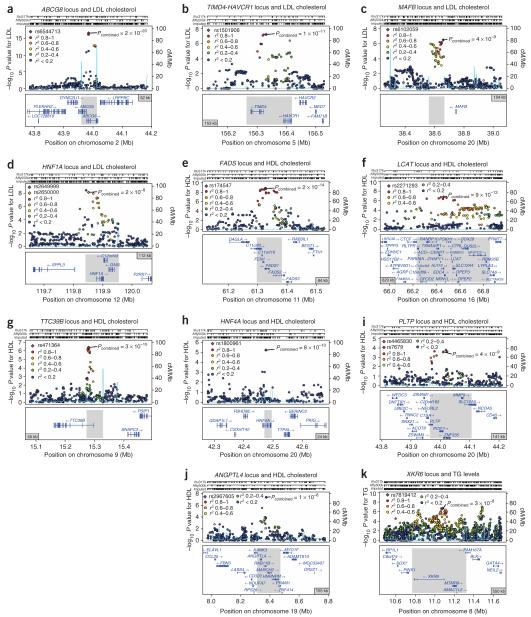
Figure 2.
Regional plots of 11 confirmed associations. (a-k) Association results for SNPs from stage 1 (-log10 P value) as a function of genomic distance (chromosomal position from National Center for Biotechnology Information build hg17) for ABCG8 (a), TIMD4-HAVCR1 (b), MAFB (c), HNF1A (d), FADS1-FADS2-FADS3 (e), LCAT (f), TTC39B (g), HNF4A (h), PLTP (i), ANGPTL4 (j) and XKR6-AMAC1L2 (k). Top three lines show genomic coverage at the locus, with each vertical tick representing directly genotyped (Illumina (Illu317k) or Affymetrix (Affy500k) platforms) or imputed SNPs. Purple diamonds indicate SNP at each locus with the strongest stage 1 association evidence. Each circle represents a SNP, with the color of the circle indicating the correlation between that SNP and the best stage 1 SNP at the locus (purple diamond). Pcombined values indicate association evidence for the SNP based on the combined stage 1 and 2 data. In most cases, the best stage 1 SNP at the locus (purple diamond) was taken forward to stage 2; however, alternate SNPs (red or orange diamonds) were taken forward at two loci (HNF1A and PLTP). Light blue lines indicate estimated recombination hot spots in HapMap. Bottom panel shows genes at each locus as annotated in the UCSC Genome Browser Annotation Database as of August 5, 2007. Gray bar indicates associated interval spanning the SNP taken forward to stage 2. Associated intervals were determined as described in Methods. TG, triglyceride.
We confirmed these 30 association signals in a second round of analysis using a uniform analysis strategy for all studies and an inverse-variance weighted meta-analysis (Supplementary Table 3 online). This analysis also allowed us to test for heterogeneity in effect sizes across studies. No significant evidence for heterogeneity was detected for any of the newly identified loci (Supplementary Tables 4-6 online).
Lipid-associated variants in human liver
The associated SNP at 1 of the 11 new loci was a nonsynonymous coding variant, HNF4A rs1800961 (T130I, 3% frequency), and the remaining 10 new associated SNPs were noncoding. We therefore explored whether lipid-associated variants might influence gene expression as cis-acting regulators of nearby genes. We genotyped DNA and profiled RNA expression of >39,000 transcripts in 957 human liver tissue samples22. We conducted expression quantitative trait locus analyses relating the SNPs in Table 2 with liver transcripts located within 500 kb to either side of the associated SNP (Table 3). Together, the lipoprotein association data and the expression quantitative trait locus analyses highlighted several biological insights.
Table 3. Cis-acting association of validated lipid polymorphisms with transcript levels in human liver.
| Lipid-associated SNP | Lipid trait | Locus | Gene(s) of interest in associated genomic interval | Transcript gene symbol | No. of liver samples | Major, minor alleles for SNP associated with liver transcript level | P for association evidence with liver transcript level | Allele modeled, direction of effect on transcript level, direction of effect on lipid level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs7679 | HDL | 20q13 | PLTP | PLTP | 885 | T, C | 6 × 10-17 | T, +, + |
| TG | T, +, - | |||||||
| rs10468017 | HDL | 15q22 | LIPC | LIPC | 950 | C, T | 2 × 10-18 | T, -, + |
| ALDH1A2 | 943 | C, T | 2 × 10-9 | T, -, + | ||||
| rs174547a | HDL | 11q12 | FADS1-FADS2-FADS3 | FADS1 | 943 | T, C | 5 × 10-35 | T, +, + |
| TG | T, +, - | |||||||
| HDL | FADS3 | 925 | T, C | 1 × 10-8 | T, +, + | |||
| TG | T, +, - | |||||||
| rs471364 | HDL | 9p22 | TTC39B | TTC39B | 955 | T, C | 3 × 10-8 | T, -, + |
| rs12740374b | LDL | 1p13 | CELSR2, PSRC1, SORT1 | SORT1 | 946 | T, C | 4 × 10-272 | T, -, + |
| PSRC1 | T, C | 2 × 10-241 | T, -, + | |||||
| CELSR2 | T, C | 6 × 10-80 | T, -, + | |||||
| rs2338104c | HDL | 12q24 | MMAB, MVK | MMAB | 957 | A, G | 4 × 10-43 | G, -, + |
| rs10889353 | TG | 1p31 | ANGPLT3 | DOCK7 | 952 | A, C | 2 × 10-27 | C, +, - |
| ANGPTL3 | 903 | A, C | 2 × 10-11 | C, +, - |
SNP associated with liver transcript level was rs102275 (r2 = 1 with rs174547 in HapMap CEU).
SNP associated with liver transcript level was rs646776 (r2 = 1 with rs12740374 in HapMap CEU).
SNP associated with liver transcript level was rs2058804 (r2 = 1 with rs2338014 in HapMap CEU).
For example, among five genes at the 20q13 locus for HDL cholesterol and triglycerides, expression of PLTP was associated with rs7679 (P = 6 × 10-17; Table 3). The rs7679 allele associated with higher PLTP transcript levels was also associated with higher HDL cholesterol and lower triglycerides (Tables 2 and 3). This is consistent with prior work in mice showing that Pltp overexpression leads to higher HDL cholesterol23, whereas targeted deletion leads to lower HDL cholesterol24. Consistency between the direction of effect on transcript levels and lipoprotein concentration was also evident at the LIPC locus. In agreement with earlier studies in which lower hepatic lipase activity and higher HDL cholesterol were associated with LIPC promoter variants25, the minor T allele at LIPC rs10468017 was associated with lower LIPC expression in our study (P = 2 × 10-18; Table 2) and increased HDL cholesterol (P = 8 × 10-23; Table 3).
Another strong signal mapped to a cluster of three fatty acid desaturase genes (FADS1-FADS2-FADS3) on 11q12 (Fig. 2e). The cluster showed association with both HDL cholesterol and triglycerides (Table 2), and the expression quantitative trait locus data suggested that the associated SNP modulates expression of FADS1 and FADS3 (Table 3). The allele associated with increased FADS1 and FADS3 expression led to higher HDL cholesterol and lower triglycerides. Fatty acid desaturases convert polyunsaturated fatty acids into cell signaling metabolites, including arachidonic acid. SNPs at this locus have been previously related to levels of arachidonic acid in serum phospholipids and red blood cell plasma membranes17. In addition, dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids—a key substrate for FADS1—are known to lower plasma triglycerides, possibly by decreasing very-low-density lipoprotein secretion26.
At 9p22, an HDL-associated SNP was associated with expression of tetratricopeptide repeat domain 39B (TTC39B; P = 3 × 10-10 for genotype-HDL cholesterol association and P = 3 × 10-8 for genotype-expression association; Fig. 2g and Tables 2 and 3). The allele associated with lower TTC39B transcript levels was also associated with higher HDL cholesterol. Tetratricopeptides, in general, seem to function in protein-protein interactions27, but TTC39B presently has no annotated function in humans.
Genes causing mendelian syndromes harbor common variants
Among the other loci to reach genome-wide significance, ABCG8 and LCAT have been shown to cause mendelian forms of dyslipidemia28,29 (Fig. 2a,f). Loss-of-function mutations at ABCG8 and LCAT lead to sitosterolemia and fish-eye disease, respectively. Common SNPs at ABCG8 and LCAT have been studied for association with plasma LDL and HDL cholesterol, respectively. In our study, common variants at both loci reached genome-wide significance for the first time (Table 2). For example, we found the previously studied ABCG8 D19H variant to be associated with LDL cholesterol (rs11887534, P = 1 × 10-11) and found an even stronger common variant signal, a SNP in intron 2 of ABCG8 (rs6544713, 0.15 s.d. unit change per copy, P = 2 × 10-29; r2 = 0.02 with ABCG8 D19H). Both D19H and a proxy for ABCG8 rs6544713 (rs4299376, r2 = 1) were recently shown to affect risk for cholesterol gallstone disease30; for both the coding and intronic variants, the allele corresponding to lower plasma LDL cholesterol in the present study has been associated with higher risk of gallstones.
The observed signals at ABCG8 and LCAT further strengthen the connection between loci for mendelian dyslipidemic syndromes and those with common variants of modest effect. For at least 11 of the 30 loci in Table 2 (ABCG8, LCAT, APOB, APOE, LDLR, PCSK9, CETP, LPL, LIPC, APOA5 and ABCA1), a biologically relevant lipoprotein gene was implicated by common variants (>5% frequency), low-frequency variants (0.5%-5% frequency) and/or rare mutations (variants unique to individual families).
Another connection between signals identified here and rare mendelian disorders occurred for HNF4A and HNF1A, two causes of maturity-onset diabetes of the young (Fig. 2d,h). Both genes encode hepatic nuclear transcription factors that regulate numerous target genes involved in lipoprotein metabolism, including apolipoproteins, cholesterol synthesis enzymes and bile acid transporters31. Although mice null for either Hnf4a or HNF1A have altered plasma cholesterol levels32,33, there has been only modest evidence to date connecting these genes to either HDL or LDL cholesterol concentrations in humans18,21.
Other validated loci
At ANGPTL4, we found that a common variant (rs2967605, 16% frequency, P = 1 × 10-8 stages 1 and 2) was strongly associated with HDL cholesterol but not in linkage disequilibrium with a previously reported low-frequency variant (ANGPTL4 E40K, 3% frequency, r2 < 0.01 with rs2967605)16. The gene is a strong mechanistic candidate because ANGPTL4 inhibits lipoprotein lipase in mice34.
Among the novel loci, the 8p23 region associated with triglycerides contained one gene of particular interest, AMAC1L2, which encodes acyl-malonyl condensing enzyme 1-like 2 (Fig. 2k) in bacteria, acylmalonyl condensing enzyme catalyzes fatty acid synthesis35. At the 5q23 and 20q12 loci associated with LDL cholesterol, the mechanism of action is less clear. At 5q23, the associated interval spanned two genes, TIMD4 and HAVCR1 (also known as TIMD1; Fig. 2b). TIMD4 and HAVCR1 were recently identified as phosphatidylserine receptors on macrophages that facilitate the engulfment of apoptotic cells36, and HAVCR1 is annotated as a target for the transcription factor TCF1 (ref. 31). At 20q12, the gene nearest to the associated SNP is MAFB (Fig. 2c), a transcription factor shown to interact with LDL-related protein37. How genes at these two loci impact LDL cholesterol remains to be defined.
Specialized lipid phenotypes
To define the full spectrum of phenotypic consequences of lipid variants at 30 distinct loci, we studied the association of each index SNP with 21 specialized lipid phenotypes measured in FHS second-generation participants (Supplementary Table 7 online). These phenotypes included apolipoproteins APOA-I, APOB, APOC-III and APOE; low-, high-, intermediate- and very low-density lipoprotein particle concentrations, as measured by nuclear magnetic resonance; HDL2 and HDL3 cholesterol subfractions after chemical precipitation; lipoprotein(a); and remnant lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides. A visual summary of the patterns of association is provided in Supplementary Figure 2 online. In several cases, we identified stronger signals for specialized phenotypes, suggesting mechanistic hypotheses. For example, the GCKR P446L allele (rs1260326) was associated with increased concentrations of APOC-III (0.20 s.d. unit increase per Leu allele; P = 9 × 10-12), an inhibitor of triglyceride catabolism that is synthesized in the liver38.
For several loci, the strength of statistical evidence did not meet our prespecified threshold of P < 5 × 10-8, but some of these loci may represent true associations. For example, LPA coding SNP rs3798220 (I4399M, 2% minor allele frequency) was associated with LDL cholesterol (P = 3 × 10-7 after stages 1 and 2). In addition, in the FHS, LPA rs3798220 was strongly associated with lipoprotein(a) level (P = 2 × 10-49), with each copy of the minor C allele increasing lipoprotein(a) level by a notable 1.8 s.d. units. These findings strongly replicate a previous observation that 4399M allele carriers have higher lipoprotein(a) concentrations39. This same SNP has also been shown to increase risk for coronary artery disease, with the 4399M allele increasing risk by two- to three-fold39. The association between LPA I4399M and risk for coronary artery disease might be mediated by elevated lipoprotein(a) and LDL cholesterol.
Allelic dosage and polygenic dyslipidemia
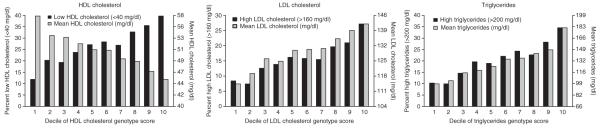
Having identified 30 loci, each with a modest effect, we next asked whether the cumulative allelic dosage of risk alleles at these loci contributes to the quantitative variation in lipoprotein levels seen in the population. We modeled the allelic dosage in each individual in the FHS second generation for the SNPs detailed in Table 2 (see Methods). Mean lipoprotein concentration decreased (for HDL cholesterol) or increased (for LDL cholesterol and triglycerides) in a stepwise fashion across deciles of genotype score (Fig. 3; P < 1 × 10-45 for each trend). The proportion of individuals exceeding clinical thresholds for ‘high’ or ‘low’ lipoprotein levels (HDL cholesterol 160 mg/dl or triglycerides > 200 mg/dl, as defined by the US national cholesterol treatment guidelines40) increased across deciles of genotype score (Fig. 3; P < 1 × 10-15 for each trend).
Figure 3.
Mean lipoprotein concentrations and proportion of individuals with low HDL cholesterol, high LDL cholesterol or high triglycerides, as a function of allelic dosage score for HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, respectively. Deciles of allelic dosage score are plotted on the x axis, and the y axis represents either mean lipoprotein concentrations within that decile (gray bars) or the proportion of individuals within that decile who met clinical criteria for ‘high’ or ‘low’ lipoprotein concentrations (black bars; cut points indicated in keys). Analyses were conducted for the following numbers of FHS second-generation participants: 3,206 for HDL cholesterol, 3,090 for LDL cholesterol and 3,216 for triglycerides. The allelic dosage score comprised 32 SNPs from the 30 loci shown in Table 2. For SNPs associated with HDL cholesterol, we modeled the allele associated with lower HDL cholesterol. For SNPs associated with LDL cholesterol or triglycerides, we modeled the allele associated with higher LDL cholesterol or higher triglycerides. Each of the six trends was highly significant (P < 10-15).
Multiple independent common alleles at a locus
At each of the 30 identified loci, multiple independent common alleles may contribute to trait variation. To identify additional associated common SNPs at these loci, we repeated the genome-wide association analysis in the seven stage 1 studies, including each of the index SNPs in Table 2 as covariates. In contrast to our original meta-analysis, in which >1,000 SNPs at 25 loci reached genome-wide significance (P < 5 × 10-8), only 105 SNPs reached genome-wide significance in this conditional analysis. These SNPs provided evidence for additional HDL association signals in the CETP (peak SNP rs289714, P = 2 × 10-25), LIPC (rs2070895, P = 6 × 10-16) and APOA1-APOC3-APOA4-APOA5 (rs10892044, P = 4 × 10-10) loci; for additional LDL association signals in the APOE-APOC1-APOC4-APOC2 (rs1985096, P = 7 × 10-17), LDLR (rs2738446, P = 1 × 10-11) and ABCG8 (rs4953023, P = 4 × 10-8) loci; and for additional triglyceride signals in the LPL locus (rs894210, P = 1 × 10-10). After combining the seven SNPs representing these independent signals with those listed in Table 2, the proportion of variance explained in each trait was 9.3% for HDL cholesterol, 7.7% for LDL cholesterol and 7.4% for triglycerides.
DISCUSSION
Using a GWAS and large-scale replication, we have convincingly mapped 30 loci that contribute to variation in lipoprotein concentrations in humans. These results suggest regions of the genome that should be sequenced fully, as well as several new directions for functional investigation and potential clinical applications.
Sequencing the positional candidate genes within the associated intervals can help define the full spectrum of alleles that contribute to lipoprotein concentrations and, in some cases, identify null alleles that can provide clues to the in vivo consequences of loss of function41. PCSK9, for example, was initially identified using linkage mapping, and rare mutations with large effects (>100 mg/dl effect size) were described42. Subsequent sequencing of PCSK9 revealed low-frequency variants with more modest effects (such as PCSK9 R46L, 1% frequency, ~16 mg/dl effect size)43. The same group found nonsense mutations in African-Americans, which proved that loss of PCSK9 function increases LDL cholesterol41. In our study and a previous one4, PCSK9 also harbored a common variant with an even more modest effect (19% frequency, ~3 mg/dl effect size). Thus, other genes identified in our common variant screen may harbor low-frequency variants and/or rare mutations that cause mendelian syndromes. Deep sequencing of the new loci in population-based samples and dyslipidemic families will be required to test these hypotheses.
Experimental manipulation of positional candidate genes in mice is an alternate approach to define the consequences of gain or loss of function. A variety of genetic techniques have been used to study lipoprotein-related genes in animal models and cell culture. Because lipoprotein metabolism is driven in large part by processes occurring in the liver, delivery of genetic modifiers by vectors that are preferentially taken up by liver can allow for analysis of the effects of genes on lipid traits. For example, multiple groups have overexpressed PCSK9 in wild-type mouse liver through tail vein injections of recombinant adenoviruses bearing the gene44-46; plasma LDL cholesterol was significantly higher in mice receiving the PCSK9 vectors compared to mice receiving control vectors. Our work provides several new targets (TTC39B, for example) for such functional investigation.
Ultimately, with a full collection of DNA sequence variants in hand, we may be able to test the hypothesis that these variants can help to identify individuals at risk for cardiovascular disease and to better target preventive interventions. As lipid genotypes have been shown to add incremental information beyond plasma lipoprotein measurements47,48, an allelic dosage score may allow for early identification and treatment of at-risk individuals, before atherosclerosis becomes advanced. Proving this hypothesis will require rigorous testing in randomized clinical trials.
METHODS
Stage 1 study samples, phenotypes and genotyping
A full description of each of the seven stage 1 studies is presented in Supplementary Methods. In each study, LDL cholesterol was calculated using the Friedewald formula, with missing values assigned to individuals with triglycerides >400 mg/dl. Individuals known to be on lipid-lowering therapy were excluded from association analysis for LDL cholesterol in all studies except the FHS. In the FHS, we imputed the untreated LDL cholesterol values using an algorithm described previously49.
All participants provided informed consent. Local ethical committees at each participating institution approved the individual study protocols. The institutional review boards at Boston Medical Center, Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the University of Michigan approved this study.
Stage 1 genome-wide association analyses
In the FHS, we modeled phenotypes in the following manner. We log-transformed triglyceride levels. To account for potential confounding by population substructure within the FHS sample (Americans of European ancestry), we used EIGENSTRAT software to define principal components of ancestry. We inferred SNP weights for each principal component using a subset of unrelated FHS individuals (n = 882) and then computed the principal component values for all others using the estimates obtained from the unrelated subset. The first two principal components showed gradients similar to those previously reported in individuals of European ancestry (northwest, southeast and Ashkenazi Jewish; Supplementary Fig. 3 online). Several principal components were associated with LDL cholesterol, so we adjusted for ten principal components in regression modeling.
For the second and third generations separately, we created sex-specific residual lipoprotein concentrations after regression adjustment for age, age2 (age squared) and ten ancestry-informative principal components (mean age across multiple visits and the square of this mean age were used for second-generation participants). We standardized residuals to have a mean of 0 and s.d. of 1. These generation- and sex-specific residual lipoprotein concentrations served as the phenotypes in genotype-phenotype association analysis. Each directly genotyped SNP was tested for association with lipid residuals, assuming an additive mode of inheritance. To account for relatedness among two generations of participants, we used linear mixed-effects models that specified a fixed genotypic effect, a random polygenic effect allowing for residual heritability and a variance-covariance structure accounting for familial correlations50. The genomic control parameters in FHS were low, at 1.01, 1.03 and 1.02 (for LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and triglycerides, respectively).
In the SUVIMAX, LOLIPOP and InCHIANTI GWASs, lipoprotein concentrations were adjusted for the effects of sex, age and age2. The SUVIMAX and LOLIPOP samples did not include related individuals and were analyzed using linear regression. The InCHIANTI GWAS included a small number of related individuals and was analyzed using a variance component-based score test that models background additive polygenic effects. In each case, an additive model was used to model SNP effects.
Stage 1 imputation and meta-analysis for directly genotyped and imputed SNPs
Details of imputation and meta-analysis are described in Supplementary Methods.
Stage 2 study samples, phenotypes and genotyping
Replication of promising association signals from stage 1 was attempted in up to 20,623 independent participants from five stage 2 studies (Table 1). Fasting lipid concentrations were available in each stage 2 study except ISIS; individuals known to be on lipid-lowering therapy were excluded. The ISIS study participants were examined in the early 1990s, before lipid-lowering therapies became common, so no exclusion based on drug therapy was necessary.
SNPs were genotyped using either the iPLEX Sequenom MassARRAY platform or allelic discrimination on an ABI 7900 instrument (Applied Biosystems). All genotyped SNPs had a genotyping call rate >95% on the replication samples and had a Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium P > 0.001.
We tested for association in each replication study using linear regression adjusting for covariates as follows: age, age2, sex and diabetes status for the MDC Cardiovascular Cohort (MDC-CC); age, age2 and sex for FINRISK97; age, age2, sex, birth province in Finland and study group with analysis stratified according to diabetes status for FUSION stage 2; age, age2 and diabetes status for METSIM; and age, age2, sex, sex × age and sex × age2 with analysis stratified according to myocardial infarction status for ISIS.
The statistical evidence from each stage 2 sample was combined with the evidence from stage 1 using the fixed-effects z-statistic meta-analysis procedure described above. A combined P < 5 × 10-8 was deemed significant based on an estimated multiple testing burden equivalent to ~1 million independent common variants10.
SNP selection for stage 2 genotyping
We took forward SNPs into stage 2 primarily on the basis of P value in stage 1 after excluding SNPs from the 19 loci that had prior definitive association evidence3,4. We selected a set of apparently independent SNPs by excluding SNPs with r2 > 0.2 or within a distance of 1 Mb from other SNPs selected for follow-up genotyping. We successfully genotyped and attempted, respectively, 66 and 70 SNPs in MDC-CC, 60 and 64 SNPs in FINRISK97, 52 and 55 SNPs in FUSION stage 2, 52 and 53 SNPs in METSIM and 45 and 50 SNPs in ISIS. Different SNP lists were genotyped in each study according to cost, constraints on the design of multiplex assays and timing of SNP selections (some SNPs were selected based on interim meta-analyses).
Variance-weighted meta-analysis
As an additional analysis, we applied a uniform analysis strategy to all sample sets to estimate regression coefficients (measuring association between each SNP and lipid levels) and their corresponding standard errors and combined regression coefficients across samples using an inverse variance-weighted meta-analysis (Supplementary Methods).
Definition of associated interval
For each index SNP in Table 2, we defined the associated interval by first determining the set of HapMap SNPs in linkage disequilibrium of r2 > 0.5 with the most significantly associated SNP. We then bounded the associated interval by the flanking HapMap recombination hotspots. These windows were likely to contain the causal polymorphisms explaining the associations.
Specialized lipoprotein-related phenotypes, cis-expression quantitative trait locus analyses and genotype score analysis in the FHS
Details for these are described in the Supplementary Methods.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The FHS authors thank the FHS participants for their long-term voluntary commitment to this study. The FHS is supported by a contract from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI; contract no. N01-HC-25195). The NHLBI’s SNP Health Association Resource research program supported the FHS genotyping. J.M.O. is supported by NHLBI grant HL-54776 and by contracts 53-K06-5-10 and 58-1950-9-001 from the US Department of Agriculture Research Service.
The DGI and MDC-CC authors thank R. Saxena, P.I. de Bakker, V. Lyssenko, M. Daly, J. Hirschhorn, S. Gabriel, H. Chen, T. Hughes, the entire DGI study team and the Botnia Study team for their roles in sample collection, phenotyping, design and conduct of the DGI study; and M. Svenson and L. Rosberg for technical assistance in Malmö. S.K. is supported by a Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Scientist Development Award, a charitable gift from the Fannie E. Rippel Foundation, the Donovan Family Foundation, a career development award from the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) and institutional support from the Department of Medicine and Cardiovascular Research Center at Massachusetts General Hospital. L.G. is supported by the Sigrid Juselius Foundation, the Finnish Diabetes Research Foundation, The Folkhalsan Research Foundation and Clinical Research Institute HUCH Ltd. His work in Malmö, Sweden, was also funded by a Linné grant from the Swedish Medical Research Council. M.O.-M. is supported by a European Foundation for the Study of Diabetes-Pfizer grant and the Novo Nordic Foundation. M.O.-M. and O.M. are supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council, the Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation, the Medical Faculty of Lund University, Malmö University Hospital, the Albert Påhlsson Research Foundation and the Crafoord Foundation. O.M. is also supported by the Swedish Medical Society, the Ernhold Lundströms Research Foundation, the Mossfelt Foundation, the King Gustav V and Queen Victoria Foundation and the Region Skane.
The FUSION and METSIM authors thank the Finnish citizens who generously participated in these studies. Support for FUSION was provided by NIH grants DK062370 (to M.B.) and DK072193 (to K.L.M.), intramural project number 1Z01 HG000024 (to F.S.C.) and a postdoctoral fellowship award from the American Diabetes Association (to C.J.W.). K.L.M. is a Pew Scholar for the Biomedical Sciences. Genome-wide genotyping was conducted by the Johns Hopkins University Genetic Resources Core Facility SNP Center at the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR), with support from CIDR NIH contract no. N01-HG-65403. Support for METSIM was provided by grant 124243 from the Academy of Finland (to M.L.).
The SardiNIA authors thank the many volunteers who generously participated in these studies. This work was supported in part by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Aging and by extramural grants from the National Human Genome Research Institute (HG02651) and the NHLBI (HL084729). Additional support was provided by the mayors, administrations and residents of Lanusei, Ilbono, Arzana and Elini and the head of Public Health Unit ASL4 in Sardinia. G.R.A. is a Pew Scholar for the Biomedical Sciences. FINRISK97 author L.P. is supported by the Center of Excellence in Complex Disease Genetics of the Academy of Finland and the Nordic Center of Excellence in Disease Genetics. V.S. was supported by the Sigrid Juselius Foundation and the Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research.
The ISIS trials and epidemiological studies were supported by the manufacturers of the study drugs and by the British Heart Foundation, Medical Research Council, Cancer Research UK, Tobacco Products Research Trust of the UK Department of Health Independent Scientific Committee on Smoking and Health, and the Oxford Genetics Knowledge Park.
Footnotes
URLs. Association results of our meta-analysis of seven GWASs, http://www.sph.umich.edu/csg/abecasis/public/lipids2008/; Markov chain haplotyping package, http://www.sph.umich.edu/csg/abecasis/MACH; METAL meta-analysis tool for GWASs, http://www.sph.umich.edu/csg/abecasis/Metal/index.html; EIGENSTRAT method for population stratification correction, http://genepath.med.harvard.edu/~reich/Software.htm.
References
- 1.Manolio TA, Brooks LD, Collins FSA. HapMap harvest of insights into the genetics of common disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2008;118:1590–1605. doi: 10.1172/JCI34772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Diabetes Genetics Initiative of Broad Institute of Harvard and MIT. Lund University. Novartis Institutes Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride levels. Science. 2007;316:1331–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.1142358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kathiresan S, et al. Six new loci associated with blood low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides in humans. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:189–197. doi: 10.1038/ng.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Willer CJ, et al. Newly identified loci that influence lipid concentrations and risk of coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:161–169. doi: 10.1038/ng.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wallace C, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies genes for biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: serum urate and dyslipidemia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2008;82:139–149. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sandhu MS, et al. LDL-cholesterol concentrations: a genome-wide association study. Lancet. 2008;371:483–491. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60208-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kannel WB, Dawber TR, Kagan A, Revotskie N, Stokes J., III Factors of risk in the development of coronary heart disease-six year follow-up experience. The Framingham Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1961;55:33–50. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-55-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kannel WB, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Garrison RJ, Castelli WP. An investigation of coronary heart disease in families. The Framingham offspring study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1979;110:281–290. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Splansky GL, et al. The Third Generation Cohort of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Framingham Heart Study: design, recruitment, and initial examination. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007;165:1328–1335. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwm021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Pe’er I, Yelensky R, Altshuler D, Daly MJ. Estimation of the multiple testing burden for genomewide association studies of nearly all common variants. Genet. Epidemiol. 2008;32:381–385. doi: 10.1002/gepi.20303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Berglund G, Elmstahl S, Janzon L, Larsson SA. The Malmo Diet and Cancer Study. Design and feasibility. J. Intern. Med. 1993;233:45–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1993.tb00647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Vartiainen E, et al. Cardiovascular risk factor changes in Finland, 1972-1997. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2000;29:49–56. doi: 10.1093/ije/29.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Scott LJ, et al. A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science. 2007;316:1341–1345. doi: 10.1126/science.1142382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.ISIS-3 (Third International Study of Infarct Survival) Collaborative Group ISIS-3. a randomised comparison of streptokinase vs tissue plasminogen activator vs anistreplase and of aspirin plus heparin vs aspirin alone among 41,299 cases of suspected acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1992;339:753–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kajinami K, Brousseau ME, Nartsupha C, Ordovas JM, Schaefer EJ. ATP binding cassette transporter G5 and G8 genotypes and plasma lipoprotein levels before and after treatment with atorvastatin. J. Lipid Res. 2004;45:653–656. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M300278-JLR200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Romeo S, et al. Population-based resequencing of ANGPTL4 uncovers variations that reduce triglycerides and increase HDL. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:513–516. doi: 10.1038/ng1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schaeffer L, et al. Common genetic variants of the FADS1 FADS2 gene cluster and their reconstructed haplotypes are associated with the fatty acid composition in phospholipids. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15:1745–1756. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ek J, et al. The functional Thr130Ile and Val255Met polymorphisms of the hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha (HNF4A): gene associations with type 2 diabetes or altered beta-cell function among Danes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005;90:3054–3059. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-2159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pare G, et al. Genetic analysis of 103 candidate genes for coronary artery disease and associated phenotypes in a founder population reveals a new association between endothelin-1 and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;80:673–682. doi: 10.1086/513286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Spirin V, et al. Common single-nucleotide polymorphisms act in concert to affect plasma levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007;81:1298–1303. doi: 10.1086/522497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hegele RA, et al. The private hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha G319S variant is associated with plasma lipoprotein variation in Canadian Oji-Cree. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000;20:217–222. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.20.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schadt EE, et al. Mapping the genetic architecture of gene expression in human liver. PLoS Biol. 2008;6:e107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0060107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jiang X, et al. Increased prebeta-high density lipoprotein, apolipoprotein AI, and phospholipid in mice expressing the human phospholipid transfer protein and human apolipoprotein AI transgenes. J. Clin. Invest. 1996;98:2373–2380. doi: 10.1172/JCI119050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jiang XC, et al. Targeted mutation of plasma phospholipid transfer protein gene markedly reduces high-density lipoprotein levels. J. Clin. Invest. 1999;103:907–914. doi: 10.1172/JCI5578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Isaacs A, Sayed-Tabatabaei FA, Njajou OT, Witteman JC, van Duijn CM. The - 514C->T hepatic lipase promoter region polymorphism and plasma lipids: a meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004;89:3858–3863. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-0188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Phillipson BE, Rothrock DW, Connor WE, Harris WS, Illingworth DR. Reduction of plasma lipids, lipoproteins, and apoproteins by dietary fish oils in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985;312:1210–1216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505093121902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Blatch GL, Lassle M. The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. Bioessays. 1999;21:932–939. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199911)21:11<932::AID-BIES5>3.0.CO;2-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Berge KE, et al. Accumulation of dietary cholesterol in sitosterolemia caused by mutations in adjacent ABC transporters. Science. 2000;290:1771–1775. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5497.1771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Funke H, et al. A molecular defect causing fish eye disease: an amino acid exchange in lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) leads to the selective loss of alpha-LCAT activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1991;88:4855–4859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Buch S, et al. A genome-wide association scan identifies the hepatic cholesterol transporter ABCG8 as a susceptibility factor for human gallstone disease. Nat. Genet. 2007;39:995–999. doi: 10.1038/ng2101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Odom DT, et al. Control of pancreas and liver gene expression by HNF transcription factors. Science. 2004;303:1378–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.1089769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hayhurst GP, Lee YH, Lambert G, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (nuclear receptor 2A1) is essential for maintenance of hepatic gene expression and lipid homeostasis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001;21:1393–1403. doi: 10.1128/MCB.21.4.1393-1403.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shih DQ, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha is an essential regulator of bile acid and plasma cholesterol metabolism. Nat. Genet. 2001;27:375–382. doi: 10.1038/86871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yoshida K, Shimizugawa T, Ono M, Furukawa H. Angiopoietin-like protein 4 is a potent hyperlipidemia-inducing factor in mice and inhibitor of lipoprotein lipase. J. Lipid Res. 2002;43:1770–1772. doi: 10.1194/jlr.c200010-jlr200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Toomey RE, Wakil SJ. Studies on the mechanism of fatty acid synthesis. XVI. Preparation and general properties of acyl-malonyl acyl carrier protein-condensing enzyme from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1966;241:1159–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Miyanishi M, et al. Identification of Tim4 as a phosphatidylserine receptor. Nature. 2007;450:435–439. doi: 10.1038/nature06307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Petersen HH, et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein interacts with MafB, a regulator of hindbrain development. FEBS Lett. 2004;565:23–27. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.03.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Aalto-Setala K, et al. Mechanism of hypertriglyceridemia in human apolipoprotein (apo) CIII transgenic mice. Diminished very low density lipoprotein fractional catabolic rate associated with increased apo CIII and reduced apo E on the particles. J. Clin. Invest. 1992;90:1889–1900. doi: 10.1172/JCI116066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Luke MM, et al. A polymorphism in the protease-like domain of apolipoprotein(a) is associated with severe coronary artery disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007;27:2030–2036. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.141291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Executive summary of the third report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) JAMA. 2001;285:2486–2497. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.19.2486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cohen J, et al. Low LDL cholesterol in individuals of African descent resulting from frequent nonsense mutations in PCSK9. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:161–165. doi: 10.1038/ng1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Abifadel M, et al. Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia. Nat. Genet. 2003;34:154–156. doi: 10.1038/ng1161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kotowski IK, et al. A spectrum of PCSK9 alleles contributes to plasma levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006;78:410–422. doi: 10.1086/500615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Maxwell KN, Fisher EA, Breslow JL. Overexpression of PCSK9 accelerates the degradation of the LDLR in a post-endoplasmic reticulum compartment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2005;102:2069–2074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409736102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Park SW, Moon YA, Horton JD. Post-transcriptional regulation of low density lipoprotein receptor protein by proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9a in mouse liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:50630–50638. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410077200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Benjannet S, et al. NARC-1/PCSK9 and its natural mutants: zymogen cleavage and effects on the low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor and LDL cholesterol. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:48865–48875. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M409699200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cohen JC, Boerwinkle E, Mosley TH, Jr, Hobbs HH. Sequence variations in PCSK9, low LDL, and protection against coronary heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:1264–1272. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa054013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kathiresan S, et al. Polymorphisms associated with cholesterol and risk of cardiovascular events. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;358:1240–1249. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0706728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kathiresan S, et al. A genome-wide association study for blood lipid phenotypes in the Framingham Heart Study. BMC Med. Genet. 2007;8(Suppl 1):S17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-S1-S17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lange K, Boehnke M. Extensions to pedigree analysis. IV. Covariance components models for multivariate traits. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1983;14:513–524. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320140315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.