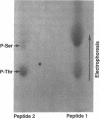
Abstract
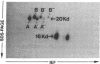
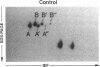
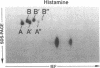
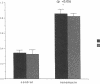
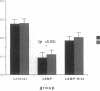
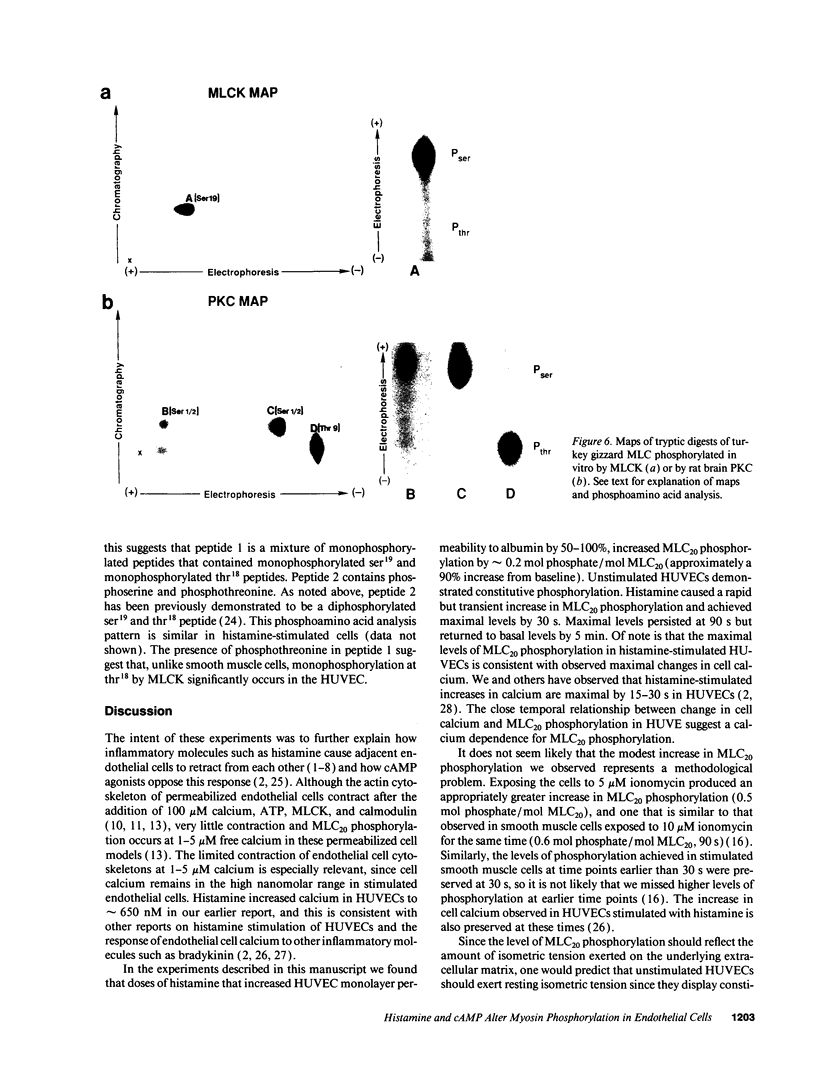
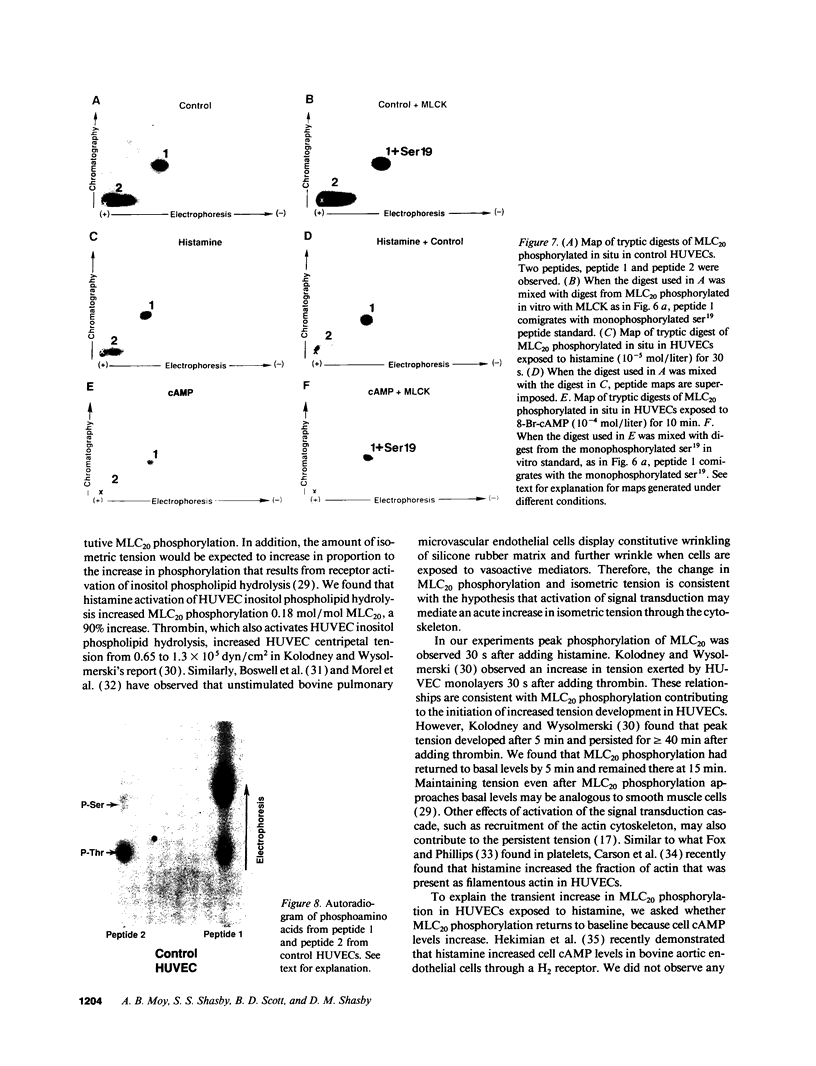
Histamine causes adjacent endothelial cells to retract from each another. We examined phosphorylation of the 20-kD myosin light chain (MLC20) in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) exposed to histamine to determine if we could find evidence to support the hypothesis that retraction of these cells in response to histamine represents an actomyosin-initiated contraction of the endothelial cytoskeleton. We found that MLC20 in HUVECs was constitutively phosphorylated with approximately 0.2 mol phosphate/mol MLC20. Histamine increased MLC20 phosphorylation by 0.18 +/- 0.05 mol phosphate/mol MLC20. This peak increase in phosphorylation occurred 30 s after initiating histamine exposure, persisted through 90s, and returned to control levels by 5 min. Agents that increase HUVEC cAMP prevent cell retraction in response to histamine. An increase in HUVEC cAMP decreased MLC20 phosphorylation by 0.18 +/- 0.02 mol phosphate/mol MLC20 and prevented the increase in MLC20 phosphorylation after exposure to histamine. Tryptic peptide maps of phosphorylated myosin light chain indicated that myosin light chain kinase phosphorylated MLC20 in HUVECs under basal, cAMP-, and histamine-stimulated conditions. Phosphoaminoacid analysis of the monophosphorylated peptide indicated that, in contrast to smooth muscle cells, ser19 and thr18 monophosphorylation occurs in HUVECs. On the basis of our results, modulation of myosin light chain kinase activity may be an important regulatory step in the control of endothelial barrier function.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertine K. H., Wiener-Kronish J. P., Koike K., Staub N. C. Quantification of damage by air emboli to lung microvessels in anesthetized sheep. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Nov;57(5):1360–1368. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.5.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell C. A., Majno G., Joris I., Ostrom K. A. Acute endothelial cell contraction in vitro: a comparison with vascular smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. Microvasc Res. 1992 Mar;43(2):178–191. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(92)90015-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson M. R., Shasby S. S., Lind S. E., Shasby D. M. Histamine, actin-gelsolin binding, and polyphosphoinositides in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 1):L664–L669. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.263.6.L664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson M. R., Shasby S. S., Shasby D. M. Histamine and inositol phosphate accumulation in endothelium: cAMP and a G protein. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 1):L259–L264. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.4.L259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti M. A., Adelstein R. S. Phosphorylation by cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase regulates myosin light chain kinase. Fed Proc. 1980 Apr;39(5):1569–1573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel J. L., Adelstein R. S. Isolation and properties of platelet myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2370–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E., Phillips D. R. Role of phosphorylation in mediating the association of myosin with the cytoskeletal structures of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4120–4126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracy R. W. Two-dimensional thin-layer methods. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:195–204. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeberle J. R., Sutton T. A., Trockman B. A. Phosphorylation of two sites on smooth muscle myosin. Effects on contraction of glycerinated vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4424–4429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai C. M., Murphy R. A. Sr2+ activates cross-bridge phosphorylation and latch state in smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 Sep;255(3 Pt 1):C401–C407. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.255.3.C401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekimian G., Côte S., Van Sande J., Boeynaems J. M. H2 receptor-mediated responses of aortic endothelial cells to histamine. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 2):H220–H224. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.1.H220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Hartshorne D. J. Phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin at two distinct sites by myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10027–10031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M. Phosphorylation of a second site for myosin light chain kinase on platelet myosin. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 31;28(22):8750–8755. doi: 10.1021/bi00448a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs W. B., Fulton A. B. Cotranslational assembly of myosin heavy chain in developing cultured skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6174–6178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh K., Hara T., Shibata N. Diphosphorylation of platelet myosin by myosin light chain kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Feb 3;1133(3):286–292. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(92)90049-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob R., Merritt J. E., Hallam T. J., Rink T. J. Repetitive spikes in cytoplasmic calcium evoked by histamine in human endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):40–45. doi: 10.1038/335040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto S., Bengur A. R., Sellers J. R., Adelstein R. S. In situ phosphorylation of human platelet myosin heavy and light chains by protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2258–2265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodney M. S., Wysolmerski R. B. Isometric contraction by fibroblasts and endothelial cells in tissue culture: a quantitative study. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):73–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C. C., Mohan S. R., Zavodny P. J., Narula S. K., Leibowitz P. J. Characterization and differential expression of human vascular smooth muscle myosin light chain 2 isoform in nonmuscle cells. Biochemistry. 1989 May 2;28(9):4027–4035. doi: 10.1021/bi00435a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb N. J., Fernandez A., Conti M. A., Adelstein R., Glass D. B., Welch W. J., Feramisco J. R. Regulation of actin microfilament integrity in living nonmuscle cells by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase and the myosin light chain kinase. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1955–1971. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeler E. G., van Hinsbergh V. W. Norepinephrine and iloprost improve barrier function of human endothelial cell monolayers: role of cAMP. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):C1052–C1059. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.5.C1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laposata M., Dovnarsky D. K., Shin H. S. Thrombin-induced gap formation in confluent endothelial cell monolayers in vitro. Blood. 1983 Sep;62(3):549–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludowyke R. I., Peleg I., Beaven M. A., Adelstein R. S. Antigen-induced secretion of histamine and the phosphorylation of myosin by protein kinase C in rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12492–12501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., PALADE G. E. Studies on inflammation. 1. The effect of histamine and serotonin on vascular permeability: an electron microscopic study. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:571–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel N. M., Dodge A. B., Patton W. F., Herman I. M., Hechtman H. B., Shepro D. Pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell contractility on silicone rubber substrate. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Dec;141(3):653–659. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041410325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaysen G. Intravascular concentrations of calcium and magnesium ions and edema formation in isolated lungs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Mar;81(3):325–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb04907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I. Histamine type I receptor occupancy increases endothelial cytosolic calcium, reduces F-actin, and promotes albumin diffusion across cultured endothelial monolayers. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2379–2387. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling W. P. Effect of membrane potential on cytosolic calcium of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Sep;257(3 Pt 2):H778–H784. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.257.3.H778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittler H. J., Wilke A., Gress T., Suttorp N., Drenckhahn D. Role of actin and myosin in the control of paracellular permeability in pig, rat and human vascular endothelium. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:379–401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R., Soboeiro M. S., Faust K., Bengur A. R., Harvey E. V. Preparation and characterization of heavy meromyosin and subfragment 1 from vertebrate cytoplasmic myosins. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):6977–6982. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Lind S. E., Shasby S. S., Goldsmith J. C., Hunninghake G. W. Reversible oxidant-induced increases in albumin transfer across cultured endothelium: alterations in cell shape and calcium homeostasis. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):605–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S. Effects of calcium on transendothelial albumin transfer and electrical resistance. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1986 Jan;60(1):71–79. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1986.60.1.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shasby D. M., Shasby S. S., Sullivan J. M., Peach M. J. Role of endothelial cell cytoskeleton in control of endothelial permeability. Circ Res. 1982 Nov;51(5):657–661. doi: 10.1161/01.res.51.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer H. A. Protein kinase C activation and myosin light chain phosphorylation in 32P-labeled arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C631–C639. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stelzner T. J., Weil J. V., O'Brien R. F. Role of cyclic adenosine monophosphate in the induction of endothelial barrier properties. J Cell Physiol. 1989 Apr;139(1):157–166. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041390122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. A., Stull J. T. Calcium dependence of myosin light chain phosphorylation in smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14456–14462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umemoto S., Bengur A. R., Sellers J. R. Effect of multiple phosphorylations of smooth muscle and cytoplasmic myosins on movement in an in vitro motility assay. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1431–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J., Winter M., Shasby D. M. Oxidants, ATP depletion, and endothelial permeability to macromolecules. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2578–2582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R. B., Lagunoff D. Inhibition of endothelial cell retraction by ATP depletion. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):28–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R. B., Lagunoff D. Involvement of myosin light-chain kinase in endothelial cell retraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R. B., Lagunoff D. Regulation of permeabilized endothelial cell retraction by myosin phosphorylation. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 1):C32–C40. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.1.C32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysolmerski R., Lagunoff D. The effect of ethchlorvynol on cultured endothelial cells. A model for the study of the mechanism of increased vascular permeability. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):505–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lanerolle P., Nishikawa M., Yost D. A., Adelstein R. S. Increased phosphorylation of myosin light chain kinase after an increase in cyclic AMP in intact smooth muscle. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.6322302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]