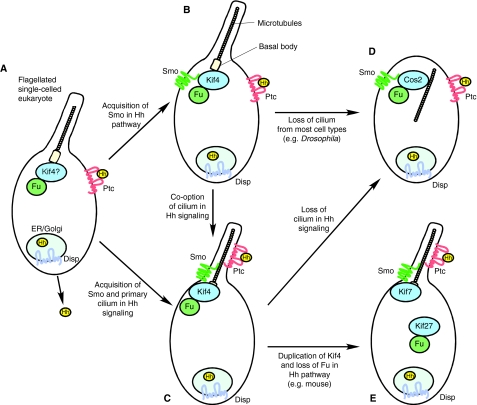
Fig. 6.
Possible routes of Hh pathway evolution. A model of Hh pathway evolution. (A) Single-celled eukaryotes (for example, the collared flagellate Monosiga brevicollis) have Disp, Ptc, Hh and Fu genes. An ancient export-import system of Hh, Ptc and Disp could have been present in this organism (Hausmann et al., 2009), and a Fu-kinesin 4 (Kif4) complex might have been required for the assembly of the 9+2 cilium/flagellum. (B,C) Smo is incorporated into a regulatory circuit with Ptc, either prior to the involvement of Smo and Ptc function with the cilium (B) or concomitantly (C). In both scenarios, the Fu-kinesin 4 complex is recruited to function with Smo. (D) In flies, the primary cilium is not utilized for Hh signaling. It is currently unclear whether cilia represent an ancestral state for Hh transduction and flies have `rewired' the pathway, or if cilia were incorporated into the pathway after divergence of arthropod and chordate lineages. (E) Gene duplication of Kif4 (subsequently generating Kif7 and 27) in tetrapod lineages has led to loss of essential Fu function in mammalian Hh signaling but Kif7 is retained. It is not known if an unrelated kinase compensates for the loss of Fu. Cos2, Costal2; Disp, Dispatched; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Fu, Fused; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; Hh, Hedgehog; Kif4, kinesin family member 4; Kif7, kinesin family member 7; Kif27, kinesin family member 27; Ptc, Patched; Smo, Smoothened; Su(fu), Suppressor of fused.