Abstract
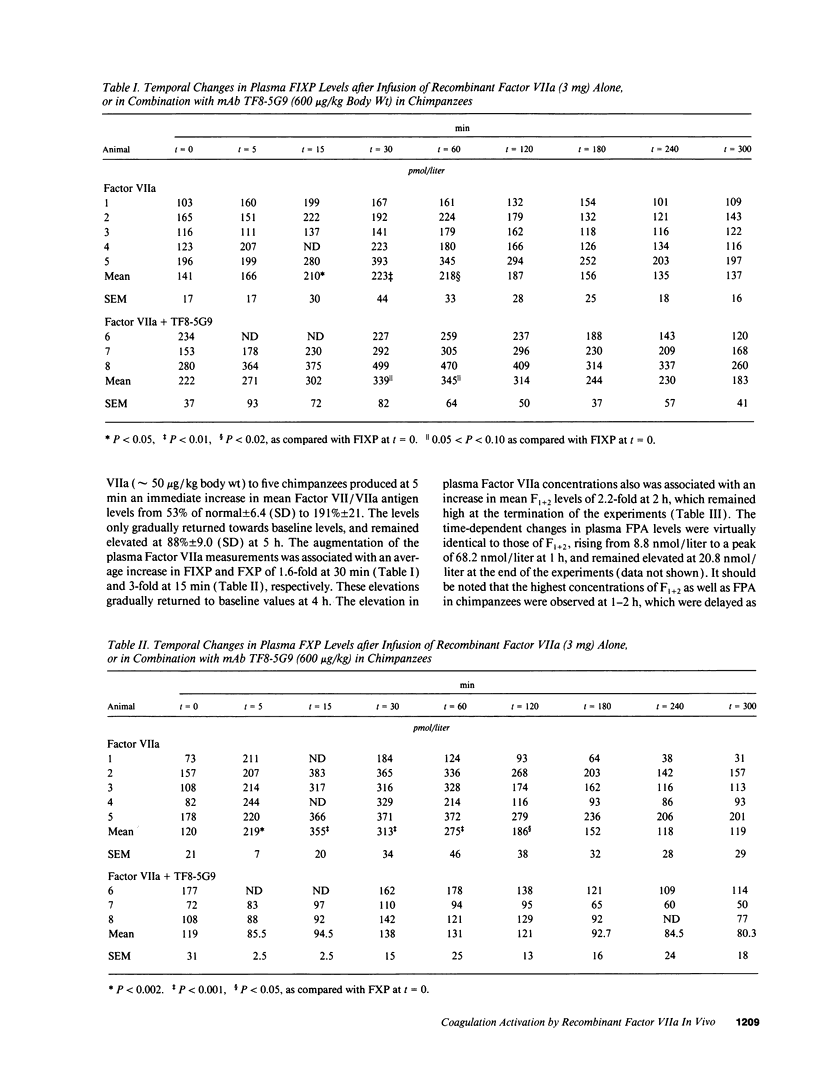
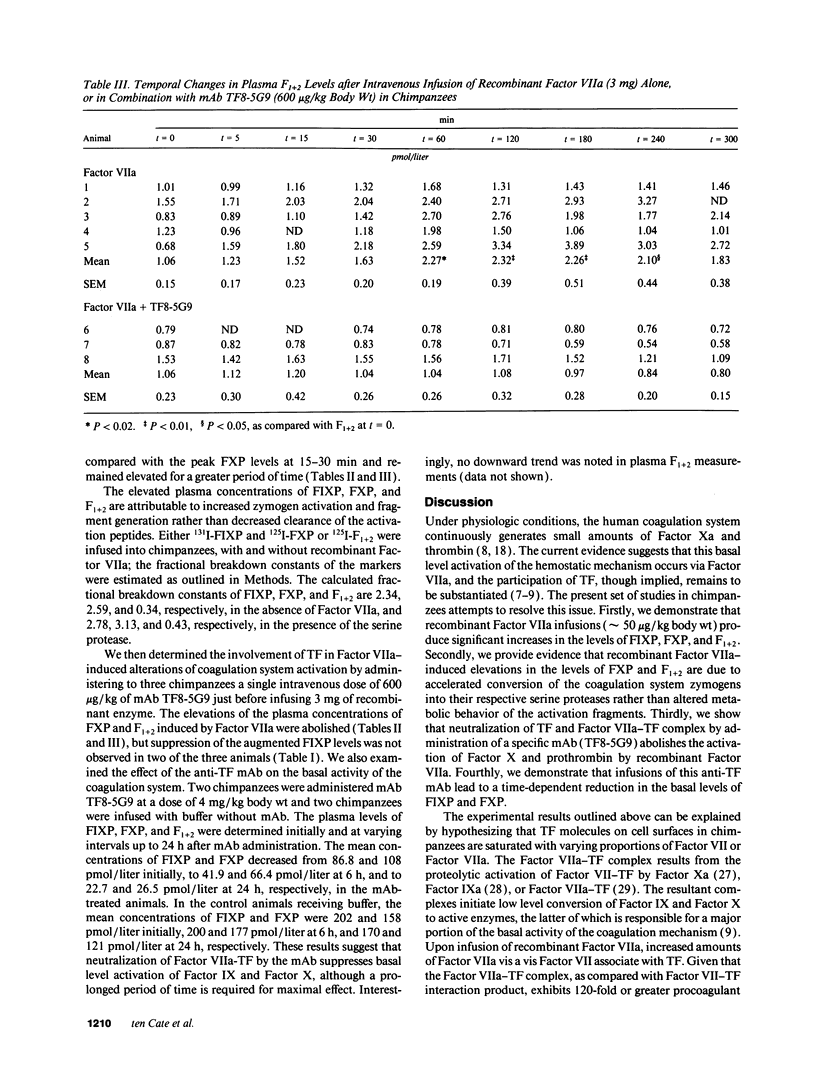
The human coagulation system continuously generates very small quantities of Factor Xa and thrombin. Current evidence suggests that basal level activation of the hemostatic mechanism occurs via Factor VIIa-dependent activation of Factor X, but direct proof has not been available for the participation of tissue factor in this pathway. To examine this issue, we infused relatively high concentrations of recombinant Factor VIIa (approximately 50 micrograms/kg body wt) into normal chimpanzees and observed significant increases in the plasma levels of Factor IX activation peptide, Factor X activation peptide, and prothrombin activation fragment F1+2. Metabolic turnover studies with radiolabeled Factor IX activation peptide, Factor X activation peptide, and F1+2 indicate that elevated levels of the activation peptides are due to accelerated conversion of the three coagulation system zymogens into serine proteases. The administration of a potent monoclonal antibody to tissue factor, which immediately neutralizes function of the Factor VIIa-tissue factor complex in vitro, abolishes the activation of Factor X and prothrombin mediated by the infused recombinant protein, and also suppresses basal level activation of Factor IX and Factor X. The above results suggest that recombinant Factor VIIa functions as a prohemostatic agent by interacting with endogenous tissue factor sites, but definitive proof will require studies in hemophilic animals using relevant hemostatic endpoints.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer K. A., Kass B. L., ten Cate H., Bednarek M. A., Hawiger J. J., Rosenberg R. D. Detection of factor X activation in humans. Blood. 1989 Nov 1;74(6):2007–2015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. A., Kass B. L., ten Cate H., Hawiger J. J., Rosenberg R. D. Factor IX is activated in vivo by the tissue factor mechanism. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):731–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. A., Mannucci P. M., Gringeri A., Tradati F., Barzegar S., Kass B. L., ten Cate H., Kestin A. S., Brettler D. B., Rosenberg R. D. Factor IXa-factor VIIIa-cell surface complex does not contribute to the basal activation of the coagulation mechanism in vivo. Blood. 1992 Apr 15;79(8):2039–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. A., Weiss L. M., Sparrow D., Vokonas P. S., Rosenberg R. D. Aging-associated changes in indices of thrombin generation and protein C activation in humans. Normative Aging Study. J Clin Invest. 1987 Dec;80(6):1527–1534. doi: 10.1172/JCI113238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P. Characterization of the inhibition of tissue factor in serum. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):150–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway E. M., Bach R., Rosenberg R. D., Konigsberg W. H. Tumor necrosis factor enhances expression of tissue factor mRNA in endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 1989 Feb 1;53(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIE E. W., RATNOFF O. D. WATERFALL SEQUENCE FOR INTRINSIC BLOOD CLOTTING. Science. 1964 Sep 18;145(3638):1310–1312. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3638.1310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake T. A., Morrissey J. H., Edgington T. S. Selective cellular expression of tissue factor in human tissues. Implications for disorders of hemostasis and thrombosis. Am J Pathol. 1989 May;134(5):1087–1097. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R., Dvorak A. M., Harvey V. S., McDonagh J. Regulation of extravascular coagulation by microvascular permeability. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1059–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.3975602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiore M. M., Neuenschwander P. F., Morrissey J. H. An unusual antibody that blocks tissue factor/factor VIIa function by inhibiting cleavage only of macromolecular substrates. Blood. 1992 Dec 15;80(12):3127–3134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gailani D., Broze G. J., Jr Factor XI activation in a revised model of blood coagulation. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):909–912. doi: 10.1126/science.1652157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedner U., Kisiel W. Use of human factor VIIa in the treatment of two hemophilia A patients with high-titer inhibitors. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1836–1841. doi: 10.1172/JCI110939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josso F., Prou-Wartelle O. Interaction of tissue factor and factor VII at the earliest phase of coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1965;17:35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau H. K., Rosenberg J. S., Beeler D. L., Rosenberg R. D. The isolation and characterization of a specific antibody population directed against the prothrombin activation fragments F2 and F1 + 2. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8751–8761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson J. H., Mann K. G. Cooperative activation of human factor IX by the human extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11317–11327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman H. A., Limentani S. A., Furie B. C., Furie B. Immunoaffinity purification of factor IX (Christmas factor) by using conformation-specific antibodies directed against the factor IX-metal complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3879–3883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACFARLANE R. G. AN ENZYME CASCADE IN THE BLOOD CLOTTING MECHANISM, AND ITS FUNCTION AS A BIOCHEMICAL AMPLIFIER. Nature. 1964 May 2;202:498–499. doi: 10.1038/202498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macik B. G., Hohneker J., Roberts H. R., Griffin A. M. Use of recombinant activated factor VII for treatment of a retropharyngeal hemorrhage in a hemophilic patient with a high titer inhibitor. Am J Hematol. 1989 Nov;32(3):232–234. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830320315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Nesheim M. E., Church W. R., Haley P., Krishnaswamy S. Surface-dependent reactions of the vitamin K-dependent enzyme complexes. Blood. 1990 Jul 1;76(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore K. L., Andreoli S. P., Esmon N. L., Esmon C. T., Bang N. U. Endotoxin enhances tissue factor and suppresses thrombomodulin expression of human vascular endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):124–130. doi: 10.1172/JCI112772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H., Fair D. S., Edgington T. S. Monoclonal antibody analysis of purified and cell-associated tissue factor. Thromb Res. 1988 Nov 1;52(3):247–261. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90084-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito K., Fujikawa K. Activation of human blood coagulation factor XI independent of factor XII. Factor XI is activated by thrombin and factor XIa in the presence of negatively charged surfaces. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7353–7358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagaki T., Foster D. C., Berkner K. L., Kisiel W. Initiation of the extrinsic pathway of blood coagulation: evidence for the tissue factor dependent autoactivation of human coagulation factor VII. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 12;30(45):10819–10824. doi: 10.1021/bi00109a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosslin B. Analysis of disappearance time-curves after single injection of labelled proteins. Ciba Found Symp. 1972;9:113–130. doi: 10.1002/9780470719923.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny W. F., Palmier M., Wun T. C., Broze G. J., Jr, Miletich J. P. Purification and properties of heparin-releasable lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):394–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B. How to measure factor VII and factor VII activation. Haemostasis. 1983;13(3):161–168. doi: 10.1159/000214722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Activation of factor IX by the reaction product of tissue factor and factor VII: additional pathway for initiating blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5260–5264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radcliffe R., Nemerson Y. Activation and control of factor VII by activated factor X and thrombin. Isolation and characterization of a single chain form of factor VII. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):388–395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L. V., Rapaport S. I. Factor VIIa-catalyzed activation of factor X independent of tissue factor: its possible significance for control of hemophilic bleeding by infused factor VIIa. Blood. 1990 Mar 1;75(5):1069–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapaport S. I. The extrinsic pathway inhibitor: a regulator of tissue factor-dependent blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):6–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf W., Edgington T. S. An anti-tissue factor monoclonal antibody which inhibits TF.VIIa complex is a potent anticoagulant in plasma. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Nov 1;66(5):529–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruf W., Rehemtulla A., Morrissey J. H., Edgington T. S. Phospholipid-independent and -dependent interactions required for tissue factor receptor and cofactor function. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2158–2166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seligsohn U., Osterud B., Brown S. F., Griffin J. H., Rapaport S. I. Activation of human factor VII in plasma and in purified systems: roles of activated factor IX, kallikrein, and activated factor XII. J Clin Invest. 1979 Oct;64(4):1056–1065. doi: 10.1172/JCI109543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teitel J. M., Bauer K. A., Lau H. K., Rosenberg R. D. Studies of the prothrombin activation pathway utilizing radioimmunoassays for the F2/F1 + 2 fragment and thrombin--antithrombin complex. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):1086–1097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telgt D. S., Macik B. G., McCord D. M., Monroe D. M., Roberts H. R. Mechanism by which recombinant factor VIIa shortens the aPTT: activation of factor X in the absence of tissue factor. Thromb Res. 1989 Dec 1;56(5):603–609. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thim L., Bjoern S., Christensen M., Nicolaisen E. M., Lund-Hansen T., Pedersen A. H., Hedner U. Amino acid sequence and posttranslational modifications of human factor VIIa from plasma and transfected baby hamster kidney cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7785–7793. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R., Nemerson Y., Hoffmann T. Evidence for the presence of tissue factor activity on subendothelium. Blood. 1989 Mar;73(4):968–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams E. B., Krishnaswamy S., Mann K. G. Zymogen/enzyme discrimination using peptide chloromethyl ketones. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7536–7545. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wissler R. W., Vesselinovitch D. Atherosclerosis in nonhuman primates. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1977;21:351–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur M., Radcliffe R. D., Oberdick J., Nemerson Y. The dual role of factor VII in blood coagulation. Initiation and inhibition of a proteolytic system by a zymogen. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5623–5631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



