Abstract
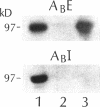
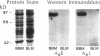
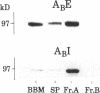
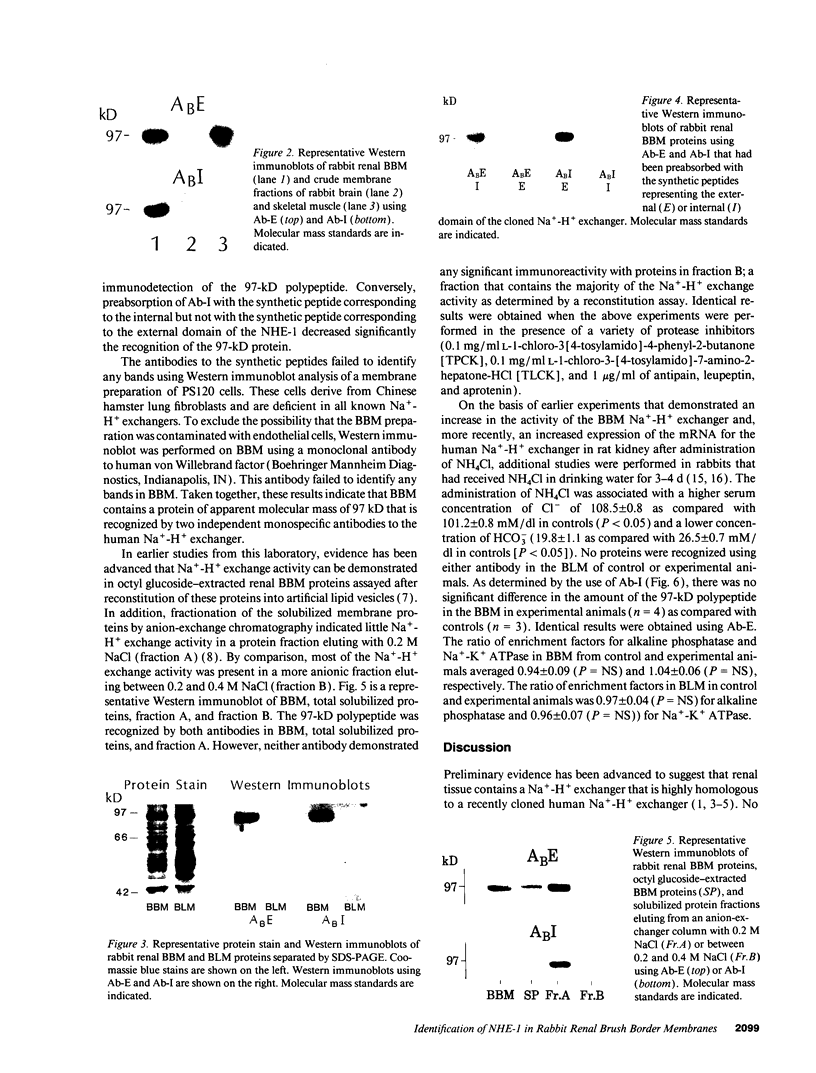
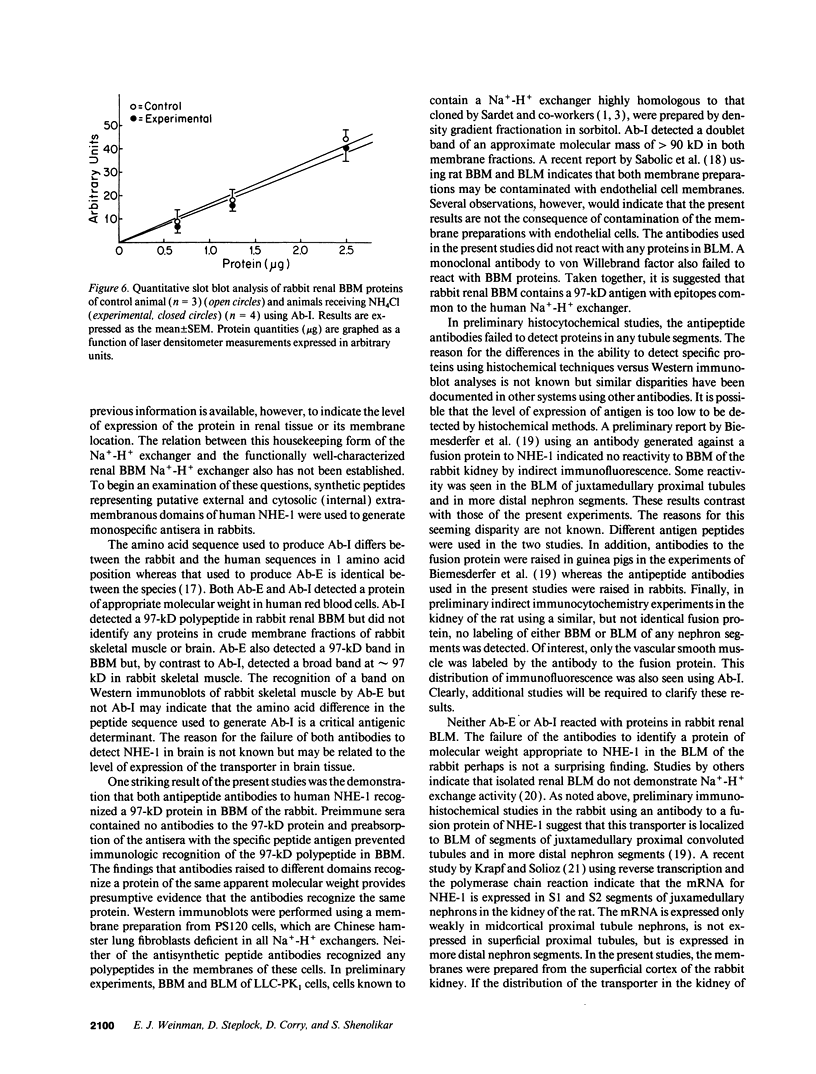
To study the relation between the human Na(+)-H+ exchanger (NHE-1) and the renal brush border membrane (BBM) Na(+)-H+ exchanger, polyclonal antibodies to synthetic peptides representing a putative external (Ab-E) and an internal cytosolic domain (Ab-I) of human NHE-1 were generated in rabbits. Western immunoblot analyses indicated that both antibodies recognized a 97-kD protein in rabbit renal BBM but not basolateral membranes (BLM). Octyl glucoside-extracted rabbit renal BBM proteins also contained the 97-kD polypeptide as did a fraction eluted from an anion-exchange column with 0.2 M NaCl (fraction A). A fraction eluting between 0.2 and 0.4 M NaCl (fraction B) did not contain this protein. Prior reconstitution studies have indicated that Na(+)-H+ exchange activity is higher significantly in fraction B than fraction A. Administration of NH4Cl for 3-7 d to rabbits, a stimulus known to increase renal BBM Na(+)-H+ exchange activity, did not result in a change in expression of the 97-kD protein in either renal BBM or BLM. The results indicate that affinity-purified polyclonal antibodies to two separate domains of the human Na(+)-H+ exchanger recognize a 97-kD protein in rabbit renal BBM but not BLM. The dissociation between recognition of the 97-kD protein using antibodies and the majority of functional Na(+)-H+ exchange activity after chromatographic fractionation of solubilized BBM proteins and in native BBM after administration of NH4Cl suggest that rabbit renal BBM contains more than one form of Na(+)-H+ exchanger.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AHMED K., JUDAH J. D. PREPARATION OF LIPOPROTEINS CONTAINING CATION-DEPENDENT ATPASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Dec 9;93:603–613. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90343-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haggerty J. G., Agarwal N., Reilly R. F., Adelberg E. A., Slayman C. W. Pharmacologically different Na/H antiporters on the apical and basolateral surfaces of cultured porcine kidney cells (LLC-PK1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6797–6801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Branham S., Weinman E. J. Mechanism of L-malate transport in rat renal basolateral membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jun;246(6 Pt 2):F779–F784. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.246.6.F779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Branham S., Weinman E. J. Mechanism of urate and p-aminohippurate transport in rat renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1983 Aug;245(2):F151–F158. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.245.2.F151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn A. M., Dolson G. M., Hise M. K., Bennett S. C., Weinman E. J. Parathyroid hormone and dibutyryl cAMP inhibit Na+/H+ exchange in renal brush border vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F212–F218. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Alpern R. J., Rector F. C., Jr, Berry C. A. Basolateral membrane Na/base cotransport is dependent on CO2/HCO3 in the proximal convoluted tubule. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Dec;90(6):833–853. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.6.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Pearce D., Lynch C., Xi X. P., Reudelhuber T. L., Pouysségur J., Rector F. C., Jr Expression of rat renal Na/H antiporter mRNA levels in response to respiratory and metabolic acidosis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):747–751. doi: 10.1172/JCI115057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krapf R., Solioz M. Na/H antiporter mRNA expression in single nephron segments of rat kidney cortex. J Clin Invest. 1991 Sep;88(3):783–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI115377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski J., Kandasamy R. A., Shull G. E. Molecular cloning of putative members of the Na/H exchanger gene family. cDNA cloning, deduced amino acid sequence, and mRNA tissue expression of the rat Na/H exchanger NHE-1 and two structurally related proteins. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9331–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly R. F., Hildebrandt F., Biemesderfer D., Sardet C., Pouysségur J., Aronson P. S., Slayman C. W., Igarashi P. cDNA cloning and immunolocalization of a Na(+)-H+ exchanger in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 2):F1088–F1094. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.6.F1088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Culić O., Lin S. H., Brown D. Localization of ecto-ATPase in rat kidney and isolated renal cortical membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):F217–F228. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardet C., Franchi A., Pouysségur J. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and expression of the human growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ antiporter. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90901-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. J., Ives H. E., Alpern R. J., Yee V. J., Warnock D. G., Rector F. C., Jr Increased Vmax for Na+/H+ antiporter activity in proximal tubule brush border vesicles from rabbits with metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F339–F343. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Brant S. R., Walker M. S., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and sequencing of a rabbit cDNA encoding an intestinal and kidney-specific Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-3). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9340–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Ma A. I., Yang V. W., Watson A. J., Levine S., Montrose M. H., Potter J., Sardet C., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Molecular cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding the rabbit ileal villus cell basolateral membrane Na+/H+ exchanger. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):1957–1967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi S., Fafournoux P., Sardet C., Pouysségur J. The Na+/H+ antiporter cytoplasmic domain mediates growth factor signals and controls "H(+)-sensing". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2424–2428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Fisher K., Steplock D., Dinh Q., Chang L., Shenolikar S. Regulation of reconstituted renal Na+/H+ exchanger by calcium-dependent protein kinases. J Membr Biol. 1988 Aug;103(3):237–244. doi: 10.1007/BF01993983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Dubinsky W. P., Shenolikar S. Reconstitution of cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulated renal Na+-H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1988;101(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF01872815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Dubinsky W. P. Solubilization and reconstitution of renal brush border Na+-H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1988;101(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF01872814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S., Kahn A. M. cAMP-associated inhibition of Na+-H+ exchanger in rabbit kidney brush-border membranes. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jan;252(1 Pt 2):F19–F25. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.1.F19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Shenolikar S. Protein kinase C activates the renal apical membrane Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;93(2):133–139. doi: 10.1007/BF01870805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinman E. J., Steplock D., Bui G., Yuan N., Shenolikar S. Regulation of renal Na(+)-H+ exchanger by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1254–F1258. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita T., Kawakita M. Reconstitution of Na+/H(+)-antiporter of bovine renal brush-border membrane into proteoliposomes and detection of a 110 kDa protein cross-reactive with antibodies against a human Na+/H(+)-antiporter partial peptide in antiport-active fractions after partial fractionation. J Biochem. 1992 Feb;111(2):162–167. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]