Abstract
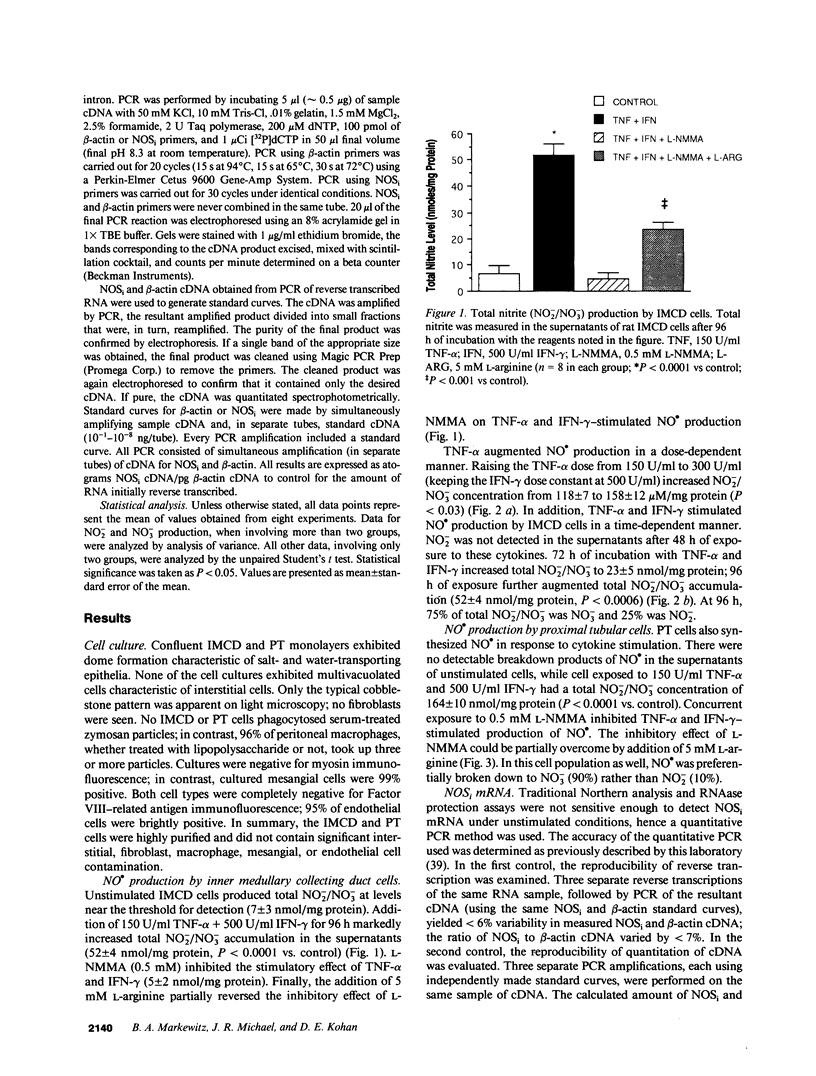
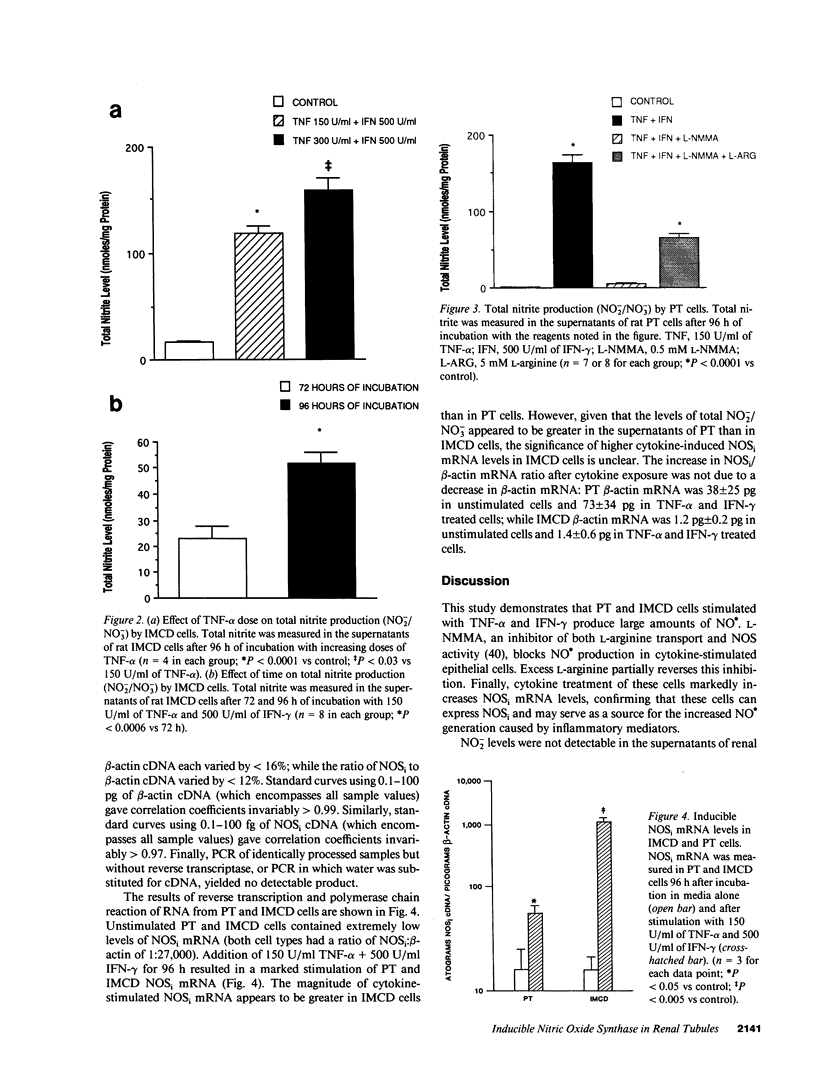
Nitric oxide (NO.) has been implicated in the regulation of renal vascular tone and tubular sodium transport. While the endothelial cell is a well known source of NO(.), recent studies suggest that tubular epithelial cells may constitutively generate NO(.). An inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase which produces far greater quantities of NO. exists in some cell types. We sought to determine whether kidney epithelial cells exposed to cytokines could express an inducible nitric oxide synthase. Primary cultures of rat proximal tubule and inner medullary collecting duct cells generated NO. on exposure to TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma. NO. production by both cell types was inhibited by NG-monomethyl-L-arginine; this inhibition was partially reversed by the addition of excess L-arginine. Stimulation of kidney epithelial cells with TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma dramatically increased the level of inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA. In summary, renal proximal tubule and inner medullary collecting duct cells can produce NO. via expression of an inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amber I. J., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Cytokines induce an L-arginine-dependent effector system in nonmacrophage cells. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 Jul;44(1):58–65. doi: 10.1002/jlb.44.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B. A rapid method for the assay of nitrate in urine using the nitrate reductase enzyme of Escherichia coli. Food Chem Toxicol. 1984 Jul;22(7):541–543. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(84)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley D., Schwartz J. H., Brenner B. M. Interleukin 1 induces prolonged L-arginine-dependent cyclic guanosine monophosphate and nitrite production in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):602–608. doi: 10.1172/JCI115036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Stuehr D. J., Stadler J., Simmons R. L., Murray S. A. Inducible cytosolic enzyme activity for the production of nitrogen oxides from L-arginine in hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1034–1040. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91133-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Stuehr D. J., West M. A., Bentz B. G., Simmons R. L. An L-arginine-dependent mechanism mediates Kupffer cell inhibition of hepatocyte protein synthesis in vitro. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1467–1472. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biondi M. L., Bolterman R. J., Romero J. C. Zonal changes of guanidine 3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate related to endothelium-derived relaxing factor in dog renal medulla. Ren Physiol Biochem. 1992 Jan-Feb;15(1):16–22. doi: 10.1159/000173437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Hwang P. M., Glatt C. E., Lowenstein C., Reed R. R., Snyder S. H. Cloned and expressed nitric oxide synthase structurally resembles cytochrome P-450 reductase. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):714–718. doi: 10.1038/351714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook H. T., Sullivan R. Glomerular nitrite synthesis in in situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat. Am J Pathol. 1991 Nov;139(5):1047–1052. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran R. D., Billiar T. R., Stuehr D. J., Hofmann K., Simmons R. L. Hepatocytes produce nitrogen oxides from L-arginine in response to inflammatory products of Kupffer cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1769–1774. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M. Tumor necrosis factor and granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor stimulate human macrophages to restrict growth of virulent Mycobacterium avium and to kill avirulent M. avium: killing effector mechanism depends on the generation of reactive nitrogen intermediates. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Apr;49(4):380–387. doi: 10.1002/jlb.49.4.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapier J. C., Hibbs J. B., Jr Differentiation of murine macrophages to express nonspecific cytotoxicity for tumor cells results in L-arginine-dependent inhibition of mitochondrial iron-sulfur enzymes in the macrophage effector cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2829–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eizirik D. L., Cagliero E., Björklund A., Welsh N. Interleukin-1 beta induces the expression of an isoform of nitric oxide synthase in insulin-producing cells, which is similar to that observed in activated macrophages. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 24;308(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81285-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ercan Z. S., Soydan A. S., Türker R. K. Possible involvement of endothelium in the responses of various vasoactive agents in rabbit isolated perfused kidney. Gen Pharmacol. 1990;21(2):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(90)90902-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt R. C., Kimelberg H. K. Protein analysis of mammalian cells in monolayer culture using the bicinchoninic assay. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):41–45. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Perfect J. R., Durack D. T. Metabolic fate of L-arginine in relation to microbiostatic capability of murine macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):264–273. doi: 10.1172/JCI114422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenier F. C., Rollins T. E., Smith W. L. Kinin-induced prostaglandin synthesis by renal papillary collecting tubule cells in culture. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F94–104. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z. Macrophage cytotoxicity: role for L-arginine deiminase and imino nitrogen oxidation to nitrite. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):473–476. doi: 10.1126/science.2432665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Vavrin Z., Taintor R. R. L-arginine is required for expression of the activated macrophage effector mechanism causing selective metabolic inhibition in target cells. J Immunol. 1987 Jan 15;138(2):550–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. K., Cline R. C., Kohan D. E. Alterations in renal endothelin-1 production in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertension. 1992 Nov;20(5):666–673. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.5.666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii K., Chang B., Kerwin J. F., Jr, Wagenaar F. L., Huang Z. J., Murad F. Formation of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in porcine kidney epithelial LLC-PK1 cells: an intra- and intercellular messenger for activation of soluble guanylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jan;256(1):38–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Johnson C. S., Carretero O. A. Modulation of angiotensin II-induced vasoconstriction by endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the isolated microperfused rabbit afferent arteriole. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1656–1663. doi: 10.1172/JCI115181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Belloni P. Endothelial cell production of nitrogen oxides in response to interferon gamma in combination with tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, or endotoxin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990 May 2;82(9):772–776. doi: 10.1093/jnci/82.9.772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E. Endothelin synthesis by rabbit renal tubule cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):F221–F226. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.2.F221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E., Fiedorek F. T., Jr Endothelin synthesis by rat inner medullary collecting duct cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1991 Aug;2(2):150–155. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V22150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohan D. E. Interleukin-1 regulation of prostaglandin E2 synthesis by the papillary collecting duct. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Dec;114(6):717–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahera V., Salom M. G., Fiksen-Olsen M. J., Raij L., Romero J. C. Effects of NG-monomethyl-L-arginine and L-arginine on acetylcholine renal response. Hypertension. 1990 Jun;15(6 Pt 1):659–663. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.6.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahera V., Salom M. G., Fiksen-Olsen M. J., Romero J. C. Mediatory role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in renal vasodilatory and excretory effects of bradykinin. Am J Hypertens. 1991 Mar;4(3 Pt 1):260–262. doi: 10.1093/ajh/4.3.260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahera V., Salom M. G., Miranda-Guardiola F., Moncada S., Romero J. C. Effects of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester on renal function and blood pressure. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 2):F1033–F1037. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.6.F1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas S., Michel T., Brenner B. M., Marsden P. A. Nitric oxide synthesis in endothelial cells: evidence for a pathway inducible by TNF-alpha. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Pt 1):C634–C641. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.4.C634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levillain O., Hus-Citharel A., Morel F., Bankir L. Localization of arginine synthesis along rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F916–F923. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons C. R., Orloff G. J., Cunningham J. M. Molecular cloning and functional expression of an inducible nitric oxide synthase from a murine macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6370–6374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Ballermann B. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates soluble guanylate cyclase in bovine glomerular mesangial cells via an L-arginine-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1843–1852. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. S., Hevel J. M., Marletta M. A., Ward P. A. Tissue injury caused by deposition of immune complexes is L-arginine dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6338–6342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero J. C., Lahera V., Salom M. G., Biondi M. L. Role of the endothelium-dependent relaxing factor nitric oxide on renal function. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992 Mar;2(9):1371–1387. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V291371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovin B. H., Wurst E., Kohan D. E. Production of reactive oxygen species by tubular epithelial cells in culture. Kidney Int. 1990 Jun;37(6):1509–1514. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoos B. A., Carretero O. A., Farhy R. D., Scicli G., Garvin J. L. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits transport and increases cGMP content in cultured mouse cortical collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):761–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI115653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Griffith O. W. Mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1992;65:287–346. doi: 10.1002/9780470123119.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Induction of nitrite/nitrate synthesis in murine macrophages by BCG infection, lymphokines, or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):518–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Marletta M. A. Mammalian nitrate biosynthesis: mouse macrophages produce nitrite and nitrate in response to Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(22):7738–7742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.22.7738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal M. J., Romero J. C., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits renin release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):401–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90679-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinay P., Gougoux A., Lemieux G. Isolation of a pure suspension of rat proximal tubules. Am J Physiol. 1981 Oct;241(4):F403–F411. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.4.F403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Felmayer G., Werner E. R., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Wachter H. Tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent formation of nitrite and nitrate in murine fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1599–1607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





