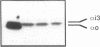Abstract
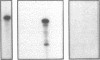
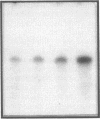
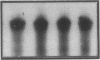
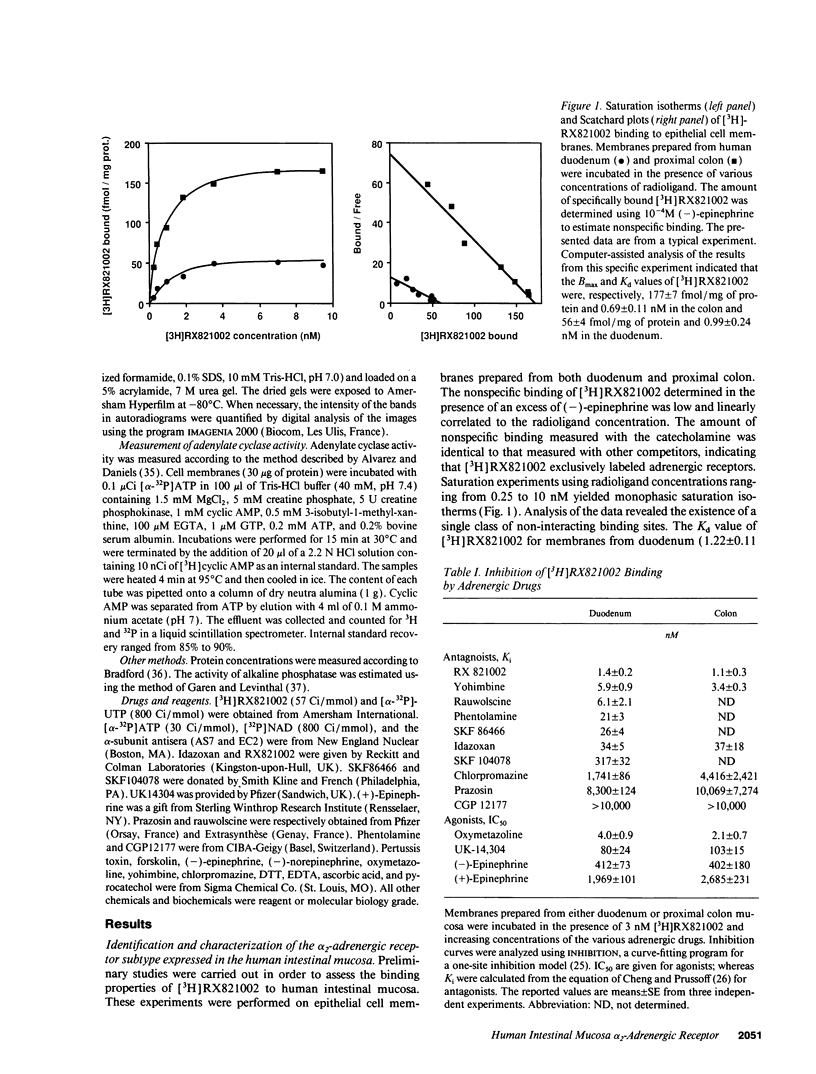
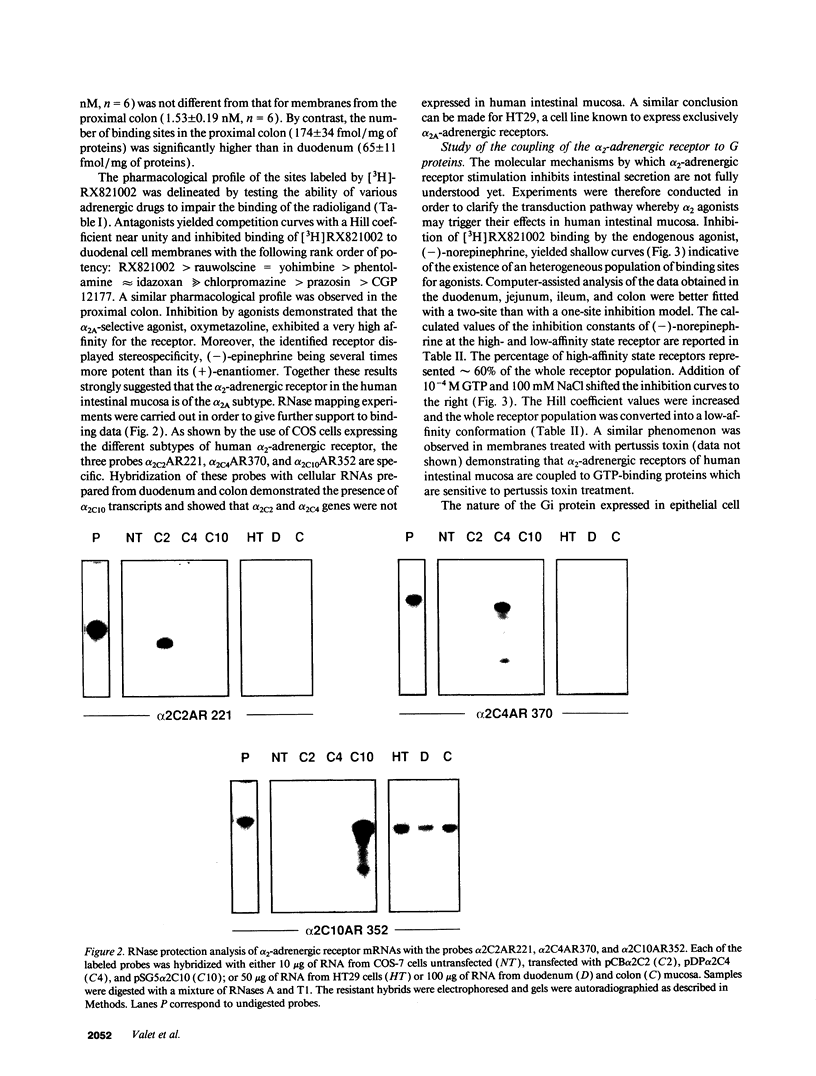
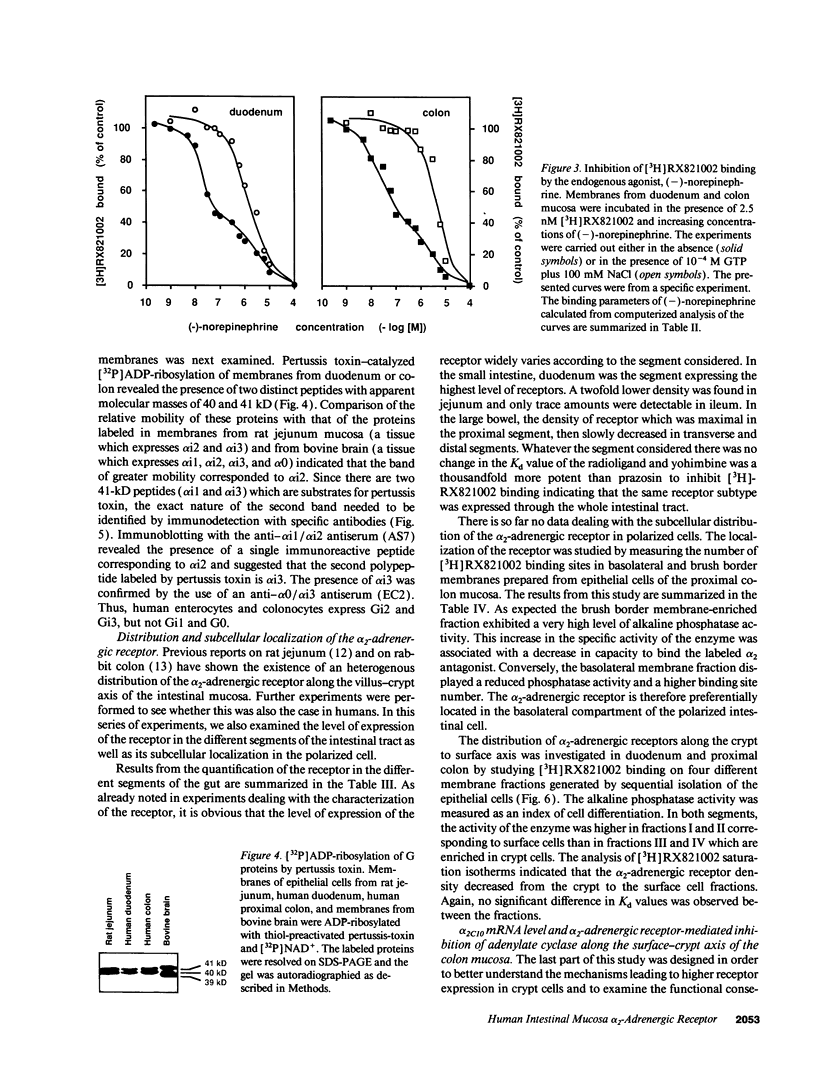
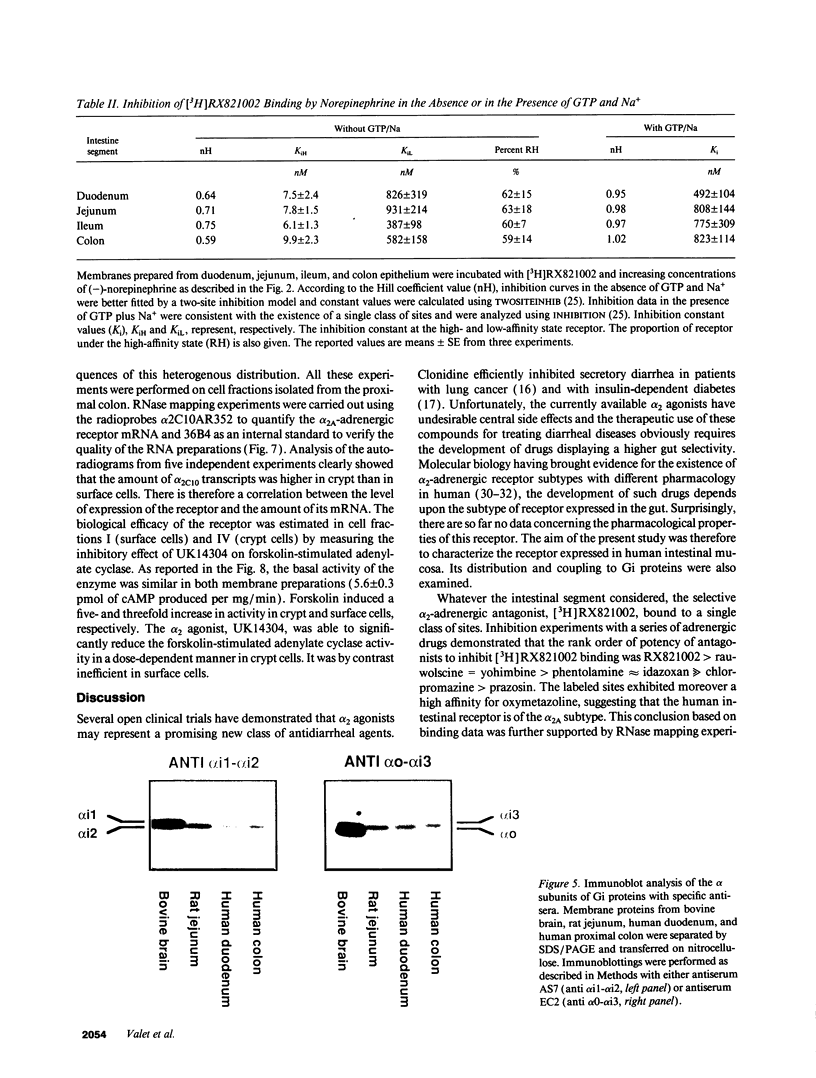
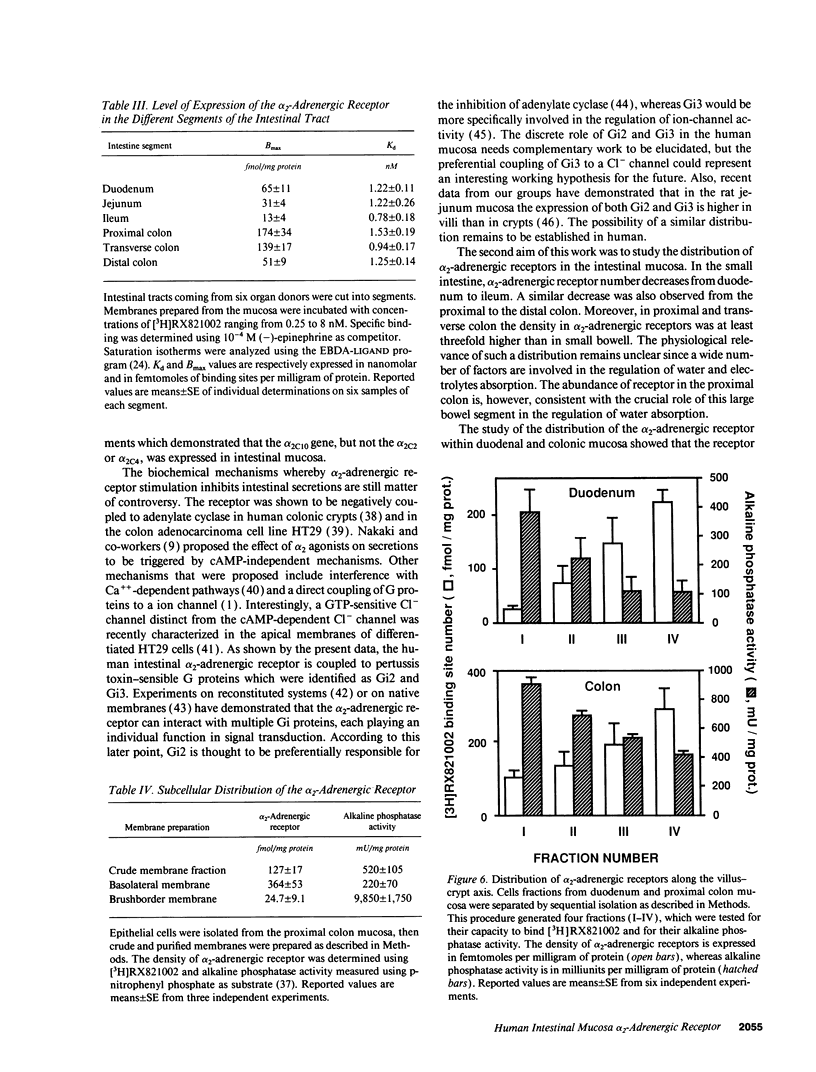
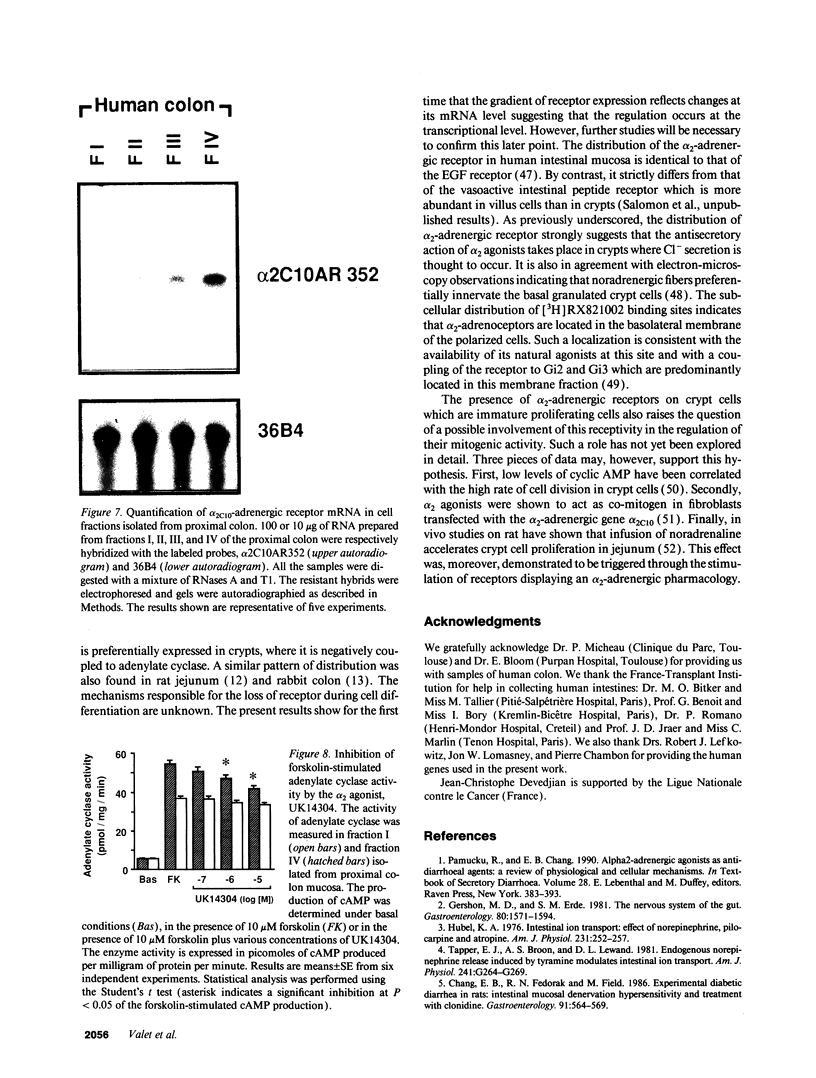
The subtype and the expression of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor were investigated in the normal mucosa from human intestine by means of radioligand binding, RNase mapping, and measurement of adenylate cyclase activity. The study of the binding of the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist, [3H]RX821002, to epithelial cell membranes indicated the existence of a single class of noninteracting sites displaying a high affinity for the radioligand (Kd = 1.1 +/- 0.5 nM). The rank order of potency of antagonists to inhibit [3H]RX821002 binding (RX821002 > yohimbine = rauwolscine > phentolamine approximately idazoxan >> chlorpromazine > prazosin) suggested that the receptor is of the alpha 2A subtype. A conclusion which is confirmed by the fact that only alpha 2C10 transcripts were found in the human intestine mucosa. Competition curves with (-)-norepinephrine demonstrated that 60% of the receptor population exhibited high affinity for agonists. This high-affinity state was abolished by the addition of GTP plus Na+ or by prior treatment of the membranes with pertussis toxin indicating it corresponded to G protein-coupled receptors. [32P]ADP-ribosylation and immunoblotting experiments identified two pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins corresponding to Gi2 and Gi3. The study of the distribution of the receptor indicated that (a) the proximal colon is the intestine segment exhibiting the highest receptor density and (b) the receptor is predominantly expressed in crypts and is preferentially located in the basolateral membrane of the polarized cell. The distribution of the receptor along the crypt-surface axis of the colon mucosa can be correlated with a higher level of alpha 2C10-specific mRNA and a higher efficiency of UK14304 to inhibit adenylate cyclase in crypt cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez R., Daniels D. V. A single column method for the assay of adenylate cyclase. Anal Biochem. 1990 May 15;187(1):98–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90423-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Stow J. L., Cantiello H. F., de Almeida J. B., Benos D. J. Purified epithelial Na+ channel complex contains the pertussis toxin-sensitive G alpha i-3 protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4759–4765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boige N., Munck A., Laburthe M. Adrenergic versus VIPergic control of cyclic AMP in human colonic crypts. Peptides. 1984 Mar-Apr;5(2):379–383. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90238-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouscarel B., Cortinovis C., Carpene C., Murat J. C., Paris H. alpha 2-Adrenoceptors in the HT 29 human colon adenocarcinoma cell line: characterization with [3H]clonidine; effects on cyclic AMP accumulation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jan 2;107(2):223–231. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptors: pharmacological and molecular biological evidence converge. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Oct;9(10):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. B., Fedorak R. N., Field M. Experimental diabetic diarrhea in rats. Intestinal mucosal denervation hypersensitivity and treatment with clonidine. Gastroenterology. 1986 Sep;91(3):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. B., Field M., Miller R. J. Enterocyte alpha 2-adrenergic receptors: yohimbine and p-aminoclonidine binding relative to ion transport. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):G76–G82. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.244.1.G76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang E. B., Field M., Miller R. J. alpha 2-Adrenergic receptor regulation of ion transport in rabbit ileum. Am J Physiol. 1982 Mar;242(3):G237–G242. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1982.242.3.G237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotterell D. J., Munday K. A., Poat J. A. The binding of [3H]prazosin and [3H]clonidine to rat jejunal epithelial cell membranes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 1;33(5):751–756. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couvineau A., Darmoul D., Blais A., Rouyer-Fessard C., Daviaud D., Voisin T., Paris H., Rouot B., Laburthe M. Gs and Gi protein subunits during cell differentiation in intestinal crypt-villus axis: regulation at the mRNA level. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):C1478–C1484. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.6.C1478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox H. M., Cuthbert A. W. Antisecretory activity of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, xylazine in rat jejunal epithelium. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;339(6):669–674. doi: 10.1007/BF00168660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Cyclic nucleotide metabolism in rat colonic epithelial cells with different proliferative activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 17;676(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devedjian J. C., Fargues M., Denis-Pouxviel C., Daviaud D., Prats H., Paris H. Regulation of the alpha 2A-adrenergic receptor in the HT29 cell line. Effects of insulin and growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14359–14366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmsathaphorn K. Alpha 2-adrenergic agonists: a newer class of antidiarrheal drug. Gastroenterology. 1986 Sep;91(3):769–770. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90650-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiJoseph J. F., Taylor J. A., Mir G. N. Alpha-2 receptors in the gastrointestinal system: a new therapeutic approach. Life Sci. 1984 Sep 3;35(10):1031–1042. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorak R. N., Field M., Chang E. B. Treatment of diabetic diarrhea with clonidine. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Feb;102(2):197–199. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-2-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., McColl I. Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. 3. Effects of catecholamines. Am J Physiol. 1973 Oct;225(4):852–857. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.4.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon M. D., Erde S. M. The nervous system of the gut. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jun;80(6):1571–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homburger V., Brabet P., Audigier Y., Pantaloni C., Bockaert J., Rouot B. Immunological localization of the GTP-binding protein Go in different tissues of vertebrates and invertebrates. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Apr;31(4):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubel K. A. Intestinal ion transport: effect of norepinephrine, pilocarpine, and atropine. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jul;231(1):252–257. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.1.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurose H., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Functional interactions of recombinant alpha 2 adrenergic receptor subtypes and G proteins in reconstituted phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3335–3341. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laburthe M., Amiranoff B., Boissard C. Alpha-Adrenergic inhibition of cyclic AMP accumulation in epithelial cells isolated from rat small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 13;721(1):101–108. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laburthe M., Chenut B., Rouyer-Fessard C., Tatemoto K., Couvineau A., Servin A., Amiranoff B. Interaction of peptide YY with rat intestinal epithelial plasma membranes: binding of the radioiodinated peptide. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):1910–1917. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-1910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Allen L. F., King K., Regan J. W., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Expansion of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor family: cloning and characterization of a human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype, the gene for which is located on chromosome 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5094–5098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McArthur K. E., Anderson D. S., Durbin T. E., Orloff M. J., Dharmsathaphorn K. Clonidine and lidamidine to inhibit watery diarrhea in a patient with lung cancer. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Mar;96(3):323–325. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-3-323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Carr C., Gould G. W., Mullaney I., Lavan B. E. Agonist-dependent, cholera toxin-catalyzed ADP-ribosylation of pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins following transfection of the human alpha 2-C10 adrenergic receptor into rat 1 fibroblasts. Evidence for the direct interaction of a single receptor with two pertussis toxin-sensitive G-proteins, Gi2 and Gi3. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6447–6455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ménard D., Pothier P. Radioautographic localization of epidermal growth factor receptors in human fetal gut. Gastroenterology. 1991 Sep;101(3):640–649. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90520-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Nakadate T., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptor in intestinal epithelial cells. Identification by [3H]yohimbine and failure to inhibit cyclic AMP accumulation. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;23(1):228–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newson B., Ahlman H., Dahlström A., Das Gupta T. K., Nyhus L. M. On the innervation of the ileal mucosa in the rat--a synapse. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Mar;105(3):387–389. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb06357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris H., Taouis M., Galitzky J. In vitro study of alpha 2-adrenoceptor turnover and metabolism using the adenocarcinoma cell line HT29. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Nov;32(5):646–654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paris H., Voisin T., Remaury A., Rouyer-Fessard C., Daviaud D., Langin D., Laburthe M. Alpha-2 adrenoceptor in rat jejunum epithelial cells: characterization with [3H]RX821002 and distribution along the villus-crypt axis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Sep;254(3):888–893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Kobilka B. K. Cloning and expression of a human kidney cDNA for an alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6301–6305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro-Neto F. A., Mattera R., Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Field J. B., Birnbaumer L., Sekura R. D. ADP-ribosylation of membrane components by pertussis and cholera toxin. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:566–572. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09115-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio M. C., Bellocq J. P., Gairard B., Rasmussen U. B., Krust A., Koehl C., Calderoli H., Schiff V., Renaud R., Chambon P. Specific expression of the pS2 gene in subclasses of breast cancers in comparison with expression of the estrogen and progesterone receptors and the oncogene ERBB2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9243–9247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J., Preiser H., Maestracci D., Ghosh B. K., Cerda J. J., Crane R. K. Purification of the human intestinal brush border membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 27;323(1):98–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senard J. M., Langin D., Estan L., Paris H. Identification of alpha 2-adrenoceptors and non-adrenergic idazoxan binding sites in rabbit colon epithelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 20;191(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94096-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seuwen K., Magnaldo I., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Regan J. W., Lefkowitz R. J., Pouysségur J. Alpha 2-adrenergic agonists stimulate DNA synthesis in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts transfected with a human alpha 2-adrenergic receptor gene. Cell Regul. 1990 May;1(6):445–451. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.6.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Goldsmith P. K., Codina J., Unson C. G., Spiegel A. M. Gi2 mediates alpha 2-adrenergic inhibition of adenylyl cyclase in platelet membranes: in situ identification with G alpha C-terminal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7809–7813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sénard J. M., Mauriège P., Daviaud D., Paris H. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor in HT29 human colon adenocarcinoma cell-line: study of [3H](-)-adrenaline binding. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 21;162(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapper E. J., Bloom A. S., Lewand D. L. Endogenous norepinephrine release induced by tyramine modulates intestinal ion transport. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):G264–G269. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.3.G264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly B. C., Kansen M., van Gageldonk P. G., van den Berghe N., Galjaard H., Bijman J., de Jonge H. R. G-proteins mediate intestinal chloride channel activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2036–2040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tutton P. J., Barkla D. H. Biogenic amines as regulators of the proliferative activity of normal and neoplastic intestinal epithelial cells (review). Anticancer Res. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berghe N., Nieuwkoop N. J., Vaandrager A. B., de Jonge H. R. Asymmetrical distribution of G-proteins among the apical and basolateral membranes of rat enterocytes. Biochem J. 1991 Sep 1;278(Pt 2):565–571. doi: 10.1042/bj2780565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]